template <typename T>class smart_ptr {…smart_ptr(smart_ptr&& other) noexcept//拷贝构造参数改为右值引用 变为移动构造函数{ptr_ = other.release();}smart_ptr& operator=(smart_ptr rhs)//不传入引用而传入对象{//传入对象构造形参rhs时 因为只定义了移动构造所以在调用op=必须传入右值引用或者右值(临时对象),来构造形参 传入左值会出错rhs.swap(*this);return *this;}//原//smart_ptr& operator=(smart_ptr& rhs)//{//smart_ptr(rhs).swap(*this);//return *this;//}…};
根据 C++ 的规则,如果我提供了移动构造函数而没有手动提供拷贝构造函数,那后者自动被禁用(记住,C++ 里那些复杂的规则也是为方便编程而设立的)。于是,我们自然地得到了以下结果:
smart_ptr<shape> ptr1{create_shape(shape_type::circle)};//移动构造smart_ptr<shape> ptr2{ptr1}; // 编译出错 因为没写拷贝构造smart_ptr<shape> ptr3;ptr3 = ptr1; // 编译出错 因为没写拷贝构造在调用op=时 无法通过拷贝构造来构造形参ptr3 = std::move(ptr1); // OK,可以 调用op=时 通过移动构造来构造形参smart_ptr<shape> ptr4{std::move(ptr3)}; // OK,可以 移动构造
这也是 C++11 的 unique_ptr 的基本行为。
子类指针向父类指针的转换(将子类指针强转为父类指针 可实现多态 ) 隐式模板类型转换
circle(子类指针) 是可以隐式转换成 shape(父类指针) 的,但上面的 smart_ptr
添加一个构造函数,就能实现smart_ptr
template <typename U>smart_ptr(smart_ptr<U>&& other){ptr_ = other.release();}
添加了这个构造函数后,能实现smart_ptr
需要注意smart_ptr(smart_ptr&& other)这个函数不会被编译器当作移动构造函数,因而不会自动触发删除拷贝构造函数的行为。如果我们想要实现自动移动,需要显示地将拷贝构造函数标记为=delete,或者定义含模板参数的拷贝构造函数
引用计数
上面讲的smart_ptr就是std中unique_ptr,unique_ptr算是较为安全的智能指针。但是一个堆上内存(或者其他资源)只能被单个unique_ptr所拥有—unique_ptr的op= 或者构造 会将右边的资源移到左边,右边的资源指针清为null,这也就导致了只有一个unique_ptr能拥有资源。下面来讲一下std中的shared_ptr,多个shared_ptr智能指针能同时拥有一个堆上内存(或者其他资源),当所有shared_ptr失效(生命周期结束)才会去释放这个资源。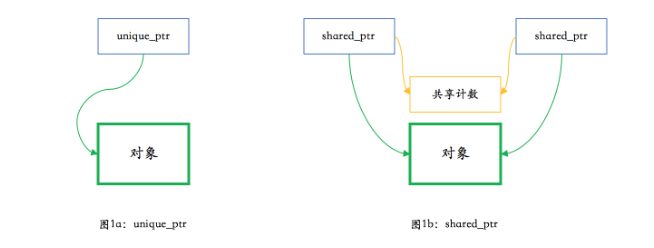
shared_ptr实现共享同一个对象的功能需要同时共享一个计数,记录当前有多少个shared_ptr共享了这一资源,引用计数为1时的这个shared_ptr生命周期结束才释放资源。
共享引用计数的接口
class shared_count {public:shared_count();void add_count();//增加计数long reduce_count();//减少计数 需要返回减少后的计数值以便调用者判断 计数是否变为0了long get_count() const;//返回计数};
多线程安全版本的引用计数需要用到一些目前还没学到的知识 先实现一个简单版本的
class shared_count {public://因为在移动构造中有用到下面这些代码 所以全部都需要添加 不会报错的声明noexceptshared_count() noexcept : count_(1) {}void add_count() noexcept{++count_;}long reduce_count() noexcept{return --count_;}long get_count() const noexcept{return count_;}private:long count_;};
实现shared_ptr
template <typename T>class smart_ptr {public:// 模板的各个实例间并不天然就有 friend 关系,// 因而不能互访私有成员 ptr_ 和 shared_count_。// 我们需要在 smart_ptr 的定义中显式声明// smart_ptr<T>和smart_ptr<U>不是同一个类!!!!template <typename U>friend class smart_ptr;explicit smart_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr): ptr_(ptr) //explicit 标识该构造函数的调用必须是显示的//不能隐式调用(传入一个T*指针给一个smart_ptr类型形参 让编译器构造自动调用构造函数去构造这个形参){if (ptr) {shared_count_ =new shared_count();}}~smart_ptr(){if (ptr_ &&!shared_count_->reduce_count()) {//资源ptr存在 并且当前为//最后一个指向该资源的指针(引用计数为0)才析构释放资源delete ptr_;delete shared_count_;}}#include <utility>// std::swapvoid swap(smart_ptr& rhs)//用于资源交换{using std::swap;swap(ptr_, rhs.ptr_);swap(shared_count_,rhs.shared_count_);}smart_ptr(const smart_ptr& other)//拷贝构造{//使this 共享 other的资源ptr_ = other.ptr_;if (ptr_) {other.shared_count_->add_count();//与other一样指向同一块资源 此资源的引用计数+1shared_count_ =other.shared_count_;}}template <typename U>smart_ptr(const smart_ptr<U>& other) noexcept //隐式类型转换(子类转父类) 拷贝构造{//使this 共享 other的资源ptr_ = other.ptr_;if (ptr_) {other.shared_count_->add_count();shared_count_ =other.shared_count_;}}template <typename U>smart_ptr(smart_ptr<U>&& other) noexcept//移动构造的本质是“偷”,所以直接other的资源偷来//不是与other共享ptr资源而是 直接替代other所以引用计数不需要加//隐式类型转换(子类转父类) 或者 同类型(U和T的类别一样) 的移动构造{ptr_ = other.ptr_;if (ptr_) {shared_count_ =other.shared_count_;//不是与other共享ptr资源而是 直接替代other所以引用计数不需要加other.ptr_ = nullptr;//偷走other的资源后 将other的资源置为null}}//为了实现强制的smart_ptr模板参数类型转换,添加下面这个构造函数//允许在对智能指针内部的指针对象ptr赋值时,//使用一个现有的智能指针的共享计数template <typename U>smart_ptr(const smart_ptr<U>& other,T* ptr) noexcept{//将ptr作为资源 将other资源的引用计数+1作为这个ptr的引用计数ptr_ = ptr; //ptr是外面传进来的,不是other资源指针if (ptr_) {other.shared_count_->add_count();shared_count_ = other.shared_count_;}}//依据传入的实参是右值还是左值来构造形参rhs//形参得到传入实参的资源后(实参是左值拷贝资源 实参是右值偷走资源)//与this进行资源的互换 返回this,函数结束//自动析构形参 因为形参的资源由实参而来 所以函数结束就释放形参资源(引用计数--)smart_ptr& operator=(smart_ptr rhs) noexcept{rhs.swap(*this);return *this;}//返回共享资源指针T* get() const noexcept { return ptr_; }//用于调试 返回当前资源ptr的引用计数long use_count() const noexcept{if (ptr_) {return shared_count_->get_count();} else {return 0;}}// 添加下面3个操作符重载使smart_ptr行为更像指针T& operator*() const noexcept { return *ptr_; }T* operator->() const noexcept { return ptr_; }operator bool() const noexcept { return ptr_; }private:T* ptr_;shared_count* shared_count_;};
强制类型转换 实现父类->子类的强制转换
// 调用时子类是T,父类是Utemplate <typename T>void swap(smart_ptr<T>& lhs,smart_ptr<T>& rhs) noexcept{lhs.swap(rhs);}template <typename T, typename U>smart_ptr<T> static_pointer_cast(const smart_ptr<U>& other) noexcept{T* ptr = static_cast<T*>(other.get());return smart_ptr<T>(other, ptr);}template <typename T, typename U>smart_ptr<T> reinterpret_pointer_cast(const smart_ptr<U>& other) noexcept{T* ptr = reinterpret_cast<T*>(other.get());return smart_ptr<T>(other, ptr);}template <typename T, typename U>smart_ptr<T> const_pointer_cast(const smart_ptr<U>& other) noexcept{T* ptr = const_cast<T*>(other.get());return smart_ptr<T>(other, ptr);}// smart_ptr<circle> ptr1(new circle());// smart_ptr<shape> ptr2;// ptr2 = ptr1;// smart_ptr<circle> ptr3 = dynamic_pointer_cast<circle>(ptr2);//ptr2 shape->circle 父类转为子类// 调用时circle是T,shape是U// printf("use count of ptr3 is %ld\n",ptr3.use_count());//use count of ptr3 is 3template <typename T, typename U>smart_ptr<T> dynamic_pointer_cast(const smart_ptr<U>& other) noexcept{T* ptr = dynamic_cast<T*>(other.get());//将other 内部的U* shape* -> T* circlereturn smart_ptr<T>(other, ptr);}

