对象(object)到底是什么?
- 对象是单个实物的抽象。
- e.g. : 一本书、一辆汽车、一个人都可以是对象
- 当实物被抽象成对象,实物之间的关系就变成了对象之间的关系,从而就可以模拟现实情况,针对对象进行编程。
- 对象是一个容器,封装了属性(property)和方法(method)。
- 属性是对象的状态
- 方法是对象的行为(完成某种任务)。
- 比如,我们可以把动物抽象为
animal对象,使用“属性”记录具体是哪一种动物,使用“方法”表示动物的某种行为(奔跑、捕猎、休息等等)。
- 比如,我们可以把动物抽象为
构造函数(constructor)
JavaScript 语言的对象体系,不是基于“类”的,而是基于构造函数(constructor)和原型链(prototype)。
- 每个函数都有
**prototype**属性 - 每个
**prototype**对象都有**constructor**属性 - 每个
**constructor**属性的值都是它的函数自身function P() {}P.prototype.constructor === P // true
constructor属性的作用:是可以得知某个实例对象,到底是哪一个构造函数产生的。
什么是构造函数?
构造函数作为对象的模板。就是专门用来生成实例对象的函数。
- 可以构造出对象的函数
代码规范:
大小写
- 所有构造函数(专门用于创建对象的函数)首字母大写
- 所有被构造出来的对象,首字母小写
function Dog(){} // Dog 首字母大写let dog1 = new Dog() // dog1 首字母小写
词性
- new 后面的函数(构造函数),使用名词形式
- 如 new Person()、new Object()
- 其他函数,一般使用动词开头
- 如 createSquare(5)、createElement(‘div’)
- 其他规则以后再说
let arr1 = new Array()能接受几个参数?- 如果只传一个参数,
let arr1 = new Array(3)- 那么表示的就是数组的长度,长度为3的空数组
- 如果传两个参数,
let arr2 = new Array(3,5)- 意思就是第一个元素是3,第二个元素是5
- 如果只传一个参数,
new 命令
new命令的作用:就是执行构造函数,返回一个实例对象。 ```javascript var Vehicle = function () { this.price = 1000; };
var v = new Vehicle(); v.price // 1000 // new命令执行时,构造函数内部的this,就代表了新生成的实例对象,this.price表示实例对象有一个price属性,值是1000。
- **new X() 自动做了四件事情**- 自动创建空对象- 自动为空对象关联原型,原型地址指定为 X.prototype- 自动将空对象作为 this 关键字运行构造函数- 自动 return this- **构造函数 X**- `X` 函数本身负责给对象本身**添加**属性- `X.prototype` 对象负责**保存**对象的共有属性**如果忘了使用 **`**new**`** 命令,直接调用构造函数会发生什么事?**- 这种情况下,构造函数就变成了普通函数,并不会生成实例对象。而且由于后面会说到的原因,`this` 这时代表全局对象,将造成一些意想不到的结果。```javascriptvar Vehicle = function (){this.price = 1000;};var v = Vehicle();v // undefinedprice // 1000
- 为了保证构造函数必须与
new命令一起使用的解决办法:- 构造函数内部使用严格模式,即第一行加上
use strict。 ```javascript / 加上’use strict’ / function Fubar(foo, bar){ ‘use strict’;
this._foo = foo; this._bar = bar; }
- 构造函数内部使用严格模式,即第一行加上
Fubar() // TypeError: Cannot set property ‘_foo’ of undefined
由于严格模式中,函数内部的 this 不能指向全局对象,默认等于undefined, 导致不加new 调用会报错(JavaScript 不允许对undefined添加属性)。
函数与原型结合,写**正方形**示例:```javascript/* 代码1 */let squareList = []let widthList = [5,6,5,6,5,6,5,6,5,6,5,6]function createSquare(width){let obj = Object.create(createSquare.squarePrototype)obj.width = widthreturn obj}createSquare.squarePrototype = { //把原型放到函数上getArea(){return this.width * this.width},getLength(){return this.width * 4},constructor: createSquare //方便通过原型找到构造函数}for(let i = 0; i<12; i++){squareList[i] = createSquare(widthList[i])console.log(squareList[i].constructor)// constructor 可以知道谁构造了这个对象:你妈是谁?}
用构造函数简化代码1
function Square(width){this.width = width}Square.prototype.getArea = function(){return this.width * this.width}Square.prototype.getLength = function(){return this.width * 4}let square = new Square(5)square.widthsquare.getArea()square.getLength()
圆形
function Circle(radius){this.radius = radius}Circle.prototype.getArea = function(){return Math.pow(this.radius,2) * Math.PI}Circle.prototype.getLength = function(){return this.radius * 2 * Math.PI}let circle = new Circle(5)circle.radiuscircle.getArea()circle.getLength()
长方形
function Rect(width, height){this.width = widththis.height = height}Rect.prototype.getArea = function(){return this.width * this.height}Rect.prototype.getLength = function(){return (this.width + this.height) * 2}let react = new Rect(4,5)rect.widthrect.heightrect.getArea()rect.getLength()
class 语法
ES 6 引入了新语法:class
到底有多少新语法
- ES 6 新特性列表
- 关于类和对象的新语法有类,对象初始化和解构赋值
用 class 重写 Square
class Square{static x = 1 // static的意思是 x属性是 Square的,要用x时只需 Square.xwidth = 0 // 初始化 this.widthconstructor(width){this.width = width}getArea(){return this.width * this.width}getLength(){return this.width * 4}get area2(){ // 只读属性return this.width * this.width}}
用 class 重写 Circle
class Circle{constructor(radius){this.radius = radius}getArea(){return Math.pow(this.radius,2) * Math.PI}getLength(){return this.radius * 2 * Math.PI}}let circle = new Circle(5)circle.radiuscircle.getArea()circle.getLength()
用 class 重写 Rect
代码class Rect{constructor(width, height){this.width = widththis.height = height}getArea(){return this.width * this.height}getLength(){return (this.width + this.height) * 2}}let react = new Rect(4,5)rect.widthrect.heightrect.getArea()rect.getLength()
class 中两种函数写法的区别
语法1:class Person{sayHi(name){}}//等价于function Person(){}Person.prototype.sayHi = function(name){}语法2:注意冒号变成了等于号class Person{sayHi = (name)=>{} // 注意,一般我们不在这个语法里使用普通函数,多用箭头函数}// 等价于function Person(){this.sayHi = (name)=>{}}
不要强求完全转换成 ES5
- 大部分 class 语法都可以转为 ES5 语法,但并不是 100% 能转
- 有些 class 语法意思理解就行,不需要强行转换为 ES5。
对象为什么需要分类
- 理由一
- 有很多对象拥有一样的属性和行为,需要把它们分为同一类,创建类似对象的时候就很方便
- 如 square1 和 square2
- 有很多对象拥有一样的属性和行为,需要把它们分为同一类,创建类似对象的时候就很方便
- 理由二
- 还有很多对象拥有其他的属性和行为,就需要不同的分类
- 比如 Square / Circle / Rect 就是不同的分类
- Array / Function 也是不同的分类
- Object 创建出来的对象,是最没有特点的对象
- 还有很多对象拥有其他的属性和行为,就需要不同的分类
类型 V.S. 类
- 类型
- 类型是 JS 数据的分类,有 7 种:
- 四基两空一对象
- 类
- 类是针对于对象的分类,有无数种
- 有特点的类常见的有 Array、Function、Date、RegExp 等
数组对象
定义一个数组
let arr = [1,2,3]let arr = new Array(1,2,3) // 元素为 1,2,3let arr = new Array(3) // 长度为 3
数组对象的自身属性
- ‘0’ / ‘1’ / ‘2’ / ‘length’
- 【注意】属性名没有数字,只有字符串
- 数组对象的共用属性
'push' / 'pop' / 'shift' / 'unshift' / 'join'- 用法都在 MDN
函数对象
定义一个函数
function fn(x,y){return x+y} // function,函数,参数,函数体let fn2 = function fn(x,y){return x+y} // 赋值语句let fn = (x,y) => x+y // 箭头函数 参数->值let fn = new Function('x','y', 'return x+y') // new Function
函数对象自身属性
'name' / 'length'
- 函数对象共用属性
'call' / 'apply' / 'bind'
JS 终极一问
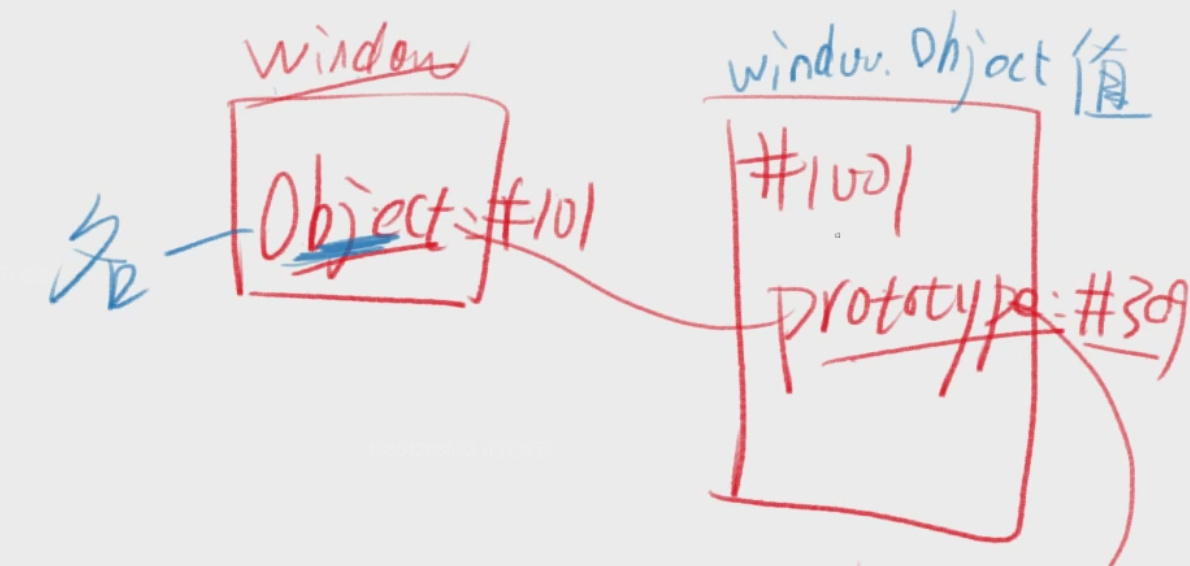
window 是谁构造的
Window-
window.Object 是谁构造的
window.Function-
window.Function 是谁构造的
window.Function- 因为所有函数都是 window.Function 构造的
- 浏览器构造了 Function,然后指定它的构造者是自己
属性名和属性值是两个概念
问:
let square = new Square(5)square 的原型(square.__proto__ 的值)是什么?
Square.prototype
Object.prototype是哪个函数构造出来的?- 不知道,它没有父母
- Object.prototype 的原型是什么?
- 根对象没有原型
- Object.prototype.proto?
null
原型公式