一、分布式配置中心概述
- 微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务。由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能够运行,所以一套集中式的,动态的配置管理设施是必不可少的。
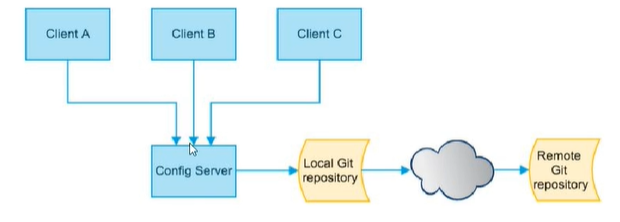
- SpringCloud Config为微服务架构中的微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,配置服务器为各个不同微服务应用的所有环境提供了一个中心化的外部配置。
- SpringCloud提供了ConfigServer【配置中心】来解决这个问题,我们每一个微服务自己都带着一个
application.yaml,上百个配置文件的管理就要管理上百个application.yaml。其主要作用如下:- 集中管理配置文件:不同环境不同配置,动态化的配置更新,分环境部署,比如dev/test/prod/beta/release
- 运行期间动态调整配置,不再需要在每个服务部署的机器上编写配置文件,服务会向配置中心统一拉取配置自己的信息。
- 当配置发生变动时,服务不需要重启即可感知到配置的变化并应用新的配置
- 将配置信息以REST接口的形式暴露。
二、搭建Config分布式配置
1、Config服务端与Gitee整合
- 新建模块 spring-config-center-3344
写pom
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId></dependency>
写yml ```yaml server: port: 3344
spring: application: name: cloud-config-center cloud: config: server: git: uri: https://gitee.com/codesofun-tao/gitee-springcloud-config.git username: password:
# 搜索目录
search-paths:
- gitee-springcloud-config
# 分支
label: master
4. 写主启动类
```java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer //开启配置中心
public class ConfigApplication3344 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigApplication3344.class, args);
}
}
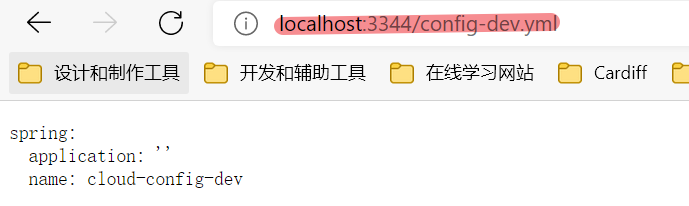
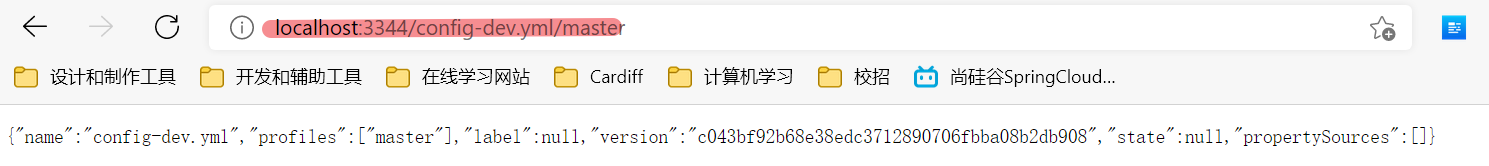
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}] # 读取结果是一个json
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml # 读取结果是一个yml,推荐使用这种格式
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
2、Config客户端配置
- 创建模块 cloud-config-client-3355
写pom
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency>写yml:从配置中心服务端取配置文件
application.yml配置文件是用户级的资源配置项bootstrap.yml是系统级的资源配置项,它的优先级更高- SpringCloud会创建一个Bootstrap Context,作为Spring应用的Application Context的父上下文。初始化的时候,BootstrapContext负责从外部资源加载配置属性并解析配置。这两个上下文共享一个从外部获取的Environment。Bootstrap属性有高优先级,默认情况下,它们不会被本地配置覆盖。Bootstrap Context和Application Context有着不同的约定,所以新增了一个bootstrap.yml文件,保证Bootstrap Context和Application Context配置的分离。
- 要将Client模块下的application.yml文件改为bootstrap.yml,这是很关键的,因为bootstrap.yml是比application.yml先加载的。
server:
port: 3355
spring:
application:
name: config-client
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:3344
name: config
profile: dev
label: master
# 合起来就是 master分支上的 config-dev.yml
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication public class ConfigClient3355 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigClient3355.class, args); } }三、随之而来的问题
随之而来的问题:如果说我们想要对某个配置文件的内容进行修改,那么修改之后刷新Config的服务端,配置中心会立即响应,但是它的客户端没有任何响应,除非客户端自己重启或者重新加载。这就是Config配置中心的分布式配置的动态刷新问题。
1、@Refresh动态刷新手动版
修改客户端模块的pom文件,加入actuator监控
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency>修改
bootstrap.yml配置文件,添加暴露监控端口配置# 暴露监控端点 actuator management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'业务类添加
@RefreshScope注解@RefreshScope @RestController public class TestController { @Value("${config.info}") private String value; @GetMapping("/show") public String index() { System.out.println(value); return value; } }运维人员手动发送POST请求通知客户端配置已经修改。
curl -X POST "http://localhost:3355/actuator/refresh"2、原理
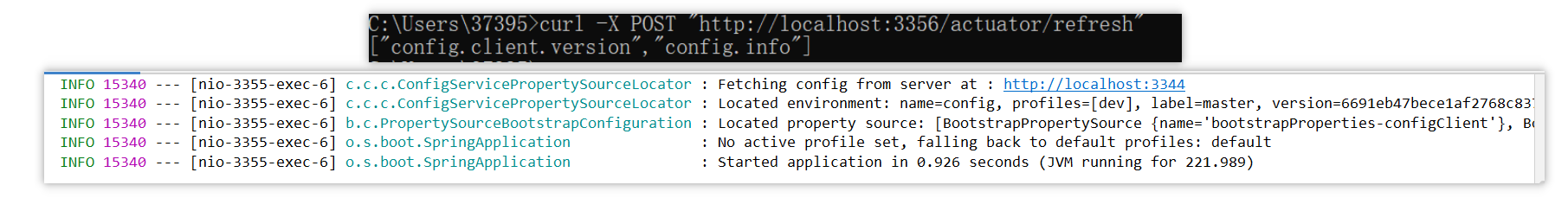
本质是通过 springboot 的监控配置,重启服务器。