一、MyBatis事务(spring时再讲)
在创建sqlsession对象时传一个参数进去 true时 得到的SqlSession的事务自动提交时开启的SqlSession sqlSession = ``**build.openSession(**``**true**``**); **``(开发时用的少)
二、动态sql
1、 标签
在映射配置文件中这样写
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="com.yixuexi.entity.User" parameterType="com.yixuexi.entity.User">select * from user where 1 = 1 // 使用if标签 where 1=1不能省略<if test="name != null">and name = #{name}</if></select>
- 这里面的if 并且的关系是and 或者的关系是or
- 其实就是sql语句的拼接 在select语句后面 加个if就是拼接上if里面的内容
- 如果有多个条件 可以添加多个if
多个if都会执行select * from user where 1 = 1 <if test="name != null"> and name = #{name} </if> <if test="password != null"> and password = #{password} </if>
2、where标签
- 使用where标签可以省略 where 1 = 1
- 就是在 if标签外面套一层 where包裹起来
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="com.yixuexi.entity.User" parameterType="com.yixuexi.entity.User"> select * from user <where> <if test="name != null"> and name = #{name} </if> <if test="password != null"> and password = #{password} </if> </where> </select>3、foreach标签
```xml
---
<a name="BE8gI"></a>
# 三、多表查询
<a name="983ce102"></a>
## 1、一对一的数据库查询
<a name="GvXEy"></a>
### 1、创建Account子类的方式 (不常用)
`SQL`语句是这样的 (一个用户对一个账户)
```sql
SELECT
a.* , u.name AS NAME ,u.password AS PASSWORD
FROM
account a
JOIN
USER u
ON
a.uid = u.id
- 此时mybatis需要准备好两张表 一张Account表 和 一张继承Account的表 继承的表里面有需要查出来的别的字段
- AccountUser子表 需要重写toString() 并且重写时,调用父类的toString() super.toString()
- 然后在AccountDao接口中创建一个方法
List``**<AccountUser**``> findAllAccountUser();- 返回值需是Account的子类,因为子类中有父类没有的属性 name 和 password
然后在映射文件中写sql语句
<select id="findAllAccountUser" resultType="AccountUser"> <!--因为这里再主配置文件中配置了typeAliases所以直接写类名即可--> select a.* , u.name ,u.password from account a join user u on a.uid = u.id </select>这里的数据库列名需要和实体类中的属性名一致,所以再创建子类的时候 属性名要写好
2、从表中有实体引用(常用)
1) 从表实体类中应该含一个主表实体的包对象引用
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private Integer uid;
private Double money;
//从表实体类中应该有一个主表的对象
private User user;
}
student学生表 引用了外键 class的id 班级表 那么说 student就是从表 class就是主表
2) SQL语句
select
a.*,u.id,u.name,u.password
from
account a
join
user u
on
a.uid = u.id
3) 因为Account(子表)表中有一个主表的对象,那么再查询结果封装的时候是 没办法把User封装进去的,需要这样设置
<!--定义一个能封装account和user的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="accountUserMap" type="Account">
<!--定义主键字段-->
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<!--定义非主键字段-->
<result property="uid" column="uid"></result>
<result property="money" column="money"></result>
<!--一对一的关系映射:配置user的内容-->
<!--property:该实体类中的哪个对应关系的主表属性-->
<!--column:通过哪一个 字段进行获取的-->
<!--javaType:最后的结果封装到哪个类 正常写法是com.xxx.xx 用了TypeAlia..所以直接类名-->
<association property="user" column="uid" javaType="User">
<!--在里面写User的属性和数据库对应起来-->
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
4) sql语句原封不动的写就行
<select id="findAll" resultMap="**accountUserMap**">这里写上resultMap起的id名
2、一对多(一个用户有多个账户)
- 账户表的外键引用了用户表的主键,那么说账户表是从表,用户表示主表
- 一对多关系映射:主表实体中应该包含从表实体的集合引用
1、UserDao接口中的方法
List<User> findAll();2、User实体类中的属性
public class User { private Integer id; private String name; private String password; //一对多关系映射:主表实体中应该包含从表实体的集合引用 private List<Account> accounts; }3、SQL语句
```sql select u.*,a.id as aid ,a.uid,a.money from user u left join account a on u.id = a.uid
因为有两个id所以给account表中的id起一个别名
<a name="34be61b6"></a>
### 4、在映射配置文件中写对应关系
```xml
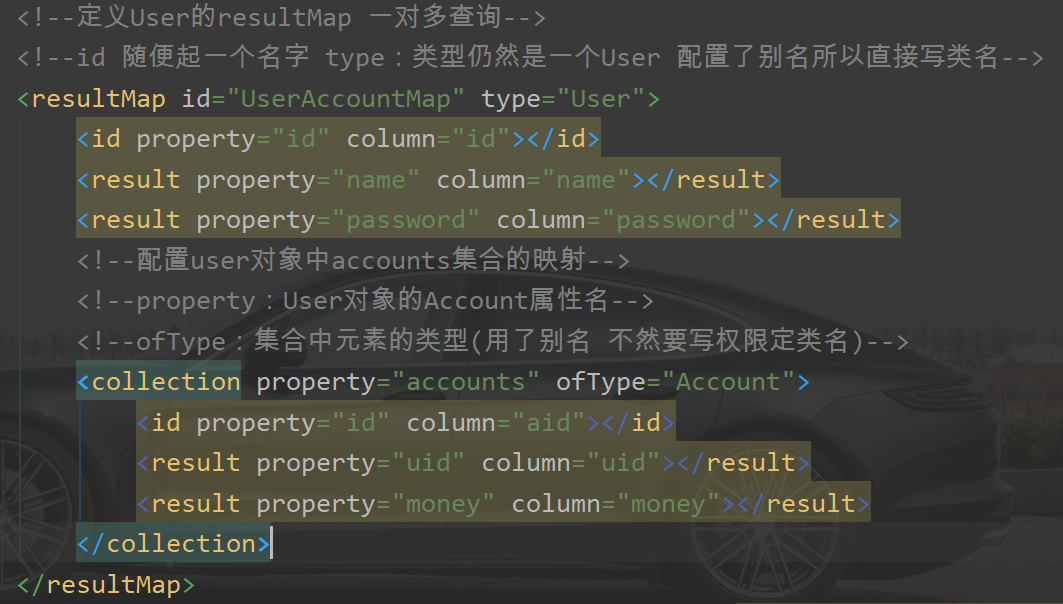
<!--定义User的resultMap 一对多查询-->
<!--id 随便起一个名字 type:类型仍然是一个User 配置了别名所以直接写类名-->
<resultMap id="UserAccountMap" type="User">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
<!--配置user对象中accounts集合的映射-->
<!--property:User对象的Account属性名-->
<!--ofType:集合中元素的类型(用了别名 不然要写权限定类名)-->
<!--一对多需要用 collection标签 -->
<collection property="accounts" ofType="Account">
<id property="id" column="aid"></id>
<result property="uid" column="uid"></result>
<result property="money" column="money"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
3、多对多
多对多,三张表,关系表两个外键
示例:用户和角色
- 一个用户有多个角色
- 一个角色可以赋予多个用户
各自包含对方一个集合引用
- 当我们查询用户是,可以同时得到用户所包含的角色信息
- 当我们查询角色是,可以同时得到角色的所赋予的用户信息
1、SQL语句
查询身份并且显示对应的用户信息
SELECT
u.*,r.id AS role_id,r.role_name,r.role_desc
FROM
USER u
JOIN
user_role ur #连接关系表 条件是用户表的id等于关系表的uid
ON
u.id = ur.uid
JOIN
role r ##连接身份表 条件是身份表的id等于关系表的rid
ON
r.id = ur.rid
数据库里面的id会有重复 所以要起一个别名,不过不要忘了配置文件的cloumn属性也改成别名
2、在RoleDao中创建一个方法
public interface RoleDao {
/**
* 查询所有角色
* @return
*/
List<Role> findAll();
}
3、Role实体类中的属性是这样的
public class Role implements Serializable {
private Integer roleId;
private String roleName;
private String roleDesc;
//多对多的关系映射,一个角色可以赋予多个用户
private List<User> users;
}
4、在RoleDaoMapper.xml文件中配置一下对应关系
<!--id就是起个名字 type:是什么类型,(全限定类名,但是又typeAlia)-->
<resultMap id="roleUserMap" type="Role">
<!--配置主键 properties:类中的属性 column:数据库中的字段-->
<id property="roleId" column="role_id"></id>
<result property="roleName" column="role_name"></result>
<result property="roleDesc" column="role_desc"></result>
<!--配置role对象中的users集合映射关系-->
<!--properties:写要配置哪个属性名-->
<!--ofType:集合里面是什么数据类型(全限定类名 …)-->
<collection property="users" ofType="User" >
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="password" column="password"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
5、编写测试类
RoleDao mapper = session.getMapper(RoleDao.class);
List<Role> all = mapper.findAll();
for (Role role : all) {
System.out.print(role);
System.out.println(role.getUsers());
}
- 在循环的时候调用一下
role.getUsers(); - 或者直接把users重写进
toString()// 这样会直接输出 list集合的toString()而哪个List集合的toString()已经重写

