一、双指针
11. 盛最多水的容器
难度中等2130
给你 n 个非负整数 a,a...,a``n每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, a) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, a) 和 (i, 0) 。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
示例 1: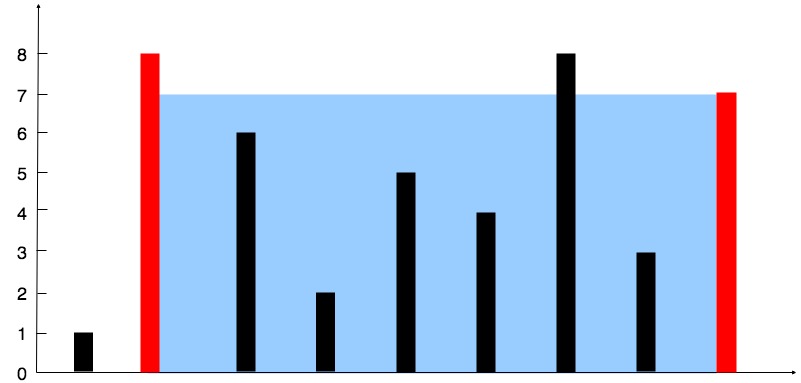
输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
输出:49
解释:图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
示例 2:
输入:height = [1,1]
输出:1
示例 3:
输入:height = [4,3,2,1,4]
输出:16
示例 4:
输入:height = [1,2,1]
输出:2
提示:
n = height.length2 <= n <= 3 * 100 <= height[i] <= 3 * 10<br />
class Solution {public int maxArea(int[] height) {if(height == null || height.length == 0){return 0;}int i = 0;int j = height.length - 1;int maxArea = 0;while ( i < j ){//处理逻辑int h = Math.min(height[i],height[j]);int w = j - i;int area = h * w;maxArea = Math.max(area,maxArea);//移动位置if(height[i] < height[j]){i++;}else{j--;}}return maxArea;}}
283. 移动零
难度简单922
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
说明:
- 必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。
- 尽量减少操作次数。
class Solution {public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {//判断if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){return;}//逻辑int i = 0;//始终指向下一个非0元素将要存放的位置int j = 0;//遍历数组的时候,从开头走到尾for (j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {if(nums[j] != 0){//交换位置int temp = nums[j];nums[j] = nums[i];nums[i] = temp;i++;}}}}
15. 三数之和
难度中等2905
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 _a + b + c = _0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[]
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 3000-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
int len = 0;
if( nums == null || (len = nums.length) == 0){
return result;
}
//先排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//跳过重复值
if( i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
//目标数 a + b + c = 0 <===> a + b = -c
int target = -nums[i];
//定义双指针来寻找另外两个数
int j = i + 1;
int k = len - 1;
while ( j < k ){
//如果a + b = -c
if( nums[j] + nums[k] == target){
//封装数据
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums[i]);
list.add(nums[j]);
list.add(nums[k]);
result.add(list);
//往中间逼近,因为这两个位置都使用过了所以首先各自先移动位置
j++;
k--;
//检查左边是否有重复的
while ( j < len && nums[j] == nums[j-1]){
j++;
}
//检查右边是否有重复的
while ( k > j && nums[k] == nums[ k + 1 ] ){
k--;
}
// a + b > -c 说明数大了,要减小
}else if( nums[j] + nums[k] > target){
k--;
//a + b < -c 说明数小了,要增大
}else {
j++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
26. 删除排序数组中的重复项
难度简单1794
给定一个排序数组,你需要在 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
示例 1:
给定数组 nums = [1,1,2],
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
给定 nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且原数组 nums 的前五个元素被修改为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int i = 0;//始终记录第一个不是重复的数
for (int j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if(nums[i] != nums[j]){
nums[++i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}
}
88. 合并两个有序数组
难度简单740
给你两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,请你将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使 nums1 成为一个有序数组。
初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n 。你可以假设 nums1 的空间大小等于 m + n,这样它就有足够的空间保存来自 nums2 的元素。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
输出:[1,2,2,3,5,6]
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
输出:[1]
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
if (m == 0) {
nums1[0] = nums2[0];
}
m--;
n--;
while (m >= 0 && n >= 0) {
if (nums1[m] > nums2[n]) {
nums1[m + n + 1] = nums1[m];
m--;
} else {
nums1[m + n + 1] = nums2[n];
n--;
}
}
int index = m + n + 1;
if (m == -1 && n >= 0) {
while (n >= 0) {
nums1[index--] = nums2[n--];
}
}
if (m >= 0 && n == -1) {
while (m >= 0)
nums1[index--] = nums1[m--];
}
}
}
二、dp动态规划
70. 爬楼梯
难度简单1430
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
示例 1:
输入: 2
输出: 2
解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 2 阶
示例 2:
输入: 3
输出: 3
解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
class Solution {
static public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n <= 2){
return n;
}
int dp[] = new int[n+1];
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3;i <= n;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}
三、自底向上
189. 旋转数组
难度中等862
给定一个数组,将数组中的元素向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
进阶:
- 尽可能想出更多的解决方案,至少有三种不同的方法可以解决这个问题。
你可以使用空间复杂度为 O(1) 的 原地 算法解决这个问题吗?
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
输出:[5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
解释:
向右旋转 1 步:[7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
向右旋转 2 步:[6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
向右旋转 3 步:[5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2
输出:[3,99,-1,-100]
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: [99,-1,-100,3]
向右旋转 2 步: [3,99,-1,-100]
class Solution { public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) { int len = nums.length; //自底向上 for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { //记录要放到前面的数字 int temp = nums[len-1]; //向后挪动 for (int j = len-1; j > 0; j--) { nums[j] = nums[j-1]; } //赋值 nums[0] = temp; } } }
四、Hash表解法
1. 两数之和
难度简单10128
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出:[0,1]
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] indexs = new int[2];
// 双重循环 循环极限为(n^2-n)/2
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
for(int j = nums.length - 1; j > i; j --){
if(nums[i]+nums[j] == target){
indexs[0] = i;
indexs[1] = j;
return indexs;
}
}
}
return indexs;
}
// public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// int[] result = new int[2];
// Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
// for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
// result[1] = i;
// result[0] = map.get(target - nums[i]);
// return result;
// }
// map.put(nums[i], i);
// }
// return result;
// }
}
五、取模法
66. 加一
难度简单616
给定一个由 整数 组成的 非空 数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。
最高位数字存放在数组的首位, 数组中每个元素只存储单个数字。
你可以假设除了整数 0 之外,这个整数不会以零开头。
示例 1:
输入:digits = [1,2,3]
输出:[1,2,4]
解释:输入数组表示数字 123。
示例 2:
输入:digits = [4,3,2,1]
输出:[4,3,2,2]
解释:输入数组表示数字 4321。
示例 3:
输入:digits = [0]
输出:[1]
class Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
for (int i = digits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
digits[i]++;
digits[i] = digits[i] % 10;
if (digits[i] != 0) return digits;
}
digits = new int[digits.length + 1];
digits[0] = 1;
return digits;
}
}
六、数组实现xxx
641. 设计循环双端队列
难度中等70
设计实现双端队列。
你的实现需要支持以下操作:
- MyCircularDeque(k):构造函数,双端队列的大小为k。
- insertFront():将一个元素添加到双端队列头部。 如果操作成功返回 true。
- insertLast():将一个元素添加到双端队列尾部。如果操作成功返回 true。
- deleteFront():从双端队列头部删除一个元素。 如果操作成功返回 true。
- deleteLast():从双端队列尾部删除一个元素。如果操作成功返回 true。
- getFront():从双端队列头部获得一个元素。如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
- getRear():获得双端队列的最后一个元素。 如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
- isEmpty():检查双端队列是否为空。
- isFull():检查双端队列是否满了。
示例:
MyCircularDeque circularDeque = new MycircularDeque(3); // 设置容量大小为3
circularDeque.insertLast(1); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertLast(2); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(3); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 已经满了,返回 false
circularDeque.getRear(); // 返回 2
circularDeque.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.deleteLast(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 返回 true
circularDeque.getFront(); // 返回 4
class MyCircularDeque {
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k. */
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
}
/** Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
}
/** Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
}
/** Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deleteFront() {
}
/** Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deleteLast() {
}
/** Get the front item from the deque. */
public int getFront() {
}
/** Get the last item from the deque. */
public int getRear() {
}
/** Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
}
/** Checks whether the circular deque is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularDeque obj = new MyCircularDeque(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.insertFront(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.insertLast(value);
* boolean param_3 = obj.deleteFront();
* boolean param_4 = obj.deleteLast();
* int param_5 = obj.getFront();
* int param_6 = obj.getRear();
* boolean param_7 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_8 = obj.isFull();
*/
解法:
public class MyCircularDeque {
// 1、不用设计成动态数组,使用静态数组即可
// 2、设计 head 和 tail 指针变量
// 3、head == tail 成立的时候表示队列为空
// 4、tail + 1 == head
private int capacity;
private int[] arr;
private int front;
private int rear;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k.
*/
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
capacity = k + 1;
arr = new int[capacity];
// 头部指向第 1 个存放元素的位置
// 插入时,先减,再赋值
// 删除时,索引 +1(注意取模)
front = 0;
// 尾部指向下一个插入元素的位置
// 插入时,先赋值,再加
// 删除时,索引 -1(注意取模)
rear = 0;
}
/**
* Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.
*/
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
front = (front - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
arr[front] = value;
return true;
}
/**
* Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.
*/
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
arr[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
/**
* Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.
*/
public boolean deleteFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
// front 被设计在数组的开头,所以是 +1
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
/**
* Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful.
*/
public boolean deleteLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
// rear 被设计在数组的末尾,所以是 -1
rear = (rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity;
return true;
}
/**
* Get the front item from the deque.
*/
public int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return arr[front];
}
/**
* Get the last item from the deque.
*/
public int getRear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
// 当 rear 为 0 时防止数组越界
return arr[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];
}
/**
* Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not.
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
/**
* Checks whether the circular deque is full or not.
*/
public boolean isFull() {
// 注意:这个设计是非常经典的做法
return (rear + 1) % capacity == front;
}
}
七、单调递减栈解数组
42. 接雨水
难度困难1964
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:
输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
示例 2:
输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
输出:9
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
int water = 0;
//特殊情况
if(height.length <3){
return 0;
}
for(int i = 0; i < height.length; i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]){
//栈顶元素
int popnum = stack.pop();
//相同元素的情况例1,1
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&height[popnum] == height[stack.peek()]){
stack.pop();
}
//计算该层的水的单位
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
int temp = height[stack.peek()];//栈顶元素值
//高
int hig = Math.min(temp-height[popnum],height[i]-height[popnum]);
//宽
int wid = i-stack.peek()-1;
water +=hig * wid;
}
}
//这里入栈的是索引
stack.push(i);
}
return water;
}
}

