基本操作符
. 成员访问操作符
System.IO.File.Create("D:\\HelloWorld.txt");1 2 3var myForm = new Form();myForm.Text = "Hello, World";4myForm.ShowDialog();4
- 访问外层名称空间中的子名称空间
- 访问名称空间中的类型
- 访问类型的静态成员
- 访问对象中的实例成员
f(x) 方法调用操作符
C# 里方法调用都要用到()。
Action 是委托,委托在创建时只需要知道方法的名称,不调用方法,所以只会用到方法名(不加())。当然最终myAction();也用到了方法调用操作符()。
namespace OperatorsExample{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculator c = new Calculator();double x = c.Add(3.0, 4.6);Console.WriteLine(x);Action myAction = new Action(c.PrintHello);//Action是委托,这里PrintHello没有加括号myAction();}}class Calculator{public double Add(double a,double b){return a + b;}public void PrintHello(){Console.WriteLine("Hello");}}}
a[x] 元素访问操作符
访问数组元素:
int[] myIntArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };Console.WriteLine(myIntArray[0]);Console.WriteLine(myIntArray[myIntArray.Length - 1]);
索引字典中的元素
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Dictionary<string, Student> stuDic = new Dictionary<string, Student>();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){Student stu = new Student(){Name = "s_" + i.ToString(),Score = 100 - i};stuDic.Add(stu.Name, stu);}Console.WriteLine(stuDic["s_6"].Score);}}class Student{public string Name;public int Score;}
x++ x-- 后置自增、自减操作符
先赋值,再自增。
int x = 100;int y = x++;Console.WriteLine(x);Console.WriteLine(y);

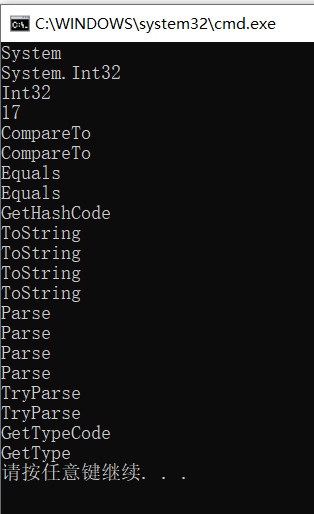
typeof 操作符
检测类型元数据(Metadata)。
// MetadataType t = typeof(int);Console.WriteLine(t.Namespace);Console.WriteLine(t.FullName);Console.WriteLine(t.Name);int c = t.GetMethods().Length;Console.WriteLine(c);foreach (var m in t.GetMethods()){Console.WriteLine(m.Name);}