1. 4 Steps
1.business process
Business
processes are the operational activities performed by an organization.
These
processes are called “facts”.Ex:
- Processing an insurance claim
- Taking customer orders
- Tracking customer web clicks
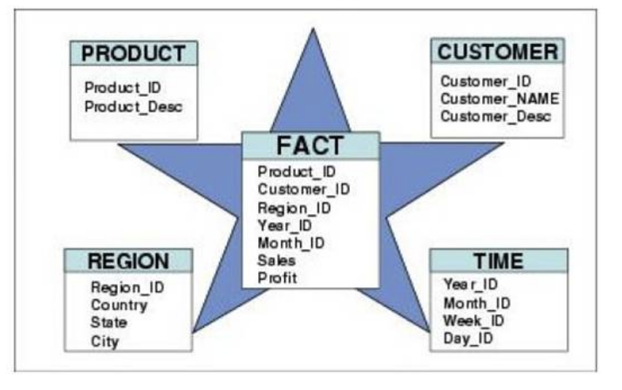
Each fact becomes a row in the fact
table (need PK)
Separate
business processes belong in their own fact tables (i.e. entities)
2.grain
The
grain establishes exactly what a single
fact table row represents
Ex: the granularity of a
dimensional model that consists of the dimensions Date, Store, and
Product
is product sold in store by day1
Atomic
grain is the lowest most granular level at which data is captured by business
process
More granularity allows most
flexible querying for analytics
3.dimension
Dimensions provide the “who, what, where, when, why, and how” context surrounding a business process event
Dimension tables contain descriptive attributes for filtering and grouping the facts
4.fact
Facts are the measurements that result from a business process event and are almost always numeric