1. Tips
/short statement is better
collapse the two sql statements from before into one
/
2. SQL Window Functions
Case1
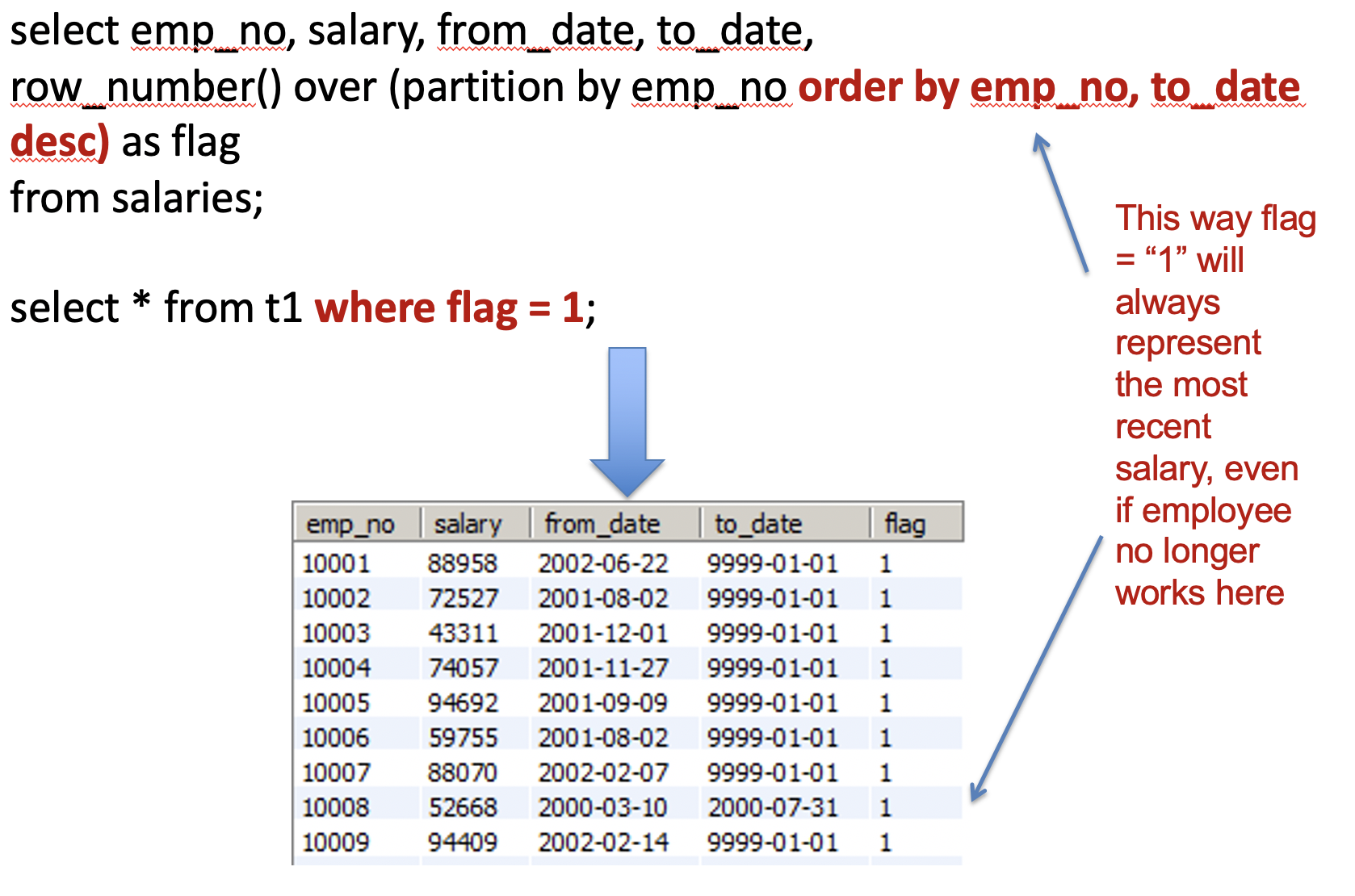
•Business
Use Case – We want to isolate only rows for employees with the their most recent salaries
•Could
be still active
employees, i.e. to_date =
‘9999-01-01’ or
employees
who have left the company**,
what was their salary when they left?
3. Fact and Demension Table Structures
1.fact types
1) Additive facts
can be
summed across any of the dimensions associated with the fact table.
eg: Sales can be summed by weeks, months, years
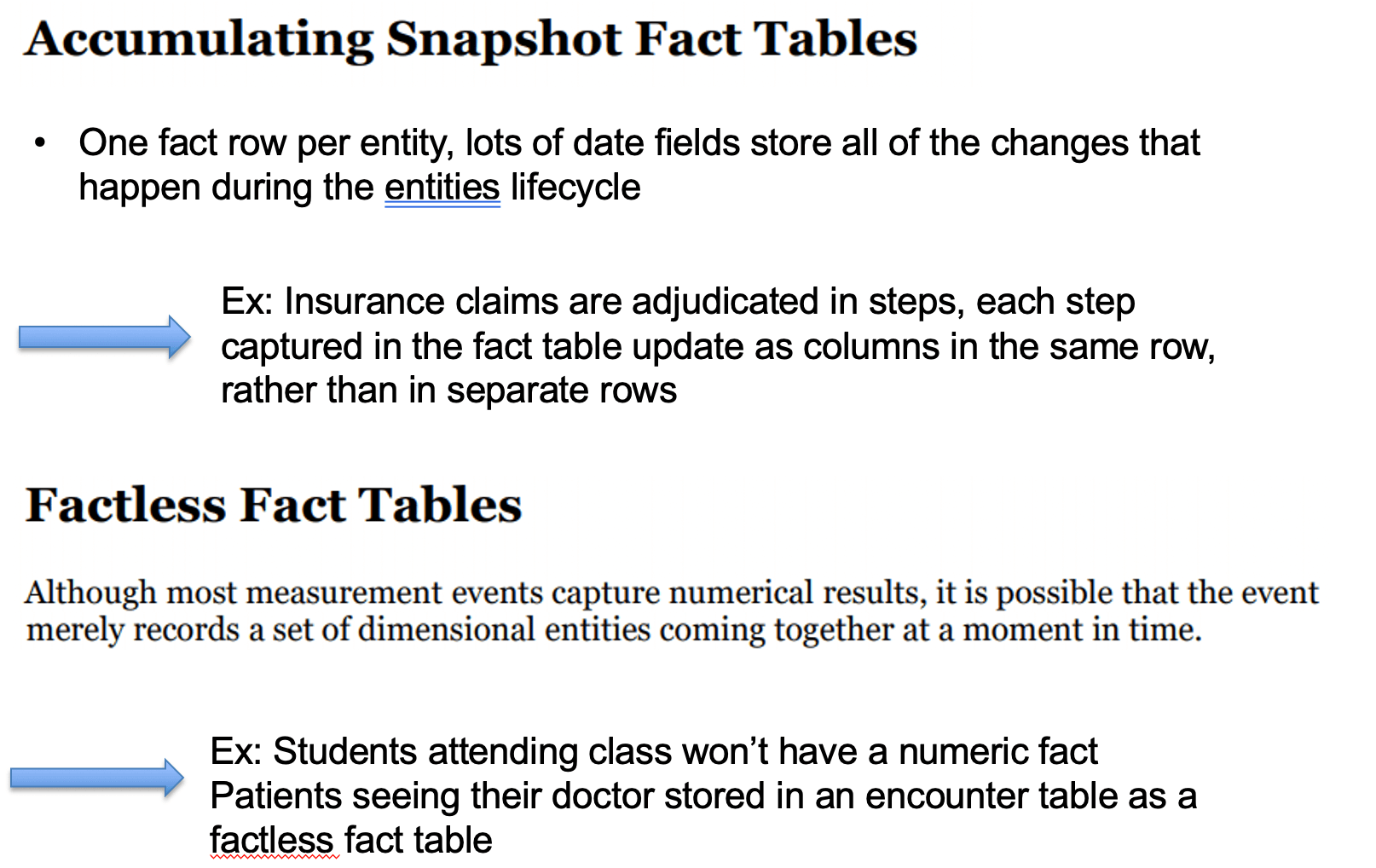
2) Semi-additive
can be
summed across some
dimensions, but not all
eg: daily balance in checking amount
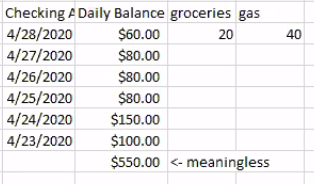
3) Non-additive
such
as ratios
or percentages.
eg: it doesn’t make sense that discounts of different items are added together
2.table types
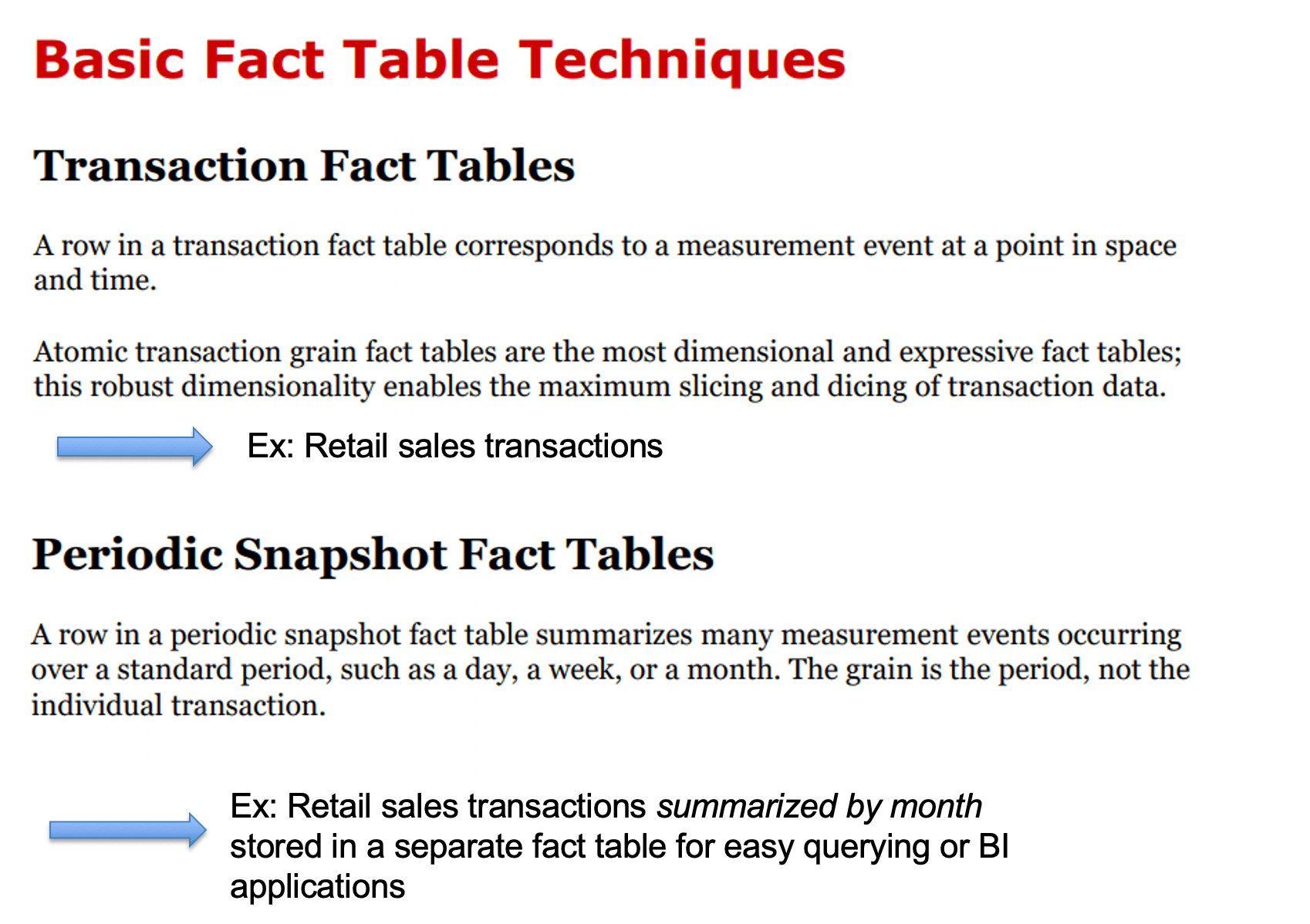
1) Transaction fact table
2) Periodic snapshot fact table
summarizes many measurement events occuring during over a standard period
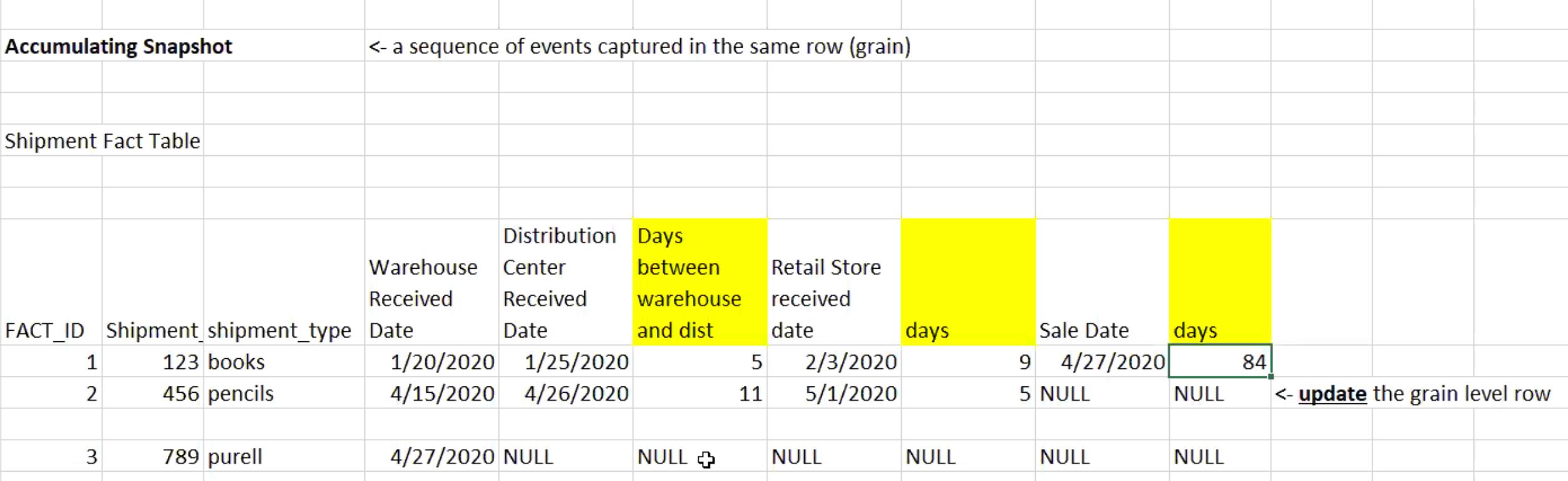
3) Accumulating snapshot fact table
a sequence of events captured in the same row
4) Factless table
5) Transaction fact table VS Periodic snapshot fact table
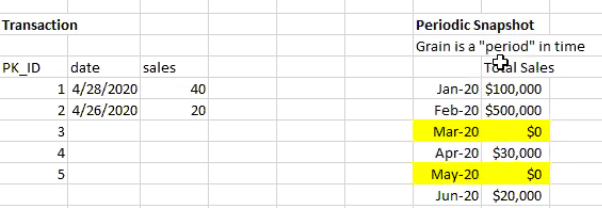
for periodic snapshot fact table, even during a period nothing happens, it still has a record.
6) Accummulating snapshot fact table
3.Primary Keys to use in Dimension Tables
1) Natural Key
- Found in the raw data
identifies unique row (e.g. CPT Code from lecture 2, or city from HW1 location table)
2) Surrogate Key
Artificially generated, usually an integer from 1 to n (e.g. the Index ID from HW1)
- can’t be the Natural Key
4.Dimension Types
1) Snowflaked Dimensions
– Hierarchical relationship is normalized across several tables, e.g. city table links to state on state_id per HW1
2) De-normalized Flattened Dimension
– Intentionally violate 3NF for ease of use, all attributes available on one row in the dimension table
3) Multiple Hierarchies in Dimensions
– e.g. geography
4) Calendar Date Dimensions
– attached to fact tables to allow dates, months, quarters, years, week start date, etc
5) Degenerate Dimension
– no content except for the PK, usually stored in a fact table but nowhere else
6) Junk Dimensions
– misc.
low cardinality flags all stored together in one junk dimension (i.e. not a
single entity)
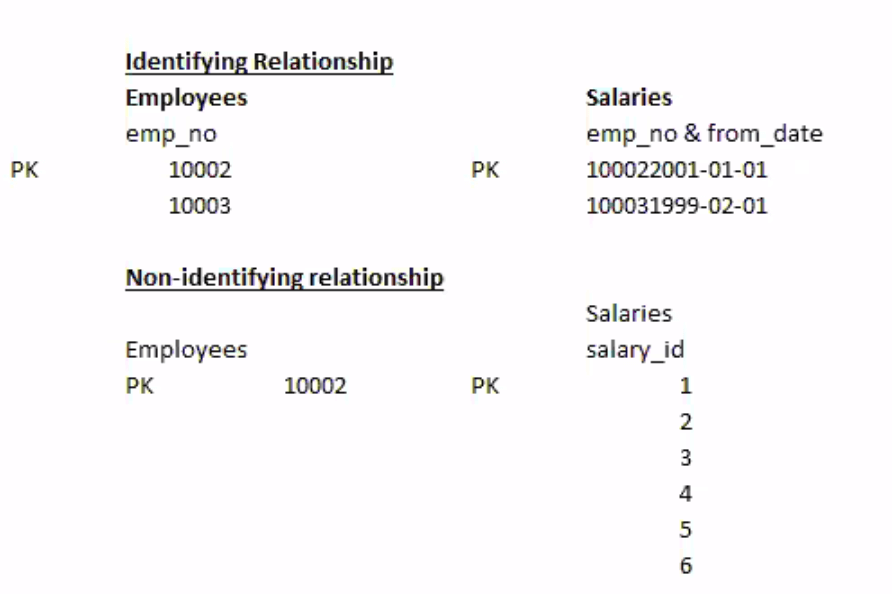
4. ERD补充
- 两个pk组成一个unique pk,不一定要重新设一个unique pk
- char和varchar区别

- non-identifying relationship ——> dash line join ❌
- 一个表中可以有多个pk,共同定义行