单行函数和组函数
单行函数是对单个行进行计算,并且每一行返回一个结果。
多行函数是对成组的行进行操作,以行组为单位返回一个结果。
两者都是处理数据库中的数据,但单行函数结果是一对一的关系,多行函数的结果是多对一的关系。
单行函数的特点:
- 出现的位置:select、where、order by(与记录相关的地方)
- 每一行记录返回一个结果
单行函数的分类:字符函数、数值函数、日期函数、转换函数、通用函数。
字符函数
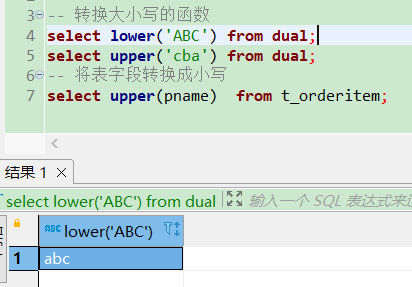
转换大小写函数upper/lower
-- 将字符串转换为大小写select lower('ABC') from dual;select upper('cba') from dual;-- 将表字段转换成小写select upper(pname) from t_orderitem;
字符串处理函数
- concat:字符串拼接
- substr:截取子串
- length:获取字符串长度
- lpad:右对齐
- rpad:左对齐
- trim:清除字符串左右两端指定的字符
- replace:替换字符串中指定的某个字符
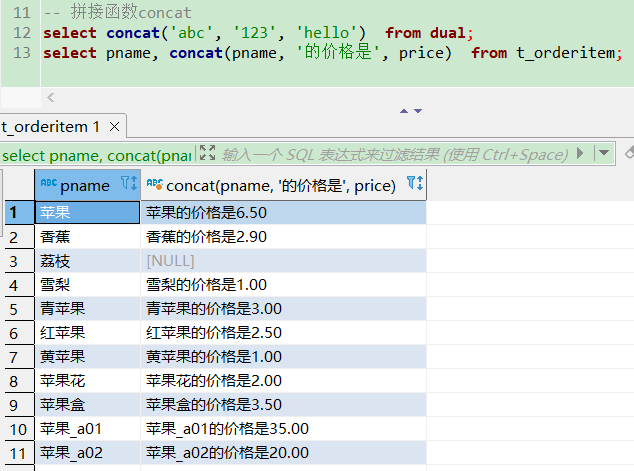
concat字符串拼接
-- 拼接函数concat
select concat('abc', '123', 'hello') from dual;
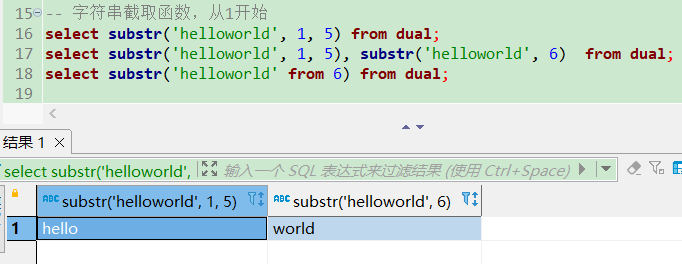
substr截取子串
-- 字符串截取函数,pos: 起始位置从1开始,len:截取的长度
select substr('helloworld', 1, 5) from dual;
select substr('helloworld', 1, 5), substr('helloworld', 6) from dual;
select substr('helloworld' from 6), substr('helloworld' from 1 for 5) from dual;
select substr(pname, 1, 3) from t_orderitem;
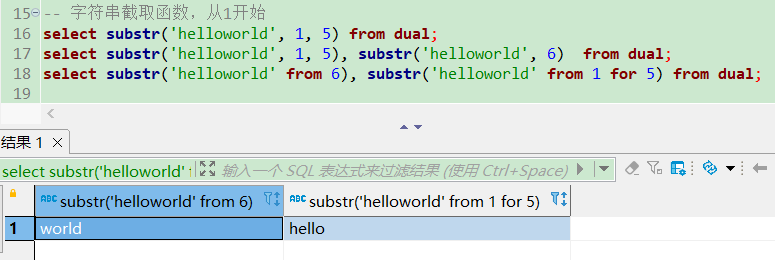
length获取字符串长度
-- 获取字符串长度,中文用三个字节表示
select length('abcdefg') from dual;
select pname, length(pname) from t_orderitem;
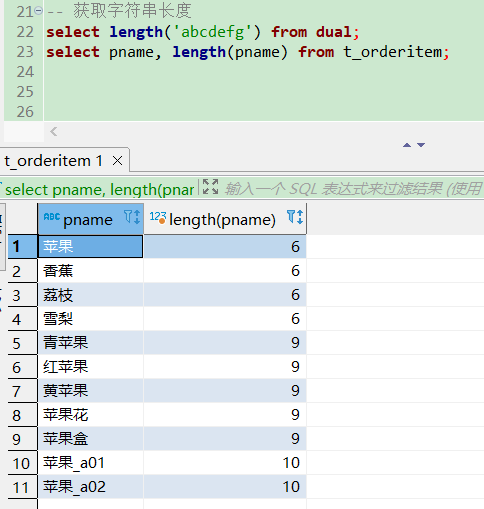
lpad左填充\rpad右填充
-- 左右填充
select lpad(123, 10, '*'), rpad(123456, 10, '*') from dual;
select pname, lpad(pname, 10, '*'), rpad(pname, 10, '*') from t_orderitem;
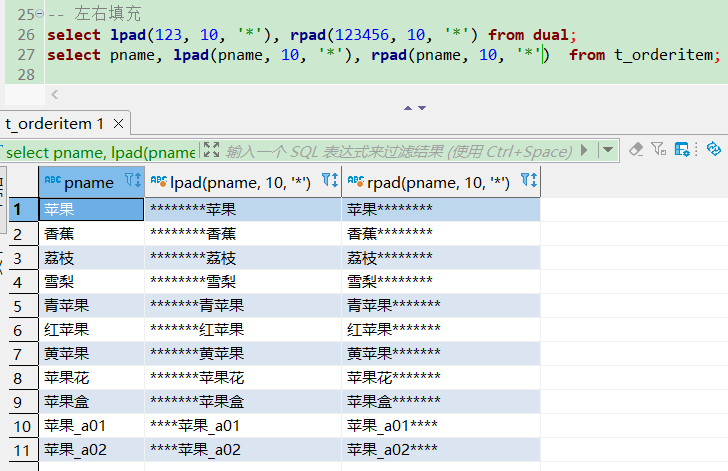
trim清除字符串左右两端指定的字符
-- 清空字符串两端空白
select length(' hello world '), length(trim(' hello world ')) from dual;
select pname, length(pname), length(trim(pname)) from t_orderitem;
replace替换字符串中指定字符
-- 替换replace
select replace('ABCAEF', 'A', '#') from dual;
-- 将‘果’替换为'#'
select replace(pname, '果', '#') from t_orderitem;

数值函数
round四舍五入
-- ronud四舍五入
select round(12.3), round(4.5), round(-12.7) from dual;
truncate截断
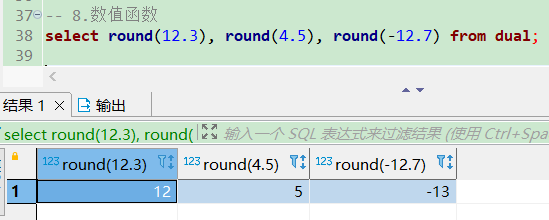
-- truncate(x,d) x:截断数值,d:正数是截断小数位,负数是截断整数位
select truncate(12.2234, 2), truncate(12.2234, 0), truncate(12.2234, -1) from dual;
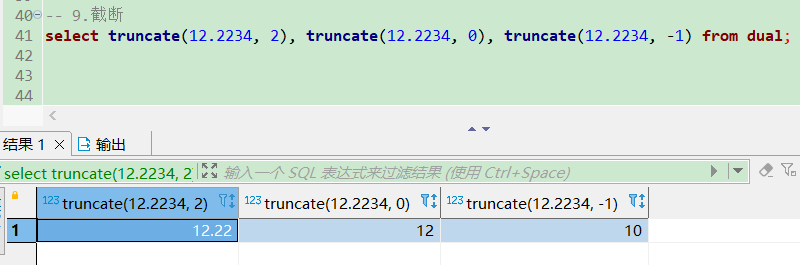
mod求余
select mod(10, 3), mod(10, 2) from dual;
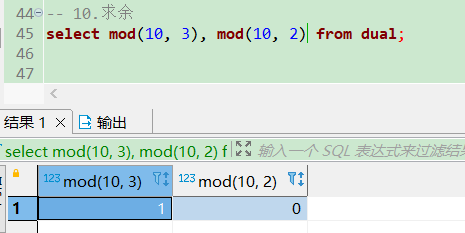
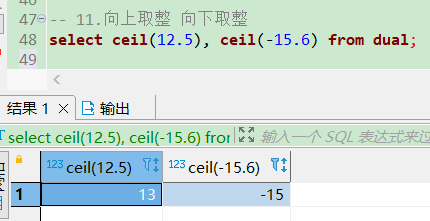
ceil向上取整、floor向下取整
-- 向上取整、向下取整
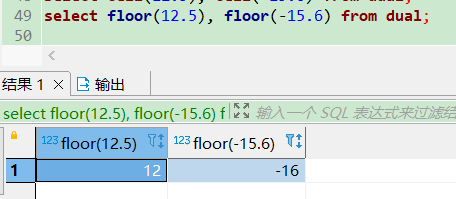
select ceil(12.5), ceil(-15.6) from dual;
select floor(12.5), floor(-15.6) from dual;
日期函数
now返回当前系统日期+时间
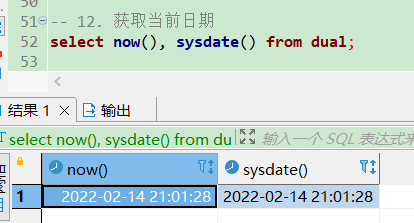
now 是 mysql 内置的函数,sysdate 是通用的函数。
-- 获取当前日期
select now(), sysdate() from dual;
curdate返回当前系统日期,不包含时间
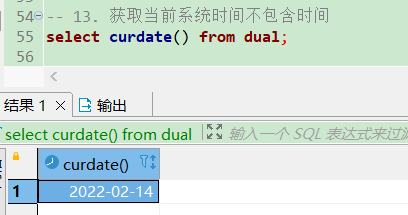
-- 获取当前系统时间不包含时间
select curdate() from dual;
date_add增加天数
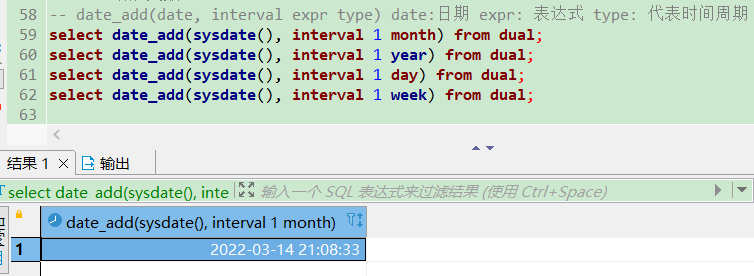
-- date_add(date, interval expr type) date:日期 expr: 表达式 type: 代表时间周期month\year\day\week\hour
select date_add(sysdate(), interval 1 month) from dual;
select date_add(sysdate(), interval 1 year) from dual;
select date_add(sysdate(), interval 1 day) from dual;
select date_add(sysdate(), interval 1 week) from dual;
select date_add(sysdate(), interval 1 hour) from dual;
date_sub减少天数
-- 14. 减少天数
-- date_sub(date, interval expr type) date:日期 expr: 表达式 type: 代表时间周期
select date_sub(sysdate(), interval 1 month) from dual;
select date_sub(sysdate(), interval 1 year) from dual;
select date_sub(sysdate(), interval 1 day) from dual;
select date_sub(sysdate(), interval 1 week) from dual;
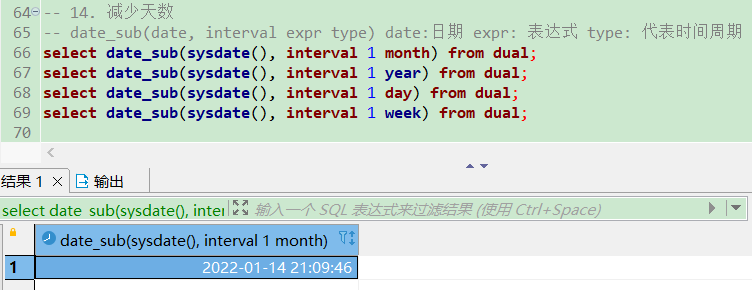
datediff(expr, expr2) 返回起始时间expr和结束时间expr2之间的天数
select datediff(sysdate(), '2020-01-01') from dual;
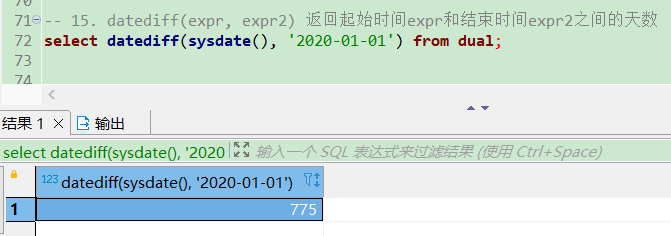
str_to_date、date_format将字符转换成日期
| 格式符 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| %Y | 四位的年份 |
| %y | 两位的年份 |
| %m | 月份(01, 02, 03…) |
| %c | 月份(1,2,3,4….) |
| %d | 日期(01,02,03…) |
| %H | 小时(24小时制) |
| %h | 小时(12小时制) |
| %i | 分钟(00,01, …59) |
| %s | 秒(00,01,….59) |
-- a.将字符串转换成指定格式的日期
select str_to_date('2020-05-03', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s') from dual;
select date_format('2020-05-04', '%Y-%m-%d') from dual;
-- b.将日期转换成字符串
select date_format(now(), '%Y年%m月%d日') from dual;
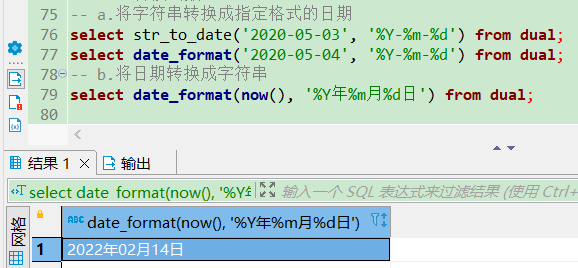
cast转换函数
cast(expr AS type) 将任意类型的表达式 expr 转换成指定类型 type 的值。convert(expr, type) 将表达式转换成指定类型。
-- cast(expr AS type)
select cast(123 as char);
select cast(now() as char);
select cast('2020-01-13' as datetime);
select cast('28.82abc' as decimal);
select cast('28.82abc' as decimal(4, 2)); -- 保留两位有效数字
-- convert(expr, type)
select convert('28.28abc', decimal(4, 2));
select convert(now(), char);
-- convert(expr USING charset_name) 把字符串从一种字符集转换成另一种字符集
select convert('abc' using ascii);
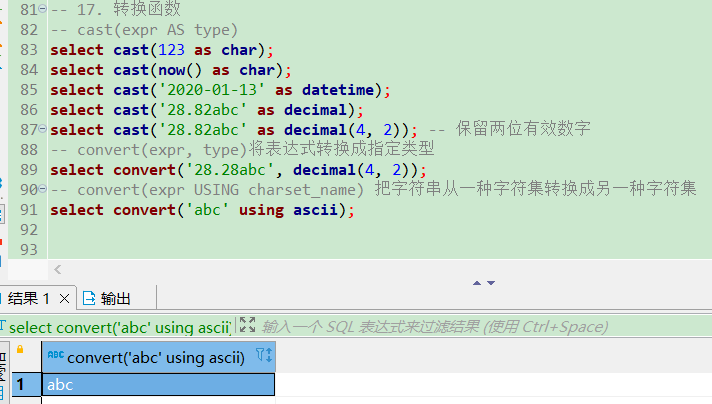
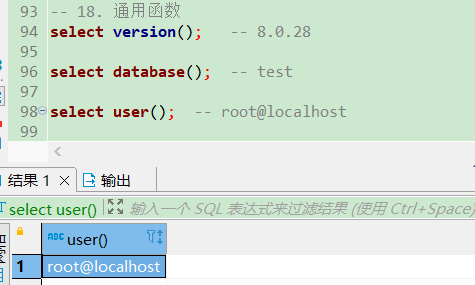
通用函数
-- 获取版本号
select version(); -- 8.0.28
-- 获取数据库名
select database(); -- test
-- 获取用户
select user(); -- root@localhost
多行函数
用作统计使用,又称聚合函数或统计函数或组函数或分组函数。
常用的函数:
- sum 求和
- avg 平均值
- max 最大值
- min 最小值
- count 计算个数
【注意点】
- sum、avg 一般用于处理数值型;
- max、min、count 可以处理任何类型;
- 全部函数都忽略 null 值,null 值不计入统计;
- count(1) 和 count(*) 外,count() 函数在统计时不考虑 null;
- 和 distinct 配合使用,和 all 配合使用(默认);
多行函数简单用法。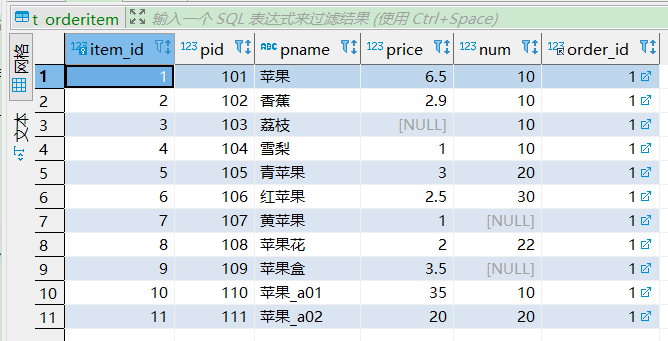
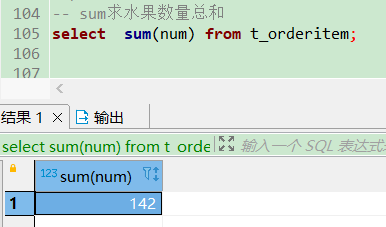
-- sum求水果数量总和
select sum(num) from t_orderitem;
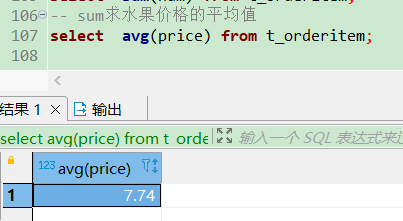
-- sum求水果价格的平均值
select avg(price) from t_orderitem;
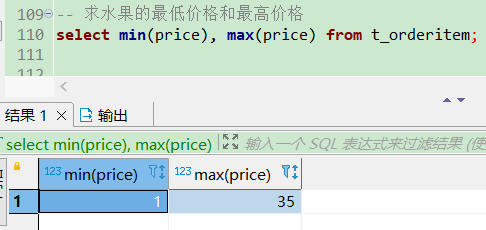
-- 求水果的最低价格和最高价格
select min(price), max(price) from t_orderitem;
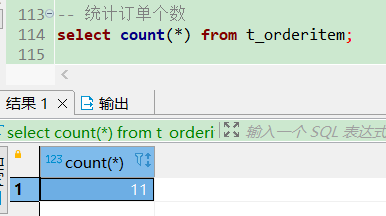
-- 统计订单个数
select count(*) from t_orderitem; -- 11
select count(1) from t_orderitem; -- 11
select count(price) from t_orderitem; -- 10,null值不计入
group by和having一起使用
和分组函数一同查询的字段要求是 group by 后的字段。
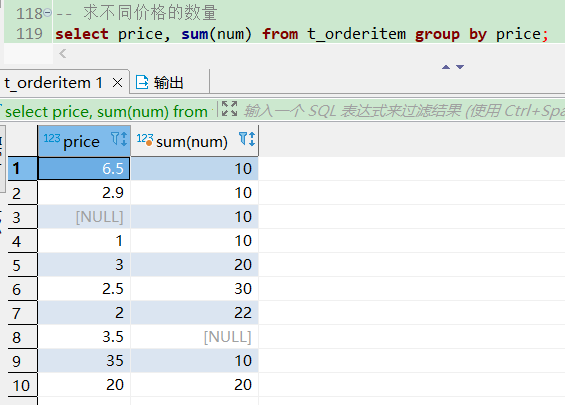
-- 求不同价格的数量,按价格分组
select price, sum(num) from t_orderitem group by price;
having 子句是对分组后的数据进行过滤。
有 having子句的 select 语句执行过程:
- 行被分组
- 将 having 子句的条件应用到每个分组上
- 只有符合 having 条件的组被保留,再应用 select 后面的组函数对每组数据进行处理;

【总结】where 子句和 having 子句区别
- 过滤数据不同:where 子句过滤的是行,having 子句过滤的是分组中的数据;
- 使用函数不同:where 子句包含单行函数,having 子句只能包含 group by 后面跟的表达式和组函数;
- 执行顺序不同:where 子句执行在前,having 子句执行在后;
- where 子句和 having 子句都不允许使用别名
- 前面我们讲过 sql 的执行顺序,而 group by 是在 where 后面执行的,所以在 group by 后不能跟 where, 要过滤就需要使用 having。
示例。为了分组多加一列 type 区分商品种类。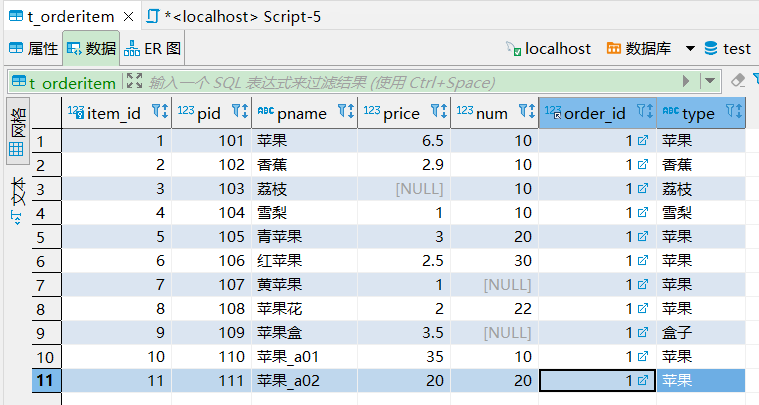
-- 求各种类商品的平均价格大于5块
select type, avg(price) from t_orderitem group by type;
select type, avg(price) from t_orderitem group by type having avg(price) > 5;
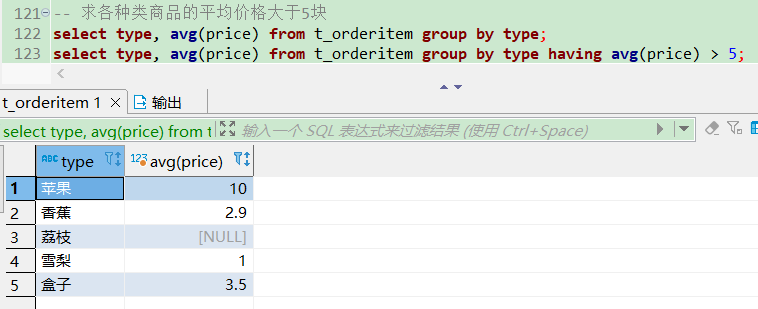
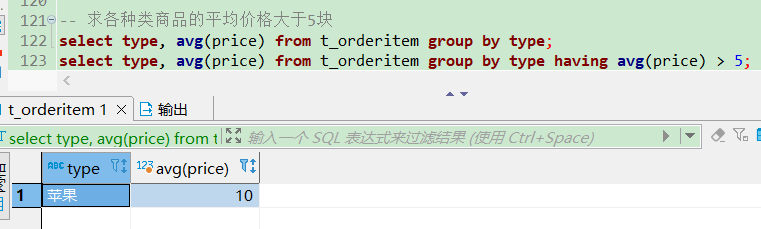
加上一些限制条件。不过写法二效率更高。因为 where 是要一条条数据去查找是否符合条件,数据量越大效率越低,而 having 是先按 type 分组完成后再排除整个 type 分组,数据量就少很多了。
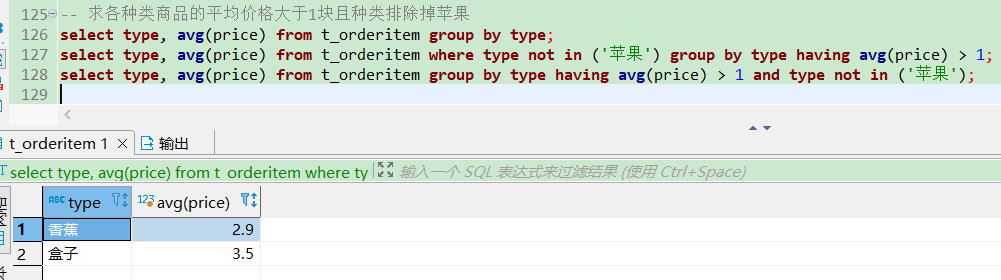
-- 求各种类商品的平均价格大于1块且种类排除掉苹果
select type, avg(price) from t_orderitem group by type;
写法一
select type, avg(price) from t_orderitem where type not in ('苹果') group by type having avg(price) > 1;
写法二(推崇)
select type, avg(price) from t_orderitem group by type having avg(price) > 1 and type not in ('苹果');
to be continue…

