4. Netty高级引用
4.1 Netty编解码器
4.1.1 java的编解码
- 编码(encode)称为序列化,它将对象序列化为字节数组,用于网络传输、数据持久化或者其它用途
- 解码(Decode)称为反序列化,它把从网络、磁盘等读取的字节数组还原成原始对象(通常是原始对象的拷贝),以方便后续的业务逻辑操作
java序列化对象只需要实现java.io.Serializable接口并生成序列化ID,这个类就能够通过java.io.ObjectInput和java.io.ObjectOutput序列化和反序列化。
Java序列化目的:1.网络传输。2.对象持久化。
Java序列化缺点:1.无法跨语言。 2.序列化后码流太大。3.序列化性能太低。
Java序列化仅仅是Java编解码技术的一种,由于它的种种缺陷,衍生出了多种编解码技术和框
架,这些编解码框架实现消息的高效序列化。
4.1.2 Netty的编解码
4.1.2.1 概念
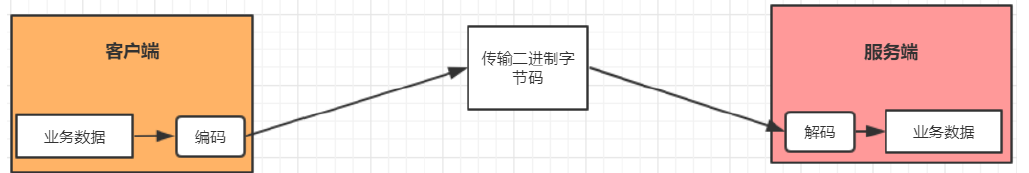
在网络应用中需要实现某种编解码器,将原始字节数据与自定义的消息对象进行互相转换。网络
中都是以字节码的数据形式来传输数据的,服务器编码数据后发送到客户端,客户端需要对数据进
行解码。
对于Netty而言,编解码器由两部分组成:编码器、解码器。
- 解码器:负责将消息从字节或其他序列形式转成指定的消息对象。
- 编码器:将消息对象转成字节或其他序列形式在网络上传输。
Netty 的编(解)码器实现了 ChannelHandlerAdapter,也是一种特殊的 ChannelHandler,所
以依赖于 ChannelPipeline,可以将多个编(解)码器链接在一起,以实现复杂的转换逻辑。
Netty里面的编解码: 解码器:负责处理“入站 InboundHandler”数据。 编码器:负责“出站
OutboundHandler” 数据。
4.1.2.2 解码器(Decoder)
解码器负责 解码“入站”数据从一种格式到另一种格式,解码器处理入站数据是抽象
ChannelInboundHandler的实现。需要将解码器放在ChannelPipeline中。对于解码器,Netty中
主要提供了抽象基类ByteToMessageDecoder和MessageToMessageDecoder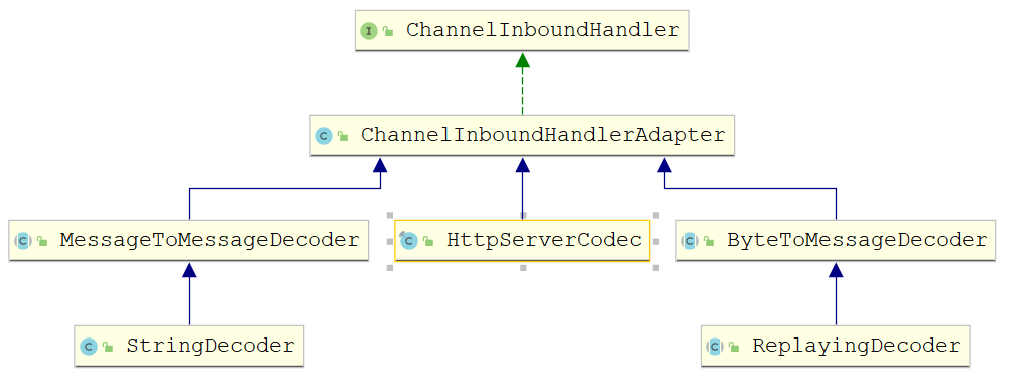
抽象解码器
- ByteToMessageDecoder: 用于将字节转为消息,需要检查缓冲区是否有足够的字节
- ReplayingDecoder: 继承ByteToMessageDecoder,不需要检查缓冲区是否有足够的字节,但是 ReplayingDecoder速度略慢于ByteToMessageDecoder,同时不是所有的ByteBuf都支持。项目复杂性高则使用ReplayingDecoder,否则使用ByteToMessageDecoder
- MessageToMessageDecoder: 用于从一种消息解码为另外一种消息(例如POJO到POJO)
核心方法:
decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out)
代码实现:
解码器:
package com.lagou.codec;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageDecoder;import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;import java.util.List;/*** 消息解码-可以将字符串消息进行在进行解码. 只有消息入站时才会进行解码 */public class MessageDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder<ByteBuf> {@Overrideprotected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in,List<Object> out) throws Exception {System.out.println("正在进行消息解码");out.add(in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}}
通道读取方法:
/*** 通道读取事件** @param ctx* @param msg* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {System.out.println("客户端发送过来的消息:" + msg);}
启动类:
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//8. 向pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handlerch.pipeline().addLast(new MessageDecoder());//添加解码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());}
4.1.2.3 编码器(Encoder)
与ByteToMessageDecoder和MessageToMessageDecoder相对应,Netty提供了对应的编码器
实现MessageToByteEncoder和MessageToMessageEncoder,二者都实现
ChannelOutboundHandler接口。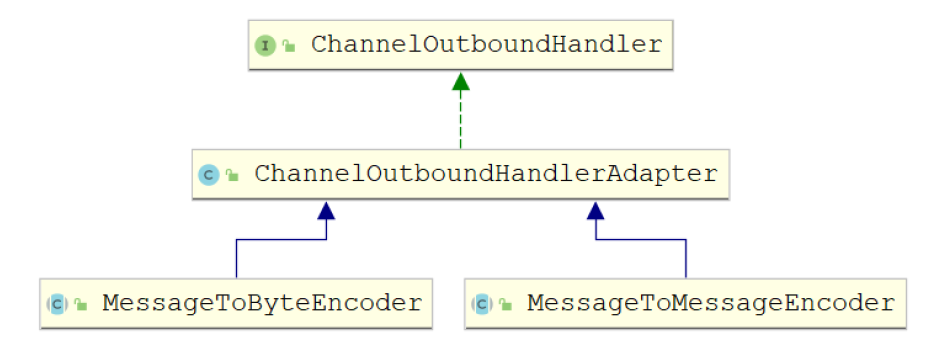
抽象编码器
- MessageToByteEncoder: 将消息转化成字节
- MessageToMessageEncoder: 用于从一种消息编码为另外一种消息(例如POJO到POJO)
核心方法:
encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg, List<Object> out)
代码实现:
编码器:
package com.lagou.codec;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageEncoder;import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;import java.util.List;/*** 编码器 */public class MessageEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder<String> {@Overrideprotected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg,List<Object> out) throws Exception {System.out.println("消息进行消息编码");out.add(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(msg, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}}
消息发送:
/*** 通道就绪事件** @param ctx* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush("你好呀.我是Netty客户端");future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception{if (future.isSuccess()) {System.out.println("数据发送成功!");} else {System.out.println("数据发送失败!");}}});}
启动类:
@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//6. 向pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handlerch.pipeline().addLast(new MessageDecoder());//添加解码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new MessageEncoder());//添加编码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler());}
4.1.2.4 编码解码器(Codec)
编码解码器: 同时具有编码与解码功能,特点同时实现了ChannelInboundHandler和
ChannelOutboundHandler接口,因此在数据输入和输出时都能进行处理。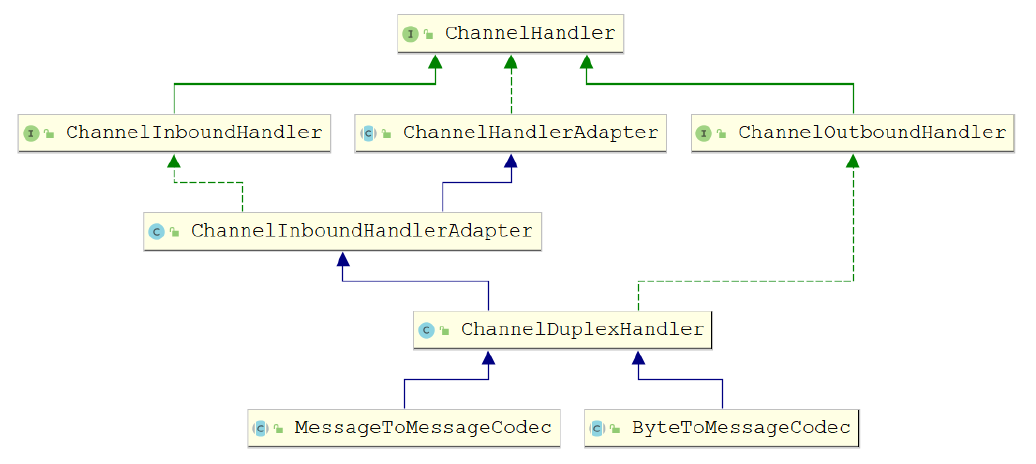
Netty提供提供了一个ChannelDuplexHandler适配器类,编码解码器的抽象基类
ByteToMessageCodec ,MessageToMessageCodec都继承与此类.
代码实现:
/*** 编解码器*/public class MessageCoder extends MessageToMessageCodec {@Overrideprotected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List out) throws Exception {System.out.println("正在进行消息编码");String str = (String) msg;out.add(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}@Overrideprotected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, List out) throws Exception {System.out.println("正在进行消息解码");ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;out.add(byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}}
启动类:
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//8. 向pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handlerch.pipeline().addLast(new MessageCoder());//添加编解码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());}
4.2 案例 - 群聊天
案例要求:
1. 编写一个 Netty 群聊系统,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据简单通讯
2. 实现多人群聊
3. 服务器端:可以监测用户上线,离线,并实现消息转发功能
4. 客户端:可以发送消息给其它所有用户,同时可以接受其它用户发送的消息
4.2.1 聊天室服务端编写
- NettyChatServer ```java package com.lagou.chat; import com.lagou.demo.NettyServerHandler; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; /*
- 聊天室服务端
*/
public class NettyChatServer {
//端口号
private int port;
public NettyChatServer(int port) {
} public void run() throws InterruptedException {this.port = port;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//1. 创建bossGroup线程组: 处理网络事件--连接事件EventLoopGroup bossGroup = null;//2. 创建workerGroup线程组: 处理网络事件--读写事件 2*处理器线程数EventLoopGroup workerGroup = null;try {bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//3. 创建服务端启动助手ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//6. 参数设置.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//8. 向pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler//添加编解码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());// todoch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyChatServerHandler());}});//9. 启动服务端并绑定端口,同时将异步改为同步ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port);future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {if (future.isSuccess()) {System.out.println("端口绑定成功!");} else {System.out.println("端口绑定失败!");}}});System.out.println("聊天室服务端启动成功.");//10. 关闭通道(并不是真正意义上关闭,而是监听通道关闭的状态)和关闭连接池future.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}
} } ```new NettyChatServer(9998).run();
- NettyChatServerHandle ```java package com.lagou.chat; import io.netty.channel.Channel; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /**
- 聊天室业务处理类
/
public class NettyChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
{ public static List channelList = new ArrayList<>(); /* - 通道就绪事件 *
- @param ctx
- @throws Exception / @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { Channel channel = ctx.channel(); //当有新的客户端连接的时候, 将通道放入集合 channelList.add(channel); System.out.println(“[Server]:” + channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1) + “在线.”); } /*
- 通道未就绪—channel下线 *
- @param ctx
- @throws Exception / @Override public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception{ Channel channel = ctx.channel(); //当有客户端断开连接的时候,就移除对应的通道 channelList.remove(channel); System.out.println(“[Server]:” + channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1) + “下线.”); } /*
- 通道读取事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param msg
- @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
//当前发送消息的通道, 当前发送的客户端连接
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
for (Channel channel1 : channelList) {
} } /**//排除自身通道if (channel != channel1) {channel1.writeAndFlush("[" + channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1) + "]说:" + msg);}
- 异常处理事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param cause
- @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//移除集合
channelList.remove(channel);
System.out.println(“[Server]:” +
channel.remoteAddress().toString().substring(1) + “异常.”);
}
}
```
4.2.2 聊天室客户端编写
- NettyChatClient ```java package com.lagou.chat; import com.lagou.demo.NettyClientHandler; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.Channel; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; import java.util.Scanner; /**
- 聊天室的客户端
*/
public class NettyChatClient {
private String ip;//服务端IP
private int port;//服务端端口号
public NettyChatClient(String ip, int port) {
} public void run() throws InterruptedException {this.ip = ip;this.port = port;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//1. 创建线程组EventLoopGroup group = null;try {group = new NioEventLoopGroup();//2. 创建客户端启动助手Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();//3. 设置线程组bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//4. 设置客户端通道实现为NIO.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //5.创建一个通道初始化对象@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//6. 向pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler//添加编解码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());//添加客户端的处理类ch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyChatClientHandler());}});//7. 启动客户端,等待连接服务端,同时将异步改为同步ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(ip, port).sync();Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();System.out.println("-------" +channel.localAddress().toString().substring(1) + "--------");Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {String msg = scanner.nextLine();//向服务端发送消息channel.writeAndFlush(msg);}//8. 关闭通道和关闭连接池channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {group.shutdownGracefully();}
} } ```new NettyChatClient("127.0.0.1", 9998).run();
- NettyChatClientHandle ```java package com.lagou.chat; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; /**
- 聊天室处理类
/
public class NettyChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
{ /* - 通道读取就绪事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param msg
- @throws Exception */ @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception { System.out.println(msg); } } ```
4.3 基于Netty的Http服务器开发
4.3.1 介绍
Netty的HTTP协议栈无论在性能还是可靠性上,都表现优异,非常适合在非Web容器的场景下应用,相比于传统的Tomcat、Jetty等Web容器,它更加轻量和小巧,灵活性和定制性也更好。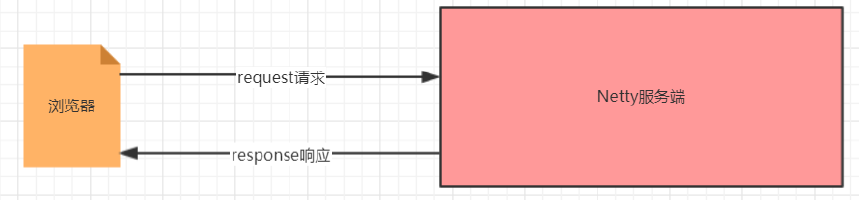
4.3.2 功能需求
- Netty 服务器在 8080 端口监听
2. 浏览器发出请求 “http://localhost:8080/ “
3. 服务器可以回复消息给客户端 “Hello! 我是Netty服务器 “ ,并对特定请求资源进行过滤.4.3.3 服务端代码实现
- NettyHttpServer ```java package com.lagou.http; import com.lagou.chat.NettyChatServer; import com.lagou.chat.NettyChatServerHandler; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; /*
- 聊天室服务端
*/
public class NettyHttpServer {
//端口号
private int port;
public NettyHttpServer(int port) {
} public void run() throws InterruptedException {this.port = port;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//1. 创建bossGroup线程组: 处理网络事件--连接事件EventLoopGroup bossGroup = null;//2. 创建workerGroup线程组: 处理网络事件--读写事件 2*处理器线程数EventLoopGroup workerGroup = null;try {bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//3. 创建服务端启动助手ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();//4. 设置bossGroup线程组和workerGroup线程组serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //5. 设置服务端通道实现为NIO.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//6. 参数设置.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,Boolean.TRUE)//6. 参数设置.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//7. 创建一个通道初始化对象@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//8. 向pipeline中添加自定义业务处理handler//添加编解码器ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());// 自定义业务处理类ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyHttpServerHandler());}});//9. 启动服务端并绑定端口,同时将异步改为同步ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port);future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {if (future.isSuccess()) {System.out.println("端口绑定成功!");} else {System.out.println("端口绑定失败!");}}});System.out.println("http服务端启动成功.");//10. 关闭通道(并不是真正意义上关闭,而是监听通道关闭的状态)和关闭连接池future.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}
} }new NettyHttpServer(8080).run();
2.NettyHttpServerHandlejava package com.lagou.http; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; /* - http服务器处理类
/
public class NettyHttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
{ /* - 读取就绪事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param msg
- @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
//1.判断请求是不是HTTP请求
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
} } } ```DefaultHttpRequest request = (DefaultHttpRequest) msg;System.out.println("浏览器请求路径:" + request.uri());if ("/favicon.ico".equals(request.uri())) {System.out.println("图标不响应");return;}//2.给浏览器进行响应ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello! 我是Netty服务器 ", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, byteBuf);//2.1 设置响应头response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html;charset=utf-8");response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, byteBuf.readableBytes());ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
4.4 基于Netty的WebSocket开发网页版聊天室
4.4.1 WebSocket简介
WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议。WebSocket使得客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据。在WebSocket API中,客户端和服务器只需要完成一次握手,两者之间就直接可以创建持久性的连接,并进行双向数据传输。
应用场景十分广泛:
1. 社交订阅
2. 协同编辑/编程
3. 股票基金报价
4. 体育实况更新
5. 多媒体聊天
6. 在线教育
4.4.2 WebSocket和HTTP的区别
http协议是用在应用层的协议,他是基于tcp协议的,http协议建立连接也必须要有三次握手才能发送信息。 http连接分为短连接,长连接,短连接是每次请求都要三次握手才能发送自己的信息。即每一个request对应一个response。长连接是在一定的期限内保持连接。保持TCP连接不断开。客户端与服务器通信,必须要有客户端先发起, 然后服务器返回结果。客户端是主动的,服务器是被动的。 客户端要想实时获取服务端消息就得不断发送长连接到服务端.
WebSocket实现了多路复用,他是全双工通信。在webSocket协议下服务端和客户端可以同时发送信息。 建立了WebSocket连接之后, 服务端可以主动发送信息到客户端。而且信息当中不必在带有head的部分信息了与http的长链接通信来说,这种方式,不仅能降低服务器的压力。而且信息当中也减少了部分多余的信息。
4.4.3 导入基础环境
- 将资料中Netty-Springboot工程导入到idea
2. 相关依赖<!--整合web模块--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><!--整合模板引擎 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency>
- 静态资源
4. yam配置server:port: 8080resources:static-locations:- classpath:/static/spring:thymeleaf:cache: falsechecktemplatelocation: trueenabled: trueencoding: UTF-8mode: HTML5prefix: classpath:/templates/suffix: .html
4.4.4 服务端开发
- 添加Netty依赖
<!--引入netty依赖 --><dependency><groupId>io.netty</groupId><artifactId>netty-all</artifactId></dependency>
- Netty相关配置
netty:port: 8081path: /chat
- Netty配置类
package com.lagou.config;import lombok.Data;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "netty")@Datapublic class NettyConfig {private int port;//netty监听的端口private String path;//websocket访问路径}
- NettyWebSocketServer开发 ```java package com.lagou.netty; import com.lagou.config.NettyConfig; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel; import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; /**
- Netty服务器
/
@Component
public class NettyWebSocketServer implements Runnable {
@Autowired
NettyConfig nettyConfig;
@Autowired
WebSocketChannelInit webSocketChannelInit;
private EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
/*
- 资源关闭—在容器销毁是关闭
*/
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
} catch (Exception e) {//1.创建服务端启动助手ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();//2.设置线程组serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);//3.设置参数serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)).childHandler(webSocketChannelInit);//4.启动ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(nettyConfig.getPort()).sync();System.out.println("--Netty服务端启动成功---");channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {e.printStackTrace();bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
} } } ```bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
- 资源关闭—在容器销毁是关闭
*/
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
- 通道初始化对象 ```java package com.lagou.netty; import com.lagou.config.NettyConfig; import io.netty.channel.Channel; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler; import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
- 通道初始化对象
*/
@Component
public class WebSocketChannelInit extends ChannelInitializer {
@Autowired
NettyConfig nettyConfig;
@Autowired
WebSocketHandler webSocketHandler;
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
} } ```ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();//对http协议的支持.pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());// 对大数据流的支持pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());//post请求分三部分. request line / request header / message body// HttpObjectAggregator将多个信息转化成单一的request或者response对象pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8000));// 将http协议升级为ws协议. websocket的支持pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler(nettyConfig.getPath()));// 自定义处理handlerpipeline.addLast(webSocketHandler);
- 处理对象 ```java package com.lagou.netty; import io.netty.channel.Channel; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /**
- 自定义处理类
- TextWebSocketFrame: websocket数据是帧的形式处理
/
@Component
@ChannelHandler.Sharable //设置通道共享
public class WebSocketHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
{ public static List channelList = new ArrayList<>(); /* - 通道就绪事件 *
- @param ctx
- @throws Exception / @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { Channel channel = ctx.channel(); //当有新的客户端连接的时候, 将通道放入集合 channelList.add(channel); System.out.println(“有新的连接.”); } /*
- 通道未就绪—channel下线 *
- @param ctx
- @throws Exception / @Override public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { Channel channel = ctx.channel(); //当有客户端断开连接的时候,就移除对应的通道 channelList.remove(channel); } /*
- 读就绪事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param textWebSocketFrame
- @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame textWebSocketFrame) throws Exception {
String msg = textWebSocketFrame.text();
System.out.println(“msg:” + msg);
//当前发送消息的通道, 当前发送的客户端连接
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
for (Channel channel1 : channelList) {
} } /**//排除自身通道if (channel != channel1) {channel1.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame(msg));}
- 异常处理事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param cause
- @throws Exception */ @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); Channel channel = ctx.channel(); //移除集合 channelList.remove(channel); } } ```
- 启动类
package com.lagou;import com.lagou.netty.NettyWebSocketServer;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class NettySpringbootApplication implements CommandLineRunner {@AutowiredNettyWebSocketServer nettyWebSocketServer;public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(NettySpringbootApplication.class, args);}@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {new Thread(nettyWebSocketServer).start();}}
- 前端js开发
$(function () {//这里需要注意的是,prompt有两个参数,前面是提示的话,后面是当对话框出来后,在对话框里的默认值var username = "";while (true) {//弹出一个输入框,输入一段文字,可以提交username = prompt("请输入您的名字", ""); //将输入的内容赋给变量 name ,if (username.trim() === ""){//如果返回的有内容alert("名称不能输入空")} else {$("#username").text(username);break;}}var ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8081/chat");ws.onopen = function () {console.log("连接成功.")}ws.onmessage = function (evt) {showMessage(evt.data);}ws.onclose = function (){console.log("连接关闭")}ws.onerror = function (){console.log("连接异常")}function showMessage(message) {// 张三:你好var str = message.split(":");$("#msg_list").append(`<li class="active"}><div class="main"><img class="avatar" width="30" height="30" src="/img/user.png"><div><div class="user_name">${str[0]}</div><div class="text">${str[1]}</div></div></div></li>`);// 置底setBottom();}$('#my_test').bind({focus: function (event) {event.stopPropagation()$('#my_test').val('');$('.arrow_box').hide()},keydown: function (event) {event.stopPropagation()if (event.keyCode === 13) {if ($('#my_test').val().trim() === '') {this.blur()$('.arrow_box').show()setTimeout(() => {this.focus()}, 1000)} else {$('.arrow_box').hide()//发送消息sendMsg();this.blur()setTimeout(() => {this.focus()})}}}});$('#send').on('click', function (event) {event.stopPropagation()if ($('#my_test').val().trim() === '') {$('.arrow_box').show()} else {sendMsg();}})function sendMsg() {var message = $("#my_test").val();$("#msg_list").append(`<li class="active"}><div class="main self"><div class="text">` + message +`</div></div></li>`);$("#my_test").val('');//发送消息message = username + ":" + message;ws.send(message);// 置底setBottom();}// 置底function setBottom() {// 发送消息后滚动到底部const container = $('.m-message')const scroll = $('#msg_list')container.animate({scrollTop: scroll[0].scrollHeight - container[0].clientHeight +container.scrollTop() + 100});}});
4.5 Netty中粘包和拆包的解决方案
4.5.1 粘包和拆包简介
粘包和拆包是TCP网络编程中不可避免的,无论是服务端还是客户端,当我们读取或者发送消息的时候,都需要考虑TCP底层的粘包/拆包机制。
TCP是个“流”协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据。TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分,所以在业务上认为,一个完整的包可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也有可能把多个小的包封装成一个大的数据包发送,这就是所谓的TCP粘包和拆包问题。
如图所示,假设客户端分别发送了两个数据包D1和D2给服务端,由于服务端一次读取到的字节数是不确定的,故可能存在以下4种情况。
1. 服务端分两次读取到了两个独立的数据包,分别是D1和D2,没有粘包和拆包;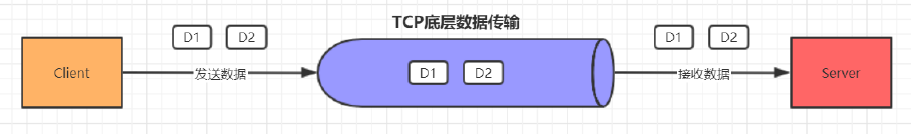
2. 服务端一次接收到了两个数据包,D1和D2粘合在一起,被称为TCP粘包;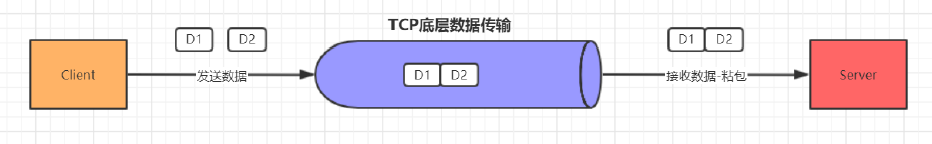
3. 如果D2的数据包比较大, 服务端分两次读取到了两个数据包,第一次读取到了完整的D1包和D2包的部分内容,第二次读取到了D2包的剩余内容,这被称为TCP拆包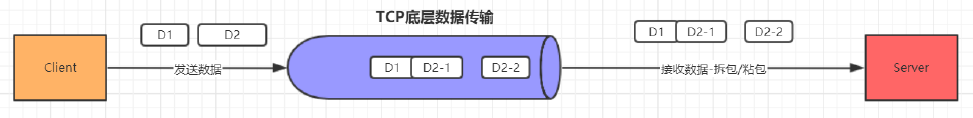
4. 如果D1, D2的数据包都很大, 服务端分多次才能将D1和D2包接收完全,期间发生多次拆包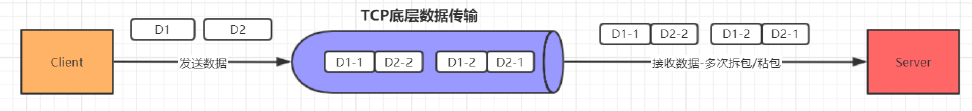
TCP粘包和拆包产生的原因:
数据从发送方到接收方需要经过操作系统的缓冲区,而造成粘包和拆包的主要原因就在这个缓冲区上。粘包可以理解为缓冲区数据堆积,导致多个请求数据粘在一起,而拆包可以理解为发送的数据大于缓冲区,进行拆分处理。
4.5.2 粘包和拆包代码演示
- 粘包
客户端 ```java /**
- 通道就绪事件 *
- @param ctx
- @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
} }ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("你好呀.我是Netty客户端" + i,CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
服务端java public int count = 0; /** - 通道读取事件 *
- @param ctx
- @param msg
- @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(“客户端发送过来的消息:” + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println(“读取次数:”+(++count));
}
运行结果:<br />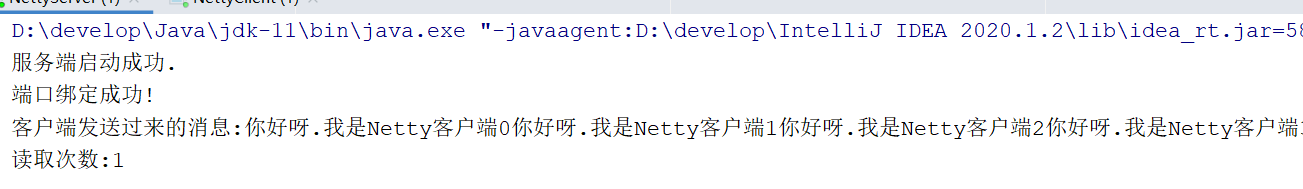<br />**服务端一次读取了客户端发送过来的消息,应该读取10次. 因此发生粘包.**<br />2. 拆包<br />客户端```javapublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//一次发送102400字节数据byte[] bytes = new byte[102400];Arrays.fill(bytes, (byte) 10);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(bytes));}}
服务端
public int count = 0;/*** 通道读取事件** @param ctx* @param msg* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;System.out.println("长度是:" + byteBuf.readableBytes());System.out.println("读取次数 = " + (++count));}
运行结果: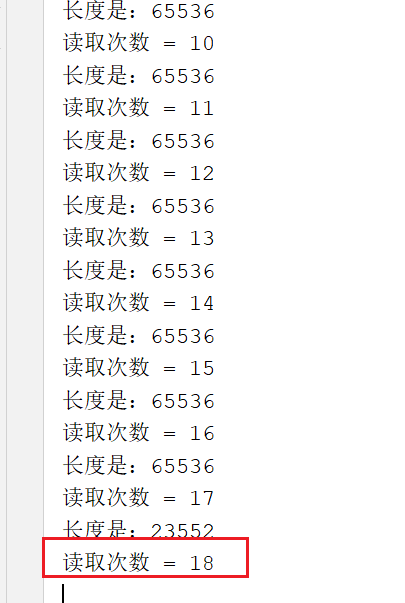
当客户端发送的数据包比较大的时候, 读取了18次, 应该读取10次, 则发送拆包事件.
4.5.3 粘包和拆包的解决方法
业内解决方案
由于底层的TCP无法理解上层的业务数据,所以在底层是无法保证数据包不被拆分和重组的,这个问题只能通过上层的应用协议栈设计来解决,根据业界的主流协议的解决方案,可以归纳如下。- 消息长度固定,累计读取到长度和为定长LEN的报文后,就认为读取到了一个完整的信息
- 将换行符作为消息结束符
- 将特殊的分隔符作为消息的结束标志,回车换行符就是一种特殊的结束分隔符
- 通过在消息头中定义长度字段来标识消息的总长度
Netty中的粘包和拆包解决方案
Netty提供了4种解码器来解决,分别如下:- 固定长度的拆包器 FixedLengthFrameDecoder,每个应用层数据包的都拆分成都是固定长度的大小
- 行拆包器 LineBasedFrameDecoder,每个应用层数据包,都以换行符作为分隔符,进行分割拆分
- 分隔符拆包器 DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,每个应用层数据包,都通过自定义的分隔符,进行分割拆分
- 基于数据包长度的拆包器 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,将应用层数据包的长度,作为接收端应用层数据包的拆分依据。按照应用层数据包的大小,拆包。这个拆包器,有一个要求,就是应用层协议中包含数据包的长度
代码实现
LineBasedFrameDecoder解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(2048));
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("你好呀,我是Netty客户端"+i+"\n", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder解码器
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(2048, byteBuf));
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("你好呀,我是Netty客户端"+i+"$", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));

