SpringMVC狂神说笔记
idea tips:
1. 只要了改了java代码就要reload一下 ( 只要没改xml )2. 只要改了配置文件就刷新tomcat3. 只要改了前端页面 就刷新一下就好了
1、回顾MVC
1.1、什么是MVC
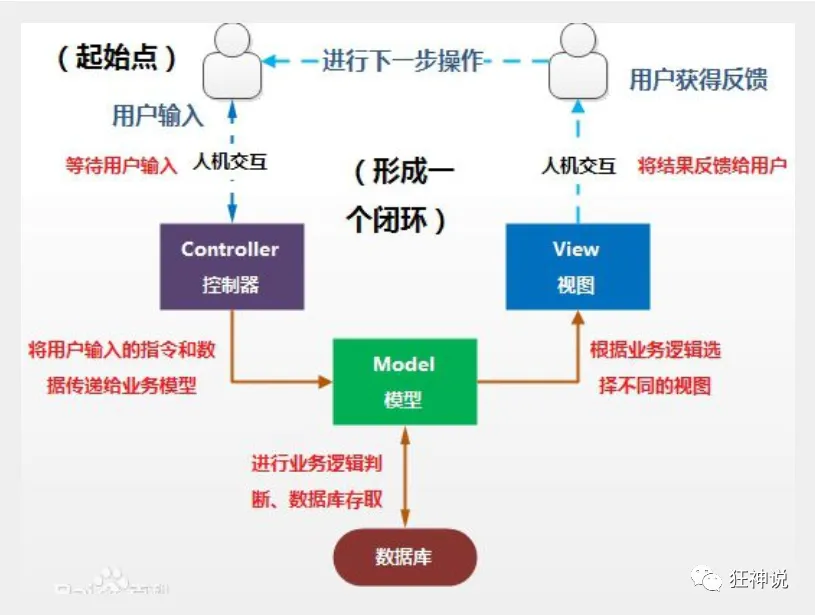
- MVC是模型(Model)、视图(View)、控制器(Controller)的简写,是一种软件设计规范。
- 是将业务逻辑、数据、显示分离的方法来组织代码。
- MVC主要作用是降低了视图与业务逻辑间的双向偶合。
- MVC不是一种设计模式,MVC是一种架构模式。当然不同的MVC存在差异。
Model(模型):数据模型,提供要展示的数据,因此包含数据和行为,可以认为是领域模型或JavaBean组件(包含数据和行为),不过现在一般都分离开来:Value Object(数据Dao) 和 服务层(行为Service)。也就是模型提供了模型数据查询和模型数据的状态更新等功能,包括数据和业务。
View(视图):负责进行模型的展示,一般就是我们见到的用户界面,客户想看到的东西。
Controller(控制器):接收用户请求,委托给模型进行处理(状态改变),处理完毕后把返回的模型数据返回给视图,由视图负责展示。也就是说控制器做了个调度员的工作。
最典型的MVC就是JSP + servlet + javabean的模式。
1.2、Model1时代
- 在web早期的开发中,通常采用的都是Model1。
- Model1中,主要分为两层,视图层和模型层。
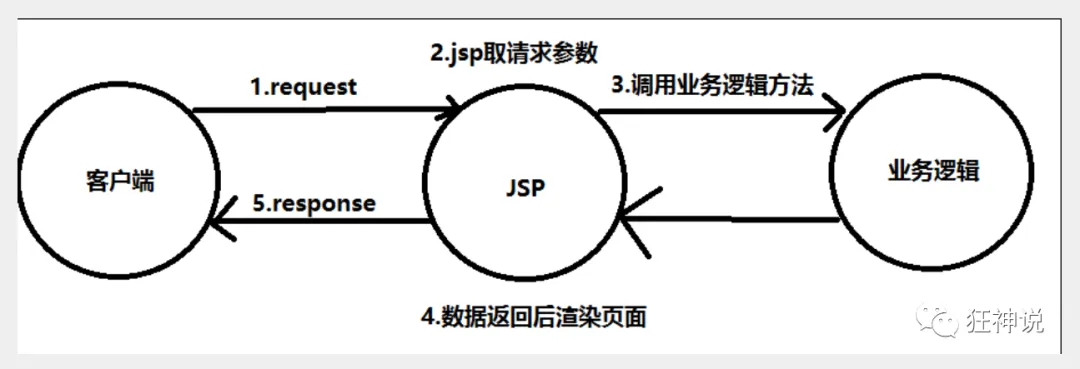
Model1优点:架构简单,比较适合小型项目开发;
Model1缺点:JSP职责不单一,职责过重,不便于维护;
1.3、Model2时代
Model2把一个项目分成三部分,包括视图、控制、模型。
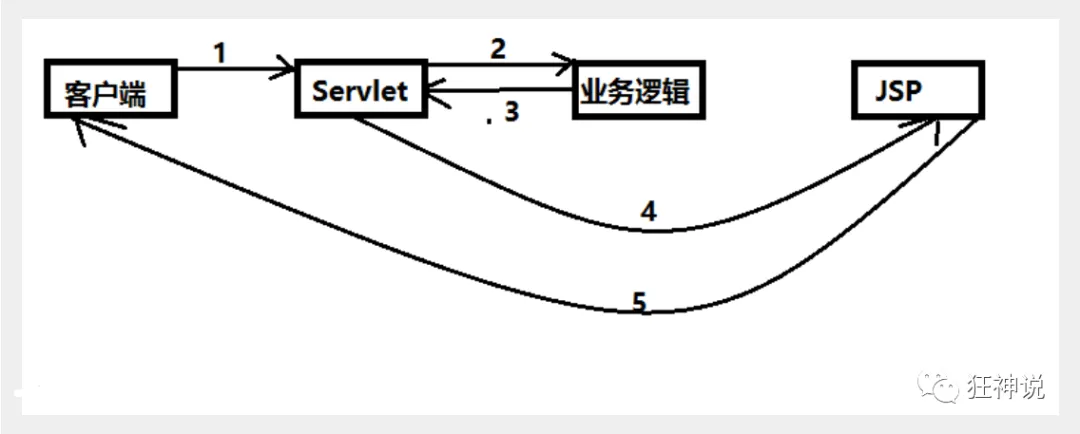
- 用户发请求
- Servlet接收请求数据,并调用对应的业务逻辑方法
- 业务处理完毕,返回更新后的数据给servlet
- servlet转向到JSP,由JSP来渲染页面
- 响应给前端更新后的页面
职责分析:
Controller:控制器
- 取得表单数据
- 调用业务逻辑
- 转向指定的页面
Model:模型
- 业务逻辑
- 保存数据的状态
View:视图
- 显示页面
Model2这样不仅提高的代码的复用率与项目的扩展性,且大大降低了项目的维护成本。Model 1模式的实现比较简单,适用于快速开发小规模项目,Model1中JSP页面身兼View和Controller两种角色,将控制逻辑和表现逻辑混杂在一起,从而导致代码的重用性非常低,增加了应用的扩展性和维护的难度。Model2消除了Model1的缺点。
1.4、回顾Servlet
- 新建一个Maven工程当做父工程!pom依赖!
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.12</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId><version>2.5</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId><artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId><version>2.2</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>jstl</artifactId><version>1.2</version></dependency></dependencies>
- 建立一个Moudle:springmvc-01-servlet , 添加Web app的支持!
- 导入servlet 和 jsp 的 jar 依赖
<dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId><version>2.5</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId><artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId><version>2.2</version></dependency>
- 编写一个Servlet类,用来处理用户的请求 ```java package com.kuang.servlet;
//实现Servlet接口 public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //取得参数 String method = req.getParameter(“method”); if (method.equals(“add”)){ req.getSession().setAttribute(“msg”,”执行了add方法”); } if (method.equals(“delete”)){ req.getSession().setAttribute(“msg”,”执行了delete方法”); } //业务逻辑 //视图跳转 req.getRequestDispatcher(“/WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp”).forward(req,resp); }
@Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req,resp); } }
5. 编写Hello.jsp,在WEB-INF目录下新建一个jsp的文件夹,新建hello.jsp```html<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>Kuangshen</title></head><body>${msg}</body></html>
- 在web.xml中注册Servlet
```xml
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8”?>
<web-app xmlns=”http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee“
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0">
HelloServlet com.kuang.servlet.HelloServlet HelloServlet /user
7. 配置Tomcat,并启动测试8.- localhost:8080/user?method=add- localhost:8080/user?method=delete**MVC框架要做哪些事情**1. 将url映射到java类或java类的方法 .2. 封装用户提交的数据 .3. 处理请求--调用相关的业务处理--封装响应数据 .4. 将响应的数据进行渲染 . jsp / html 等表示层数据 .**说明:**常见的服务器端MVC框架有:Struts、Spring MVC、ASP.NET MVC、Zend Framework、JSF;常见前端MVC框架:vue、angularjs、react、backbone;由MVC演化出了另外一些模式如:MVP、MVVM 等等....<a name="2f73ee94"></a>## 2、什么是SpringMVC<a name="91461e1e"></a>### 2.1、概述Spring MVC是Spring Framework的一部分,是基于Java实现MVC的轻量级Web框架。查看官方文档:[https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.2.0.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/web.html#spring-web](https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.2.0.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/web.html#spring-web)**我们为什么要学习SpringMVC呢?**Spring MVC的特点:1. 轻量级,简单易学2. 高效 , 基于请求响应的MVC框架3. 与Spring兼容性好,无缝结合4. 约定优于配置5. 功能强大:RESTful、数据验证、格式化、本地化、主题等6. 简洁灵活Spring的web框架围绕**DispatcherServlet** [ 调度Servlet ] 设计。DispatcherServlet的作用是将请求分发到不同的处理器。从Spring 2.5开始,使用Java 5或者以上版本的用户可以采用基于注解形式进行开发,十分简洁;正因为SpringMVC好 , 简单 , 便捷 , 易学 , 天生和Spring无缝集成(使用SpringIoC和Aop) , 使用约定优于配置 . 能够进行简单的junit测试 . 支持Restful风格 .异常处理 , 本地化 , 国际化 , 数据验证 , 类型转换 , 拦截器 等等......所以我们要学习 .**最重要的一点还是用的人多 , 使用的公司多 .**<a name="dc6f89ee"></a>### 2.2、中心控制器Spring的web框架围绕DispatcherServlet设计。DispatcherServlet的作用是将请求分发到不同的处理器。从Spring 2.5开始,使用Java 5或者以上版本的用户可以采用基于注解的controller声明方式。Spring MVC框架像许多其他MVC框架一样, **以请求为驱动** , **围绕一个中心Servlet分派请求及提供其他功能**,**DispatcherServlet是一个实际的Servlet (它继承自HttpServlet 基类)**。SpringMVC的原理如下图所示:当发起请求时被前置的控制器拦截到请求,根据请求参数生成代理请求,找到请求对应的实际控制器,控制器处理请求,创建数据模型,访问数据库,将模型响应给中心控制器,控制器使用模型与视图渲染视图结果,将结果返回给中心控制器,再将结果返回给请求者。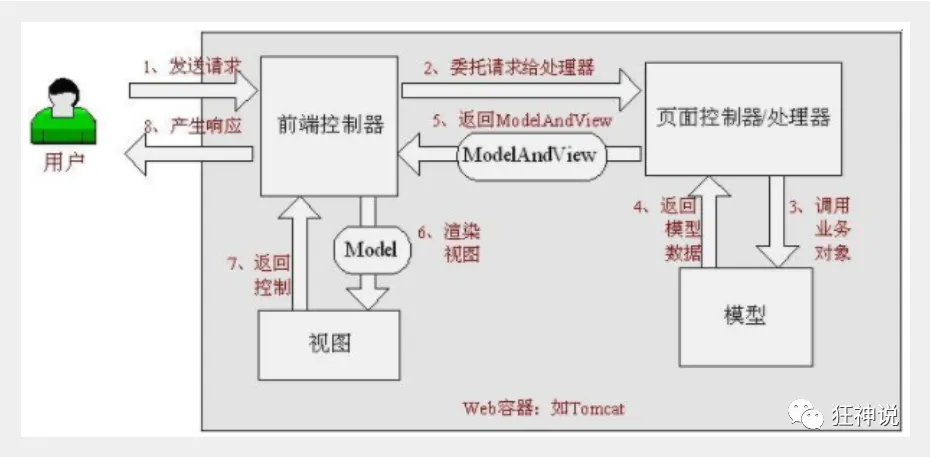<a name="2c8d09c4"></a>### 2.3、SpringMVC执行原理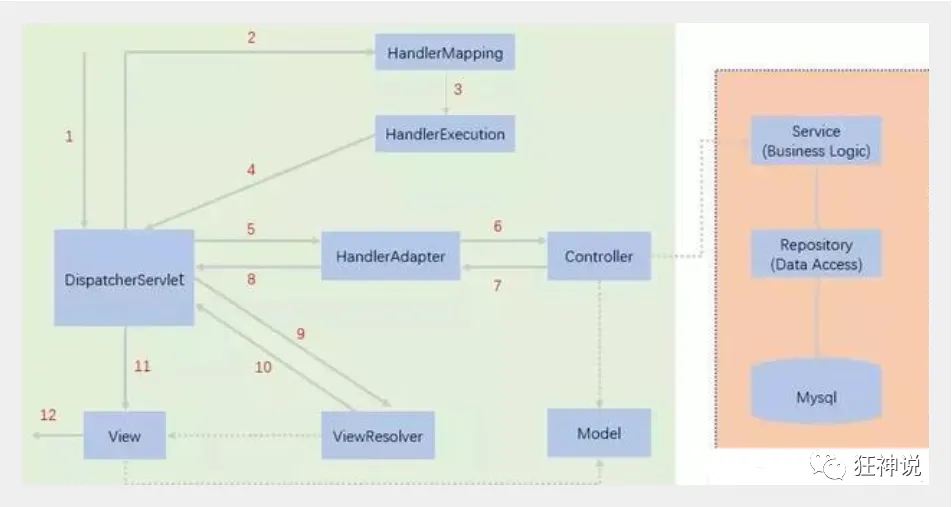图为SpringMVC的一个较完整的流程图,实线表示SpringMVC框架提供的技术,不需要开发者实现,虚线表示需要开发者实现。**简要分析执行流程**1. DispatcherServlet表示前置控制器,是整个SpringMVC的控制中心。用户发出请求,DispatcherServlet接收请求并拦截请求。<br />我们假设请求的url为 : [http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/hello](http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/hello)<br />**如上url拆分成三部分:**<br />http://localhost:8080服务器域名<br />SpringMVC部署在服务器上的web站点<br />hello表示控制器<br />通过分析,如上url表示为:请求位于服务器localhost:8080上的SpringMVC站点的hello控制器。2. HandlerMapping为处理器映射。DispatcherServlet调用HandlerMapping,HandlerMapping根据请求url查找Handler。3. HandlerExecution表示具体的Handler,其主要作用是根据url查找控制器,如上url被查找控制器为:hello。4. HandlerExecution将解析后的信息传递给DispatcherServlet,如解析控制器映射等。5. HandlerAdapter表示处理器适配器,其按照特定的规则去执行Handler。(就是去找controller)6. Handler让具体的Controller执行。7. Controller将具体的执行信息返回给HandlerAdapter,如ModelAndView。8. HandlerAdapter将视图逻辑名或模型传递给DispatcherServlet。9. DispatcherServlet调用视图解析器(ViewResolver)来解析HandlerAdapter传递的逻辑视图名。1. 获取了ModuleAndView 中的数据1. 解析ModuleAndView 的视图名字1. 拼接视图名字,找到对应的视图1. 将数据渲染到视图10. 视图解析器将解析的逻辑视图名传给DispatcherServlet。11. DispatcherServlet根据视图解析器解析的视图结果,调用具体的视图。12. 最终视图呈现给用户。在这里先听一遍原理,不理解没有关系,我们马上来写一个对应的代码实现大家就明白了,如果不明白,那就写10遍,没有笨人,只有懒人!在上一节中,我们讲解了 什么是SpringMVC以及它的执行原理现在我们来看看如何快速使用SpringMVC编写我们的程序吧!<a name="f0c3f0e0"></a>### 配置版1、新建一个Moudle , springmvc-02-hello , 添加web的支持!2、确定导入了SpringMVC 的依赖!3、配置web.xml , 注册DispatcherServlet```xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0"><!--1.注册DispatcherServlet--><servlet><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><!--关联一个springmvc的配置文件:【servlet-name】-servlet.xml--><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value></init-param><!--启动级别-1--><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><!--/ 匹配所有的请求;(不包括.jsp)--><!--/* 匹配所有的请求;(包括.jsp)--><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
4、编写SpringMVC 的 配置文件!名称:springmvc-servlet.xml : [servletname]-servlet.xml
说明,这里的名称要求是按照官方来的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"></beans>
5、添加 处理映射器
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/>
6、添加 处理器适配器
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"/>
7、添加 视图解析器
<!--视图解析器:DispatcherServlet给他的ModelAndView--><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver"><!--前缀--><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/><!--后缀--><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/></bean>
8、编写我们要操作业务Controller ,要么实现Controller接口,要么增加注解;需要返回一个ModelAndView,装数据,封视图;
package com.zzb.controller;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;//注意:这里我们先导入Controller接口public class HelloController implements Controller {@Overridepublic ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {//ModelAndView 模型和视图ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();//封装对象,放在ModelAndView中。Modelmv.addObject("msg","HelloSpringMVC!");// 封装要跳转的视图,放在ModelAndView中mv.setViewName("hello"); //: /WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jspreturn mv; }}
9、将自己的类交给SpringIOC容器,注册bean
<!--Handler--><bean id="/hello" class="com.zzb.controller.HelloController"/>
10、写要跳转的jsp页面,显示ModelandView存放的数据,以及我们的正常页面;
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>Title</title></head><body>${msg}</body></html>
11、配置Tomcat 启动测试!
可能遇到的问题:访问出现404,排查步骤:
- 查看控制台输出,看一下是不是缺少了什么jar包。
- 如果jar包存在,显示无法输出,就在IDEA的项目发布中,添加lib依赖!
- 重启Tomcat 即可解决!
小结:看这个估计大部分同学都能理解其中的原理了,但是我们实际开发才不会这么写,不然就疯了,还学这个玩意干嘛!我们来看个注解版实现,这才是SpringMVC的精髓,到底有多么简单,看这个图就知道了。

注解版
1. 新建一个Moudle,springmvc-03-hello-annotation 。添加web支持!
2. 由于Maven可能存在资源过滤的问题,我们将配置完善
<build><!--处理资源导出问题--><resources><resource><directory>src/main/java</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource></resources></build>
3. 在pom.xml文件引入相关的依赖:主要有Spring框架核心库、Spring MVC、servlet , JSTL等。我们在父依赖中已经引入了!
4. 配置web.xml
注意点:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0"><!--1.注册DispatcherServlet--><servlet><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><!--关联一个springmvc的配置文件:【servlet-name】-servlet.xml--><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value></init-param><!--启动级别-1: 服务器一启动就开始启动--><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><!--/ 匹配所有的请求;(不包括.jsp)--><!--/* 匹配所有的请求;(包括.jsp)--><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
/ 和 /* 的区别:< url-pattern > / </ url-pattern > 不会匹配到.jsp, 只针对我们编写的请求;即:.jsp 不会进入spring的 DispatcherServlet类 。< url-pattern > / </ url-pattern > 会匹配 .jsp,会出现返回 jsp视图 时再次进入spring的DispatcherServlet 类,导致找不到对应的controller所以报404错。
- 注意web.xml版本问题,要最新版!
- 注册DispatcherServlet
- 关联SpringMVC的配置文件
- 启动级别为1
- 映射路径为 / 【不要用/*,会404】
5. 添加Spring MVC配置文件
在resource目录下添加springmvc-servlet.xml配置文件,配置的形式与Spring容器配置基本类似,为了支持基于注解的IOC,设置了自动扫描包的功能,具体配置信息如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttps://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttps://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"><!-- 自动扫描包,让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器统一管理 --><context:component-scan base-package="com.zzb.controller"/><!-- 让Spring MVC不处理静态资源 --><mvc:default-servlet-handler /><!-- 支持mvc注解驱动在spring中一般采用@RequestMapping注解来完成映射关系要想使@RequestMapping注解生效必须向上下文中注册DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping和一个AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter实例这两个实例分别在类级别和方法级别处理。而annotation-driven配置帮助我们自动完成上述两个实例的注入。 --><mvc:annotation-driven /><!-- 视图解析器 --><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"id="internalResourceViewResolver"><!-- 前缀 --><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /><!-- 后缀 --><property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /></bean></beans>
在视图解析器中我们把所有的视图都存放在/WEB-INF/目录下,这样可以保证视图安全,因为这个目录下的文件,客户端不能直接访问。
- 让IOC的注解生效
- 静态资源过滤 :HTML . JS . CSS . 图片 , 视频 …..
- MVC的注解驱动
- 配置视图解析器
6. 创建Controller
编写一个Java控制类:com.kuang.controller.HelloController , 注意编码规范
package com.zzb.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@Controller@RequestMapping("/hello")//@RestController 不会被视图解析器解析public class HelloController {//真实访问地址 : 项目名/hello/hi@RequestMapping("/hi")public String hello(Model model){//封装数据model.addAttribute("msg","hello,springMVCAnnotation");return "hello"; //会被视图解析器处理}}
- @Controller是为了让Spring IOC容器初始化时自动扫描到;
- @RequestMapping是为了映射请求路径,这里因为类与方法上都有映射所以访问时应该是/HelloController/hello;
- 方法中声明Model类型的参数是为了把Action中的数据带到视图中;
- 方法返回的结果是视图的名称hello,加上配置文件中的前后缀变成WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp。
7. 创建视图层
在WEB-INF/ jsp目录中创建hello.jsp , 视图可以直接取出并展示从Controller带回的信息;
可以通过EL表示取出Model中存放的值,或者对象;
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>SpringMVC</title></head><body>${msg}</body></html>
8. 配置Tomcat运行
配置Tomcat , 开启服务器 , 访问 对应的请求路径!
OK,运行成功!
小结
实现步骤其实非常的简单:
- 新建一个web项目
- 导入相关jar包
- 编写web.xml , 注册DispatcherServlet
- 编写springmvc配置文件
- 接下来就是去创建对应的控制类 , controller
- 最后完善前端视图和controller之间的对应
- 测试运行调试.
使用springMVC必须配置的三大件:
处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器
通常,我们只需要手动配置视图解析器,而处理器映射器和处理器适配器只需要开启注解驱动即可,而省去了大段的xml配置
再来回顾下原理吧~
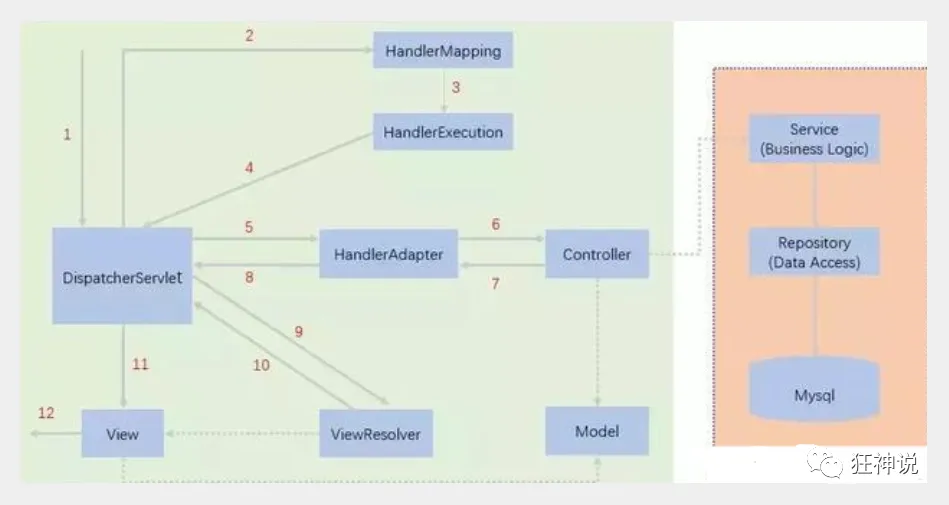
在上一节中,我们编写了我们的第一个SpringMVC程序!
现在我们来看看里面的控制器和路径请求的具体内容吧!
控制器Controller
- 控制器复杂提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现。
- 控制器负责解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型。
- 在Spring MVC中一个控制器类可以包含多个方法
- 在Spring MVC中,对于Controller的配置方式有很多种
实现Controller接口
Controller是一个接口,在org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc包下,接口中只有一个方法;
//实现该接口的类获得控制器功能public interface Controller {//处理请求且返回一个模型与视图对象ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2) throws Exception;}
测试
- 新建一个Moudle,springmvc-04-controller 。将刚才的03 拷贝一份, 我们进行操作!
- 删掉HelloController
- mvc的配置文件只留下 视图解析器!
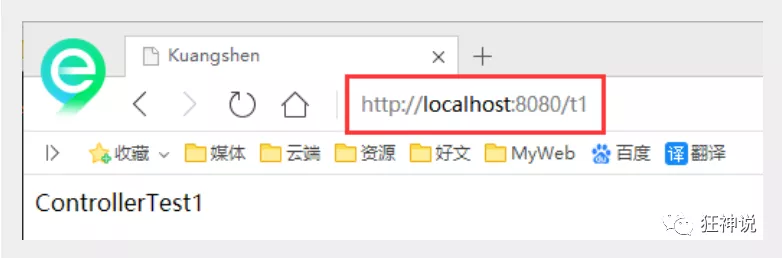
编写一个Controller类,ControllerTest1
//定义控制器//注意点:不要导错包,实现Controller接口,重写方法;public class ControllerTest1 implements Controller {public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception {//返回一个模型视图对象ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();mv.addObject("msg","Test1Controller");mv.setViewName("test");return mv;}}
- 编写完毕后,去Spring配置文件中注册请求的bean;name对应请求路径,class对应处理请求的类
<bean name="/t1" class="com.kuang.controller.ControllerTest1"/>
- 编写前端test.jsp,注意在WEB-INF/jsp目录下编写,对应我们的视图解析器
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>Kuangshen</title></head><body>${msg}</body></html>
- 配置Tomcat运行测试,我这里没有项目发布名配置的就是一个 / ,所以请求不用加项目名,OK!
说明:
- 实现接口Controller定义控制器是较老的办法
- 缺点是:一个控制器中只有一个方法,如果要多个方法则需要定义多个Controller;定义的方式比较麻烦;
使用注解@Controller
注解等效:
@controller 组件@Service service@Controller controller@Repository dao
- @Controller注解类型用于声明Spring类的实例是一个控制器(在讲IOC时还提到了另外3个注解);
- Spring可以使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类,为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描。
<!-- 自动扫描指定的包,下面所有注解类交给IOC容器管理 --><context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang.controller"/>
增加一个ControllerTest2类,使用注解实现; ```java //@Controller注解的类会自动添加到Spring上下文中 @Controller public class ControllerTest2{
//映射访问路径 @RequestMapping(“/t2”) public String index(Model model){
//Spring MVC会自动实例化一个Model对象用于向视图中传值model.addAttribute("msg", "ControllerTest2");//返回视图位置return "test";
}
}
- 运行tomcat测试**可以发现,我们的两个请求都可以指向一个视图,但是页面结果的结果是不一样的,从这里可以看出视图是被复用的,而控制器与视图之间是弱偶合关系。****注解方式是平时使用的最多的方式!**<a name="RequestMapping"></a>### RequestMapping[**@RequestMapping **](/RequestMapping )** **- @RequestMapping注解用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法。可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。- 为了测试结论更加准确,我们可以加上一个项目名测试 myweb- 只注解在方法上面```java@Controllerpublic class TestController {@RequestMapping("/h1")public String test(){return "test";}}
访问路径:http://localhost:8080 / 项目名 / h1
- 同时注解类与方法
@Controller@RequestMapping("/admin")public class TestController {@RequestMapping("/h1")public String test(){return "test";}}
访问路径:http://localhost:8080 / 项目名/ admin /h1 , 需要先指定类的路径再指定方法的路径;
RestFul 风格
概念
Restful就是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格。不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
功能
资源:互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源
资源操作:使用POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,使用不同方法对资源进行操作。
分别对应 添加、 删除、修改、查询。
传统方式操作资源 :通过不同的参数来实现不同的效果!方法单一,post 和 get
[http://127.0.0.1/item/queryItem.action?id=1](http://127.0.0.1/item/queryItem.action?id=1) 查询,GET[http://127.0.0.1/item/saveItem.action](http://127.0.0.1/item/saveItem.action) 新增,POST[http://127.0.0.1/item/updateItem.action](http://127.0.0.1/item/updateItem.action) 更新,POST[http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteItem.action?id=1](http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteItem.action?id=1) 删除,GET或POST
使用RESTful操作资源 :可以通过不同的请求方式来实现不同的效果!如下:请求地址一样,但是功能可以不同!
[http://127.0.0.1/item/1](http://127.0.0.1/item/1) 查询,GET[http://127.0.0.1/item](http://127.0.0.1/item) 新增,POST[http://127.0.0.1/item](http://127.0.0.1/item) 更新,PUT[http://127.0.0.1/item/1](http://127.0.0.1/item/1) 删除,DELETE
学习测试
- 在新建一个类 RestFulController
@Controllerpublic class RestFulController {}
在Spring MVC中可以使用 @PathVariable 注解,让方法参数的值对应绑定到一个URI模板变量上。
```java @Controller public class RestFulController {//映射访问路径 @RequestMapping(“/commit/{p1}/{p2}”) public String index(@PathVariable int p1, @PathVariable int p2, Model model){
int result = p1+p2; //Spring MVC会自动实例化一个Model对象用于向视图中传值 model.addAttribute(“msg”, “结果:”+result); //返回视图位置 return “test”;
}
}
3. 我们来测试请求查看下<br />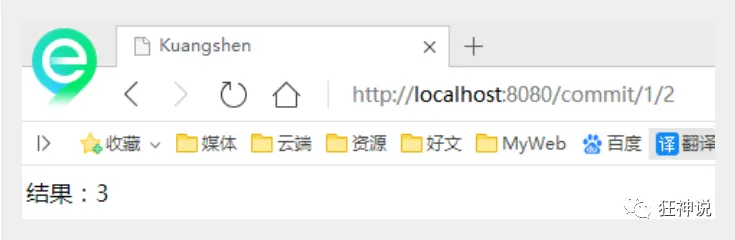4. 思考:使用路径变量的好处?1. 使路径变得更加简洁;1. 高效1. 获得参数更加方便,框架会自动进行类型转换。1. 通过路径变量的类型可以约束访问参数,如果类型不一样,则访问不到对应的请求方法,如这里访问是的路径是/commit/1/a,则路径与方法不匹配,而不会是参数转换失败。1. 安全 隐藏参数详情5. 我们来修改下对应的参数类型,再次测试```java//映射访问路径@RequestMapping("/commit/{p1}/{p2}")public String index(@PathVariable int p1, @PathVariable String p2, Model model){String result = p1+p2;//Spring MVC会自动实例化一个Model对象用于向视图中传值model.addAttribute("msg", "结果:"+result);//返回视图位置return "test";}
使用method属性指定请求类型
用于约束请求的类型,可以收窄请求范围。指定请求谓词的类型如GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE等
我们来测试一下:
- 增加一个方法
//映射访问路径,必须是POST请求@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = {RequestMethod.POST})public String index2(Model model){model.addAttribute("msg", "hello!");return "test";}
- 我们使用浏览器地址栏进行访问默认是Get请求,会报错405:
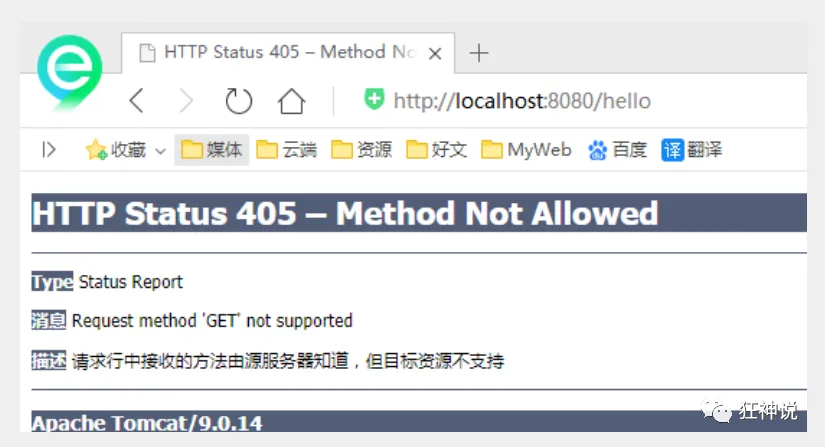
- 如果将POST修改为GET则正常了;
//映射访问路径,必须是Get请求@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = {RequestMethod.GET})public String index2(Model model){model.addAttribute("msg", "hello!");return "test";}
小结:
Spring MVC 的 @RequestMapping 注解能够处理 HTTP 请求的方法, 比如 GET, PUT, POST, DELETE 以及 PATCH。
所有的地址栏请求默认都会是 HTTP GET 类型的。
方法级别的注解变体有如下几个:组合注解
@GetMapping@PostMapping@PutMapping@DeleteMapping@PatchMapping
@GetMapping 是一个组合注解,平时使用的会比较多!
它所扮演的是 @RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.GET) 的一个快捷方式。
扩展:小黄鸭调试法
场景一:我们都有过向别人(甚至可能向完全不会编程的人)提问及解释编程问题的经历,但是很多时候就在我们解释的过程中自己却想到了问题的解决方案,然后对方却一脸茫然。
场景二:你的同行跑来问你一个问题,但是当他自己把问题说完,或说到一半的时候就想出答案走了,留下一脸茫然的你。
其实上面两种场景现象就是所谓的小黄鸭调试法(Rubber Duck Debuging),又称橡皮鸭调试法,它是我们软件工程中最常使用调试方法之一。

此概念据说来自《程序员修炼之道》书中的一个故事,传说程序大师随身携带一只小黄鸭,在调试代码的时候会在桌上放上这只小黄鸭,然后详细地向鸭子解释每行代码,然后很快就将问题定位修复了。
在上一节中,我们了解了控制器和Restful风格操作
现在我们来看看SpringMVC参数接收处理和结果跳转处理吧!
3、结果跳转方式
ModelAndView
设置ModelAndView对象 , 根据view的名称 , 和视图解析器跳到指定的页面 .
页面 : {视图解析器前缀} + viewName +{视图解析器后缀}
<!-- 视图解析器 --><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"id="internalResourceViewResolver"><!-- 前缀 --><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /><!-- 后缀 --><property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /></bean>
对应的controller类
public class ControllerTest1 implements Controller {public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception {//返回一个模型视图对象ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();mv.addObject("msg","ControllerTest1");mv.setViewName("test");return mv;}}
ServletAPI
通过设置ServletAPI , 不需要视图解析器 .
1、通过HttpServletResponse进行输出
2、通过HttpServletResponse实现重定向
3、通过HttpServletResponse实现转发
@Controllerpublic class ResultGo {@RequestMapping("/result/t1")public void test1(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp) throws IOException {rsp.getWriter().println("Hello,Spring BY servlet API");}@RequestMapping("/result/t2")public void test2(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp) throws IOException {rsp.sendRedirect("/index.jsp");}@RequestMapping("/result/t3")public void test3(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp) throws Exception {//转发req.setAttribute("msg","/result/t3");req.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/jsp/test.jsp").forward(req,rsp);}}
SpringMVC
通过SpringMVC来实现转发和重定向 - 无需视图解析器;
测试前,需要将视图解析器注释掉
@Controllerpublic class ResultSpringMVC {@RequestMapping("/rsm/t1")public String test1(){//转发return "/index.jsp";}@RequestMapping("/rsm/t2")public String test2(){//转发二return "forward:/index.jsp";}@RequestMapping("/rsm/t3")public String test3(){//重定向return "redirect:/index.jsp";}}
通过SpringMVC来实现转发和重定向 - 有视图解析器;
重定向 , 不需要视图解析器 , 本质就是重新请求一个新地方嘛 , 所以注意路径问题.
可以重定向到另外一个请求实现 .
@Controllerpublic class ResultSpringMVC2 {@RequestMapping("/rsm2/t1")public String test1(){//转发return "test";}@RequestMapping("/rsm2/t2")public String test2(){//重定向return "redirect:/index.jsp";//return "redirect:hello.do"; //hello.do为另一个请求/}}
4、数据处理
处理提交数据
1、提交的域名称和处理方法的参数名一致
提交数据 : http://localhost:8080/hello?name=kuangshen
处理方法 :
@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(String name){System.out.println(name);return "hello";}
后台输出 : kuangshen
2、提交的域名称和处理方法的参数名不一致
提交数据 : http://localhost:8080/hello?username=kuangshen
处理方法 :
//@RequestParam("username") : username提交的域的名称 .@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(@RequestParam("username") String name){System.out.println(name);return "hello";}
后台输出 : kuangshen
3、提交的是一个对象
要求提交的表单域和对象的属性名一致 , 参数使用对象即可
1、实体类
public class User {private int id;private String name;private int age;//构造//get/set//tostring()}
2、提交数据 : http://localhost:8080/mvc04/user?name=kuangshen&id=1&age=15
3、处理方法 :
@Controller@RequestMapping("/user")public String user(User user){//localhost: 8080/user/t1?name=xxx;@GetMapping("/t1")public String test1(String name , Model model){//1. 接受前端参数System.out.println("接受的前端的参数为: " + name);//2. 将返回的结果传递给前端 , Modelmodel.addAttribute("msg" + name);//3. 视图跳转return "test";}}
后台输出 : User { id=1, name=’kuangshen’, age=15 }
说明:如果使用对象的话,前端传递的参数名和对象名必须一致,否则就是null。
数据显示到前端
第一种 : 通过ModelAndView
我们前面一直都是如此 . 就不过多解释
public class ControllerTest1 implements Controller {public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception {//返回一个模型视图对象ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();mv.addObject("msg","ControllerTest1");mv.setViewName("test");return mv;}}
第二种 : 通过ModelMap
ModelMap
@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(@RequestParam("username") String name, ModelMap model){//封装要显示到视图中的数据//相当于req.setAttribute("name",name);model.addAttribute("name",name);System.out.println(name);return "hello";}
第三种 : 通过Model
Model
@RequestMapping("/ct2/hello")public String hello(@RequestParam("username") String name, Model model){//封装要显示到视图中的数据//相当于req.setAttribute("name",name);model.addAttribute("msg",name);System.out.println(name);return "test";}
对比
就对于新手而言简单来说使用区别就是:
Model 只有寥寥几个方法只适合用于储存数据,简化了新手对于Model对象的操作和理解;ModelMap 继承了 LinkedMap ,除了实现了自身的一些方法,同样的继承 LinkedMap 的方法和特性;ModelAndView 可以在储存数据的同时,可以进行设置返回的逻辑视图,进行控制展示层的跳转。
当然更多的以后开发考虑的更多的是性能和优化,就不能单单仅限于此的了解。
请使用80%的时间打好扎实的基础,剩下18%的时间研究框架,2%的时间去学点英文,框架的官方文档永远是最好的教程。
乱码问题
测试步骤:
1、我们可以在首页编写一个提交的表单
<form action="/e/t" method="post"><input type="text" name="name"><input type="submit"></form>
2、后台编写对应的处理类
@Controllerpublic class Encoding {@RequestMapping("/e/t")public String test(Model model,String name){model.addAttribute("msg",name); //获取表单提交的值return "test"; //跳转到test页面显示输入的值}}
3、输入中文测试,发现乱码
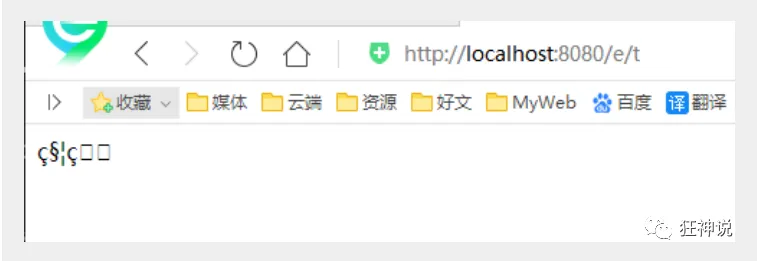
不得不说,乱码问题是在我们开发中十分常见的问题,也是让我们程序猿比较头大的问题!
以前乱码问题通过过滤器解决 , 而SpringMVC给我们提供了一个过滤器 , 可以在web.xml中配置 .
修改了xml文件需要重启服务器!
<filter><filter-name>encoding</filter-name><filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class><init-param><param-name>encoding</param-name><param-value>utf-8</param-value></init-param></filter><filter-mapping><filter-name>encoding</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping>
但是我们发现 , 有些极端情况下.这个过滤器对get的支持不好 .
处理方法 :
1、修改tomcat配置文件 :设置编码!
<Connector URIEncoding="utf-8" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"connectionTimeout="20000"redirectPort="8443" />
2、自定义过滤器
package com.kuang.filter;import javax.servlet.*;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequestWrapper;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;import java.util.Map;/*** 解决get和post请求 全部乱码的过滤器*/public class GenericEncodingFilter implements Filter {@Overridepublic void destroy() {}@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {//处理response的字符编码HttpServletResponse myResponse=(HttpServletResponse) response;myResponse.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");// 转型为与协议相关对象HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;// 对request包装增强HttpServletRequest myrequest = new MyRequest(httpServletRequest);chain.doFilter(myrequest, response);}@Overridepublic void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {}}//自定义request对象,HttpServletRequest的包装类class MyRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {private HttpServletRequest request;//是否编码的标记private boolean hasEncode;//定义一个可以传入HttpServletRequest对象的构造函数,以便对其进行装饰public MyRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {super(request);// super必须写this.request = request;}// 对需要增强方法 进行覆盖@Overridepublic Map getParameterMap() {// 先获得请求方式String method = request.getMethod();if (method.equalsIgnoreCase("post")) {// post请求try {// 处理post乱码request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");return request.getParameterMap();} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {e.printStackTrace();}} else if (method.equalsIgnoreCase("get")) {// get请求Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();if (!hasEncode) { // 确保get手动编码逻辑只运行一次for (String parameterName : parameterMap.keySet()) {String[] values = parameterMap.get(parameterName);if (values != null) {for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {try {// 处理get乱码values[i] = new String(values[i].getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "utf-8");} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}hasEncode = true;}return parameterMap;}return super.getParameterMap();}//取一个值@Overridepublic String getParameter(String name) {Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = getParameterMap();String[] values = parameterMap.get(name);if (values == null) {return null;}return values[0]; // 取回参数的第一个值}//取所有值@Overridepublic String[] getParameterValues(String name) {Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = getParameterMap();String[] values = parameterMap.get(name);return values;}}
这个也是我在网上找的一些大神写的,一般情况下,SpringMVC默认的乱码处理就已经能够很好的解决了!
然后在web.xml中配置这个过滤器即可!
乱码问题,需要平时多注意,在尽可能能设置编码的地方,都设置为统一编码 UTF-8!
5、整合SSM
环境要求
环境:
- IDEA
- MySQL 5.7.19
- Tomcat 9
- Maven 3.6
要求:
- 需要熟练掌握MySQL数据库,Spring,JavaWeb及MyBatis知识,简单的前端知识;
结构
- spring-dao.xml
- 整合mybatis
- 关联数据库文件 prperties
- 配置数据库连接池
- 配置sqlSessionFactory对象
- 注入数据库连接池
- 配置MyBaties全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
- 配置扫描Dao接口包,动态实现Dao接口注入到spring容器中
- 注入sqlSessionFactory
- 给出需要扫描Dao接口包
- 整合mybatis
- spring-mvc.xml
- 扫描包
- 静态资源过滤
- 注册驱动
- 视图解析器
- spring-service.xml
- 扫描包
- 手动配置bean
- 事务管理
- database.properties
- 数据库连接
- applicationContext
- 整合以上
- mybatis-config.xml
- 设置别名
- 扫描包
- web.xml
- servlet
- 配置过滤器
- session
数据库环境
创建一个存放书籍数据的数据库表
CREATE DATABASE `ssmbuild`;USE `ssmbuild`;CREATE TABLE `books`(`bookID` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '书id',`bookName` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '书名',`bookCounts` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '数量',`detail` VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL COMMENT '描述',KEY `bookID`(`bookID`))ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;INSERT INTO `books`(`bookID`,`bookName`,`bookCounts`,`detail`) VALUES(1,'Java',1,'从入门到放弃'),(2,'MySQL',10,'从删库到跑路'),(3,'Linux',5,'从进门到进牢');
基本环境搭建
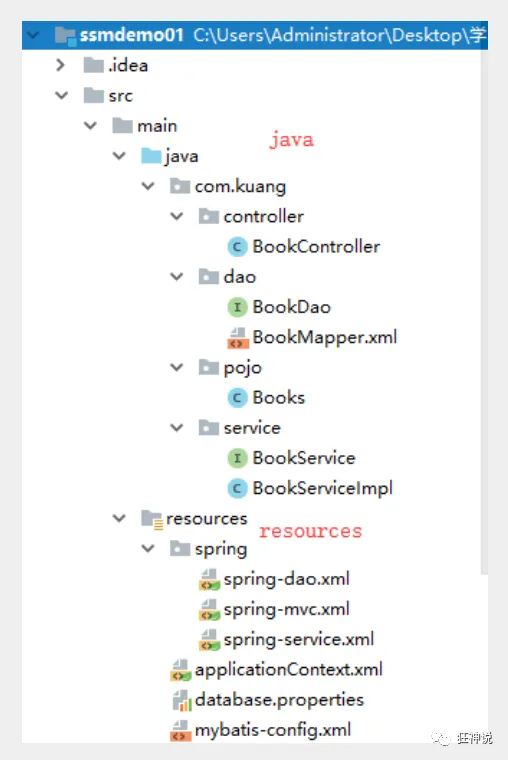
1、新建一Maven项目!ssmbuild , 添加web的支持
2、导入相关的pom依赖!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.kuang</groupId><artifactId>SSM-build1</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><packaging>war</packaging><name>SSM-build1 Maven Webapp</name><!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --><url>http://www.example.com</url><properties><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding><maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.11</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><!--Mybatis部分--><!--数据库驱动包--><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.47</version></dependency><!--mybatis的包--><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis</artifactId><version>3.5.9</version></dependency><!--Mybatis部分完结--><!--Spring部分--><!--mybatis-srping整合包--><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId><version>2.0.6</version></dependency><!--第三方数据源:c3p0--><dependency><groupId>com.mchange</groupId><artifactId>c3p0</artifactId><version>0.9.5.5</version></dependency><!--spring系列--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.3.15</version></dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId><version>5.3.15</version></dependency><!--Spring部分完结--><!--SpringMVC需要的前端和Servlet包--><!--servlet--><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>4.0.1</version></dependency><!--jsp--><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId><artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId><version>2.2</version></dependency><!--jstl--><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>jstl</artifactId><version>1.2</version></dependency><!--Servlet - JSP --><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId><version>2.5</version></dependency><!--lombok--><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>1.18.22</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency></dependencies></project>
3、Maven资源过滤设置
<build><resources><resource><directory>src/main/java</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource></resources></build>
4、建立基本结构和配置框架!
- com.kuang.pojo
- com.kuang.dao
- com.kuang.service
- com.kuang.controller
- mybatis-config.xml
```xml
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8” ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
- applicationContext.xml```xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"></beans>
Mybatis层编写
1、数据库配置文件 database.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverjdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssmbuild?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8# 如果要是使用mysql8.0以上 增加一个时区的配置; &serverTimezone=Asia/Beijingjdbc.username=rootjdbc.password=123456
2、IDEA关联数据库
3、编写MyBatis的核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><!--可以添加日志 但是不加的话比较清楚--><setting><setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/></setting><typeAliases><package name="com.kuang.pojo"/></typeAliases><mappers><mapper resource="com/kuang/dao/BookMapper.xml"/><!-- 适用于类路径下,直接加载mybatis对应的映射文件,用/进行分割,对于文件名称和文件位置没有强制限制条件,比较灵活,不容易出错 --><!-- 不建议使用 class<mapper class= "com.kuang.dao.BookMapper">仅适用于类路径下,接口文件与映射文件在同一路径下,且接口名与映射文件名相同,并且映射文件命名为接口全类名的情况,使用.分割,有智能提示,限制条件较多,容易出错--></mappers></configuration>
4、编写数据库对应的实体类 com.kuang.pojo.Books
使用lombok插件!
package com.kuang.pojo;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class Books {private int bookID;private String bookName;private int bookCounts;private String detail;}
5、编写Dao层的 Mapper接口!
package com.kuang.dao;import com.kuang.pojo.Books;import java.util.List;public interface BookMapper {//增加一个Bookint addBook(Books book);//根据id删除一个Bookint deleteBookById(@Param("bookID") int id);//更新Bookint updateBook(Books books);//根据id查询,返回一个BookBooks queryBookById(@Param("bookID") int id);//查询全部Book,返回list集合List<Books> queryAllBook();}
6、编写接口对应的 Mapper.xml 文件。需要导入MyBatis的包;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.kuang.dao.BookMapper"><!--增加一个Book--><insert id="addBook" parameterType="Books">insert into ssmbuild.books(bookName,bookCounts,detail)values (#{bookName}, #{bookCounts}, #{detail})</insert><!--根据id删除一个Book--><delete id="deleteBookById" parameterType="int">delete from ssmbuild.books where bookID=#{bookID}</delete><!--更新Book--><update id="updateBook" parameterType="Books">update ssmbuild.booksset bookName = #{bookName},bookCounts = #{bookCounts},detail = #{detail}where bookID = #{bookID}</update><!--根据id查询,返回一个Book--><select id="queryBookById" resultType="Books">select * from ssmbuild.bookswhere bookID = #{bookID}</select><!--查询全部Book--><select id="queryAllBook" resultType="Books">SELECT * from ssmbuild.books</select></mapper>
7、编写Service层的接口和实现类
接口:
package com.kuang.service;import com.kuang.pojo.Books;import java.util.List;//BookService:底下需要去实现,调用dao层public interface BookService {//增加一个Bookint addBook(Books book);//根据id删除一个Bookint deleteBookById(int id);//更新Bookint updateBook(Books books);//根据id查询,返回一个BookBooks queryBookById(int id);//查询全部Book,返回list集合List<Books> queryAllBook();}
实现类:
package com.kuang.service;import com.kuang.dao.BookMapper;import com.kuang.pojo.Books;import java.util.List;public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {//service层调用dao层的操作,设置一个set接口,方便Spring管理private BookMapper bookMapper;public void setBookMapper(BookMapper bookMapper) {this.bookMapper = bookMapper;}//set方法Spring就可以注入了public int addBook(Books book) {return bookMapper.addBook(book);}public int deleteBookById(int id) {return bookMapper.deleteBookById(id);}public int updateBook(Books books) {return bookMapper.updateBook(books);}public Books queryBookById(int id) {return bookMapper.queryBookById(id);}public List<Books> queryAllBook() {return bookMapper.queryAllBook();}}
OK,到此,底层需求操作编写完毕!
Spring层
1、配置Spring整合MyBatis,我们这里数据源使用c3p0连接池;
2、我们去编写Spring整合Mybatis的相关的配置文件;spring-dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttps://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!-- 配置整合mybatis --><!-- 1.关联数据库文件 --><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:database.properties"/><!-- 2.数据库连接池 --><!--数据库连接池dbcp 半自动化操作 不能自动连接c3p0 自动化操作(自动的加载配置文件 并且设置到对象里面)--><!--<bean id="dataSource" class="java.sql.DriverManager"></bean>--><bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"><!-- 配置连接池属性 --><property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/><!-- c3p0连接池的私有属性 --><!-- 设置最大连接大小 --><property name="maxPoolSize" value="30"/><!-- 设置最小连接大小 --><property name="minPoolSize" value="10"/><!-- 关闭连接后不自动commit --><property name="autoCommitOnClose" value="false"/><!-- 获取连接超时时间 --><property name="checkoutTimeout" value="10000"/><!-- 当获取连接失败重试次数 --><property name="acquireRetryAttempts" value="2"/></bean><!-- 3.配置SqlSessionFactory对象 --><bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"><!-- 注入数据库连接池 --><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/><!-- 配置MyBaties全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml --><property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/></bean><!-- 4.配置扫描Dao接口包,动态实现Dao接口注入到spring容器中 --><!--解释 :https://www.cnblogs.com/jpfss/p/7799806.html--><bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"><!-- 注入sqlSessionFactory --><property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/><!-- 给出需要扫描Dao接口包 --><property name="basePackage" value="com.kuang.dao"/></bean></beans>
3、Spring整合service层
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!-- 1.扫描service相关的bean --><context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang.service" /><!-- 2.将所有的业务类,注入到Spring,可以通过配置,或者注解实现.(BookServiceImpl注入到IOC容器中)--><bean id="BookServiceImpl" class="com.kuang.service.BookServiceImpl"><property name="bookMapper" ref="bookMapper"/></bean><!-- 3.声明式配置事务管理器 --><bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><!-- 注入数据库连接池(注入数据源) --><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /></bean></beans>
Spring层搞定!再次理解一下,Spring就是一个大杂烩,一个容器!对吧!
SpringMVC层
1、web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"version="4.0"><!--DispatcherServlet--><servlet><servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><!--一定要注意:我们这里加载的是总的配置文件,之前被这里坑了!--><param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><!--encodingFilter--><filter><filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name><filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class><init-param><param-name>encoding</param-name><param-value>utf-8</param-value></init-param></filter><filter-mapping><filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping><!--Session过期时间--><session-config><session-timeout>15</session-timeout></session-config></web-app>
排错思路
步骤:
1. 查看这个bean是否注入成功2. Junit单元测试类,看我们的代码是否能够查询出来结果3. 问题,一定不在我们的底层 是Spring出了问题4. SpringMVC, 整合的时候没有调用我们的service层的bean;1. applicantionContext.xml 没有注入bean2. web.xml 中,我们也绑定过配置文件! 发现问题 我们配置的是Spring-mvc.xml 这里面确实没有service bean 所以报空指针
2、spring-mvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/mvchttps://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"><!-- 配置SpringMVC --><!-- 1.开启SpringMVC注解驱动 --><mvc:annotation-driven /><!-- 2.静态资源默认servlet配置(静态资源过滤)--><mvc:default-servlet-handler/><!-- 3.配置jsp 显示ViewResolver视图解析器 --><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView" /><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /><property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /></bean><!-- 4.扫描web相关的bean --><context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang.controller" /></beans>
3、Spring配置整合文件,applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><import resource="spring-dao.xml"/><import resource="spring-service.xml"/><import resource="spring-mvc.xml"/><!-- 整合三个容器 --></beans>
配置文件,暂时结束!Controller 和 视图层编写
Controller 和 视图层编写
1、BookController 类编写 , 方法一:查询全部书籍
@Controller@RequestMapping("/book")public class BookController {//controller层调用service层@Autowired@Qualifier("BookServiceImpl")private BookService bookService;//查询全部书籍,并且返回带一个书籍展示页面@RequestMapping("/allBook")public String list(Model model) {List<Books> list = bookService.queryAllBook();model.addAttribute("list", list);return "allBook";}}
2、编写首页 index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" %><!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head><title>首页</title><style type="text/css">a {text-decoration: none;color: black;font-size: 18px;}h3 {width: 180px;height: 38px;margin: 100px auto;text-align: center;line-height: 38px;background: deepskyblue;border-radius: 4px;}</style></head><body><h3><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/allBook">点击进入列表页</a></h3></body></html>
3、书籍列表页面 allbook.jsp
<taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" /><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>书籍列表</title><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><!-- 引入 Bootstrap --><link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"></head><body><div class="container"><div class="row clearfix"><div class="col-md-12 column"><div class="page-header"><h1><small>书籍列表 —— 显示所有书籍</small></h1></div></div></div><div class="row"><div class="col-md-4 column"><a class="btn btn-primary" href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/toAddBook">新增</a></div></div><div class="row clearfix"><div class="col-md-12 column"><table class="table table-hover table-striped"><thead><tr><th>书籍编号</th><th>书籍名字</th><th>书籍数量</th><th>书籍详情</th><th>操作</th></tr></thead><tbody><c:forEach var="book" items="${requestScope.get('list')}"><tr><td>${book.getBookID()}</td><td>${book.getBookName()}</td><td>${book.getBookCounts()}</td><td>${book.getDetail()}</td><td><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/toUpdateBook?id=${book.getBookID()}">更改</a> | <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/del/${book.getBookID()}">删除</a></td></tr></c:forEach></tbody></table></div></div></div>
4、BookController 类编写 , 方法二:添加书籍
//跳转到添加书籍界面@RequestMapping("/toAddBook")public String toAddPaper() {return "addBook";}//添加书籍的请求@RequestMapping("/addBook")public String addPaper(Books books) {System.out.println(books);bookService.addBook(books);return "redirect:/book/allBook";}
5、添加书籍页面:addBook.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>新增书籍</title><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><!-- 引入 Bootstrap --><link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"></head><body><div class="container"><div class="row clearfix"><div class="col-md-12 column"><div class="page-header"><h1><small>新增书籍</small></h1></div></div></div><form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/addBook" method="post"><div class="form-group"><label>书籍名称:</label><input type="text" name="bookName" class="form-control" required><!-- 这里的name要和实体类的属性一样 否则报none--></div><div class="form-group"><label>书籍数量:</label><input type="text" name="bookCounts" class="form-control" required></div><div class="form-group"><label>书籍描述:</label><input type="text" name="detail" class="form-control" required></div><div class="form-group"><input type="submit" class="form-control" value="添加"></div></form></div>
6、BookController 类编写 , 方法三:修改书籍
//跳转到修改页面@RequestMapping("/toUpdateBook")public String toUpdateBook(Model model, int id) {Books books = bookService.queryBookById(id);System.out.println(books);model.addAttribute("book",books );return "updateBook";}//修改书籍@RequestMapping("/updateBook")public String updateBook(Model model, Books book) {System.out.println(book);bookService.updateBook(book);Books books = bookService.queryBookById(book.getBookID());model.addAttribute("books", books);return "redirect:/book/allBook";}
7、修改书籍页面 updateBook.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>修改信息</title><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><!-- 引入 Bootstrap --><link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"></head><body><div class="container"><div class="row clearfix"><div class="col-md-12 column"><div class="page-header"><h1><small>修改信息</small></h1></div></div></div><form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/book/updateBook" method="post"><%--出现的问题:我们提交了修改的sql请求,但是修改失败,初次考虑,是事务问题.配置完毕事务依旧失败看一下sql语句,是否执行成功: Sql执行失败,修改未完成修改 : 前端传递隐藏域--%><input type="hidden" name="bookID" value="${book.bookID}"><div class="form-group"><label>书籍名称:</label><input type="text" name="bookName" class="form-control" value="${book.bookName})" required><!-- 这里的name要和实体类的属性一样 否则报none--></div><div class="form-group"><label>书籍数量:</label><input type="text" name="bookCounts" class="form-control" value="${book.bookCounts})" required></div><div class="form-group"><label>书籍描述:</label><input type="text" name="detail" class="form-control" value="${book.detail})" required></div><div class="form-group"><input type="submit" class="form-control" value="添加"></div></form></div>
8、BookController 类编写 , 方法四:删除书籍
@RequestMapping("/del/{bookId}")public String deleteBook(@PathVariable("bookId") int id) {bookService.deleteBookById(id);return "redirect:/book/allBook";}
配置Tomcat,进行运行!
到目前为止,这个SSM项目整合已经完全的OK了,可以直接运行进行测试!这个练习十分的重要,大家需要保证,不看任何东西,自己也可以完整的实现出来!
新增查询功能
项目结构图
小结及展望
这个是同学们的第一个SSM整合案例,一定要烂熟于心!
SSM框架的重要程度是不言而喻的,学到这里,大家已经可以进行基本网站的单独开发。但是这只是增删改查的基本操作。可以说学到这里,大家才算是真正的步入了后台开发的门。也就是能找一个后台相关工作的底线。
或许很多人,工作就做这些事情,但是对于个人的提高来说,还远远不够!
我们后面还要学习一些 SpringMVC 的知识!
- Ajax 和 Json
- 文件上传和下载
- 拦截器
6. 什么是JSON?
- JSON(JavaScript Object Notation, JS 对象标记) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,目前使用特别广泛。
- 采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。
- 简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。
- 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
在 JavaScript 语言中,一切都是对象。因此,任何JavaScript 支持的类型都可以通过 JSON 来表示,例如字符串、数字、对象、数组等。看看他的要求和语法格式:
- 对象表示为键值对,数据由逗号分隔
- 花括号保存对象
- 方括号保存数组
JSON 键值对是用来保存 JavaScript 对象的一种方式,和 JavaScript 对象的写法也大同小异,键/值对组合中的键名写在前面并用双引号 “” 包裹,使用冒号 : 分隔,然后紧接着值:
{"name": "QinJiang"}{"age": "3"}{"sex": "男"}
很多人搞不清楚 JSON 和 JavaScript 对象的关系,甚至连谁是谁都不清楚。其实,可以这么理解:
JSON 是 JavaScript 对象的字符串表示法,它使用文本表示一个 JS 对象的信息,本质是一个字符串。
var obj = {a: 'Hello', b: 'World'}; //这是一个对象,注意键名也是可以使用引号包裹的var json = '{"a": "Hello", "b": "World"}'; //这是一个 JSON 字符串,本质是一个字符串
JSON 和 JavaScript 对象互转
要实现从JSON字符串转换为JavaScript 对象,使用 JSON.parse() 方法:
var obj = JSON.parse('{"a": "Hello", "b": "World"}');//结果是 {a: 'Hello', b: 'World'}
要实现从JavaScript 对象转换为JSON字符串,使用 JSON.stringify() 方法:
var json = JSON.stringify({a: 'Hello', b: 'World'});
//结果是 '{"a": "Hello", "b": "World"}'
代码测试
1、新建一个module ,springmvc-05-json , 添加web的支持
2、在web目录下新建一个 json-1.html , 编写测试内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>JSON_秦疆</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
//编写一个js的对象
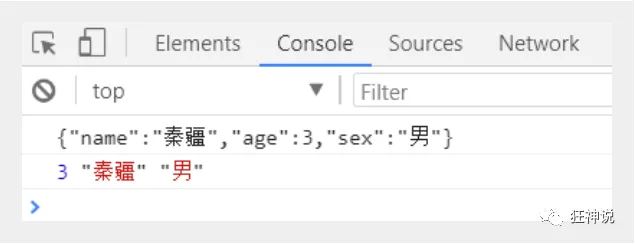
var user = {
name:"秦疆",
age:3,
sex:"男"
};
//将js对象转换成json字符串
var str = JSON.stringify(user);
console.log(str);
//将json字符串转换为js对象
var user2 = JSON.parse(str);
console.log(user2.age,user2.name,user2.sex);
</script>
</body>
</html>
3、在IDEA中使用浏览器打开,查看控制台输出!
Controller返回JSON数据
Jackson应该是目前比较好的json解析工具了
当然工具不止这一个,比如还有阿里巴巴的 fastjson 等等。
我们这里使用Jackson,使用它需要导入它的jar包;
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.8</version>
</dependency>
配置SpringMVC需要的配置
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--配置过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<!--<filter-class>com.kuang.filter.GenericEncodingFilter</filter-class>-->
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<!--/* 包括.jsp-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
springmvc-servlet.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang.controller"/>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<!--JSON格式乱码处理方式-->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<constructor-arg value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="objectMapper">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperFactoryBean">
<property name="failOnEmptyBeans" value="false"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
我们随便编写一个User的实体类,然后我们去编写我们的测试Controller;
package com.kuang.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
}
这里我们需要两个新东西,一个是@ResponseBody,一个是ObjectMapper对象,我们看下具体的用法
编写一个Controller;
package com.kuang.controller;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.kuang.pojo.User;
import com.kuang.utils.JsonUtils;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.developer.SerializationFeature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@Controller //经过视图解析器
//@RestController 只返回字符串
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/json1")
//思考问题,我们正常返回他会走视图解析器,而json需要返回的是一个字符串;
//市面上有很多的第三方jar包可以实现这个功能,jackson.只需要一个简单的注解就可以实现了;
//@ResponseBody , 将服务器端返回的对象转换为json对象响应回去;
@ResponseBody //和@Controller配合使用
public String json1() throws JsonProcessingException {
//需要一个jackson的对象映射器,就是一个类,使用它可以直接将对象转换为json字符串;
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//创建一个对象
User user = new User("秦疆1号",1,"男");
System.out.println(user);
//将Java对象转换为json字符串;
String str = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
System.out.println(str);
return str; //由于使用了@ResponseBody注解,这里会将str以json格式的字符串返回,十分方便;
}
//发现一个问题,乱码了,怎么解决?给@RequestMapping加一个属性
//发现出现了乱码问题,我们需要设置一下他的编码格式为utf-8,以及它返回的类型;
// 通过@RequestMaping的produces属性来实现,修改下代码
//produces:指定响应体返回类型和编码
@RequestMapping(value = "/json2",produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8")
@ResponseBody //不会走视图解析器,会直接给返回一个字符串
public String json2() throws JsonProcessingException {
User user = new User("秦疆1号",1,"男");
return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/json3")
@ResponseBody
public String json3() throws JsonProcessingException {
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
User user1 = new User("秦疆1号",1,"男");
User user2 = new User("秦疆2号",1,"男");
User user3 = new User("秦疆3号",1,"男");
User user4 = new User("秦疆4号",1,"男");
list.add(user1);
list.add(user2);
list.add(user3);
list.add(user4);
return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(list);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/time1")
@ResponseBody
public String json4() throws JsonProcessingException {
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
//发现问题:时间默认返回的json字符串变成了时间戳的格式:1564711481926 Timestamp。
return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(date);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/time2")
@ResponseBody
public String json5() throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//1.如何让他不返回时间戳!所以我们要关闭它的时间戳功能
mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS,false);
//2.时间格式化问题!自定日期格式对象;
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//3.让mapper指定时间日期格式为simpleDateFormat;
mapper.setDateFormat(sdf);
//写一个日期对象
Date date = new Date();
return mapper.writeValueAsString(date);
}
//发现问题,重复代码太多,给它编写一个工具类;
@RequestMapping(value = "/time3")
@ResponseBody
public String json6() throws JsonProcessingException {
return JsonUtils.getJson(new Date());
}
}
配置Tomcat , 启动测试一下!
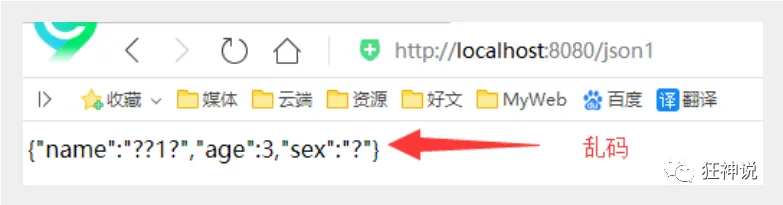
发现出现了乱码问题,我们需要设置一下他的编码格式为utf-8,以及它返回的类型;
通过@RequestMaping的produces属性来实现,修改下代码
//produces:指定响应体返回类型和编码
@RequestMapping(value = "/json1",produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8")
再次测试, http://localhost:8080/json1 , 乱码问题OK!
【注意:使用json记得处理乱码问题】
代码优化(乱码)
乱码统一解决
上一种方法比较麻烦,如果项目中有许多请求则每一个都要添加,可以通过Spring配置统一指定,这样就不用每次都去处理了!
我们可以在springmvc的配置文件上添加一段消息StringHttpMessageConverter转换配置!
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<constructor-arg value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="objectMapper">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperFactoryBean">
<property name="failOnEmptyBeans" value="false"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
返回json字符串统一解决
在类上直接使用 @RestController ,这样子,里面所有的方法都只会返回 json 字符串了,不用再每一个都添加@ResponseBody !我们在前后端分离开发中,一般都使用 @RestController ,十分便捷!
@RestController
public class UserController {
//produces:指定响应体返回类型和编码
@RequestMapping(value = "/json1")
public String json1() throws JsonProcessingException {
//创建一个jackson的对象映射器,用来解析数据
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//创建一个对象
User user = new User("秦疆1号", 3, "男");
//将我们的对象解析成为json格式
String str = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
//由于@ResponseBody注解,这里会将str转成json格式返回;十分方便
return str;
}
}
启动tomcat测试,结果都正常输出!
测试集合输出
增加一个新的方法
@RequestMapping("/json2")
public String json2() throws JsonProcessingException {
//创建一个jackson的对象映射器,用来解析数据
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//创建一个对象
User user1 = new User("秦疆1号", 3, "男");
User user2 = new User("秦疆2号", 3, "男");
User user3 = new User("秦疆3号", 3, "男");
User user4 = new User("秦疆4号", 3, "男");
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(user1);
list.add(user2);
list.add(user3);
list.add(user4);
//将我们的对象解析成为json格式
String str = mapper.writeValueAsString(list);
return str;
}
运行结果 : 十分完美,没有任何问题!
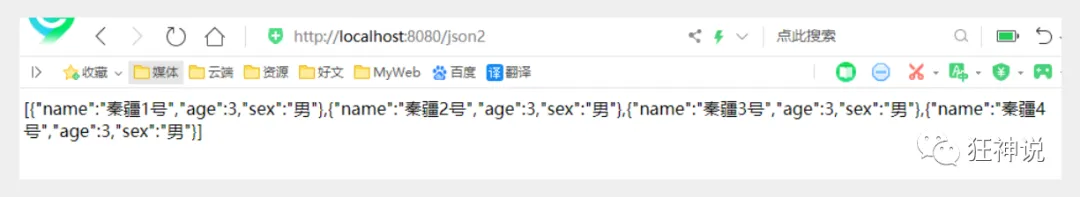
输出时间对象
增加一个新的方法
@RequestMapping("/json3")
public String json3() throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//创建时间一个对象,java.util.Date
Date date = new Date();
//将我们的对象解析成为json格式
String str = mapper.writeValueAsString(date);
return str;
}
运行结果 :
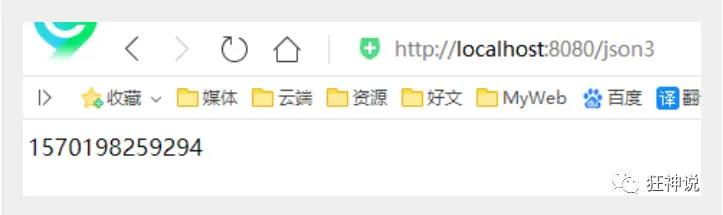
- 默认日期格式会变成一个数字,是1970年1月1日到当前日期的毫秒数!
- Jackson 默认是会把时间转成timestamps形式
解决方案:取消timestamps形式 , 自定义时间格式
@RequestMapping("/json4")
public String json4() throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//不使用时间戳的方式
mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);
//自定义日期格式对象
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//指定日期格式
mapper.setDateFormat(sdf);
Date date = new Date();
String str = mapper.writeValueAsString(date);
return str;
}
运行结果 : 成功的输出了时间!
抽取为工具类
如果要经常使用的话,这样是比较麻烦的,我们可以将这些代码封装到一个工具类中;我们去编写下
package com.kuang.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class JsonUtils {
//代码的复用
public static String getJson(Object object){
return getJson(object,"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
public static String getJson(Object object,String dateFormat){
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//1.如何让他不返回时间戳!所以我们要关闭它的时间戳功能
mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS,false);
//2.时间格式化问题!自定日期格式对象;
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(dateFormat);
//3.让mapper指定时间日期格式为simpleDateFormat;
mapper.setDateFormat(sdf);
try {
return mapper.writeValueAsString(object);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
我们使用工具类,代码就更加简洁了!
@RequestMapping("/json5")
public String json5() throws JsonProcessingException {
Date date = new Date();
String json = JsonUtils.getJson(date);
return json;
}
大功告成!完美!
FastJson
fastjson.jar是阿里开发的一款专门用于Java开发的包,可以方便的实现json对象与JavaBean对象的转换,实现JavaBean对象与json字符串的转换,实现json对象与json字符串的转换。实现json的转换方法很多,最后的实现结果都是一样的。
fastjson 的 pom依赖!
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>
fastjson 三个主要的类:
JSONObject 代表 json 对象
- JSONObject实现了Map接口, 猜想 JSONObject底层操作是由Map实现的。
- JSONObject对应json对象,通过各种形式的get()方法可以获取json对象中的数据,也可利用诸如size(),isEmpty()等方法获取”键:值”对的个数和判断是否为空。其本质是通过实现Map接口并调用接口中的方法完成的。
JSONArray 代表 json 对象数组
- 内部是有List接口中的方法来完成操作的。
JSON代表 JSONObject和JSONArray的转化
- JSON类源码分析与使用
- 仔细观察这些方法,主要是实现json对象,json对象数组,javabean对象,json字符串之间的相互转化。
代码测试,我们新建一个FastJsonDemo 类
package com.kuang.controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.kuang.pojo.User;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class FastJsonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个对象
User user1 = new User("秦疆1号", 3, "男");
User user2 = new User("秦疆2号", 3, "男");
User user3 = new User("秦疆3号", 3, "男");
User user4 = new User("秦疆4号", 3, "男");
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(user1);
list.add(user2);
list.add(user3);
list.add(user4);
System.out.println("*******Java对象 转 JSON字符串*******");
String str1 = JSON.toJSONString(list);
System.out.println("JSON.toJSONString(list)==>"+str1);
String str2 = JSON.toJSONString(user1);
System.out.println("JSON.toJSONString(user1)==>"+str2);
System.out.println("\n****** JSON字符串 转 Java对象*******");
User jp_user1=JSON.parseObject(str2,User.class);
System.out.println("JSON.parseObject(str2,User.class)==>"+jp_user1);
System.out.println("\n****** Java对象 转 JSON对象 ******");
JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) JSON.toJSON(user2);
System.out.println("(JSONObject) JSON.toJSON(user2)==>"+jsonObject1.getString("name"));
System.out.println("\n****** JSON对象 转 Java对象 ******");
User to_java_user = JSON.toJavaObject(jsonObject1, User.class);
System.out.println("JSON.toJavaObject(jsonObject1, User.class)==>"+to_java_user);
}
}
这种工具类,我们只需要掌握使用就好了,在使用的时候在根据具体的业务去找对应的实现。和以前的commons-io那种工具包一样,拿来用就好了!
7. Ajax研究
简介
- AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML(异步的 JavaScript 和 XML)。
- AJAX 是一种在无需重新加载整个网页的情况下,能够更新部分网页的技术。
- Ajax 不是一种新的编程语言,而是一种用于创建更好更快以及交互性更强的Web应用程序的技术。
- 在 2005 年,Google 通过其 Google Suggest 使 AJAX 变得流行起来。Google Suggest能够自动帮你完成搜索单词。
- Google Suggest 使用 AJAX 创造出动态性极强的 web 界面:当您在谷歌的搜索框输入关键字时,JavaScript 会把这些字符发送到服务器,然后服务器会返回一个搜索建议的列表。
- 就和国内百度的搜索框一样!
- 传统的网页(即不用ajax技术的网页),想要更新内容或者提交一个表单,都需要重新加载整个网页。
- 使用ajax技术的网页,通过在后台服务器进行少量的数据交换,就可以实现异步局部更新。
- 使用Ajax,用户可以创建接近本地桌面应用的直接、高可用、更丰富、更动态的Web用户界面。
伪造Ajax
我们可以使用前端的一个标签来伪造一个ajax的样子。iframe标签
1、新建一个module :sspringmvc-06-ajax , 导入web支持!
2、编写一个 ajax-frame.html 使用 iframe 测试,感受下效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>kuangshen</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var myDate = new Date();
document.getElementById('currentTime').innerText = myDate.getTime();
};
function LoadPage(){
var targetUrl = document.getElementById('url').value;
console.log(targetUrl);
document.getElementById("iframePosition").src = targetUrl;
}
</script>
<div>
<p>请输入要加载的地址:<span id="currentTime"></span></p>
<p>
<input id="url" type="text" value="https://www.baidu.com/"/>
<input type="button" value="提交" onclick="LoadPage()">
</p>
</div>
<div>
<h3>加载页面位置:</h3>
<iframe id="iframePosition" style="width: 100%;height: 500px;"></iframe>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3、使用IDEA开浏览器测试一下!
利用AJAX可以做:
- 注册时,输入用户名自动检测用户是否已经存在。
- 登陆时,提示用户名密码错误
- 删除数据行时,将行ID发送到后台,后台在数据库中删除,数据库删除成功后,在页面DOM中将数据行也删除。
- ….等等
jQuery.ajax
纯JS原生实现Ajax我们不去讲解这里,直接使用jquery提供的,方便学习和使用,避免重复造轮子,有兴趣的同学可以去了解下JS原生XMLHttpRequest !
Ajax的核心是XMLHttpRequest对象(XHR)。XHR为向服务器发送请求和解析服务器响应提供了接口。能够以异步方式从服务器获取新数据。
jQuery 提供多个与 AJAX 有关的方法。
通过 jQuery AJAX 方法,您能够使用 HTTP Get 和 HTTP Post 从远程服务器上请求文本、HTML、XML 或 JSON – 同时您能够把这些外部数据直接载入网页的被选元素中。
jQuery 不是生产者,而是大自然搬运工。
jQuery Ajax本质就是 XMLHttpRequest,对他进行了封装,方便调用!
jQuery.ajax(...)
部分参数:
url:请求地址
type:请求方式,GET、POST(1.9.0之后用method)
headers:请求头
data:要发送的数据
contentType:即将发送信息至服务器的内容编码类型(默认: "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8")
async:是否异步
timeout:设置请求超时时间(毫秒)
beforeSend:发送请求前执行的函数(全局)
complete:完成之后执行的回调函数(全局)
success:成功之后执行的回调函数(全局)
error:失败之后执行的回调函数(全局)
accepts:通过请求头发送给服务器,告诉服务器当前客户端可接受的数据类型
dataType:将服务器端返回的数据转换成指定类型
"xml": 将服务器端返回的内容转换成xml格式
"text": 将服务器端返回的内容转换成普通文本格式
"html": 将服务器端返回的内容转换成普通文本格式,在插入DOM中时,如果包含JavaScript标签,则会尝试去执行。
"script": 尝试将返回值当作JavaScript去执行,然后再将服务器端返回的内容转换成普通文本格式
"json": 将服务器端返回的内容转换成相应的JavaScript对象
"jsonp": JSONP 格式使用 JSONP 形式调用函数时,如 "myurl?callback=?" jQuery 将自动替换 ? 为正确的函数名,以执行回调函数
我们来个简单的测试,使用最原始的HttpServletResponse处理 , .最简单 , 最通用
1、配置web.xml 和 springmvc的配置文件,复制上面案例的即可 【记得静态资源过滤和注解驱动配置上】
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 自动扫描指定的包,下面所有注解类交给IOC容器管理 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.kuang.controller"/>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- 视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"
id="internalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- 前缀 -->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" />
<!-- 后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>
2、编写一个AjaxController
@Controller
public class AjaxController {
@RequestMapping("/a1")
public void ajax1(String name , HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
if ("admin".equals(name)){
response.getWriter().print("true");
}else{
response.getWriter().print("false");
}
}
}
3、导入jquery , 可以使用在线的CDN , 也可以下载导入
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/statics/js/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
4、编写index.jsp测试
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
<%--<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>--%>
<script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/statics/js/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
function a1(){
$.post({
url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/a1",
data:{'name':$("#txtName").val()},
success:function (data,status) {
alert(data);
alert(status);
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<%--onblur:失去焦点触发事件--%>
用户名:<input type="text" id="txtName" onblur="a1()"/>
</body>
</html>
5、启动tomcat测试!打开浏览器的控制台,当我们鼠标离开输入框的时候,可以看到发出了一个ajax的请求!是后台返回给我们的结果!测试成功!
ajax的springmvc实现
Springmvc实现
实体类user
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
}
我们来获取一个集合对象,展示到前端页面
@RequestMapping("/a2")
public List<User> ajax2(){
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(new User("秦疆1号",3,"男"));
list.add(new User("秦疆2号",3,"男"));
list.add(new User("秦疆3号",3,"男"));
return list; //由于@RestController注解,将list转成json格式返回
}
前端页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" id="btn" value="获取数据"/>
<table width="80%" align="center">
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
<td>性别</td>
</tr>
<tbody id="content">
</tbody>
</table>
<script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/statics/js/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btn").click(function () {
$.post("${pageContext.request.contextPath}/a2",function (data) {
console.log(data)
var html="";
for (var i = 0; i <data.length ; i++) {
html+= "<tr>" +
"<td>" + data[i].name + "</td>" +
"<td>" + data[i].age + "</td>" +
"<td>" + data[i].sex + "</td>" +
"</tr>"
}
$("#content").html(html);
});
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
成功实现了数据回显!可以体会一下Ajax的好处!
注册提示效果
我们再测试一个小Demo,思考一下我们平时注册时候,输入框后面的实时提示怎么做到的;如何优化
我们写一个Controller
@RequestMapping("/a3")
public String ajax3(String name,String pwd){
String msg = "";
//模拟数据库中存在数据
if (name!=null){
if ("admin".equals(name)){
msg = "OK";
}else {
msg = "用户名输入错误";
}
}
if (pwd!=null){
if ("123456".equals(pwd)){
msg = "OK";
}else {
msg = "密码输入有误";
}
}
return msg; //由于@RestController注解,将msg转成json格式返回
}
前端页面 login.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>ajax</title>
<script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/statics/js/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
function a1(){
$.post({
url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/a3",
data:{'name':$("#name").val()},
success:function (data) {
if (data.toString()=='OK'){
$("#userInfo").css("color","green");
}else {
$("#userInfo").css("color","red");
}
$("#userInfo").html(data);
}
});
}
function a2(){
$.post({
url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/a3",
data:{'pwd':$("#pwd").val()},
success:function (data) {
if (data.toString()=='OK'){
$("#pwdInfo").css("color","green");
}else {
$("#pwdInfo").css("color","red");
}
$("#pwdInfo").html(data);
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>
用户名:<input type="text" id="name" onblur="a1()"/>
<span id="userInfo"></span>
</p>
<p>
密码:<input type="text" id="pwd" onblur="a2()"/>
<span id="pwdInfo"></span>
</p>
</body>
</html>
【记得处理json乱码问题】
测试一下效果,动态请求响应,局部刷新,就是如此!

获取baidu接口Demo
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>JSONP百度搜索</title>
<style>
#q{
width: 500px;
height: 30px;
border:1px solid #ddd;
line-height: 30px;
display: block;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 0 10px;
font-size: 14px;
}
#ul{
width: 520px;
list-style: none;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 0;
border:1px solid #ddd;
margin-top: -1px;
display: none;
}
#ul li{
line-height: 30px;
padding: 0 10px;
}
#ul li:hover{
background-color: #f60;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
<script>
// 2.步骤二
// 定义demo函数 (分析接口、数据)
function demo(data){
var Ul = document.getElementById('ul');
var html = '';
// 如果搜索数据存在 把内容添加进去
if (data.s.length) {
// 隐藏掉的ul显示出来
Ul.style.display = 'block';
// 搜索到的数据循环追加到li里
for(var i = 0;i<data.s.length;i++){
html += '<li>'+data.s[i]+'</li>';
}
// 循环的li写入ul
Ul.innerHTML = html;
}
}
// 1.步骤一
window.onload = function(){
// 获取输入框和ul
var Q = document.getElementById('q');
var Ul = document.getElementById('ul');
// 事件鼠标抬起时候
Q.onkeyup = function(){
// 如果输入框不等于空
if (this.value != '') {
// ☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆JSONPz重点☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆☆
// 创建标签
var script = document.createElement('script');
//给定要跨域的地址 赋值给src
//这里是要请求的跨域的地址 我写的是百度搜索的跨域地址
script.src = 'https://sp0.baidu.com/5a1Fazu8AA54nxGko9WTAnF6hhy/su?wd='+this.value+'&cb=demo';
// 将组合好的带src的script标签追加到body里
document.body.appendChild(script);
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="q" />
<ul id="ul">
</ul>
</body>
</html>
8. 拦截器
概述
SpringMVC的处理器拦截器类似于Servlet开发中的过滤器Filter,用于对处理器进行预处理和后处理。开发者可以自己定义一些拦截器来实现特定的功能。
过滤器与拦截器的区别:拦截器是AOP思想的具体应用。
过滤器
- servlet规范中的一部分,任何java web工程都可以使用
- 在url-pattern中配置了/*之后,可以对所有要访问的资源进行拦截
拦截器
- 拦截器是SpringMVC框架自己的,只有使用了SpringMVC框架的工程才能使用
- 拦截器只会拦截访问的控制器方法, 如果访问的是jsp/html/css/image/js是不会进行拦截的
自定义拦截器
那如何实现拦截器呢?
想要自定义拦截器,必须实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口。
1、新建一个Moudule , springmvc-07-Interceptor , 添加web支持
2、配置web.xml 和 springmvc-servlet.xml 文件
3、编写一个拦截器
package com.kuang.interceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//在请求处理的方法之前执行
//如果返回true执行下一个拦截器
//如果返回false就不执行下一个拦截器
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o) throws Exception {
System.out.println("------------处理前------------");
return true;
}
//在请求处理方法执行之后执行
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("------------处理后------------");
}
//在dispatcherServlet处理后执行,做清理工作.
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {
System.out.println("------------清理------------");
}
}
4、在springmvc的配置文件中配置拦截器
<!--关于拦截器的配置-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!--/** 包括路径及其子路径-->
<!--/admin/* 拦截的是/admin/add等等这种 , /admin/add/user不会被拦截-->
<!--/admin/** 拦截的是/admin/下的所有-->
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<!--bean配置的就是拦截器-->
<bean class="com.kuang.interceptor.MyInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
5、编写一个Controller,接收请求
package com.kuang.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
//测试拦截器的控制器
@Controller
public class InterceptorController {
@RequestMapping("/interceptor")
@ResponseBody
public String testFunction() {
System.out.println("控制器中的方法执行了");
return "hello";
}
}
6、前端 index.jsp
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/interceptor">拦截器测试</a>
7、启动tomcat 测试一下!

验证用户是否登录 (认证用户)
实现思路
1、有一个登陆页面,需要写一个controller访问页面。
2、登陆页面有一提交表单的动作。需要在controller中处理。判断用户名密码是否正确。如果正确,向session中写入用户信息。返回登陆成功。
3、拦截用户请求,判断用户是否登陆。如果用户已经登陆。放行, 如果用户未登陆,跳转到登陆页面
测试:
1、编写一个登陆页面 login.jsp
在web-inf 下的所有页面或者资源,只能通过 controller 或者 servlet 进行访问
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<h1>登录页面</h1>
<hr>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/login">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>
密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
2、编写一个Controller处理请求
package com.kuang.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
//跳转到登陆页面
@RequestMapping("/jumplogin")
public String jumpLogin() throws Exception {
return "login";
}
//跳转到成功页面
@RequestMapping("/jumpSuccess")
public String jumpSuccess() throws Exception {
return "success";
}
//登陆提交
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(HttpSession session, String username, String pwd) throws Exception {
// 向session记录用户身份信息
System.out.println("接收前端==="+username);
session.setAttribute("user", username);
return "success";
}
//退出登陆
@RequestMapping("logout")
public String logout(HttpSession session) throws Exception {
// session 过期
session.invalidate();
return "login";
}
}
3、编写一个登陆成功的页面 success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录成功页面</h1>
<hr>
${user}
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/logout">注销</a>
</body>
</html>
4、在 index 页面上测试跳转!启动Tomcat 测试,未登录也可以进入主页!
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<hr>
<%--登录--%>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/jumplogin">登录</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/jumpSuccess">成功页面</a>
</body>
</html>
5、编写用户登录拦截器
package com.kuang.interceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 如果是登陆页面则放行
System.out.println("uri: " + request.getRequestURI());
if (request.getRequestURI().contains("login")) {
return true;
}
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
// 如果用户已登陆也放行
if(session.getAttribute("user") != null) {
return true;
}
// 用户没有登陆跳转到登陆页面
request.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/jsp/login.jsp").forward(request, response);
return false;
}
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {
}
}
6、在Springmvc的配置文件中注册拦截器
<!--关于拦截器的配置-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean id="loginInterceptor" class="com.kuang.interceptor.LoginInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
7、再次重启Tomcat测试!
OK,测试登录拦截功能无误.
文件上传和下载
准备工作
文件上传是项目开发中最常见的功能之一 ,springMVC 可以很好的支持文件上传,但是SpringMVC上下文中默认没有装配MultipartResolver,因此默认情况下其不能处理文件上传工作。如果想使用Spring的文件上传功能,则需要在上下文中配置MultipartResolver。
前端表单要求:为了能上传文件,必须将表单的method设置为POST,并将enctype设置为multipart/form-data。只有在这样的情况下,浏览器才会把用户选择的文件以二进制数据发送给服务器;
对表单中的 enctype 属性做个详细的说明:
- application/x-www=form-urlencoded:默认方式,只处理表单域中的 value 属性值,采用这种编码方式的表单会将表单域中的值处理成 URL 编码方式。
- multipart/form-data:这种编码方式会以二进制流的方式来处理表单数据,这种编码方式会把文件域指定文件的内容也封装到请求参数中,不会对字符编码。
- text/plain:除了把空格转换为 “+” 号外,其他字符都不做编码处理,这种方式适用直接通过表单发送邮件。
<form action="" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" name="file"/>
<input type="submit">
</form>
一旦设置了enctype为multipart/form-data,浏览器即会采用二进制流的方式来处理表单数据,而对于文件上传的处理则涉及在服务器端解析原始的HTTP响应。在2003年,Apache Software Foundation发布了开源的Commons FileUpload组件,其很快成为Servlet/JSP程序员上传文件的最佳选择。
- Servlet3.0规范已经提供方法来处理文件上传,但这种上传需要在Servlet中完成。
- 而Spring MVC则提供了更简单的封装。
- Spring MVC为文件上传提供了直接的支持,这种支持是用即插即用的MultipartResolver实现的。
- Spring MVC使用Apache Commons FileUpload技术实现了一个MultipartResolver实现类:
- CommonsMultipartResolver。因此,SpringMVC的文件上传还需要依赖Apache Commons FileUpload的组件。
文件上传
1、导入文件上传的jar包,commons-fileupload , Maven会自动帮我们导入他的依赖包 commons-io包;
<!--文件上传-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--servlet-api导入高版本的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
2、配置bean:multipartResolver
【注意!!!这个bean的id必须为:multipartResolver , 否则上传文件会报400的错误!在这里栽过坑,教训!】
<!--文件上传配置-->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!-- 请求的编码格式,必须和jSP的pageEncoding属性一致,以便正确读取表单的内容,默认为ISO-8859-1 -->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="utf-8"/>
<!-- 上传文件大小上限,单位为字节(10485760=10M) -->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="10485760"/>
<property name="maxInMemorySize" value="40960"/>
</bean>
CommonsMultipartFile 的 常用方法:
- String getOriginalFilename():获取上传文件的原名
- InputStream getInputStream():获取文件流
- void transferTo(File dest):将上传文件保存到一个目录文件中
我们去实际测试一下
3、编写前端页面
<form action="/upload" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" name="file"/>
<input type="submit" value="upload">
</form>
4、Controller
package com.kuang.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.*;
@Controller
public class FileController {
//@RequestParam("file") 将name=file控件得到的文件封装成CommonsMultipartFile 对象
//批量上传CommonsMultipartFile则为数组即可
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public String fileUpload(@RequestParam("file") CommonsMultipartFile file , HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//获取文件名 : file.getOriginalFilename();
String uploadFileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
//如果文件名为空,直接回到首页!
if ("".equals(uploadFileName)){
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
System.out.println("上传文件名 : "+uploadFileName);
//上传路径保存设置
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
//如果路径不存在,创建一个
File realPath = new File(path);
if (!realPath.exists()){
realPath.mkdir();
}
System.out.println("上传文件保存地址:"+realPath);
InputStream is = file.getInputStream(); //文件输入流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File(realPath,uploadFileName)); //文件输出流
//读取写出
int len=0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
os.flush();
}
os.close();
is.close();
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
}
5、测试上传文件,OK!
采用file.Transto 来保存上传的文件
1、编写Controller
/*
* 采用file.Transto 来保存上传的文件
*/
@RequestMapping("/upload2")
public String fileUpload2(@RequestParam("file") CommonsMultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//上传路径保存设置
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File realPath = new File(path);
if (!realPath.exists()){
realPath.mkdir();
}
//上传文件地址
System.out.println("上传文件保存地址:"+realPath);
//通过CommonsMultipartFile的方法直接写文件(注意这个时候)
file.transferTo(new File(realPath +"/"+ file.getOriginalFilename()));
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
2、前端表单提交地址修改
3、访问提交测试,OK!
文件下载
文件下载步骤:
1、设置 response 响应头
2、读取文件 — InputStream
3、写出文件 — OutputStream
4、执行操作
5、关闭流 (先开后关)
代码实现:
@RequestMapping(value="/download")
public String downloads(HttpServletResponse response ,HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception{
//要下载的图片地址
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
String fileName = "基础语法.jpg";
//1、设置response 响应头
response.reset(); //设置页面不缓存,清空buffer
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); //字符编码
response.setContentType("multipart/form-data"); //二进制传输数据
//设置响应头
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition",
"attachment;fileName="+URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
File file = new File(path,fileName);
//2、 读取文件--输入流
InputStream input=new FileInputStream(file);
//3、 写出文件--输出流
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] buff =new byte[1024];
int index=0;
//4、执行 写出操作
while((index= input.read(buff))!= -1){
out.write(buff, 0, index);
out.flush();
}
out.close();
input.close();
return null;
}
前端
<a href="/download">点击下载</a>
测试,文件下载OK,大家可以和我们之前学习的JavaWeb原生的方式对比一下,就可以知道这个便捷多了!
拦截器及文件操作在我们开发中十分重要,一定要学会使用!

