逆元简介
同余符号 ≡
先 bb 一下 ≡,这个符号有三个意思,再这里用到的意思为 “同余符号”。≡ 的介绍
两个整数 a,b,若它们除以整数 m 所得的余数相等,则称 a,b 对于模 m 同余
记作 a≡b(mod m)
读作 a 同余于 b 模 m,或读作 a 与 b 关于模 m 同余。
比如 26≡14(mod 12)。
什么是逆元
如果一个线性同余方程 ax ≡ 1(mod b) ,则 x 称为 a mod b 的逆元.
逆元的含义
模 b 意义下,1 个数 a 如果有逆元 x,那么除以 a 相当于乘以 x。
也就是 (a/b)%p=(ax)%p=(a%p)(b%p)%p
~ 那么问题来了,这逆元有啥用吗,这个问题问的好啊~
如果我们要求一个组合数 C(n,m)%p=(n!/(n-m)!*m!)%p, 但是取模的性质对于除法不适用啊。
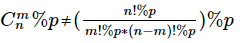
但当这个 n 和 m 很大时又不得不取模,不取模就会溢出。所以就可以用逆元来把乘法代替除法。
怎么求逆元
暴力 O(P) 求逆元
先举这个最简单最暴力的方法,这样便于理解逆元。具体思路就是枚举 1~p-1,检查是否有符合条件的 a*x=1(mod p)。时间复杂度为 O(P)。
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>using namespace std;int main(){int a,p;cin>>a>>p;for(int x=1;x<p;x++){if(x*a%p==1) {printf("%d\n",x);break;}}return 0;}
扩展欧几里得法
给定模数 p,求 a 的逆元相当于求解 ax=1(mod p)
这个方程可以转化为 ax-py=1
然后套用求二元一次方程的方法,用扩展欧几里得算法求得一组 x0,y0 和 gcd (最大公约)
检查 gcd 是否为 1
gcd 不为 1 则说明逆元不存在 ,若为 1,则把 x0 调整到 0~m-1 的范围中即可
( ①:extgcd 目的 求 x ,y ; ②:逆元 目的 求 x )
一个数有逆元的充分必要条件是 gcd(a,n)=1,如果 gcd(a,n)>1, 则不存在逆元
int exgcd(int a,int b,int &x,int &y){if(b==0) {x=1,y=0;return a;}int r = exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);int t = x;x = y;y = t - a/b*y;return r;}
快速幂法
这个要运用 费马小定理 :
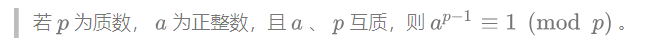
再看看推导过程:

由以上推导就可以通过求一个幂运算很简单的求出逆元辽。
上一个代码,具体功能就是求 n 和 m 的组合数 mod1e9+7
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;const ll Mod=1e9 + 7;ll fac[100010];ll inv[100010];ll quick(ll a,int b){ll ans=1;while(b){if(b&1)ans=(ans*a)%Mod;a=a*a%Mod;b>>=1;}return ans;}void getfac(){fac[0]=inv[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++){fac[i]=fac[i-1]*i%Mod;inv[i]=quick(fac[i],Mod-2);}}ll getans(ll n,ll m){return fac[n]*inv[n-m]%Mod*inv[m]%Mod;}int main(){getfac();ll n,m;while(cin>>n>>m){ll ans=getans(n,m);cout<<ans<<endl;}}
Lucas 定理
对于大组合数取模,n,m 不大于 10 ^ 5 的话,用逆元的方法,可以解决。对于 n,m 大于 10 ^ 5 的话,那么要求 p<10 ^ 5,这样就是 Lucas 定理了,将 n,m 转化到 10^5 以内解。
Lucas 定理是用来求 c(n,m) mod p,p 为素数的值。
C(n,m)%p=C(n/p,m/p)C(n%p,m%p)%p
也就是 Lucas(n,m)%p=Lucas(n/p,m/p)C(n%p,m%p)%p
求上式的时候,Lucas 递归出口为 m=0 时返回 1,原因是因为Lucas(a,0,q)=1;
模板:
#include <cstdio>#include <iostream>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define maxn 100010typedef long long LL;LL m,n,p;LL Pow(LL a,LL b,LL mod){LL ans=1;while(b){if(b&1)ans=(ans*a)%mod;a=a*a%mod;b>>=1;}return ans;}LL C(LL n,LL m){if(n<m)return 0;LL ans=1;for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ans=ans*(((n-m+i)%p)*Pow(i,p-2,p)%p)%p;}return ans;}LL Lucas(LL n,LL m){if(m==0)return 1;return (Lucas(n/p,m/p)*C(n%p,m%p))%p;}int main(){int t;scanf("%d",&t);while(t--){scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&p);printf("%lld\n",Lucas(n,m));}return 0;}

