Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning allows us to approach problems with little or no idea what our results should look like. We can derive structure from data where we don’t necessarily know the effect of the variables.
We can derive this structure by clustering the data based on relationships among the variables in the data.
With unsupervised learning there is no feedback based on the prediction results.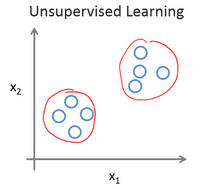
Example:
Clustering:
Take a collection of 1,000,000 different genes, and find a way to automatically group these genes into groups that are somehow similar or related by different variables, such as lifespan, location, roles, and so on.
Non-clustering:
The “Cocktail Party Algorithm”, allows you to find structure in a chaotic environment. (i.e. identifying individual voices and music from a mesh of sounds at a cocktail party).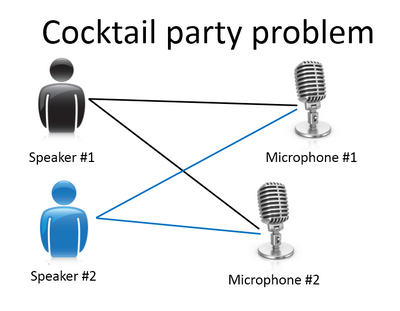
无监督学习(Unsupervised Learning),与监督学习相对,其数据是没有被标记的。这方面的经典案例是聚类;另外 Ng 举了一个图片的例子,是他的学生的项目,通过对图片聚类来构建 3D 模型;还有一个例子是“鸡尾酒会问题”,当很多人在说话时,如何在嘈杂的背景音中提取目标声音,Ng 举了一个两个人的实例,效果很好,一行 matlab 代码就能搞定这个问题。
[W,s,v] = svd((repmat(sum(x.*x,1),size(x,1),1).*x)*x');

