在本实验中,您将了解Web代理服务器的工作原理及其基本功能之一 —— 缓存。
您的任务是开发一个能够缓存网页的小型Web代理服务器。这是一个很简单的代理服务器,它只能理解简单的GET请求,但能够处理各种对象 —— 不仅仅是HTML页面,还包括图片。
通常,当客户端发出一个请求时,请求将被直接发送到Web服务器。然后Web服务器处理该请求并将响应消息发送客户端。为了提高性能,我们在客户端和Web服务器之间建立一个代理服务器。现在,客户端发送的请求消息和Web服务器返回的响应消息都要经过代理服务器。换句话说,客户端通过代理服务器请求对象。代理服务器将客户端的请求转发到Web服务器。然后,Web服务器将生成响应消息并将其传递给代理服务器,代理服务器又将其发送给客户端。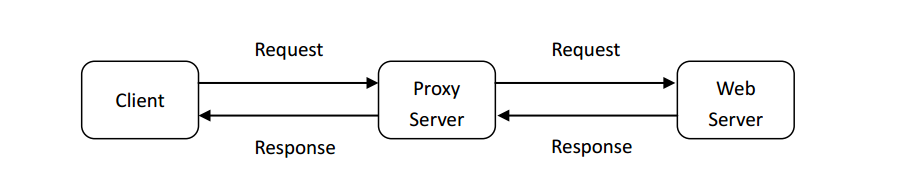
代码
您将在下面找到客户端的代码框架。 您需要完成代码框架。需要您填写代码的地方标有#Fill in start和#Fill in end。 每个地方都需要填写至少一行代码。
运行代理服务器
使用命令行模式运行您的代理服务器程序,然后从您的浏览器发送一个网页请求,将IP地址和端口号指向代理服务器。 例如:http://localhost:8888/www.google.com 为了在独立的计算机上使用浏览器和代理服务器, 因此,在运行代理服务器时,您需要将“localhost”更换为代理服务器的所在机器的IP地址。您还需要将“8888”替换您在代理服务程序中使用的端口号。
配置浏览器
您还可以直接配置您的Web浏览器以使用您的代理服务。 具体取决于您的浏览器。在Internet Explorer中,您可以在 工具 > Internet选项 > 连接选项卡 > LAN设置 中设置代理。 在Netscape(包括衍生浏览器,如Mozilla)中,您可以在 工具 > 选项 > 高级选项 > 网络选项 > 连接设置 中设置代理。 在这两种情况下你都需要给出代理服务器的地址和端口号。你首先要毫无问题地在同一台计算机上运行代理服务器和浏览器。这种方式下,使用代理服务器获取网页就只需提供页面的URL。 例如 http://www.google.com
要提交的内容
您需要提交提交完整的代理服务器代码和一张客户端屏幕截图,用于验证您是否 确实通过代理服务器获取了网页。
代理服务器的Python代码框架
from socket import *import sysif len(sys.argv) <= 1:print 'Usage : "python ProxyServer.py server_ip"\n[server_ip : It is the IP Address Of Proxy Server'sys.exit(2)# Create a server socket, bind it to a port and start listeningtcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)# Fill in start.# Fill in end.while 1:# Strat receiving data from the clientprint 'Ready to serve...'tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()print 'Received a connection from:', addrmessage = # Fill in start. # Fill in end.print message# Extract the filename from the given messageprint message.split()[1]filename = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2]print filenamefileExist = "false"filetouse = "/" + filenameprint filetousetry:# Check wether the file exist in the cachef = open(filetouse[1:], "r")outputdata = f.readlines()fileExist = "true"# ProxyServer finds a cache hit and generates a response messagetcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n")tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n")# Fill in start.# Fill in end.print 'Read from cache'# Error handling for file not found in cacheexcept IOError:if fileExist == "false":# Create a socket on the proxyserverc = # Fill in start. # Fill in end.hostn = filename.replace("www.","",1)print hostntry:# Connect to the socket to port 80# Fill in start.# Fill in end.# Create a temporary file on this socket and ask port 80for the file requested by the clientfileobj = c.makefile('r', 0)fileobj.write("GET "+"http://" + filename + " HTTP/1.0\n\n")# Read the response into buffer# Fill in start.# Fill in end.# Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.# Also send the response in the buffer to client socket and the corresponding file in the cachetmpFile = open("./" + filename,"wb")# Fill in start.# Fill in end.except:print "Illegal request"else:# HTTP response message for file not found# Fill in start.# Fill in end.# Close the client and the server socketstcpCliSock.close()# Fill in start.# Fill in end.
可选练习
- 目前代理服务器不能处理错误。这可能会导致一些问题,当客户端请求一个不可用的对象时,由于“404 Not Found”响应通常没有响应正文,而代理服务器会假设有正文并尝试读取它。
- 当前代理服务器只支持HTTP GET方法。通过添加请求体来增加对POST的支持。
- 缓存:每当客户端发出特定请求时,典型的代理服务器会缓存网页。缓存的基本功能如下:当代理获得一个请求时,它将检查请求的对象是否已经在缓存中,如果是,则从缓存返回对象,从而不用联系服务器。如果对象未被缓存,则代理从服务器获取该对象,向客户端返回该对象,并缓存一个拷贝以备将来的请求。在实际环境下,代理服务器必须验证被缓存的响应是否仍然有效,并且它们能对客户端正确响应。您可以在RFC 2068中阅读有关缓存及其在HTTP中实现方式的更多细节。添加上述简单的缓存功能。您不需要实现任何替换或验证策略。然而您需要实现的是,将请求和响应写入磁盘(即缓存)并能从磁盘中获取它们,用于缓存被请求命中时。为此,您需要在代理中实现一些内部数据结构,以便跟踪哪些请求处于缓存中时,以及它们在磁盘上的位置。您也可以将此数据结构保存在内存中,因为没有必要关机之后持续保存这些数据。
答案
作业4答案
```python改为Python3格式
from socket import * import sys import os
if len(sys.argv) <= 1: print(‘Usage : “python ProxyServer.py server_ip”\n[server_ip : It is the IP Address Of Proxy Server’) sys.exit(2)
Create a server socket, bind it to a port and start listening
tcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM) tcpSerPort = int(sys.argv[1]) tcpSerSock.bind((“”, tcpSerPort)) print(tcpSerPort) tcpSerSock.listen(10) while 1:
# Strat receiving data from the clientprint('Ready to serve...')tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()print('Received a connection from:', addr)message = tcpCliSock.recv(1024)message = message.decode()print("message:", message)if(message == ''):continue# Extract the filename from the given messageprint("message.split()[1]:", message.split()[1])filename = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2]print("filename:", filename)fileExist = "false"filetouse = "/" + filenameprint("filetouse:", filetouse)try:# Check wether the file exist in the cachef = open("WEB/" + filetouse[1:], "rb")outputdata = f.read()f.close()fileExist = "true"# ProxyServer finds a cache hit and generates a response messagetcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send(outputdata)print('Read from cache')# Error handling for file not found in cacheexcept IOError:if fileExist == "false":# Create a socket on the proxyserverc = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)hostn = filename.replace("www.","",1)print("hostn:", hostn)try:# Connect to the socket to port 80serverName = hostn.partition("/")[0]serverPort = 80print((serverName, serverPort))c.connect((serverName, serverPort))askFile = ''.join(filename.partition('/')[1:])print("askFile:", askFile)# Create a temporary file on this socket and ask port 80# for the file requested by the clientfileobj = c.makefile('rwb', 0)fileobj.write("GET ".encode() + askFile.encode() + " HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: ".encode() + serverName.encode() + "\r\n\r\n".encode())# Read the response into bufferserverResponse = fileobj.read()if serverResponse.split()[0] != b'404':print('404')tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.close()continue# Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.# Also send the response in the buffer to client socket and the corresponding file in the cachefilename = "WEB/" + filenamefilesplit = filename.split('/')for i in range(0, len(filesplit) - 1):if not os.path.exists("/".join(filesplit[0:i+1])):os.makedirs("/".join(filesplit[0:i+1]))tmpFile = open(filename, "wb")print(serverResponse)serverResponse = serverResponse.split(b'\r\n\r\n')[1]print(serverResponse)tmpFile.write(serverResponse)tmpFile.close()tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send(serverResponse)except:print("Illegal request")c.close()else:# HTTP response message for file not foundprint("NET ERROR")# Close the client and the server socketstcpCliSock.close()
tcpSerSock.close()
<a name="uX7Hu"></a>## 可选练习1答案```python#改为Python3格式from socket import *import sysimport osif len(sys.argv) <= 1:print('Usage : "python ProxyServer.py server_ip"\n[server_ip : It is the IP Address Of Proxy Server')sys.exit(2)# Create a server socket, bind it to a port and start listeningtcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)tcpSerPort = int(sys.argv[1])tcpSerSock.bind(("", tcpSerPort))print(tcpSerPort)tcpSerSock.listen(10)while 1:# Strat receiving data from the clientprint('Ready to serve...')tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()print('Received a connection from:', addr)message = tcpCliSock.recv(1024)message = message.decode()print("message:", message)if(message == ''):continue# Extract the filename from the given messageprint("message.split()[1]:", message.split()[1])filename = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2]print("filename:", filename)fileExist = "false"filetouse = "/" + filenameprint("filetouse:", filetouse)try:# Check wether the file exist in the cachef = open("WEB/" + filetouse[1:], "rb")outputdata = f.read()f.close()fileExist = "true"# ProxyServer finds a cache hit and generates a response messagetcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send(outputdata)print('Read from cache')# Error handling for file not found in cacheexcept IOError:if fileExist == "false":# Create a socket on the proxyserverc = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)hostn = filename.replace("www.","",1)print("hostn:", hostn)try:# Connect to the socket to port 80serverName = hostn.partition("/")[0]serverPort = 80print((serverName, serverPort))c.connect((serverName, serverPort))askFile = ''.join(filename.partition('/')[1:])print("askFile:", askFile)# Create a temporary file on this socket and ask port 80# for the file requested by the clientfileobj = c.makefile('rwb', 0)fileobj.write("GET ".encode() + askFile.encode() + " HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: ".encode() + serverName.encode() + "\r\n\r\n".encode())# Read the response into bufferserverResponse = fileobj.read()if serverResponse.split()[0] != b'404':print('404')tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.close()continue# Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.# Also send the response in the buffer to client socket and the corresponding file in the cachefilename = "WEB/" + filenamefilesplit = filename.split('/')for i in range(0, len(filesplit) - 1):if not os.path.exists("/".join(filesplit[0:i+1])):os.makedirs("/".join(filesplit[0:i+1]))tmpFile = open(filename, "wb")print(serverResponse)serverResponse = serverResponse.split(b'\r\n\r\n')[1]print(serverResponse)tmpFile.write(serverResponse)tmpFile.close()tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send(serverResponse)except:print("Illegal request")c.close()else:# HTTP response message for file not foundprint("NET ERROR")# Close the client and the server socketstcpCliSock.close()tcpSerSock.close()
可选练习2答案
# 找不到网站测试#改为Python3格式from socket import *import sysimport osif len(sys.argv) <= 1:print('Usage : "python ProxyServer.py server_ip"\n[server_ip : It is the IP Address Of Proxy Server')sys.exit(2)# Create a server socket, bind it to a port and start listeningtcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)tcpSerPort = int(sys.argv[1])tcpSerSock.bind(("", tcpSerPort))print(tcpSerPort)tcpSerSock.listen(10)while 1:# Strat receiving data from the clientprint('Ready to serve...')tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()print('Received a connection from:', addr)message = tcpCliSock.recv(1024)message = message.decode()print("message:", message)if(message == ''):continue# Extract the filename from the given messageprint("message.split()[1]:", message.split()[1])filename = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2]print("filename:", filename)fileExist = "false"filetouse = "/" + filenameprint("filetouse:", filetouse)try:# Check wether the file exist in the cachef = open("WEB/" + filetouse[1:], "rb")outputdata = f.read()f.close()fileExist = "true"# ProxyServer finds a cache hit and generates a response messagetcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send(outputdata)print('Read from cache')# Error handling for file not found in cacheexcept IOError:if fileExist == "false":# Create a socket on the proxyserverc = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)hostn = filename.replace("www.","",1)print("hostn:", hostn)try:# Connect to the socket to port 80serverName = hostn.partition("/")[0]serverPort = 80print((serverName, serverPort))c.connect((serverName, serverPort))askFile = ''.join(filename.partition('/')[1:])print("askFile:", askFile)# Create a temporary file on this socket and ask port 80# for the file requested by the clientfileobj = c.makefile('rwb', 0)if(message.split()[0] == 'GET'):fileobj.write("GET ".encode() + askFile.encode() + " HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: ".encode() + serverName.encode() + "\r\n\r\n".encode())else: #POSTfileobj.write("POST ".encode() + askFile.encode() + " HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: ".encode() + serverName.encode() + "\r\n\r\n".encode())fileobj.write(message.split("\r\n\r\n")[1].encode())# Read the response into bufferserverResponse = fileobj.read()if serverResponse.split()[0] != b'404':print('404')tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.close()continue# Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.# Also send the response in the buffer to client socket and the corresponding file in the cachefilename = "WEB/" + filenamefilesplit = filename.split('/')for i in range(0, len(filesplit) - 1):if not os.path.exists("/".join(filesplit[0:i+1])):os.makedirs("/".join(filesplit[0:i+1]))tmpFile = open(filename, "wb")print(serverResponse)serverResponse = serverResponse.split(b'\r\n\r\n')[1]print(serverResponse)tmpFile.write(serverResponse)tmpFile.close()tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n\r\n".encode())tcpCliSock.send(serverResponse)except:print("Illegal request")c.close()else:# HTTP response message for file not foundprint("NET ERROR")# Close the client and the server socketstcpCliSock.close()tcpSerSock.close()

