第一题
当前有多个包含 0 到 9 的数字串列表, 找出与制定数字串具有关联特征值的序列。特征值使之数字串中比给定临界值小的数字按顺序组成的数字串。如果给定数字串的特征值为当前数字串的特征值的子字符串,则认为当前字符串与给定字符串具有关联特征值。
输入描述:
单个数字串位数不超过 100,输入的数字序列长度 N 范围为(2<=N<=20)。倒数第一行为给定的字符串,倒数第二行的数字是临
界值 A ,范围为(1<A<=9)
输出描述:
输出匹配的数字串序列,输出顺序与输入顺序保持一致。
示例:
输入:**
135682318 23457 14282123 14231728 3 1724153
输出:**
135682318 14231728
说明:**
在临界值 3 的情况下,当前数字串:[**135682318,23457 ,14282123,14231728]的特征值分别为 121,2, 12212,1212,而给定字符串1724153的特征值为121。因此数字串135682318 ,14282123与给定字符串1724153具有关联特征值。**
**
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);while (sc.hasNext()){ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();int bound =0;while(sc.hasNext()){String str = sc.nextLine();if(str.length()==1){bound= Integer.parseInt(str);break;}arrayList.add(str);}String Strg = sc.nextLine();String Val = solveFunc(Strg,bound);for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {String comp = solveFunc(arrayList.get(i),bound);if (checkSub(comp,Val))System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));}}}public static boolean checkSub(String comp, String val){for (int i = 0,j=val.length(); j <= comp.length(); i++,j++) {if (comp.substring(i,j).equals(val)) {return true;}}return false;}public static String solveFunc(String Str, int bound){char[] charArray = Str.toCharArray();String result = "";for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {String tmp = charArray[i]+"";if(Integer.parseInt(tmp)<bound)result= result+tmp;}return result;}}
第三题
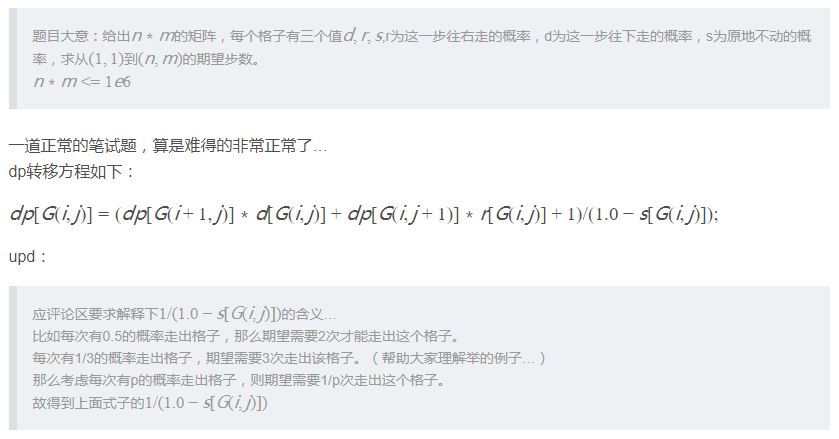
给出一个 n*m 的网格,每一个格子上有三个数:pD、pR、pS满足 0<=pD、pR、pS<=1,且pD+pR+pS=1. pD 表示在当前格子,下一步移动到下方格子的概率;pR 表示下一步移动到右方格子的概率,pS 表示下一步仍然停留在原地的概率。 求从网格左上角移动到右下角所需要的步数的期望。数据保证答案存在。
输入描述:
第一行包含两个整数 n,m,表示网格的大小(0<=n*m<=100000) 接下来共n行,每行包含 3*m 个实数。 第i行的第 3j,3j+1, 3j+2 个数表示第 i 行,第 j 列格子上的 *pD、pR、pS。**
输出描述:**
输出从左上角走到右下角所需要的步数的期望。(如有 0.5 的概率可以在两步内从左上角走到右下角;有 0.3 的概率可以在三步内走到;有0.2 的概率可以在四步内走到,那么步数的期望为 0.52+0.33+0.2*4=2.7)

示例:
输入
2 2 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.0
输出**
3.0
输出说明:
第一步以100%的概率从(0, 0)移动到(1, 0); 从(1, 0)移动到(1, 1)锁期望的步数为2步,所以答案为 3 。
备注:考虑到浮点数精度问题,假设你的答案输出为yourvalue,标准答案为stdvalue,当abs(yourvalue-stdvalue)/max(1.0,abs(stdvalue))<1e-3时,你的答案会被判定为正确。**
**
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {final int threshold = 100050;double[][] node = new double[threshold][3];double[] dp = new double[threshold];Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int n = sc.nextInt();int m = sc.nextInt();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {int k = convertIndex(i,j,m);shuru(node,k,sc);}}for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {for (int j = m-1; j >=0; j--) {if(i==n-1&&j==m-1)continue;int k = convertIndex(i,j,m);dp[k] = 1.0;if (i+1 <n) {dp[k] += dp[convertIndex(i+1,j,m)]*node[k][1];}if (j+1 < m) {dp[k] += dp[convertIndex(i,j+1,m)]*node[k][0];}dp[k] /= (1.0-node[k][2]);}}System.out.println(dp[0]);}public static void shuru(double[][] node,int k,Scanner sc){node[k][1] = sc.nextDouble();node[k][0] = sc.nextDouble();node[k][2] = sc.nextDouble();}public static int convertIndex(int a, int b, int m){return a*m+b;}}
**

