地上有一个m行和n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。 例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
可以用深度优先搜索:每走一步都要判断这一步能不能走,显然最外围一圈不能走,然后根据题意,格子行列各个位加起来不能大于阈值threshold。然后走到下一个格子,走法是一样的,所以可以递归实现。注意:被访问过的格子需要用记录一下。不然会一个格子会被访问多次。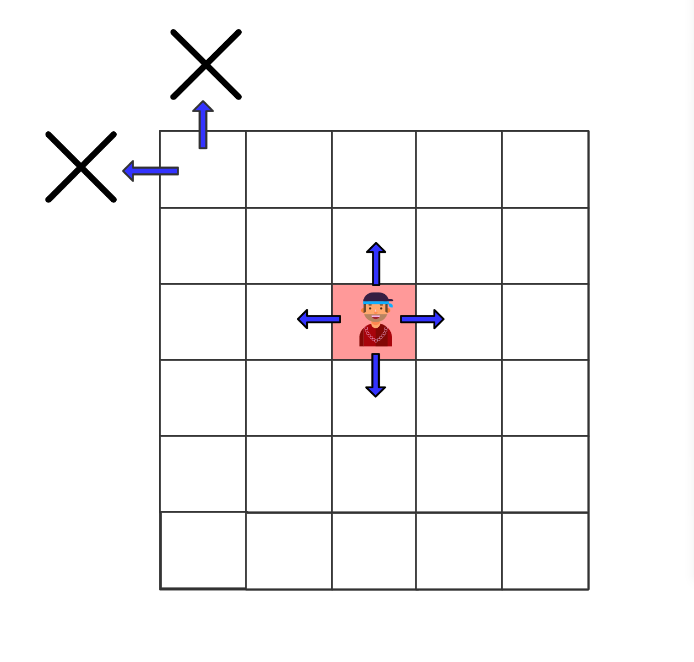
DFS解法
public class Solution {public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols){if (rows <= 0 || cols <= 0 || threshold < 0)return 0;boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[rows][cols];return movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, 0, 0, isVisited);}public int movingCountIntervals(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, boolean[][] isVisited){if (row<0 || row>=rows || col<0 || col>=cols || checkSum(col)+checkSum(row)>threshold || isVisited[row][col]){return 0;}isVisited[row][col] = true;//其实当前节点的左节点和上节点已经被访问过了所以下面的movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, row-1, col, isVisited)和//movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, row, col-1, isVisited)是多余的return 1 + movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, row+1, col, isVisited)+ movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, row-1, col, isVisited)+ movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, row, col+1, isVisited)+ movingCountIntervals(threshold, rows, cols, row, col-1, isVisited);}public int checkSum(int num){int sum=0;while(num>0){sum += num%10;num /= 10;}return sum;}}
BFS解法
import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;public class BFS {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(BFS.movingCount(3,10,10));}public static int checkSum(int num){int sum=0;while(num>0){sum += num%10;num /= 10;}return sum;}public static int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols){if(rows<=0 || cols<=0 || threshold<0)return 0;int result=0;//BFSQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[rows][cols];queue.offer(0);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int row = queue.peek()/cols;int col = queue.peek()%cols;if(row<rows && col<cols && checkSum(row)+checkSum(col)<=threshold && !isVisited[row][col]){result++;isVisited[row][col] = true;queue.offer((row+1)*cols+col);queue.offer(row*cols+col+1);}queue.poll();}return result;}}
DFS+回溯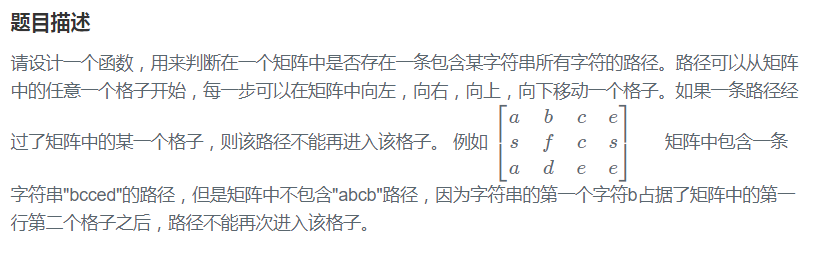
由于每一个位置都有可能是搜索的起点,对于每一个搜索的位置来说,用DFS递归查找需要的路径。
先定义递归DFS函数:find(){第一步,递归出口第二步,检查元素是否被访问过``<br />第三步,都没有返回,继续递归find()回溯}
public boolean find(char[][] array, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, char[] str, int str_pos, boolean isVisited[][]){//递归出口条件//当 row<0 || row>=rows || col<0 || col>=cols || isVisited[row][col] || array[row][col] != str[str_pos] 满足任意一条返回 false,说明此路不通;//当 str_pos == str.length 返回 true, 表示数组中有这条路径,递归结束;if(row<0 || row>=rows || col<0 || col>=cols || isVisited[row][col] || array[row][col] != str[str_pos])return false;if(str_pos == str.length)return true;//标记这个位置已经被访问过了isVisited[row][col] = true;//程序能走到这里说明当前位置没有越界,并且array[row][col] == str[str_pos],这样就可以继续往下搜索了boolean result = find(array, rows, cols, row-1, col, str, str_pos+1, isVisited)|| find(array, rows, cols, row, col+1, str, str_pos+1, isVisited)|| find(array, rows, cols, row+1, col, str, str_pos+1, isVisited)|| find(array, rows, cols, row, col-1, str, str_pos+1, isVisited);//非常重要的一步:回溯. 如果不回溯的话,假设某一次递归时,访问到当前位置设为(x,y), 但是此路不通,//也就是说这条路径搜索不到我们想要的字符串。这时,所有的递归都不能访问该位置,程序就是错的isVisited[row][col] = false;return result;}//输入的是一维字符数组,转成二维数组,容易理解public boolean hasPath(char[] matrix, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {visit = new int[rows][cols];char[][] array = new char[rows][cols];for (int i = 0; i < rows ; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {array[i][j] = matrix[i*cols + j];}}for (int i = 0; i < rows ; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {if(find(array,rows,cols,str,i,j,0)){return true;}}}return false;}

