Environment
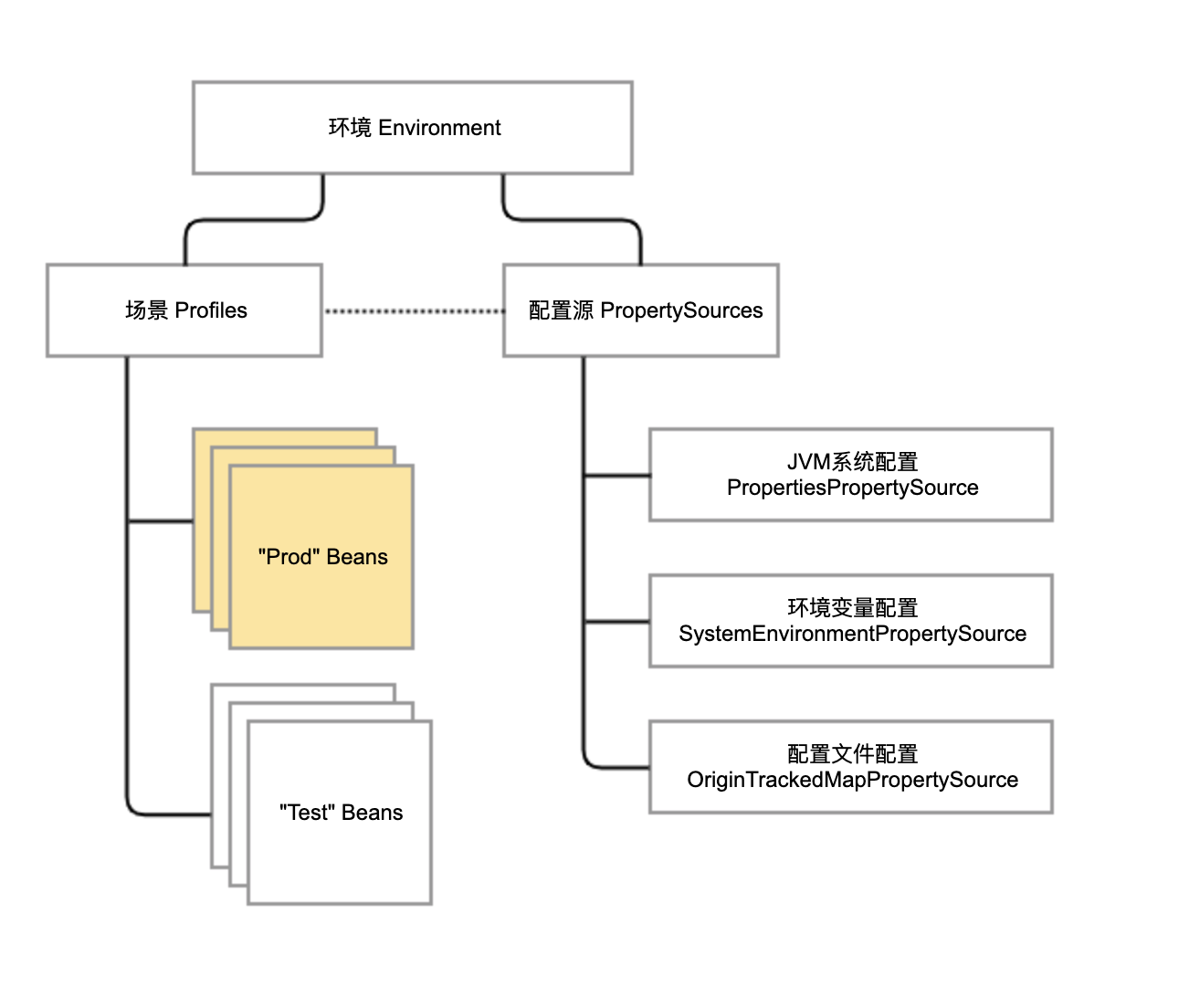
spring 的环境配置,从上层 Environment 接口抽象出了 profile 和 property
针对 Property,又抽象出各种 PropertySource 类代表配置源。一个环境下可能有多个配置源,每个配置源中有诸多配置项。在查询配置信息时,需要按照配置源优先级进行查询。
Profile 定义了场景的概念。通常,我们会定义类似 dev、test、stage 和 prod 等环境作为不同的Profile,用于按照场景对 Bean 进行逻辑归属。同时,Profile 和配置文件也有关系,每个环境都有独立的配置文件,但我们只会激活某一个环境来生效特定环境的配置文件。
property 和 profile 的关系如下:
demo,通过 standardEnvironment,查看 spring 所有的 propertySource 配置
@Component@Slf4jpublic class LocalEnvironment {@Autowiredprivate StandardEnvironment env;@PostConstructpublic void init() {Arrays.asList("server.port", "spring.application.name", "customized.demon.name").forEach(k -> {env.getPropertySources().forEach(p -> {if (p.containsProperty(k)) {log.info("LocalEnvironment propertySource:{},value:{}", p, p.getProperty(k));}});});log.info("@----");Iterator<PropertySource<?>> iterator = env.getPropertySources().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {System.out.println(iterator.next());}}}
打印结果:
2021-11-21 18:18:06.539 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : LocalEnvironment propertySource:ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource {name='configurationProperties'},value:88882021-11-21 18:18:06.541 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : LocalEnvironment propertySource:OriginTrackedMapPropertySource {name='applicationConfig: [classpath:/bootstrap.yml]'},value:88882021-11-21 18:18:06.541 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : LocalEnvironment propertySource:ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource {name='configurationProperties'},value:springboot-mybatis2021-11-21 18:18:06.541 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : LocalEnvironment propertySource:OriginTrackedMapPropertySource {name='applicationConfig: [classpath:/bootstrap.yml]'},value:springboot-mybatis2021-11-21 18:18:06.541 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : LocalEnvironment propertySource:ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource {name='configurationProperties'},value:micahel2021-11-21 18:18:06.541 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : LocalEnvironment propertySource:OriginTrackedMapPropertySource {name='applicationConfig: [classpath:/bootstrap.yml]'},value:micahel2021-11-21 18:18:06.541 INFO 5333 --- [ main] c.a.d.m.environment.LocalEnvironment : @ == ==ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource {name='configurationProperties'}StubPropertySource {name='servletConfigInitParams'}ServletContextPropertySource {name='servletContextInitParams'}MapPropertySource {name='systemProperties'}OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'}RandomValuePropertySource {name='random'}MapPropertySource {name='springCloudClientHostInfo'}OriginTrackedMapPropertySource {name='applicationConfig: [classpath:/bootstrap.yml]'}MapPropertySource {name='defaultProperties'}
如果需要获取spring 的某一个配置,直接注入 Envrironment 接口,调用它的 getProperty()方法即可;
�spring 配置的优先级, 版本 2.6.1:链接
Spring Boot lets you externalize your configuration so that you can work with the same application code in different environments. You can use a variety of external configuration sources, include Java properties files, YAML files, environment variables, and command-line arguments.
Property values can be injected directly into your beans by using the @Value annotation, accessed through Spring’s Environment abstraction, or be bound to structured objects through @ConfigurationProperties.
Spring Boot uses a very particular PropertySource order that is designed to allow sensible overriding of values. Properties are considered in the following order (with values from lower items overriding earlier ones):
- Default properties (specified by setting SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties).
- @PropertySource annotations on your @Configuration classes. Please note that such property sources are not added to the Environment until the application context is being refreshed. This is too late to configure certain properties such as logging. and spring.main. which are read before refresh begins.
- Config data (such as application.properties files).
- A RandomValuePropertySource that has properties only in random.*.
- OS environment variables.
- Java System properties (System.getProperties()).
- JNDI attributes from java:comp/env.
- ServletContext init parameters.
- ServletConfig init parameters.
- Properties from SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON (inline JSON embedded in an environment variable or system property).
- Command line arguments.
- properties attribute on your tests. Available on @SpringBootTest and the test annotations for testing a particular slice of your application.
- @TestPropertySource annotations on your tests.
- Devtools global settings properties in the $HOME/.config/spring-boot directory when devtools is active.
Config data files are considered in the following order:
- Application properties packaged inside your jar (application.properties and YAML variants).
- Profile-specific application properties packaged inside your jar (application-{profile}.properties and YAML variants).
- Application properties outside of your packaged jar (application.properties and YAML variants).
- Profile-specific application properties outside of your packaged jar (application-{profile}.properties and YAML variants).
ConfigurationProperties +EnableConfigurationProperties
配置文件如何注入到 spring 容器?
使用注解 @ConfigurationProperties ,@NestedConfigurationProperty ,配合注解
@EnableConfigurationProperties 可以映射配置文件的配置到 spring 容器中的 java 对象。栗子:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "magic-api")public class MagicAPIProperties {private String prefix;@NestedConfigurationPropertyprivate ResourceConfig resource = new ResourceConfig();}
public class ResourceConfig {/*** 存储类型,默认是文件*/private String type = "file";/*** 文件存储位置*/private String location = "/data/magic-api/";/*** 是否是只读模式*/private boolean readonly = false;/*** 前缀*/private String prefix = "magic-api";/*** 使用数据库存储时的表名*/private String tableName = "magic_api_file";/*** 使用数据库存储时使用的数据源*/private String datasource;// 省略 set get}
@Configuration@EnableConfigurationProperties(MagicAPIProperties.class)public class MagicAPIAutoConfiguration {private final MagicAPIProperties properties;public MagicAPIAutoConfiguration(MagicAPIProperties properties){this.properties = properties;}@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "magic-api", name = "resource.type", havingValue = "redis")public Resource magicRedisResource(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {ResourceConfig resource = properties.getResource();return new RedisResource(new StringRedisTemplate(connectionFactory), resource.getPrefix(), resource.isReadonly());}}
ConfigurationProperties +configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("e6.tms.customer.blx")@Configuration@Datapublic class BlxCommonProperties {private Integer corpId;private List<Integer> processEventCorpIds;}
配置文件这样写,就可以把数据注入到数组中。通过 @auwired 这个类 BlxCommonProperties ,就可以直接使用
e6.tms.customer.blx.processEventCorpIds[0] = 193729e6.tms.customer.blx.processEventCorpIds[1] = 210364
propertySource
@Configuration@PropertySource("classpath:/com/myco/app.properties")public class AppConfig {@AutowiredEnvironment env;@Beanpublic TestBean testBean() {TestBean testBean = new TestBean();testBean.setName(env.getProperty("testbean.name"));return testBean;}}
这样可以将 class路径下 app.properties 里面的键值对注入到 spring environment。链接