TreeSet同样实现了Set接口,例外还实现SortedSet接口,从而实现了:
既可以去重,又可以排序
特点
1、它内部的元素在存放时,有一定的存储顺序
2、它同样不能存放重复元素
3、TreeSet 底层是TreeMap结构,去重原理:如同HashSet,同样要比较Hash值,以及equals()
扩展方法
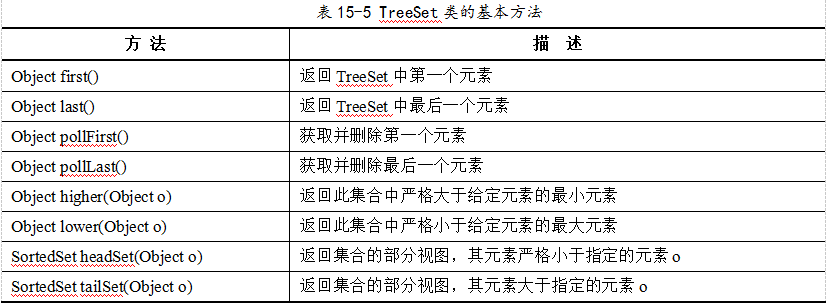
用法
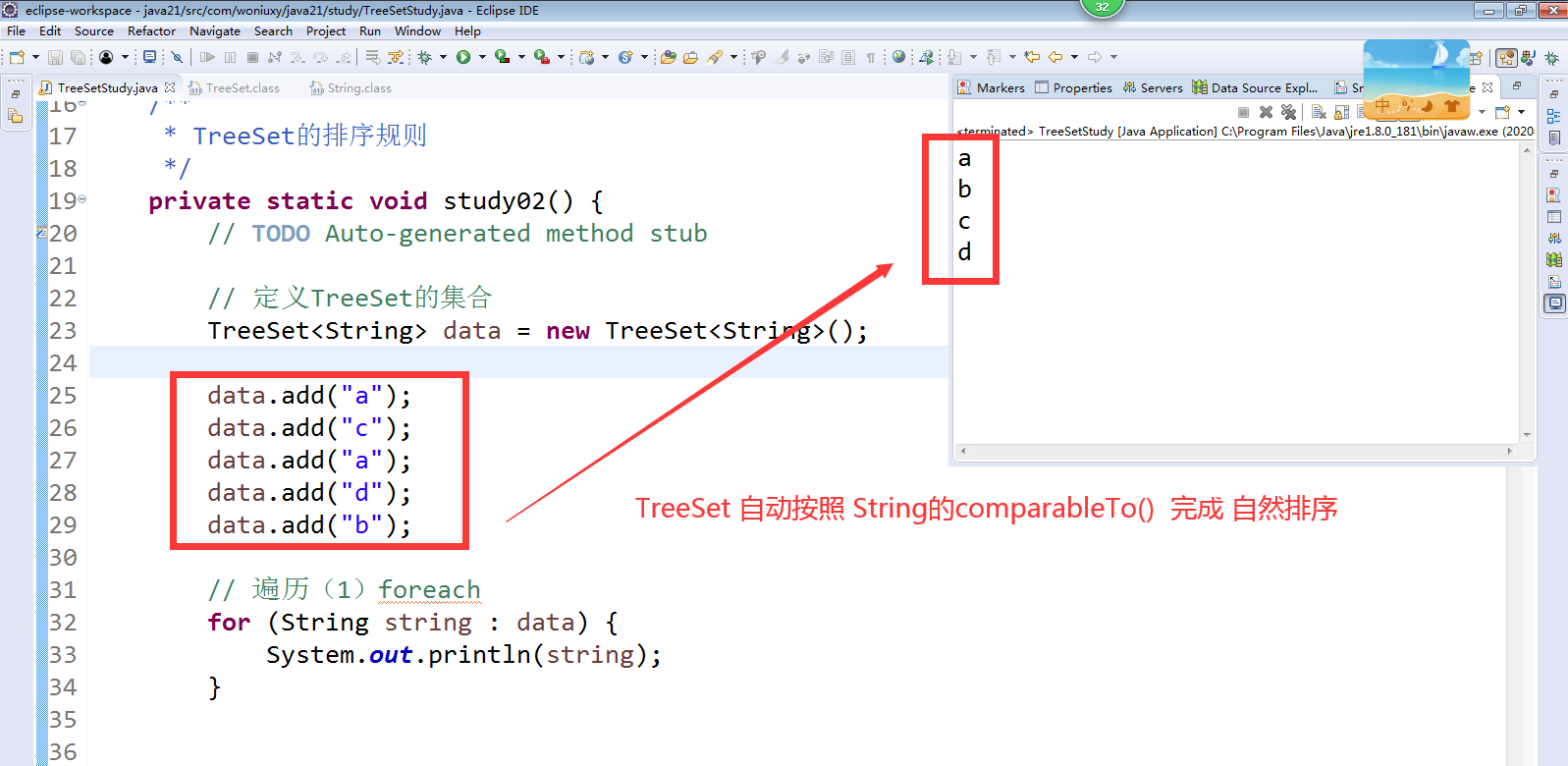
import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;import java.util.TreeSet;public class TreeSetStudy {public static void main(String[] args) {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//定义TreeSet的集合TreeSet<String> data = new TreeSet<String>();data.add("a");data.add("c");data.add("a");data.add("d");data.add("b");//得到集合长度System.out.println(data.size());//判断集合中是否包含某一个元素System.out.println(data.contains("a"));//判断集合是否为空System.out.println(data.isEmpty());// data.remove("a");//取得第1个元素System.out.println(data.first());//取得最后1个元素System.out.println(data.last());//严格返回比“b” 大的,该集合中的最小元素,如果没有此元素则返回 null (比我大的,但是又是最靠近我的)System.out.println(data.higher("b"));//返回比我小的,也是最靠近我的System.out.println(data.lower("b"));//取得集合中,比我小的所有元素System.out.println(data.headSet("c"));//取得集合中,比我大的所有元素(但是包含自己)System.out.println(data.tailSet("b"));//遍历(1)foreach// for (String string : data) {// System.out.println(string);// }//遍历(2)迭代器// Iterator<String> iterator = data.iterator();// while(iterator.hasNext()) {//// String str = iterator.next();//// System.out.println(str);// }}}
TreeSet排序规则
自然排序
在JDK类库中,有一部分类实现了Comparable接口,例如Integer、Double、String等等。Comparable接口在java.lang包中,该接口有一个compareTo(Object o)方法,返回整型数据。对于表达式x.compareTo(y),如果返回值为0,则表示x和y相等;如果返回值大于0,则表示x大于y;如果返回值小于0,则表示x小于y。TreeSet集合调用对象的compareTo()方法比较集合中的大小,然后进行升序排列,这种方式称为自然排序
如果元素要参与自然排序,需要实现一个接口Comparable
白话:凡是元素自带了排序规则的,都是属于自然排序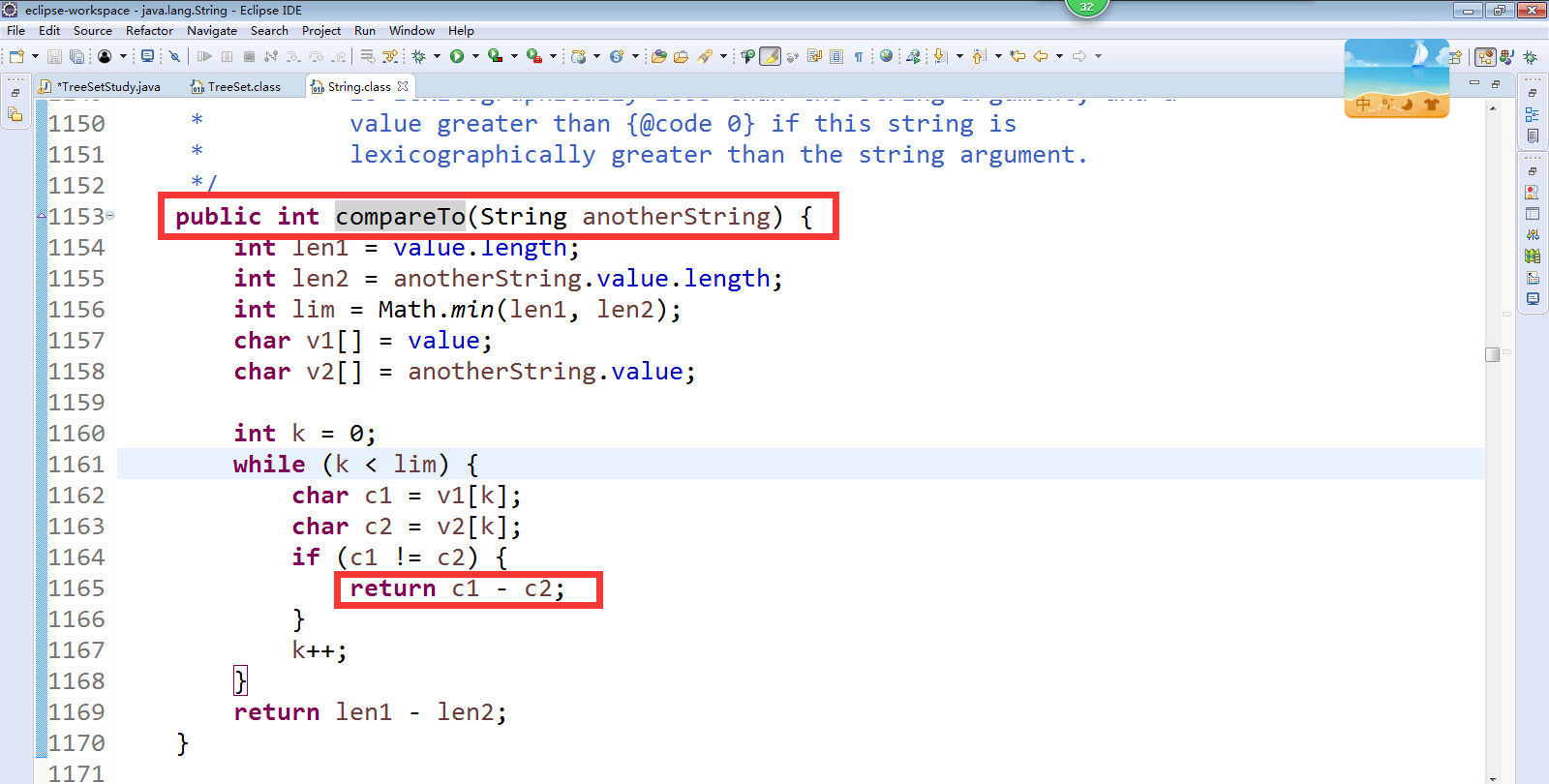
import java.io.Serializable;public class StudentBean implements Serializable,Comparable<StudentBean> {/****/private static final long serialVersionUID = -2640219895840760729L;private String name;private int age;public StudentBean(String name, int age) {super();this.name = name;this.age = age;}public StudentBean() {super();// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {final int prime = 31;int result = 1;result = prime * result + age;result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());return result;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {if (this == obj)return true;if (obj == null)return false;if (getClass() != obj.getClass())return false;StudentBean other = (StudentBean) obj;if (age != other.age)return false;if (name == null) {if (other.name != null)return false;} else if (!name.equals(other.name))return false;return true;}/*** 定义排序规则*/@Overridepublic int compareTo(StudentBean o) {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//自定义排序规则(0 ---我们地位是一样的 整数 ---你的地位比我大//负数 --- 你的地位比我小)return this.name.hashCode() - o.name.hashCode();}}
private static void study03() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubTreeSet<StudentBean> data = new TreeSet<StudentBean>();StudentBean stu01 = new StudentBean("张三",18);StudentBean stu02 = new StudentBean("李四",15);StudentBean stu03 = new StudentBean("王五",23);data.add(stu01);data.add(stu02);data.add(stu03);System.out.println(data);}
自定义排序
自定义排序 和自然排序 都是用来集合完成排序的,区别在于:
自然排序,需要在元素身上实现Comparable
而自定义排序 ,需要程序员自己制定 排序比较器
import java.util.Comparator;import com.woniuxy.java21.bean.StudentBean;/*** 自定义比较器,用来完成集合排序* @author Administrator**/public class InitStudentComparator implements Comparator<StudentBean>{/**** 0 我们地位相当* 正数 你的地位比我大 应该靠后* 负数 你的地位比我低 应该靠前*/@Overridepublic int compare(StudentBean o1, StudentBean o2) {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//升序规则return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();}}
private static void study03() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubTreeSet<StudentBean> data = new TreeSet<StudentBean>(new InitStudentComparator());StudentBean stu01 = new StudentBean("张三",18);StudentBean stu02 = new StudentBean("李四",15);StudentBean stu03 = new StudentBean("王五",23);data.add(stu01);data.add(stu02);data.add(stu03);System.out.println(data);}

