奇异值分解Singular Value Decomposition
在线性代数中,奇异值分解( the singular value decomposition (SVD))是一种实数real或者复杂矩阵的分解,在奇异处理和分析中有许多有用的应用。
令A是一个 m x n矩阵,且m >= n,则A能够按照以下方式分解: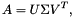 ,U是一个 m x m的正交矩阵(原文应该有误,原文是where U is a
,U是一个 m x m的正交矩阵(原文应该有误,原文是where U is a  orthonormal matrix).
orthonormal matrix).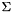 是一个m x n对角矩阵(对角线下所有元素都为0,且对角线满足
是一个m x n对角矩阵(对角线下所有元素都为0,且对角线满足 ).V是 n x n 正交矩阵。
).V是 n x n 正交矩阵。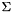 的对角线上的element被称作奇异值(singular value)
的对角线上的element被称作奇异值(singular value)
SVD函数
SVD分解适用于稀疏矩阵和密集矩阵。另外,对于非常稀疏的矩阵已经通过原生实现(native implementation)来改善性能。
密集矩阵SVD函数
svd( source_table,output_table_prefix,row_id,k,n_iterations,result_summary_table);参数
source_table
text密集矩阵的源表名
该表包含一个row_id列用来指明每行,值从1开始。其他的列包含矩阵的数据。如下2 x 2 的矩阵有两种dense表示形式。
format1:
row_id col1 col2row1 1 1 0row2 2 0 1
format2:
row_id row_vecrow1 1 {1, 0}row2 2 {0, 1}
output_table_prefix
text.输出表的前缀。
row_id
text,每行的id
k
integer,用作计算的奇异值个数
n_iterations (optional).
integer,循环的次数
注意:循环次数必须在[k,column dimension]范围内,k是奇异值个数。
result_summary_table (optional)
text,存储汇总结果集的表名
稀疏矩阵的SVD函数
如下面例子,用于稀疏格式表示的矩阵。注意,输入矩阵在SVD操作前因为计算效率原因被转换成密集矩阵。
svd_sparse( source_table,output_table_prefix,row_id,col_id,value,row_dim,col_dim,k,n_iterations,result_summary_table);
参数
source_table
稀疏矩阵的表名。
(这段稀疏矩阵介绍,就不翻译了,前面有提到)
A sparse matrix is represented using the row and column indices for each non-zero entry of the matrix. This representation is useful for matrices containing multiple zero elements. Below is an example of a sparse 4x7 matrix with just 6 out of 28 entries being non-zero. The dimensionality of the matrix is inferred using the max value in row and col columns. Note the last entry is included (even though it is 0) to provide the dimensionality of the matrix, indicating that the 4th row and 7th column contain all zeros.
row_id | col_id | value--------+--------+-------1 | 1 | 91 | 5 | 61 | 6 | 62 | 1 | 83 | 1 | 33 | 2 | 94 | 7 | 0(6 rows)
output_table_prefix
text.输出表的前缀。
row_id
text,稀疏矩阵中每个entity的row index
col_id
text,稀疏矩阵中每个entity的col index
value
text,稀疏矩阵中的非0值
row_dim
integer,矩阵中的行数
col_dim
integer,矩阵中的列数
k
integer,用作计算的奇异值的个数
n_iterations (optional).
integer,循环的次数
注意:循环次数必须在[k,column dimension]范围内,k是奇异值个数。
result_summary_table (optional)
text,存储汇总结果集的表名
稀疏矩阵的原生实现
以下函数在计算SVD的时候使用原生稀疏矩阵
注意,如果矩阵是高度稀疏的时候推荐使用该函数,因为效率更高。
函数语法
svd_sparse_native( source_table,output_table_prefix,row_id,col_id,value,row_dim,col_dim,k,n_iterations,result_summary_table);
参数
source_table
稀疏矩阵的表名。
output_table_prefix
text.输出表的前缀。
row_id
text,稀疏矩阵中每个entity的row index
col_id
text,稀疏矩阵中每个entity的col index
value
text,稀疏矩阵中的非0值
row_dim
integer,矩阵中的行数
col_dim
integer,矩阵中的列数
k
integer,用作计算的奇异值的个数
n_iterations (optional).
integer,循环的次数
注意:循环次数必须在[k,column dimension]范围内,k是奇异值个数。
result_summary_table (optional)
text,存储汇总结果集的表名
输出表
特征向量/值eigenvector/value的输出有以下3种表,
- 左奇异矩阵,表名格式为 [output_table_prefix]_u.例如’netflix_u’
- 右奇异矩阵表名格式为 [output_table_prefix]_v.例如’netflix_v’
- 奇异值表名格式为 [output_table_prefix]_s.例如’netflix_s’
左和右的奇异向量表的格式为:
row_id integer,每个奇异值的id(降序)
row_vec float8[],row_id的奇异向量element。每个数组大小(size)都是k
稀疏表格式的奇异值表,只有矩阵对角的element不是0
row_id integer,第i个特征值
col_id integer,和row_id相同
value float8,特征值
所有的row_id和col_id都是从1开始
汇总结果表the result summary table有以下列:
rows_used integer,用于SVD计算的行数
exec_time float8,执行SVD的总时间
iter integer,循环运行次数
recon_error float8,正交基底集合的整体特征分数(例如近似值质量)(Total quality score (i.e. approximation quality) for this set of orthonormal basis.)
relative_recon_error float8,关联特征分数Relative quality score.
在汇总结果表中,reconstruction error是使用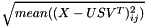 计算得来的,平均值遍及矩阵的所有element。relative reconstruction error然后计算econstruction error的比例和
计算得来的,平均值遍及矩阵的所有element。relative reconstruction error然后计算econstruction error的比例和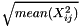 .
.
例子
查看SVD函数的帮助
SELECT madlib.svd();svd----------------------------------------------------------------------------+In linear algebra, the singular value decomposition (SVD) is a+factorization of a real or complex matrix, with many useful +applications in signal processing and statistics. +------- +For an overview on usage, run: +SELECT madlib.svd('usage'); +------- +For an example, run: +SELECT madlib.svd('example') +
创建输入数据集(密集矩阵)
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS mat,mat_sparse,svd_summary_table,svd_u, svd_v,svd_s;CREATE TABLE mat (row_id integer,row_vec double precision[]);INSERT INTO mat VALUES(1,'{396,840,353,446,318,886,15,584,159,383}'),(2,'{691,58,899,163,159,533,604,582,269,390}'),(3,'{293,742,298,75,404,857,941,662,846,2}'),(4,'{462,532,787,265,982,306,600,608,212,885}'),(5,'{304,151,337,387,643,753,603,531,459,652}'),(6,'{327,946,368,943,7,516,272,24,591,204}'),(7,'{877,59,260,302,891,498,710,286,864,675}'),(8,'{458,959,774,376,228,354,300,669,718,565}'),(9,'{824,390,818,844,180,943,424,520,65,913}'),(10,'{882,761,398,688,761,405,125,484,222,873}'),(11,'{528,1,860,18,814,242,314,965,935,809}'),(12,'{492,220,576,289,321,261,173,1,44,241}'),(13,'{415,701,221,503,67,393,479,218,219,916}'),(14,'{350,192,211,633,53,783,30,444,176,932}'),(15,'{909,472,871,695,930,455,398,893,693,838}'),(16,'{739,651,678,577,273,935,661,47,373,618}');select * from mat;row_id | row_vec--------+-------------------------------------------1 | {396,840,353,446,318,886,15,584,159,383}2 | {691,58,899,163,159,533,604,582,269,390}3 | {293,742,298,75,404,857,941,662,846,2}4 | {462,532,787,265,982,306,600,608,212,885}5 | {304,151,337,387,643,753,603,531,459,652}6 | {327,946,368,943,7,516,272,24,591,204}7 | {877,59,260,302,891,498,710,286,864,675}8 | {458,959,774,376,228,354,300,669,718,565}9 | {824,390,818,844,180,943,424,520,65,913}10 | {882,761,398,688,761,405,125,484,222,873}11 | {528,1,860,18,814,242,314,965,935,809}12 | {492,220,576,289,321,261,173,1,44,241}13 | {415,701,221,503,67,393,479,218,219,916}14 | {350,192,211,633,53,783,30,444,176,932}15 | {909,472,871,695,930,455,398,893,693,838}16 | {739,651,678,577,273,935,661,47,373,618}
在该密集矩阵上执行SVD函数
SELECT madlib.svd( 'mat', -- Input table'svd', -- Output table prefix'row_id', -- Column name with row index10, -- Number of singular values to computeNULL, -- Use default number of iterations'svd_summary_table' -- Result summary table);
查看奇异值和汇总结果表
查看奇异值SELECT * FROM svd_s ORDER BY row_id;row_id | col_id | value--------+--------+------------------1 | 1 | 6475.672252818032 | 2 | 1875.180655804153 | 3 | 1483.252284296364 | 4 | 1159.722628974275 | 5 | 1033.860925705746 | 6 | 948.4373587039657 | 7 | 795.3795727724558 | 8 | 709.0862406844699 | 9 | 462.4737759593710 | 10 | 365.87521794569710 | 10 |
查看汇总表
SELECT * FROM svd_summary_table;rows_used | exec_time (ms) | iter | recon_error | relative_recon_error-----------+----------------+------+-------------------+----------------------16 | 64.09 | 10 | 3.67643457344e-13 | 6.42133970898e-16
基于密集矩阵使用 matrix_sparsify()功能函数创建稀疏矩阵
SELECT madlib.matrix_sparsify('mat','row=row_id, val=row_vec','mat_sparse','row=row_id, col=col_id, val=value');
在稀疏矩阵上执行SVD函数
SELECT madlib.svd_sparse( 'mat_sparse', -- Input table'svd', -- Output table prefix'row_id', -- Column name with row index'col_id', -- Column name with column index'value', -- Matrix cell value16, -- Number of rows in matrix10, -- Number of columns in matrix10 -- Number of singular values to compute);
在非常稀疏的矩阵上执行SVD函数
SELECT madlib.svd_sparse_native ( 'mat_sparse', -- Input table'svd', -- Output table prefix'row_id', -- Column name with row index'col_id', -- Column name with column index'value', -- Matrix cell value16, -- Number of rows in matrix10, -- Number of columns in matrix10 -- Number of singular values to compute);
技术背景
SVD介绍,看前面的,可以把计算A的奇异三元组
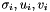 表述为和A有关的一个Hermitian矩阵的特征值问题( It is possible to formulate the problem of computing the singular triplets
表述为和A有关的一个Hermitian矩阵的特征值问题( It is possible to formulate the problem of computing the singular triplets 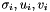 of A as an eigenvalue problem involving a Hermitian matrix related to A).有两种实现方法:
of A as an eigenvalue problem involving a Hermitian matrix related to A).有两种实现方法: - 交叉乘积矩阵(cross product matrix),
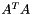 和
和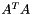
- 循环矩阵(cyclic matrix)
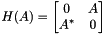 .
.
奇异值是交叉乘积矩阵的特征值的非负平方根(The singular values are the nonnegative square roots of the eigenvalues of the cross product matrix).在一个很小的奇异值上这种方法可能会导致严重的精度丢失(This approach may imply a severe loss of accuracy in the smallest singular values)。循环矩阵方法是一种替代来避免这个问题,但是会显著的增加高昂的计算代价。不推荐直接计算交叉乘积矩阵,特别是在稀疏矩阵A上。Golun和Kahan建议使用Bidiagonalization作为一种将构成不明确的交叉乘积矩阵的tridiagonalizing。(Bidiagonalization was proposed by Golub and Kahan [citation?] as a way of tridiagonalizing the cross product matrix without forming it explicitly. Consider the following decomposition)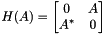 P和Q都是酉矩阵(unitary matrix)。B是 m x n 上升两对角矩阵(upper bidiagonal matrix),三对角矩阵(tridiagonal matrix) B B 类似于 A A酉矩阵,(Then the tridiagonal matrix B B is unitarily similar to A A )
P和Q都是酉矩阵(unitary matrix)。B是 m x n 上升两对角矩阵(upper bidiagonal matrix),三对角矩阵(tridiagonal matrix) B B 类似于 A A酉矩阵,(Then the tridiagonal matrix B B is unitarily similar to A A )
另外,存在特定的方法不产生 B B 来计算B的奇异值(Additionally, specific methods exist that compute the singular values of B without forming B B )。因此,在计算完B的SVD以后,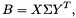 ,仅剩下在原来矩阵上使用U=PX和V=QY计算SVD.
,仅剩下在原来矩阵上使用U=PX和V=QY计算SVD.

