线程安全一
线程安全概念:当多个线程访问某一个类(对象或方法)时,这个类始终都能表现出正确的行为,那么这个类(对象或方法)就是线程安全的。
synchronized:可 以在任何对象及方法上加锁,而加锁的这段代码称为“互斥区”或“临界区”。
示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync001;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;/*** 线程安全概念:当多个线程访问某一个类(对象或方法)时,这个对象始终都能表现出正确的行为,那么这个类(对象或方法)就是线程安全的。* synchronized:可以在任意对象及方法上加锁,而加锁的这段代码称为"互斥区"或"临界区"* @author alienware**/public class MyThread extends Thread{private int count = 5 ;//synchronized加锁public void run(){count--;System.out.println(this.currentThread().getName() + " count = "+ count);}public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 分析:当多个线程访问myThread的run方法时,以排队的方式进行处理(这里排对是按照CPU分配的先后顺序而定的),* 一个线程想要执行synchronized修饰的方法里的代码:* 1 尝试获得锁* 2 如果拿到锁,执行synchronized代码体内容;拿不到锁,这个线程就会不断的尝试获得这把锁,直到拿到为止,* 而且是多个线程同时去竞争这把锁。(也就是会有锁竞争的问题)*/MyThread myThread = new MyThread();Thread t1 = new Thread(myThread,"t1");Thread t2 = new Thread(myThread,"t2");Thread t3 = new Thread(myThread,"t3");Thread t4 = new Thread(myThread,"t4");Thread t5 = new Thread(myThread,"t5");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();t4.start();t5.start();}}
线程安全二
多个线程多个锁
示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync002;
/**
* 关键字synchronized取得的锁都是对象锁,而不是把一段代码(方法)当做锁,
* 所以代码中哪个线程先执行synchronized关键字的方法,哪个线程就持有该方法所属对象的锁(Lock),
*
* 在静态方法上加synchronized关键字,表示锁定.class类,类一级别的锁(独占.class类)。
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class MultiThread {
private int num = 0;
/** static */
public synchronized void printNum(String tag){
try {
if(tag.equals("a")){
num = 100;
System.out.println("tag a, set num over!");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} else {
num = 200;
System.out.println("tag b, set num over!");
}
System.out.println("tag " + tag + ", num = " + num);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//注意观察run方法输出顺序
public static void main(String[] args) {
//俩个不同的对象
final MultiThread m1 = new MultiThread();
final MultiThread m2 = new MultiThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
m1.printNum("a");
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
m2.printNum("b");
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
对象锁的同步和异步

示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync003;
/**
* 对象锁的同步和异步问题
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class MyObject {
public synchronized void method1(){
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/** synchronized */
public void method2(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final MyObject mo = new MyObject();
/**
* 分析:
* t1线程先持有object对象的Lock锁,t2线程可以以异步的方式调用对象中的非synchronized修饰的方法
* t1线程先持有object对象的Lock锁,t2线程如果在这个时候调用对象中的同步(synchronized)方法则需等待,也就是同步
*/
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mo.method1();
}
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mo.method2();
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
脏读
示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync004;
/**
* 业务整体需要使用完整的synchronized,保持业务的原子性。
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class DirtyRead {
private String username = "bjsxt";
private String password = "123";
public synchronized void setValue(String username, String password){
this.username = username;
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.password = password;
System.out.println("setValue最终结果:username = " + username + " , password = " + password);
}
public void getValue(){
System.out.println("getValue方法得到:username = " + this.username + " , password = " + this.password);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
final DirtyRead dr = new DirtyRead();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
dr.setValue("z3", "456");
}
});
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
dr.getValue();
}
}
Synchronized

锁重入示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync005;
/**
* synchronized的重入
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class SyncDubbo1 {
public synchronized void method1(){
System.out.println("method1..");
method2();
}
public synchronized void method2(){
System.out.println("method2..");
method3();
}
public synchronized void method3(){
System.out.println("method3..");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SyncDubbo1 sd = new SyncDubbo1();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
sd.method1();
}
});
t1.start();
}
}
父子类锁重入示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync005;
/**
* synchronized的重入
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class SyncDubbo2 {
static class Main {
public int i = 10;
public synchronized void operationSup(){
try {
i--;
System.out.println("Main print i = " + i);
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class Sub extends Main {
public synchronized void operationSub(){
try {
while(i > 0) {
i--;
System.out.println("Sub print i = " + i);
Thread.sleep(100);
this.operationSup();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Sub sub = new Sub();
sub.operationSub();
}
});
t1.start();
}
}
锁异常的处理示例
package com.bjsxt.base.sync005;
/**
* synchronized异常
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class SyncException {
private int i = 0;
public synchronized void operation(){
while(true){
try {
i++;
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " , i = " + i);
if(i == 20){
//Integer.parseInt("a");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SyncException se = new SyncException();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
se.operation();
}
},"t1");
t1.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync005;
/**
* synchronized异常
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class SyncException {
private int i = 0;
public synchronized void operation(){
while(true){
try {
i++;
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " , i = " + i);
if(i == 20){
//Integer.parseInt("a");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SyncException se = new SyncException();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
se.operation();
}
},"t1");
t1.start();
}
}
其他示例

package com.bjsxt.base.sync006;
/**
* 锁对象的改变问题
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class ChangeLock {
private String lock = "lock";
private void method(){
synchronized (lock) {
try {
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始");
lock = "change lock";
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ChangeLock changeLock = new ChangeLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
changeLock.method();
}
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
changeLock.method();
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t2.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync006;
/**
* 死锁问题,在设计程序时就应该避免双方相互持有对方的锁的情况
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class DeadLock implements Runnable{
private String tag;
private static Object lock1 = new Object();
private static Object lock2 = new Object();
public void setTag(String tag){
this.tag = tag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if(tag.equals("a")){
synchronized (lock1) {
try {
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入lock1执行");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入lock2执行");
}
}
}
if(tag.equals("b")){
synchronized (lock2) {
try {
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入lock2执行");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入lock1执行");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeadLock d1 = new DeadLock();
d1.setTag("a");
DeadLock d2 = new DeadLock();
d2.setTag("b");
Thread t1 = new Thread(d1, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(d2, "t2");
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t2.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync006;
/**
* 同一对象属性的修改不会影响锁的情况
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class ModifyLock {
private String name ;
private int age ;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public synchronized void changeAttributte(String name, int age) {
try {
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 开始");
this.setName(name);
this.setAge(age);
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 修改对象内容为: "
+ this.getName() + ", " + this.getAge());
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 结束");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ModifyLock modifyLock = new ModifyLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
modifyLock.changeAttributte("张三", 20);
}
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
modifyLock.changeAttributte("李四", 21);
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t2.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync006;
/**
* 使用synchronized代码块加锁,比较灵活
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class ObjectLock {
public void method1(){
synchronized (this) { //对象锁
try {
System.out.println("do method1..");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void method2(){ //类锁
synchronized (ObjectLock.class) {
try {
System.out.println("do method2..");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private Object lock = new Object();
public void method3(){ //任何对象锁
synchronized (lock) {
try {
System.out.println("do method3..");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ObjectLock objLock = new ObjectLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
objLock.method1();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
objLock.method2();
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
objLock.method3();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync006;
/**
* 使用synchronized代码块减小锁的粒度,提高性能
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class Optimize {
public void doLongTimeTask(){
try {
System.out.println("当前线程开始:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +
", 正在执行一个较长时间的业务操作,其内容不需要同步");
Thread.sleep(2000);
synchronized(this){
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +
", 执行同步代码块,对其同步变量进行操作");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("当前线程结束:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() +
", 执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Optimize otz = new Optimize();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
otz.doLongTimeTask();
}
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
otz.doLongTimeTask();
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync006;
/**
* synchronized代码块对字符串的锁,注意String常量池的缓存功能
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class StringLock {
public void method() {
//new String("字符串常量")
synchronized ("字符串常量") {
try {
while(true){
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final StringLock stringLock = new StringLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
stringLock.method();
}
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
stringLock.method();
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
Volatile

线程执行流程图
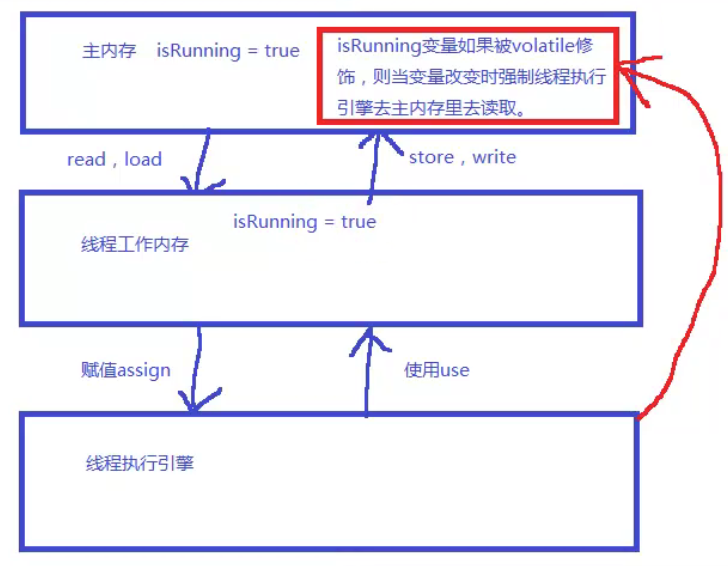
Volatile关键字的非原子性

package com.bjsxt.base.sync007;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AtomicUse {
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
//多个addAndGet在一个方法内是非原子性的,需要加synchronized进行修饰,保证4个addAndGet整体原子性
/**synchronized*/
public synchronized int multiAdd(){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count.addAndGet(1);
count.addAndGet(2);
count.addAndGet(3);
count.addAndGet(4); //+10
return count.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final AtomicUse au = new AtomicUse();
List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
ts.add(new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(au.multiAdd());
}
}));
}
for(Thread t : ts){
t.start();
}
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync007;
public class RunThread extends Thread{
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private void setRunning(boolean isRunning){
this.isRunning = isRunning;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("进入run方法..");
int i = 0;
while(isRunning == true){
//..
}
System.out.println("线程停止");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RunThread rt = new RunThread();
rt.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
rt.setRunning(false);
System.out.println("isRunning的值已经被设置了false");
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.sync007;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* volatile关键字不具备synchronized关键字的原子性(同步)
* @author alienware
*
*/
public class VolatileNoAtomic extends Thread{
//private static volatile int count;
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static void addCount(){
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
//count++ ;
count.incrementAndGet();
}
System.out.println(count);
}
public void run(){
addCount();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
VolatileNoAtomic[] arr = new VolatileNoAtomic[100];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i] = new VolatileNoAtomic();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i].start();
}
}
}

