
package com.bjsxt.base.conn008;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class ListAdd1 { private volatile static List list = new ArrayList(); public void add(){ list.add("bjsxt"); } public int size(){ return list.size(); } public static void main(String[] args) { final ListAdd1 list1 = new ListAdd1(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){ list1.add(); System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "添加了一个元素.."); Thread.sleep(500); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while(true){ if(list1.size() == 5){ System.out.println("当前线程收到通知:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " list size = 5 线程停止.."); throw new RuntimeException(); } } } }, "t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
package com.bjsxt.base.conn008;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Queue;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;/** * wait notfiy 方法,wait释放锁,notfiy不释放锁 * @author alienware * */public class ListAdd2 { private volatile static List list = new ArrayList(); public void add(){ list.add("bjsxt"); } public int size(){ return list.size(); } public static void main(String[] args) { final ListAdd2 list2 = new ListAdd2(); // 1 实例化出来一个 lock // 当使用wait 和 notify 的时候 , 一定要配合着synchronized关键字去使用 //final Object lock = new Object(); final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { //synchronized (lock) { for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){ list2.add(); System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "添加了一个元素.."); Thread.sleep(500); if(list2.size() == 5){ System.out.println("已经发出通知.."); countDownLatch.countDown(); //lock.notify(); } } //} } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //synchronized (lock) { if(list2.size() != 5){ try { //System.out.println("t2进入..."); //lock.wait(); countDownLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "收到通知线程停止.."); throw new RuntimeException(); //} } }, "t2"); t2.start(); t1.start(); } }
使用Wait和Notify模拟Queue

示例
package com.bjsxt.base.conn009;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class MyQueue {
//1 需要一个承装元素的集合
private LinkedList<Object> list = new LinkedList<Object>();
//2 需要一个计数器
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
//3 需要制定上限和下限
private final int minSize = 0;
private final int maxSize ;
//4 构造方法
public MyQueue(int size){
this.maxSize = size;
}
//5 初始化一个对象 用于加锁
private final Object lock = new Object();
//put(anObject): 把anObject加到BlockingQueue里,如果BlockQueue没有空间,则调用此方法的线程被阻断,直到BlockingQueue里面有空间再继续.
public void put(Object obj){
synchronized (lock) {
while(count.get() == this.maxSize){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//1 加入元素
list.add(obj);
//2 计数器累加
count.incrementAndGet();
//3 通知另外一个线程(唤醒)
lock.notify();
System.out.println("新加入的元素为:" + obj);
}
}
//take: 取走BlockingQueue里排在首位的对象,若BlockingQueue为空,阻断进入等待状态直到BlockingQueue有新的数据被加入.
public Object take(){
Object ret = null;
synchronized (lock) {
while(count.get() == this.minSize){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//1 做移除元素操作
ret = list.removeFirst();
//2 计数器递减
count.decrementAndGet();
//3 唤醒另外一个线程
lock.notify();
}
return ret;
}
public int getSize(){
return this.count.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final MyQueue mq = new MyQueue(5);
mq.put("a");
mq.put("b");
mq.put("c");
mq.put("d");
mq.put("e");
System.out.println("当前容器的长度:" + mq.getSize());
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mq.put("f");
mq.put("g");
}
},"t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Object o1 = mq.take();
System.out.println("移除的元素为:" + o1);
Object o2 = mq.take();
System.out.println("移除的元素为:" + o2);
}
},"t2");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t2.start();
}
}
ThreadLocal

示例
package com.bjsxt.base.conn010;
public class ConnThreadLocal {
public static ThreadLocal<String> th = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public void setTh(String value){
th.set(value);
}
public void getTh(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + this.th.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final ConnThreadLocal ct = new ConnThreadLocal();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ct.setTh("张三");
ct.getTh();
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
ct.getTh();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
单例&多线程

DubbleCheckSingleton
package com.bjsxt.base.conn011;
public class DubbleSingleton {
private static DubbleSingleton ds;
public static DubbleSingleton getDs(){
if(ds == null){
try {
//模拟初始化对象的准备时间...
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (DubbleSingleton.class) {
if(ds == null){
ds = new DubbleSingleton();
}
}
}
return ds;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(DubbleSingleton.getDs().hashCode());
}
},"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(DubbleSingleton.getDs().hashCode());
}
},"t2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(DubbleSingleton.getDs().hashCode());
}
},"t3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
InnerSingletion
package bhz.base.conn011;
public class Singletion {
private static class InnerSingletion {
private static Singletion single = new Singletion();
}
public static Singletion getInstance(){
return InnerSingletion.single;
}
}
同步类容器

示例
package com.bjsxt.base.coll012;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 多线程使用Vector或者HashTable的示例(简单线程同步问题)
* @author alienware
*/
public class Tickets {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化火车票池并添加火车票:避免线程同步可采用Vector替代ArrayList HashTable替代HashMap
final Vector<String> tickets = new Vector<String>();
//Map<String, String> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, String>());
for(int i = 1; i<= 1000; i++){
tickets.add("火车票"+i);
}
// for (Iterator iterator = tickets.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
// String string = (String) iterator.next();
// tickets.remove(20);
// }
for(int i = 1; i <=10; i ++){
new Thread("线程"+i){
public void run(){
while(true){
if(tickets.isEmpty()) break;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---" + tickets.remove(0));
}
}
}.start();
}
}
}



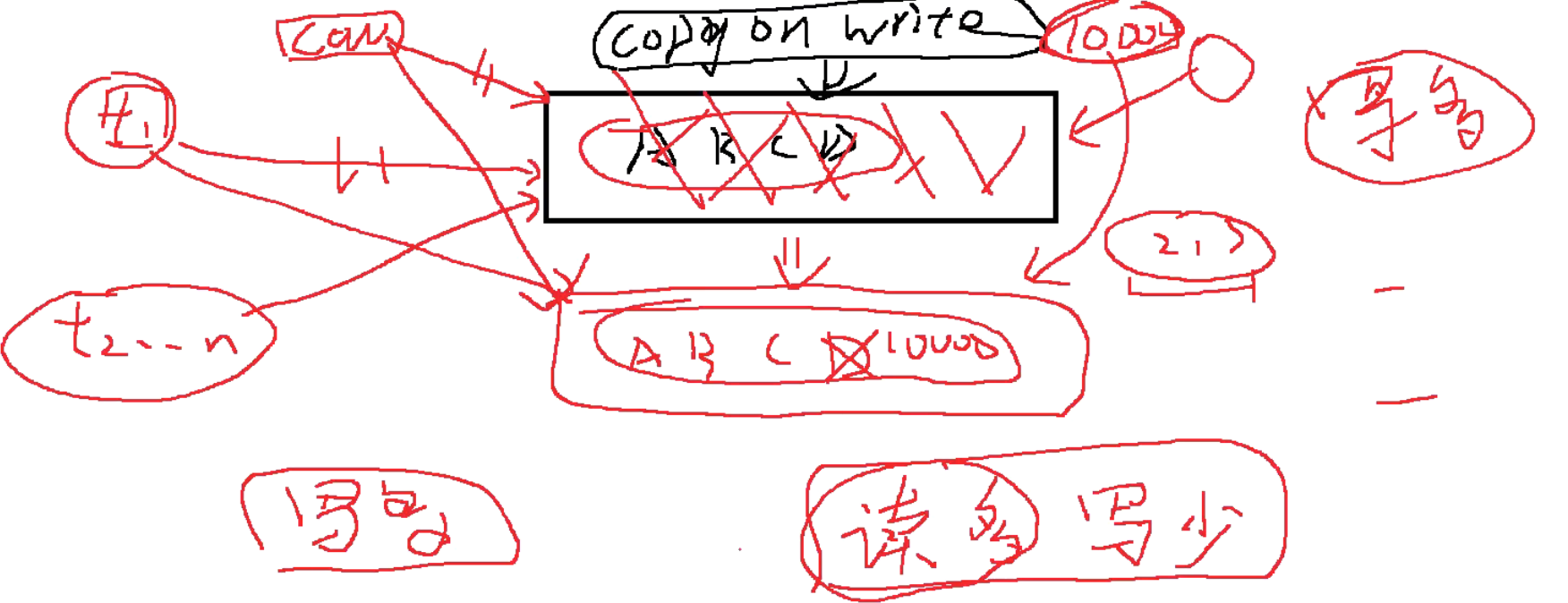
ConcurrentHashMap
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
public class UseConcurrentMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> chm = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
chm.put("k1", "v1");
chm.put("k2", "v2");
chm.put("k3", "v3");
chm.putIfAbsent("k4", "vvvv");
//System.out.println(chm.get("k2"));
//System.out.println(chm.size());
for(Map.Entry<String, Object> me : chm.entrySet()){
System.out.println("key:" + me.getKey() + ",value:" + me.getValue());
}
}
}
CopyOnWrite
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
public class UseCopyOnWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> cwal = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
CopyOnWriteArraySet<String> cwas = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<String>();
}
}
并发Queue

ConcurrentLinkedQueue

示例
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
public class UseQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//高性能无阻塞无界队列:ConcurrentLinkedQueue
/**
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>();
q.offer("a");
q.offer("b");
q.offer("c");
q.offer("d");
q.add("e");
System.out.println(q.poll()); //a 从头部取出元素,并从队列里删除
System.out.println(q.size()); //4
System.out.println(q.peek()); //b
System.out.println(q.size()); //4
*/
/**
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> array = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(5);
array.put("a");
array.put("b");
array.add("c");
array.add("d");
array.add("e");
array.add("f");
//System.out.println(array.offer("a", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
*/
/**
//阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue<String> q = new LinkedBlockingQueue<String>();
q.offer("a");
q.offer("b");
q.offer("c");
q.offer("d");
q.offer("e");
q.add("f");
//System.out.println(q.size());
// for (Iterator iterator = q.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
// String string = (String) iterator.next();
// System.out.println(string);
// }
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
System.out.println(q.drainTo(list, 3));
System.out.println(list.size());
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println(string);
}
*/
final SynchronousQueue<String> q = new SynchronousQueue<String>();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(q.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
q.add("asdasd");
}
});
t2.start();
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TimeUinitTest {
private TimeUnit timeUnit = TimeUnit.DAYS;
public static void main(String[] TimeUinitTest) {
TimeUinitTest tut = new TimeUinitTest();
tut.outInfo();
}
public void outInfo() {
System.out.println(timeUnit.name());
System.out.println(timeUnit.toDays(1));
System.out.println(timeUnit.toHours(1));
System.out.println(timeUnit.toMinutes(1));
System.out.println(timeUnit.toSeconds(1));
System.out.println(timeUnit.toMillis(1));
System.out.println(timeUnit.toMicros(1));
System.out.println(timeUnit.toNanos(1));
System.out.println((timeUnit.convert(1, TimeUnit.DAYS)) + timeUnit.name());
System.out.println((timeUnit.convert(24, TimeUnit.HOURS)) + timeUnit.name());
System.out.println((timeUnit.convert(1440, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) + timeUnit.name());
System.out.println("-------------------");
}
}
BlockingQueue接口
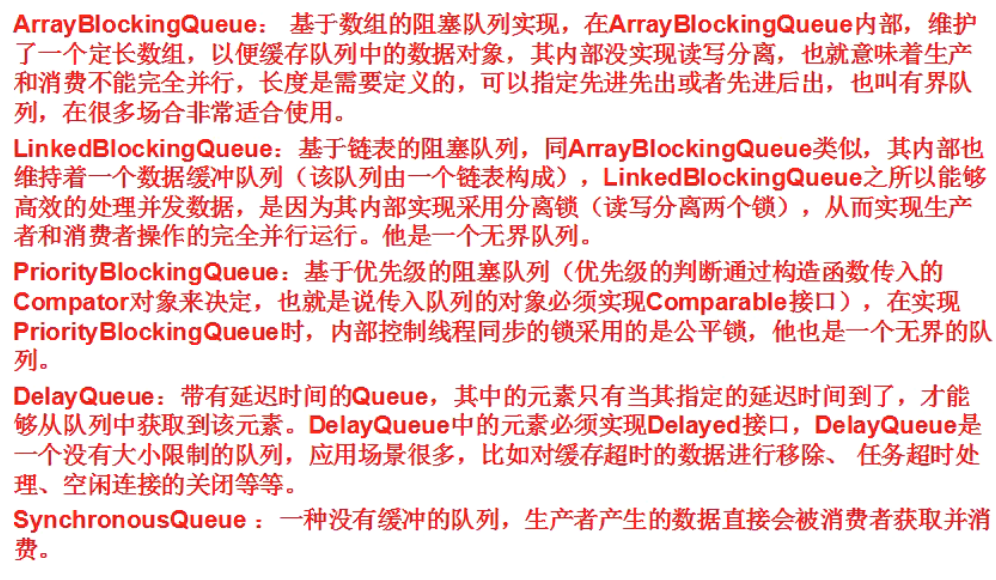
PriorityBlockingQueue示例
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
public class UsePriorityBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
PriorityBlockingQueue<Task> q = new PriorityBlockingQueue<Task>();
Task t1 = new Task();
t1.setId(3);
t1.setName("id为3");
Task t2 = new Task();
t2.setId(4);
t2.setName("id为4");
Task t3 = new Task();
t3.setId(1);
t3.setName("id为1");
//return this.id > task.id ? 1 : 0;
q.add(t1); //3
q.add(t2); //4
q.add(t3); //1
// 1 3 4
System.out.println("容器:" + q);
System.out.println(q.take().getId());
System.out.println("容器:" + q);
// System.out.println(q.take().getId());
// System.out.println(q.take().getId());
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
public class Task implements Comparable<Task>{
private int id ;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Task task) {
return this.id > task.id ? 1 : (this.id < task.id ? -1 : 0);
}
public String toString(){
return this.id + "," + this.name;
}
}
延迟队列示例
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
public class WangBa implements Runnable {
private DelayQueue<Wangmin> queue = new DelayQueue<Wangmin>();
public boolean yinye =true;
public void shangji(String name,String id,int money){
Wangmin man = new Wangmin(name, id, 1000 * money + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("网名"+man.getName()+" 身份证"+man.getId()+"交钱"+money+"块,开始上机...");
this.queue.add(man);
}
public void xiaji(Wangmin man){
System.out.println("网名"+man.getName()+" 身份证"+man.getId()+"时间到下机...");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(yinye){
try {
Wangmin man = queue.take();
xiaji(man);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
System.out.println("网吧开始营业");
WangBa siyu = new WangBa();
Thread shangwang = new Thread(siyu);
shangwang.start();
siyu.shangji("路人甲", "123", 1);
siyu.shangji("路人乙", "234", 10);
siyu.shangji("路人丙", "345", 5);
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Wangmin implements Delayed {
private String name;
//身份证
private String id;
//截止时间
private long endTime;
//定义时间工具类
private TimeUnit timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS;
public Wangmin(String name,String id,long endTime){
this.name=name;
this.id=id;
this.endTime = endTime;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getId(){
return this.id;
}
/**
* 用来判断是否到了截止时间
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
//return unit.convert(endTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - unit.convert(System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return endTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* 相互批较排序用
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed delayed) {
Wangmin w = (Wangmin)delayed;
return this.getDelay(this.timeUnit) - w.getDelay(this.timeUnit) > 0 ? 1:0;
}
}

package com.bjsxt.base.coll013;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class UseDeque {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<String> dq = new LinkedBlockingDeque<String>(10);
dq.addFirst("a");
dq.addFirst("b");
dq.addFirst("c");
dq.addFirst("d");
dq.addFirst("e");
dq.addLast("f");
dq.addLast("g");
dq.addLast("h");
dq.addLast("i");
dq.addLast("j");
//dq.offerFirst("k");
System.out.println("查看头元素:" + dq.peekFirst());
System.out.println("获取尾元素:" + dq.pollLast());
Object [] objs = dq.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < objs.length; i++) {
System.out.println(objs[i]);
}
}
}















