原型模式
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象
剖析原理
| 克隆分类 | 实现 |
|---|---|
| 浅克隆 | 只复制基本类型的数据,引用类型的数据只复制了引用的地址,引用的对象并没有复制,在新的对象中修改引用类型的数据会影响原对象中的引用。 |
| 深克隆 | 方式一:嵌套重写clone方法:实现Cloneable接口(引用数据类型也要实现Cloneable接口),重写clone方法,clone的嵌套,复制后的对象与原对象之间完全不会影响。 方式二:序列化对象:实现序列化Serializable接口(不实现Cloneable接口),(引用数据类型也要实现Serializable),对象序列化后写入流中,此时不存在引用数据类型的概念,从流中读取,生成新的对象,新对象和原对象之间也是完全互不影响的。 |
分析实现步骤
浅克隆
- 方式一:实现Cloneable,嵌套重写clone方法
- 方式二:实现序列化接口,以流的形式实现拷贝(推荐)
- 客户端测试
-
代码实现
浅克隆
实现Cloneable接口,重写clone方法 ```java /**
浅克隆 - 克隆羊 */ public class Sheep implements Cloneable{
private String name; private String color; private Sheep brother;
//———————————————————↓
//浅克隆 @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); }
//———————————————————↑
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getColor() { return color; }
public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; }
public Sheep getBrother() { return brother; }
public void setBrother(Sheep brother) { this.brother = brother; }
@Override public String toString() { return “Sheep{“ +
"name='" + name + '\'' +", color='" + color + '\'' +'}';
} }
2. 客户端测试
```java
/**
* 浅拷贝测试
*/
public class ShallowTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sheep sheep1 = new Sheep();
sheep1.setName("多莉");
sheep1.setColor("白色");
Sheep sheepBrother = new Sheep();
sheepBrother.setName("多莉兄弟");
sheepBrother.setColor("花色");
sheep1.setBrother(sheepBrother);
System.out.println("多莉:"+sheep1+",brother:"+sheep1.getBrother().hashCode());
try {
Sheep sheep2 = (Sheep)sheep1.clone();
System.out.println("克隆羊1:"+sheep2+",brother:"+sheep2.getBrother().hashCode());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//测试结果
多莉:Sheep{name='多莉', color='白色'},brother:668849042
克隆羊1:Sheep{name='多莉', color='白色'},brother:668849042
- 分析
只复制基本类型的数据,引用类型的数据(brother)只复制了引用的地址,而不是新建一个对象
深克隆
方式一:嵌套重写clone方法
嵌套重写clone方法 ```java /**
深克隆 - 方式一:嵌套重写clone方法 */ public class DeepSheep implements Cloneable{ private String name; private String color; private Sheep brother;
//———————————————————↓ /**
- 方式一:重写clone方法,实现深拷贝
- 1.先浅拷贝一次
- 2.对象clone并强转一次 *
- 注:该方式的缺陷是需要单独处理所有要克隆的类中的引用数据类型(Sheep)
*/
@Override
protected Object clone(){
DeepSheep deepSheep = null;
try {
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {//先浅拷贝一次 deepSheep = (DeepSheep) super.clone(); deepSheep.brother = (Sheep)this.brother.clone();
} return deepSheep; }e.printStackTrace();
//———————————————————↑
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Sheep getBrother() {
return brother;
}
public void setBrother(Sheep brother) {
this.brother = brother;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DeepSheep{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2. 客户端测试
```java
public class DeepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeepSheep sheep1 = new DeepSheep();
sheep1.setName("多莉");
sheep1.setColor("白色");
Sheep sheepBrother = new Sheep();
sheepBrother.setName("多莉兄弟");
sheepBrother.setColor("花色");
sheep1.setBrother(sheepBrother);
System.out.println("多莉:"+sheep1+",brother:"+sheep1.getBrother().hashCode());
DeepSheep sheep2 = (DeepSheep)sheep1.clone();
System.out.println("克隆羊1:"+sheep2+",brother:"+sheep2.getBrother().hashCode());
}
}
//测试结果
多莉:DeepSheep{name='多莉', color='白色'},brother:434176574
克隆羊1:DeepSheep{name='多莉', color='白色'},brother:2096057945
- 分析
可看出引用类型是不同的,即重新复制了一份引用对象。方式一的缺陷是需要单独处理所有要克隆的类中的引用数据类型,即每个引用类型都需要重写一个clone()方法,比较麻烦。
方式二:序列化对象(推荐)
实现序列化接口,以流的形式实现拷贝(推荐) ```java /**
深克隆 - 方式二:序列化对象 */ public class DeepSheep2 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name; private String color; //注意该对象需要Serializable,否则在转流的时候不成功 private Sheep2 brother;
//———————————————————↓ public DeepSheep2 deepClone() { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null; ObjectOutputStream oos = null; ByteArrayInputStream bis = null; ObjectInputStream ois = null; try {
//创建序列化流 bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); //将当前对象以对象流的方式输出 oos.writeObject(this); //创建反序列化流 bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()); ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); //将流对象反序列化,从而实现类的深拷贝 return (DeepSheep2) ois.readObject();} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); return null;} finally {
try { //资源释放 bos.close(); bis.close(); oos.close(); ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }} } //———————————————————↑
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Sheep2 getBrother() {
return brother;
}
public void setBrother(Sheep2 brother) {
this.brother = brother;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DeepSheep2{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
```java
/**
* 深克隆 - 克隆羊
* 注意:此处的对象是要 implements Serializable
*/
public class Sheep2 implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String color;
private Sheep2 brother;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Sheep2 getBrother() {
return brother;
}
public void setBrother(Sheep2 brother) {
this.brother = brother;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sheep{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
客户端测试 ```java /**
深拷贝测试 */ public class DeepTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) { DeepSheep2 sheep1 = new DeepSheep2(); sheep1.setName(“多莉”); sheep1.setColor(“白色”);
Sheep2 sheepBrother = new Sheep2(); sheepBrother.setName(“多莉兄弟”); sheepBrother.setColor(“花色”); sheep1.setBrother(sheepBrother); System.out.println(“多莉:”+sheep1+”,brother:”+sheep1.getBrother().hashCode());
DeepSheep2 sheep2 = sheep1.deepClone(); System.out.println(“克隆羊1:”+sheep2+”,brother:”+sheep2.getBrother().hashCode()); } }
//测试结果 多莉:DeepSheep2{name=’多莉’, color=’白色’},brother:434176574 克隆羊1:DeepSheep2{name=’多莉’, color=’白色’},brother:1874154700 ```
- 分析
一次性序列化以流的方式,一劳永逸,唯一要注意点是,引用对象是要implements Serializable否则会转流失败
框架或项目源码分析
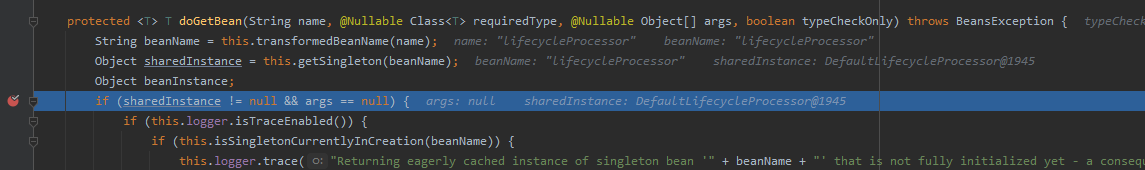
Spring以xml方式创建bean时,选择scope="prototype"时,采用的是原型模式进行创建bean
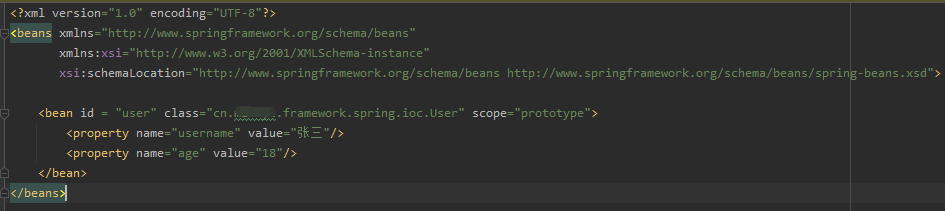
- 自定义的xml配置文件
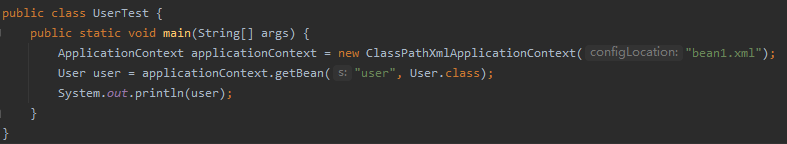
- 编写测试类
- 跟踪源码
应用场景
- 如果类的初始化需要耗费较多的资源,那么可以通过原型拷贝避免这些消耗。
- 通过new产生一个对象需要非常繁琐的数据准备或访问权限,则可以使用原型模式。
- 一个对象需要提供给其他对象访问,而且各个调用者可能都需要修改其值时,可以拷贝多个对象供调用者使用,即保护性拷贝。