第一章:周介绍
- 掌握脚手架发布模块的整体架构设计和实现原理
- 掌握前端发布流程,并了解history和hash两种路由模式的区别
- 深入理解vue-router原理
关键词
- 前端发布
- 前端路由
- vue-router
第二章:脚手架发布流程架构设计
2-1 脚手架发布功能和流程讲解
- 不依靠后端或服务端人员,使用脚手架快速对更改的内容进行项目发布。
- imooc-cli —packagePath /Users/liumingzhou/Desktop/imooc-cli/packages/publish
- git配置检查:保证远程仓库存在
- git自动提交(输入commit信息):避免本地代码提交的繁杂操作
- 云构建+云发布:检查build结果、按照依赖、云构建、云发布、云断开
2-2 绘制项目发布架构设计图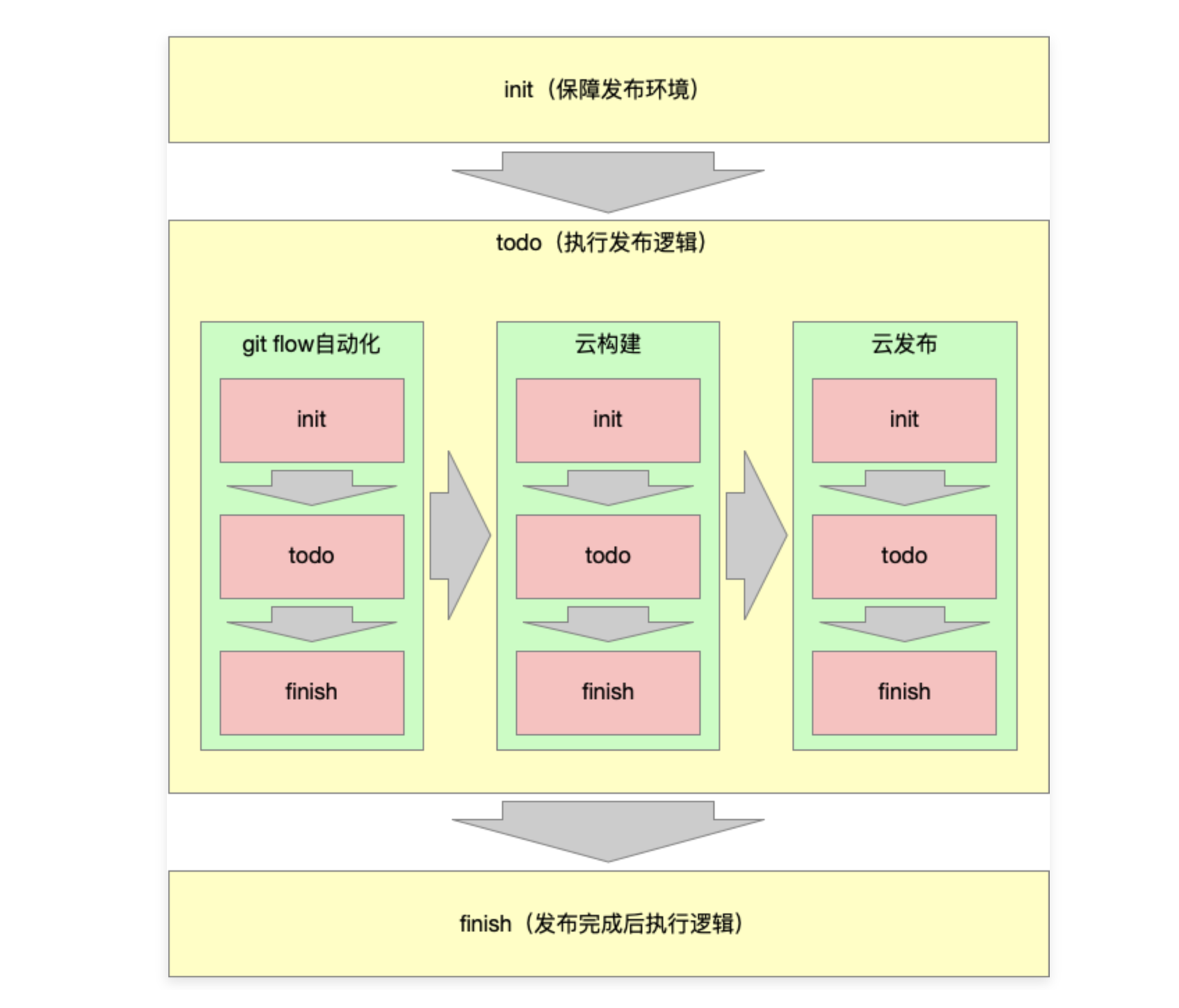
第三章:imooc-cli脚手架git flow 自动化架构设计
3-1 git flow 基础流程讲解
- git flow是2010年 Vincent Driessen设计出来的。
3-2 git flow 多人协作流程讲解(详细讲解大厂git flow流程)
3-3 脚手架git flow prepare阶段架构设计
ProcessOn画图
3-4 脚手架git flow 执行阶段架构设计 -Init
ProcessOn画图
第四章 imooc-cli 脚手架云构建 + 云发布架构设计
4-1 云构建+云发布整体流程设计
4-2 云构建+云发布详细流程设计1
4-3 云构建+云发布详细流程设计2
4-4 深入讲解云发布原理
第五章:imooc-cli脚手架publish模块开发
5-1 创建publish模块
本模块在调试的时候出现问题:
- lerna create @cloudscope-cli/publish commands
- publish模块下lib的index中,打印日志:console.log(‘publish’)
- 接着使用webstorm调试exec的时候,debug没有进去。
- 参数为:
- Node parameters:/Users/liumingzhou/Documents/imoocCourse/Web前端架构师/cloudscope-cli/core/cli/bin/index.js publish —targetPath /Users/liumingzhou/Documents/imoocCourse/Web前端架构师/cloudscope-cli/commands/publish
- Working directory: ~/Desktop/test
查找原因为:
- 首先将本地连接全部去除 : 进入到node的modules目录下将相关的脚手架liugezhou的cloudscope的全部删除
- 进入到cloudscope-cli/core/cli 下npm install
- 发现在utils下等有一些package2的包,于是去到相关包下,删除重新安装
- npm install正确后,npm link,link完毕之后在本地which cloudscole-cli 看到有了包
- 然后在webstorm中调试的 Node parameters中重新配置(在publish之前加空格)
最后在一个空目录中输入以下命令进行调试: cloudscope-cli publish —targetPath /Users/liumingzhou/Documents/imoocCourse/Web前端架构师/cloudscope-cli/commands/publish 打印出:publish
5-2 publish基本流程开发
接下来的重点就是编写业务代码:cloudscope-cli/commands/publish/lib/index.js
- 参考init中的代码,extends Command
- 必须实现init和exec方法,否则报错
- 该文件中用到的log / Command等需要npm install引入
'use strict';const Command = require('@cloudscope-cli/command')const log = require('@cloudscope-cli/log')class PublishCommand extends Command {init(){// 处理参数console.log('init',this._argv)}async exec(){try {const startTime = new Date().getTime()//1. 初始化检查this.prepare()//2.Git Flow自动化//3.云构建 + 云发布const endTime = new Date().getTime()log.info('本次发布耗时',Math.floor(endTime-startTime)/1000+'秒')} catch (e) {log.error(e.message)if(process.env.LOG_LEVEL === 'verbose'){log.error(e.message)}}}prepare(){}}function init(argv){return new PublishCommand(argv)}module.exports = initmodule.exports.PublishCommand = PublishCommand;
5-3 项目发布前预检查流程开发
结合上一节代码,本节主要内容为:
- 初始化检查prepare
- 确认项目是否npm项目
- 确认项目的package.json中是否包含name/version/scripts/scripts.build
prepare(){// 1.确认项目是否为npm项目const projectPath = process.cwd()const pkgPath = path.resolve(projectPath,'package.json')log.verbose('package.json',pkgPath)if(!fs.existsSync(pkgPath)){throw new Error('package.json不存在')}//2. 确认是否包含name\version\build命令const pkg = fse.readJsonSync(pkgPath)const {name,version,scripts} = pkgif(!name || !version || !scripts || !scripts.build ){throw new Error('package.json信息不全,请检查是否存在name、version和scripts(需提供build命令)')}this.projectInfo = {name,version,dir:projectPath}}
第6章 本周加餐:前端路由模式原理和 vue-router 源码讲解
本章内容测试代码上传至:https://github.com/liugezhou/vue-router-demo
6-1 vue-router-next完整运行流程解析
vue-router-next源码解析
vue-router常见问题:
- history和hash模式的区别是什么(涉及vue-router路由模式和前端发布原理)
- Vue dev模式下为什么不需要配置history fallback(涉及webpack-dev-server配置)
- 我们没有定义router-link和router-view,为什么代码里能直接使用(涉及vue-router初始化流程和Vue插件)
- 浏览器如何实现URL变化但页面不刷新(涉及vue-router history模式核心实现原理)
- vue-router如何实现路由匹配(涉及 vue-router Matcher 实现原理)
- router-view如何实现组件动态渲染?(涉及Vue动态组件)
通过imooc-cli脚手架安装一个vue3标准模版
- npm install -g @imooc-cli/core
- imooc-cli init test
- npm install -S vue-router(package.json中安装的版本为3.5.2,我们需要手动改成4.0.0-0,然后安装)
- 新建三个组件 src/pages/Home.vue | src/pages/Order.vue | src/pages/My.vue
- 新建src/router.js
- 并在main.js中引入,app.use(router)
- 在App.vue中使用
和
// src/router.jsconst {createWebHistory,createRouter} from 'vue-router',import Home from './pages/Home'import My from './pages/My'import Order from './pages/Order'const routes = [path:'/',name:'root',redirect:'/home'},{path:'/home',name:'home',component:Home},{path:'/my',name:'my',component:My},{path:'/order',name:'order',component:Order}]const routerHitory = createWebHistory()const router = createRouter({history:routerHitory,routes})export default router;// App.vue<template><div id="vue3">vue3 template</div><router-link to='/home'>Home | </router-link><router-link to='/order'>Order | </router-link><router-link to='/my'>My | </router-link><router-view /></template><script>export default {name: 'Vue3',}</script><style>#vue3 {width: 100%;height: 100%;}</style>
6-2 vue-router路由模式+history路由部署详细教学
Vue-router路由模式
- hash:createWebHashHistory()
- history:createWebHistory()
hash和history模式的区别
- 语法结构不同 :hash添加#意味着一个辅助说明,#后面参数发送改变后并不会加载资源,history模式只要路径改变就会重新请求资源,但是如果页面刷新的话 hash和history都是会重新加载资源的。
- 部署方式不同(history部署)
- npm run build
- nginx 静态网站服务器配置文件如下
- localhost:8081访问后,换不同的路由,页面刷新会显示404
- 此时根据Vue文档,Fallback,在nginx配置文件需要加入如下一行代码
- try_files: $uri $uri/ /index.html;
server {listen 8081;server_name resource;root /Users/liumingzhou/XXXXX/dist;autoindex on;location / {//跨域设置add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;try_files: $uri $uri/ /index.html;}// 缓存设置add_header Cache-Control "no-cache, must-revalidate";}
- SEO:hash不友好,实际开发应用为history模式。
- history模式跳转,利用的是浏览器对象中的history.pushState/replaceState/back/go/forward
- hash模式跳转,利用的是浏览器对象中的location.href
6-3 vue-cli源码调试+dev模式history fallback原理讲解
为什么Vue的dev模式下不需要配置history fallback?
说明:我们在dev模式下启动项目:npm run serve,在scripts中serve,实际执行的命令是 vue-cli-service serve,这个时候我们调试源码就在node_modules/.bin/vue-cli-service。如果执行全局 vue create,调试该命令的话我们就需要去本地全局安装的vue源码中去调试。
这个node_modules/.bin/vue-cli-service其实是link文件,我们通过 ll node_modules/.bin/vue-cli-service 就可以看出来。=》../@vue/cli-service/bin/vue-cli-service.js
- 在webstorm中新建Node.js调试,Node parameters为:./node_modules/@vue/cli-service/bin/vue-cli-service.js serve
- 然后在上面的文件中打断点,开始进入debug调试模式。
- 跟着视频课程的调试,核心代码就是webpack的genHistoryApiFallbackRewrites 与try_files一样的作用
6-4 vue-router初始化过程源码分析
我们并没有定义router-link和router-view,为什么代码里能直接使用?
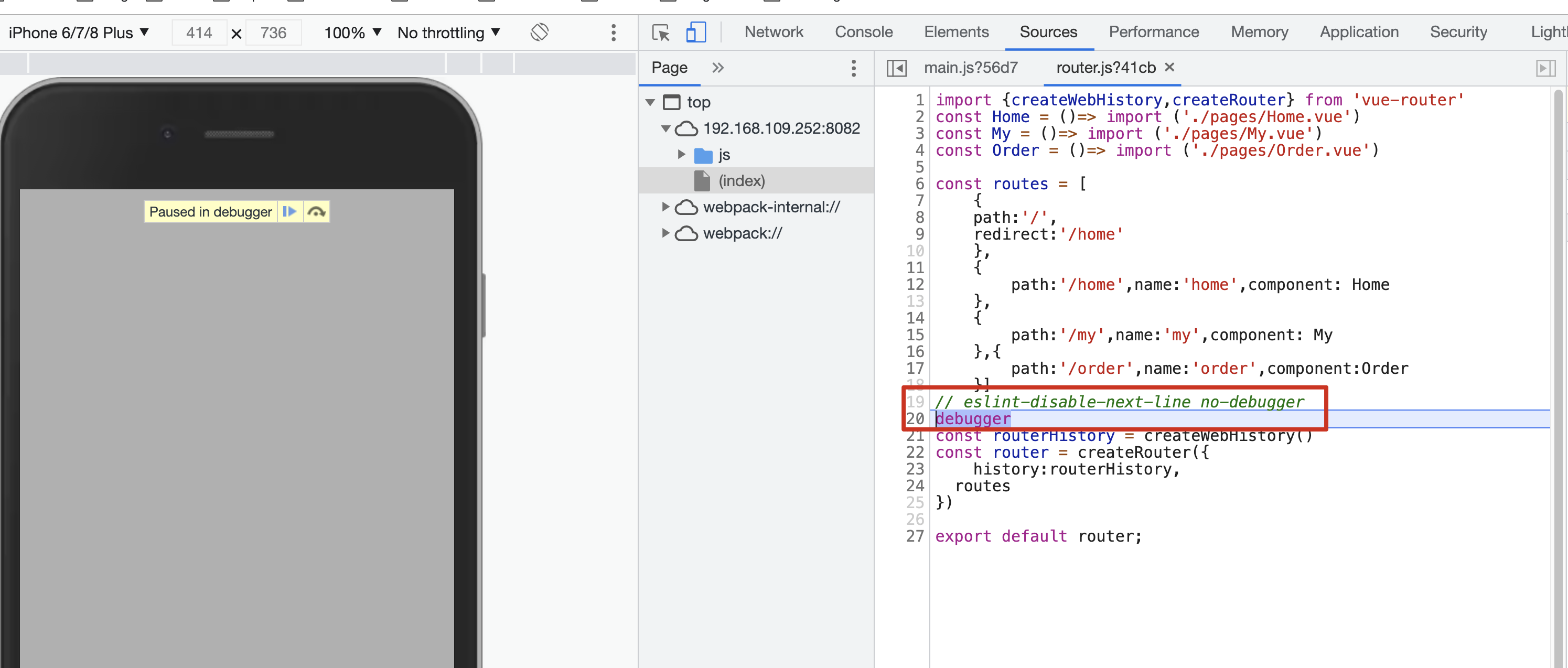
- 在vscode的router.js中添加debugger调试,没起作用,因此,该源码的调试是在webstorm中debug的。
- 项目启动之后,打开浏览器,点击刷新,会进入到调试处
- 首先进入到createWebHistory方法中去(上图第21行代码),返回的routerHistory提供了一系列的工具方法(路由跳转、监听的事件方法等),具体实现源码以及注释如下:
function createWebHistory(base) {// 传入的base进行处理base = normalizeBase(base);//historyNavigation提供了一些方法:location/push/replace/state// 该方法的实现浏览器URL变化但页面不刷新(push),核心是使用了浏览器对象模型history.pushState()和history.replaceState()方法。const historyNavigation = useHistoryStateNavigation(base);//生成一个listener:destory和listen方法const historyListeners = useHistoryListeners(base, historyNavigation.state, historyNavigation.location, historyNavigation.replace);function go(delta, triggerListeners = true) {if (!triggerListeners)historyListeners.pauseListeners();history.go(delta);}//将上面的事件拼装到一起,生成一个routerHistory对象返回const routerHistory = assign({// it's overridden right afterlocation: '',base,go,createHref: createHref.bind(null, base),}, historyNavigation, historyListeners);Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {enumerable: true,get: () => historyNavigation.location.value,});Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'state', {enumerable: true,get: () => historyNavigation.state.value,});return routerHistory;}
返回routerHistory对象后,接着进入到createRouter方法中,源码以及注释如下:
// 从调用createRouter处,options中传入的参数为:history和routesfunction createRouter(options) {// 第一步生成matcher,matcher的作用是实现路由匹配// createRouterMatcher会为每一个简单或复杂的路由生成一个正则表达式const matcher = createRouterMatcher(options.routes, options);let parseQuery$1 = options.parseQuery || parseQuery;let stringifyQuery$1 = options.stringifyQuery || stringifyQuery;// 拿到history对象,是createWebHistory或者为createWebHashHistorylet routerHistory = options.history;if ((process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') && !routerHistory)throw new Error('Provide the "history" option when calling "createRouter()":' +' https://next.router.vuejs.org/api/#history.');//一些路由守卫的初始化、useCallbacks方法返回一个闭包。//每一个路由守卫都对应了一个闭包(代码就不贴了,主要返回了三个方法:add,list,reset,主要作用是缓存路由守卫)。const beforeGuards = useCallbacks();const beforeResolveGuards = useCallbacks();const afterGuards = useCallbacks();// 生成默认routerconst currentRoute = shallowRef(START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED);………………// 一些初始化操作………………// 这里的router即为最终的router对象,包含一系列的属性和方法const router = {currentRoute,addRoute,removeRoute,hasRoute,getRoutes,resolve,options,push,replace,go,back: () => go(-1),forward: () => go(1),beforeEach: beforeGuards.add,beforeResolve: beforeResolveGuards.add,afterEach: afterGuards.add,onError: errorHandlers.add,isReady,//此处的install方法是在执行app.user(router)的时候会执行到这里(即当这个router被返回到main.js后,下一步就会执行app.user(router),然后就会进入到这方法中去)install(app) {const router = this;//在此处注册了组件RouterLink和RouterViewapp.component('RouterLink', RouterLink);app.component('RouterView', RouterView);//全局主注册了$router $routeapp.config.globalProperties.$router = router;Object.defineProperty(app.config.globalProperties, '$route', {enumerable: true,get: () => unref(currentRoute),});if (isBrowser &&!started &¤tRoute.value === START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED) {started = true;//浏览器中push后,就会进行页面的渲染push(routerHistory.location).catch(err => {if ((process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'))warn('Unexpected error when starting the router:', err);});}const reactiveRoute = {};for (let key in START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED) {reactiveRoute[key] = computed(() => currentRoute.value[key]);}// 使用app.provide来做组件的传递// router-view和router-link中的参数是通过这里传递下去的// 关于provide的用法,见本节内容往下app.provide(routerKey, router);app.provide(routeLocationKey, reactive(reactiveRoute));app.provide(routerViewLocationKey, currentRoute);let unmountApp = app.unmount;installedApps.add(app);app.unmount = function () {installedApps.delete(app);if (installedApps.size < 1) {removeHistoryListener();currentRoute.value = START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED;started = false;ready = false;}unmountApp();};},};return router;
6-5 vue3高级特性:vue插件+provide跨组件通信
浏览器中如何实现URL变化但页面不刷新
- 在控制台直接输入 history.pushState(null,null,’/Order’/),会发现浏览器窗口中地址发生了改变,但页面未刷新。
- onpopState事件主要用来监听路由回退的操作。
- 调试源码的步骤是,写一个click方法,点击debuger进行操作
<button @click="jump">Jump</button>………………<script>import { useRouter } from 'vue-router'export default {name: 'App',setup(){const router = useRouter();return{jump(){// eslint-disable-next-line no-debuggerdebuggerrouter.push('/order')}}}}</script>
然后step into到router.push方法中,由此开始调试,进入pushWithRedirect()方法中(如下图)
然后一步一步的,调试源码到最后,最终会通过history.pushState()方法,来改变地址而不发生页面的更新。
在上图的高亮部分resolve(to)是路由匹配的相关实现,下节继续。
6-7 vue-router路由匹配源码分析
我们输入路由后如何与我们自己定义的 routes中的路由进行匹配,就涉及到vue-router的核心概念 matcher。 两个关键点是:createRouter以及上一节提到的resollve方法。
本节重点讲解这个resolve方法,我们假定从 /home跳转到/order,代码以及注释如下:
function resolve(rawLocation, currentLocation) {// 第一步是拿到currentLocation,即当前路由相关信息 【/home相关的】currentLocation = assign({}, currentLocation || currentRoute.value);// 判断传进来的路由‘/order’参数是不是stringif (typeof rawLocation === 'string') {//进行一个形式的格式化吧let locationNormalized = parseURL(parseQuery$1, rawLocation, currentLocation.path);//最关键的一步是调用matcher下的resolve方法,传入两个参数 ‘/order’和‘/home’,到这里我们需要继续step into到这个方法中去调试。关键代码为: matchers.find(m => m.re.test(path));let matchedRoute = matcher.resolve({ path: locationNormalized.path }, currentLocation);let href = routerHistory.createHref(locationNormalized.fullPath);if ((process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production')) {if (href.startsWith('//'))warn(`Location "${rawLocation}" resolved to "${href}". A resolved location cannot start with multiple slashes.`);else if (!matchedRoute.matched.length) {warn(`No match found for location with path "${rawLocation}"`);}}// locationNormalized is always a new objectreturn assign(locationNormalized, matchedRoute, {params: decodeParams(matchedRoute.params),hash: decode(locationNormalized.hash),redirectedFrom: undefined,href,});}…………………………………………}
6-8 vue3新特性defineComponent讲解1 && 6-9 vue3新特性defineComponent讲解2
router-view如何实现组件动态渲染(涉及Vue动态组件)
- 本节从router对象的install方法开始,找到 app.component(‘RouterView’,RouterView)。
- 2328行定义:const RouterView = RouterViewImpl;
RouterView就是RouterViewImpl方法,该方法源码如下
通过 6-10 章节所示源码,我们看到router-view组件是以纯js实现的方式,使用defineComponent定义组件,组件的渲染使用了h函数。
- 在进一步看源码之前,我们先来写个demo看 如何使用纯js方式编写组件。
- h 函数包含的三个参数为:dom标签、dom中需要绑定的一些属性、dom当中的children。
- 下面为代码演示,注释部分为直接使用Home组件的渲染。
import { defineComponent,h } from 'vue'// import Home from '../pages/Home';const TestComponent2 = defineComponent({name:'TestComponent2',props:{},setup(props, {slots} ){return ()=> {return h('div',{class:'test-component2',onClick(){alert('click')}},slots.default())}// return () =>{// return h(Home,{// onClick(){// alert('You Clicked the Home Component!')// }// })// }}})export default TestComponent2
6-10 深入解析router-view源码
const RouterViewImpl = /*#__PURE__*/ defineComponent({name: 'RouterView',inheritAttrs: false,props: {name: {type: String,default: 'default',},route: Object,},// setup在整个组件初始化的时候只会执行一遍,但下面的render function,也就是40行的return部分会执行多次setup(props, { attrs, slots }) {(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') && warnDeprecatedUsage();// injectedRoute决定router-view的刷新const injectedRoute = inject(routerViewLocationKey);// injectedRoute.valueconst routeToDisplay = computed(() => props.route || injectedRoute.value);const depth = inject(viewDepthKey, 0);const matchedRouteRef = computed(() => routeToDisplay.value.matched[depth]);provide(viewDepthKey, depth + 1);provide(matchedRouteKey, matchedRouteRef);provide(routerViewLocationKey, routeToDisplay);// 空的ref用来装载马上要渲染的view-router实例const viewRef = ref();watch(() => [viewRef.value, matchedRouteRef.value, props.name], ([instance, to, name], [oldInstance, from, oldName]) => {if (to) {to.instances[name] = instance;if (from && from !== to && instance && instance === oldInstance) {if (!to.leaveGuards.size) {to.leaveGuards = from.leaveGuards;}if (!to.updateGuards.size) {to.updateGuards = from.updateGuards;}}}if (instance &&to &&(!from || !isSameRouteRecord(to, from) || !oldInstance)) {(to.enterCallbacks[name] || []).forEach(callback => callback(instance));}// 默认为pre属性,post在页面渲染之后执行 watch 监听}, { flush: 'post' });return () => {const route = routeToDisplay.value;const matchedRoute = matchedRouteRef.value;const ViewComponent = matchedRoute && matchedRoute.components[props.name];const currentName = props.name;if (!ViewComponent) {return normalizeSlot(slots.default, { Component: ViewComponent, route });}const routePropsOption = matchedRoute.props[props.name];const routeProps = routePropsOption? routePropsOption === true? route.params: typeof routePropsOption === 'function'? routePropsOption(route): routePropsOption: null;const onVnodeUnmounted = vnode => {// remove the instance reference to prevent leakif (vnode.component.isUnmounted) {matchedRoute.instances[currentName] = null;}};const component = h(ViewComponent, assign({}, routeProps, attrs, {onVnodeUnmounted,ref: viewRef,}));return (normalizeSlot(slots.default, { Component: component, route }) ||component);};},});