- 0003.无重复字符的最长子串.md
- 0005.最长回文子串.md
- 0007.K个一组反转链表.md
- 0009. 数组中的第K个最大元素.md
- 0015.三数之和.md
- 0031.下一个排列.md
- 0032. 最长有效括号.md
- 0033. 搜索旋转排序数组.md
- 0041.缺失的第一个正整数.md
- 0042. 接雨水.md
- 0046. 全排列.md
- 0053. 最大子序和.md
- 0054. 螺旋矩阵.md
- 0056.合并区间.md
- 0069.x的平方根.md
- 0076.最小覆盖子串.md
- 0093. 复原 IP 地址.md
- 0098.验证是否为二叉搜索树.md
- 0101.对称二叉树.md
- 0104. 二叉树的最大深度.md
- 0105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树.md
- 0106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md
- 0110. 平衡二叉树.md
- 0111. 二叉树的最小深度.md
- 0112.路径总和.md
- 0121. 买卖股票的最佳时机.md
- 0122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II.md
- 0124. 二叉树中的最大路径和.md
- 0129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和.md
- 0141. 环形链表.md
- 0143. 重排链表.md
- 0146.手撕LRU.md
- 0148.链表排序.md
- 0155. 最小栈.md
- 0160. 相交链表.md
- 0162. 寻找峰值.md
- 0199.二叉树的右视图.md
- 0200.岛屿数量.md
- 0206.反转链表.md
- 0208. 实现 Trie (前缀树).md
- 0221. 最大正方形.md
- 0232. 使用栈实现队列.md
- 使用两个栈实现先入先出队列
- 0236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先.md
- 0260. 只出现一次的数字 III.md
- 0300.最长递增序列.md
- 0328. 奇偶链表.md
- 0334.递增的三元子序列.md
- 0415.字符串相加.md
- 0704.二分查找.md
- 0912. 快速排序.md
- 20. 有效的括号.md
- 234. 回文链表.md
- 460. LFU 缓存.md
- 470. 用 Rand7() 实现 Rand10().md
- 8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi).md
- 剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数.md
- 剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数.md
- 剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符.md
- 剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对.md
- 剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值.md
- 剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组.md
- 剑指 Offer II 001. 整数除法.md
- 剑指 Offer II 002. 二进制加法.md
- 剑指 Offer II 003. 前 n 个数字二进制中 1 的个数.md
- 剑指 Offer II 004. 只出现一次的数字 .md
- 剑指 Offer II 005. 单词长度的最大乘积.md
- 剑指 Offer II 006. 排序数组中两个数字之和.md
- 剑指 Offer II 008. 和大于等于 target 的最短子数组.md
- 多线程交替打印.md
- 奇升偶降链表.md
- 字节跳动高频题——排序奇升偶降链表
- 手撕单例模式.md
- 手撕归并排序.md
- 手撕线程池.md
0003.无重复字符的最长子串.md
关键字 : 字符串 重复 最长子串 滑动窗口
给定一个字符串
s,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,”pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {if (s.length() <= 1){return s.length();}// 子串起点int startIndex = 0;// 记录最长子串长度int maxLen = 1;// 窗口右边界不断右移for (int endIndex = 1; endIndex < s.length(); endIndex++) {int tempLen = 1;// 每次右边界右移一位就需要判断窗口中是否存在当前右边界字符// 如果窗口中存在右边界字符, 则窗口左移动到窗口中重复元素的后一个位置for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex ; i++) {if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(endIndex)){startIndex = i+1;break;}}// 更新答案maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, endIndex-startIndex+1);}return maxLen;}
0005.最长回文子串.md
关键字 : 字符串 最长回文串 动归
给你一个字符串
s,找到s中最长的回文子串。
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {// 特殊用例判断int len = s.length();if (len < 2) {return s;}int maxLen = 1;int start = 0;// dp[i][j] 表示 s[i, j] 是否是回文串boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();// 单个的字符肯定是回文串for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {dp[i][i] = true;}// 计算dp[i][j]for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {if (charArray[i] != charArray[j]) {dp[i][j] = false;} else {if (j - i < 3) {dp[i][j] = true;} else {dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];}}// 只要 dp[i][j] == true 成立,就表示子串 s[i..j] 是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {maxLen = j - i + 1;start = i;}}}return s.substring(start, start + maxLen);}
0007.K个一组反转链表.md
关键字 : 链表 反转
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
// 使用一个固定长度的栈public static ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode p = head;// 栈的大小为kArrayDeque<ListNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(k);ListNode pt = new ListNode(-1);ListNode ans = pt;// p指针往后走的过程中, 将节点入栈while (p != null){stack.addFirst(p);p = p.next;// 栈中有K个节点了if (stack.size() == k){// 对栈中节点进行反转// pt指向的是当前反转的最后一个节点while (!stack.isEmpty()){pt.next = stack.removeFirst();pt = pt.next;}}}// 最后栈中还有元素, 处理剩下的不满k个的节点// 此处处理方式是, 保留原链表顺序, 即将stack以队列方式出队while (!stack.isEmpty()){pt.next = stack.removeLast();pt = pt.next;}pt.next = null;return ans.next;}
0009. 数组中的第K个最大元素.md
关键字 : 数组 第k大 快排 堆排序 优先队列
给定整数数组
nums和整数k,请返回数组中第**k**个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第
k个最大的元素,而不是第k个不同的元素。示例:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2输出: 5
方法一
// 使用优先队列(默认底层实现为最小堆)public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {pq.add(nums[i]);}for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {if (!pq.isEmpty() && nums[i] > pq.peek()){pq.remove();pq.add(nums[i]);}}return pq.peek();}
方法二
// 利用快排过程private int k;private int ans;public int findKthLargest1(int[] nums, int k) {this.k = k;sort(nums, 0, nums.length-1);return ans;}public void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right){if (left >= right) return;int p = partition(arr, left, right);// 第k大的对应第arr.length - k小的(从0开始算)if (p == arr.length - k){ans = arr[p];return;}// 左边排序sort(arr, left, p-1);// 右边排序sort(arr, p+1, right);}private int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) {// 优化点 : 随机选取枢轴元素. 将选中的枢轴元素交换到最左边int p = left + (new Random()).nextInt(right-left+1);swap(arr, left, p);// 双指针移动int i = left+1, j = right;while (true){// 从左往右找到第一个比枢纽元素大的, 注意循环条件while (i <= j && arr[i] < arr[left])i++;// 从右往左找到第一个比枢纽元素小的,注意循环条件while (i <= j && arr[j] > arr[left])j--;// 循环终止条件if (i >= j) break;// 交换两个位置的元素swap(arr, i, j);// i往后走一步, j往前走一步, 继续循环i++;j--;}// 最后交换枢纽元素和j停留的位置swap(arr, left, j);return j;}private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j){int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}
0015.三数之和.md
关键字 : 数组 三数之和 排序 双指针
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复答案。
思路 : 排序+双指针
时间复杂度 O(n^2)
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();// 先排序Arrays.sort(nums);for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {// 如果首元素大于0, 则后面不可能找出两个数的和=-首元素if(nums[i] > 0) return ans;// 跳过重复解if (i>0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){continue;}int l = i+1;int r = nums.length-1;while (l<r){if (nums[l] + nums[r] + nums[i] < 0){++l;}else if (nums[l] + nums[r] + nums[i] > 0){--r;}else {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(nums[i]);list.add(nums[l]);list.add(nums[r]);ans.add(list);// 跳过重复解while (l<r && nums[l] == nums[l+1]){++l;}++l;while (l<r && nums[r] == nums[r-1]){--r;}--r;}}}return ans;}
附赠两数之和
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (map.containsKey(nums[i])){return new int[]{map.get(nums[i]),i};}map.put(target - nums[i], i);}return null;}
0031.下一个排列.md
关键字 下一个 字典序
实现获取 下一个排列 的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列。
如果不存在下一个更大的排列,则将数字重新排列成最小的排列(即升序排列)。
必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
示例
输入:nums = [1,2,3]输出:[1,3,2]
输入:nums = [3,2,1]输出:[1,2,3]
class Solution{public static void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;// 从后往前找第一个变小的数字int i = n - 2;while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i+1]){i--;}// 除了while循环,有两种情况,一是i==-1了, 二是找到了num[i] < num[i+1]if (i >= 0){// 从后往前找第一个比num[i]大的数,与num[i]交换for (int j = n-1; j > i; j--){if (nums[j] > nums[i]){// 找到了swap(nums, i, j);break;}}}// 交换完后,需要把后面一部分整体反转,使后面一部分是最小的reverse(nums, i+1, n-1);}private static void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j){int t = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = t;}// 反转数组区间[lo, hi]private static void reverse(int[] nums, int lo, int hi){while (lo < hi){swap(nums, lo++, hi--);}}}
0032. 最长有效括号.md
给你一个只包含
'('和')'的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号子串的长度。思路 : 动态规划
我们定义 dp[_i] 表示以下标 _i* 字符结尾的最长有效括号的长度。因此我们知道以 ‘(’ 结尾的子串对应的 dp 值必定为 0 ,我们只需要求解 ‘)’ 在 dp 数组中对应位置的值。
我们从前往后遍历字符串求解 dp 值:
当s[i] = ‘)’ 的时候, 有两种情况 :
- s[i - 1] =‘(’ : 这种情况我们可以推出 : dp[i]=dp[i−2]+2
- s[i - 1] =‘)’ : 这种情况时又分两种情况
- s[ i - dp[i-1] - 1 ] = ‘(‘ : 这种情况我们可以推出 : dp[i] = dp[i−1] +2 + dp[ i− dp[i−1] − 2 ]
- s[ i - dp[i-1] - 1 ] = ‘)’ : dp[i] = 0
public static int longestValidParentheses(String s) {int[] dp = new int[s.length()];for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {if (s.charAt(i) == '('){dp[i] = 0;}else { // ')'if (i > 0 && s.charAt(i-1) == '('){if (i-2>=0)dp[i] = dp[i-2] + 2;elsedp[i] = 2;}else if (i > 0 && s.charAt(i-1) == ')'){ // ....))// 判断 i-dp[i-1]-1 是否是'('if (i-dp[i-1]-1 >= 0 && s.charAt(i-dp[i-1]-1) == '('){if (i-dp[i-1]-2 >= 0)dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 2 + dp[i-dp[i-1]-2];elsedp[i] = dp[i-1] + 2;}else {dp[i] = 0;}}}}int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);}return ans;}
0033. 搜索旋转排序数组.md
关键字 : 旋转数组 有序数组 二分查找
整数数组
nums按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。nums在预先未知的某个下标k上进行了 旋转.例如,
[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]在下标3处经旋转后可能变为[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]。给你 旋转后 的数组
nums和一个整数target,如果nums中存在这个目标值target,则返回它的下标,否则返回-1。
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;while (left <= right) {int mid = (right - left) / 2 + left;// 找到直接返回if (nums[mid] == target) {return mid;}// 如果nums[mid] >= nums[left], 说明mid在旋转点的左边if (nums[mid] >= nums[left]) {if (nums[mid] > target && target >= nums[left]) { // 去左边找right = mid - 1;} else { // 去右边找left = mid + 1;}} else { // 说明mid在旋转点的右边if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) { // 去右边找left = mid + 1;} else { // 去左边找right = mid - 1;}}}return -1;}
0041.缺失的第一个正整数.md
给你一个未排序的整数数组
nums,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数(严格大于0的数)。实现时间复杂度为
O(n)并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。
方法一 : 排序 + 二分查找
时间复杂度 O(n log n) + O(log n) = O(n log n) 空间复杂度 O(1)
代码略
方法二 : 将数字交换到它应该在的位置上去
时间复杂度为 O(n) 空间复杂度 O(1)
将 num[i] 移动到原数组下标为 num[i]-1 的地方去
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;// 循环一遍, 交换数字到应该在的位置for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= len && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {// 满足在指定范围内、并且没有放在正确的位置上,才交换// 例如:数值 3 应该放在索引 2 的位置上swap(nums, nums[i] - 1, i);}}// 遍历一遍, 找到第一个位置不符合的元素返回for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (nums[i] != i + 1) {return i + 1;}}// 上面for循环没有返回, 则说明缺失的是最大的那个数 即数组长度 + 1return len + 1;}private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {int temp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[index2] = temp;}
0042. 接雨水.md
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。思路 : 对于每一列上积攒的雨水量的计算方法是 : 找出当前列左边的最高处, 和右边的最高处, 取二者较小者就是水高线
因此, 方法一就是暴力求解, 对于每一个格子(列), 分别找它左边右边的最高点, 然后减去它自身的高度, 就是当前格子里的积水量, 然后累加在一起即可.
方法一 : 暴力解法
public int trap1(int[] height) {int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < height.length-1; i++) {int leftMaxHi = findMax(height, 0, i);int rightMaxHi = findMax(height, i+1, height.length-1);int cur = Math.min(leftMaxHi, rightMaxHi) - height[i];if (cur>0) ans += cur;}return ans;}// 在[left, right]区间找最大值private int findMax(int[] arr, int left, int right) {int ret = arr[left];while (left <= right){ret = Math.max(ret, arr[left]);left++;}return ret;}
方法二 : 动归
思路与方法一一样, 只是用了两个辅助数组分别记录num[i]左右最高点
public int trap2(int[] height) {int n = height.length; if (n <= 1) return 0;int[] leftMax = new int[n];int[] rightMax = new int[n];// 记录num[i]左边最大值(包含i)leftMax[0] = height[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i-1], height[i]);}// 记录num[i]右边最大值(包含i)rightMax[n -1] = height[n -1];for (int i = n -2; i >= 0; i--){rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i+1], height[i]);}// 求结果int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {ans += Math.min(leftMax[i], rightMax[i]) - height[i];}return ans;}
0046. 全排列.md
关键字 : 数组 字符串 全排列 回溯 深度优先
给定一个不含重复数字的数组
nums,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。注 : 如果给定一个字符串, 求字符全排列, 则将字符串转成char数组
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;boolean[] used = new boolean[len];List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();dfs(nums, used, len, 0, ans, new ArrayList<>());return ans;}private void dfs(int[] nums, boolean[] used, int len, int depth, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> list){if (len == depth){ans.add(new ArrayList<>(list));return;}for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (!used[i]){list.add(nums[i]);used[i] = true;dfs(nums, used, len, depth+1, ans, list);used[i] = false;list.remove(Integer.valueOf(nums[i]));}}}
0053. 最大子序和.md
关键字 : 数组 最大子序列和 连续子序列和 动归
给定一个整数数组
nums,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {int maxSum = nums[0];// 记录以num[i]结尾的最大子序列和for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {// 如果以nums[i-1]结尾的最大子序列和>0, 则以nums[i]结尾的最大子序列和累加上上一个, 否则就是它本身if (nums[i-1] > 0){nums[i] += nums[i-1];}// 更新答案if (nums[i] > maxSum){maxSum = nums[i];}}return maxSum;}
或者 :
f(i)=max{f(i−1)+nums[i],nums[i]}
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {int pre = 0, maxAns = nums[0];for (int x : nums) {pre = Math.max(pre + x, x);maxAns = Math.max(maxAns, pre);}return maxAns;}
0054. 螺旋矩阵.md
关键字 : 螺旋矩阵 顺时针打印 二维数组 模拟
给你一个
m行n列的矩阵matrix,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。思路 : 一层一层从外到里打印, 使用四个变量 r1, r2, c1, c2 分别存储上下左右边界值,从而定义当前最外层。
注意只有在 r1 != r2 时才打印最下一行,也就是在当前最外层的行数大于 1 时才打印最下一行
public List<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();int r1 = 0, c1 = 0;int r2 = matrix.length - 1, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) {// 上for (int i = c1; i <= c2; i++)ans.add(matrix[r1][i]);// 右for (int i = r1 + 1; i <= r2; i++)ans.add(matrix[i][c2]);if (r1 != r2)// 下for (int i = c2 - 1; i >= c1; i--)ans.add(matrix[r2][i]);if (c1 != c2)// 左for (int i = r2 - 1; i > r1; i--)ans.add(matrix[i][c1]);r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--;}return ans;}
0056.合并区间.md
关键词 : 数组 合并 区间合并 排序
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间。
输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {if (intervals.length == 0) return new int[0][2];// 按照区间第一位排序Arrays.sort(intervals, (interval1, interval2) -> interval1[0] - interval2[0]);List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList<int[]>();for (int[] interval : intervals) {int L = interval[0], R = interval[1];// 列表为空或者列表中最后一个区间右边界小于当前区间左边界,则表示不能与列表中的区间合并,新添加一个区间if (ans.size() == 0 || ans.get(ans.size() - 1)[1] < L) {ans.add(new int[]{L, R});} else { // 否则当前区间可以与列表中最后一个区间合并ans.get(ans.size() - 1)[1] = Math.max(ans.get(ans.size() - 1)[1], R);}}return ans.toArray(new int[ans.size()][]);}
0069.x的平方根.md
关键词 : 开方 平方根 二分
实现 sqrt(int x)
public int mySqrt(int x) {int l = 0, r = x, ans = -1;while (l <= r) {int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;if ((long) mid * mid <= x) {ans = mid;l = mid + 1;} else {r = mid - 1;}}return ans;}
0076.最小覆盖子串.md
关键词 : 字符串 子串 最短覆盖子串 滑动窗口
给你一个字符串
s、一个字符串t。返回s中涵盖t所有字符的最小子串。如果s中不存在涵盖t所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串""。
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"输出:"BANC"
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {if (s.length() == 0 || t.length() == 0 || s.length() < t.length()){return "";}int[] need = new int[128];//记录需要的字符的个数for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {need[t.charAt(i)]++;}//l是当前左边界,r是当前右边界,size记录窗口大小,count是需求的字符个数,start是最小覆盖串开始的indexint left = 0, right = 0, windowSize = s.length()+1, needCharCount = t.length(), start = 0;//遍历所有字符while (right < s.length()) {char c = s.charAt(right);if (need[c] > 0) { //需要字符cneedCharCount--;}// 进入窗口的所有字符都加入need数组,如果need[index]<0 , 说明是不需要的冗余字符need[c]--;//把右边的字符加入窗口if (needCharCount == 0) {//窗口中已经包含所有字符while (left < right && need[s.charAt(left)] < 0) {// 只要遇到冗余字符,则将该字符从窗口中移除,并且left++need[s.charAt(left)]++;//释放右边移动出窗口的字符left++;//指针右移}// 出了while循环表示窗口无法再缩小了,此时更新答案if (right - left + 1 < windowSize) {//不能右移时候挑战最小窗口大小,更新最小窗口开始的startwindowSize = right - left + 1;start = left;//记录下最小值时候的开始位置,最后返回覆盖串时候会用到}//更新完答案后,将left继续向左移动一位,使得窗口不满足要求,需要继续right右移寻找新的答案need[s.charAt(left)]++;left++;needCharCount++;}right++;}return windowSize == s.length()+1 ? "" : s.substring(start, start + windowSize);}
0093. 复原 IP 地址.md
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能从 s 获得的 有效 IP 地址 。你可以按任何顺序返回答案。
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 ‘.’ 分隔。
输入:s = "101023"输出:["1.0.10.23","1.0.102.3","10.1.0.23","10.10.2.3","101.0.2.3"]
输入:s = "0000"输出:["0.0.0.0"]
// 回溯private List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();public List<String> isIp(String s) {int n = s.length();if (n > 12 || n < 4) return ans;// 队列Deque<String> path = new ArrayDeque<>(4);dfs(s, 0, 4, path);return ans;}private void dfs(String s, int start, int segment, Deque<String> path) {int n = s.length();if (start == n && segment == 0) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (String str : path) {sb.append(str).append(".");}sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);ans.add(sb.toString());return ;}// 最多3位组成一个段, i位当前段的尾部下标for (int i=start;i<start+3;i++) {if (i >= n) break;// 判断剩下的字符串长度是否比要组成的段的最大长度还长,如果是,则当前答案无效,继续下一次循环if (segment * 3 < n - i) continue;if (isIpSegment(s, start, i)) {// 当前段有效,加入队列String currentSegment = s.substring(start, i + 1);path.addLast(currentSegment);// 关键, 下一段从下标为i+1的位置开始,总段数-1dfs(s, i + 1, segment - 1, path);// 回溯path.removeLast();}}}private boolean isIpSegment(String s, int left, int right) {// 如果字符串长度大于1, 且第一位是0,则不可为ip段if (right - left + 1 > 1 && s.charAt(left) == '0') return false;int res = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(left, right+1));return res >= 0 && res <= 255;}
0098.验证是否为二叉搜索树.md
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
中序遍历即可
private int preNum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return true;boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);if (!left){return false;}if (root.val <= preNum){ // 不满足中序有序规律return false;}preNum = root.val;return isValidBST(root.right);}
0101.对称二叉树.md
关键词 : 二叉树 对称
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
如
1/ \2 2/ \ / \3 4 4 3
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return true;return isSymmetric(root.left, root.right);}public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {if (node1 == null && node2 == null) return true;if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return false;// 先序判断值相等if (node1.val == node2.val){// 然后判断node1的左孩子是否和node2的右孩子对称boolean f1 = isSymmetric(node1.left, node2.right);// 然后判断node1的右孩子是否和node2的左孩子对称boolean f2 = isSymmetric(node1.right, node2.left);return f1 && f2;}elsereturn false;}
0104. 二叉树的最大深度.md
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
思路 : DFS, 后序递归
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;if (root.left == null && root.right == null )return 1;else if (root.left == null){// 左树为空, 则返回右树高度+1return maxDepth(root.right)+1;}else if (root.right == null){// 右树为空, 则返回左树高度+1return maxDepth(root.left)+1;}else {// 去左右子树高度最大值+1return Math.max(maxDepth(root.right)+1, maxDepth(root.left)+1);}}
0105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树.md
关键词 : 二叉树 重建 前序中序
给定一棵树的前序遍历
preorder与中序遍历inorder。请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
// 缓存中序遍历数组每个值对应的索引private Map<Integer, Integer> indexForInOrders = new HashMap<>();public TreeNode buildTree(int[] pre, int[] in) {// 存中序节点索引for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++)indexForInOrders.put(in[i], i);return buildTree(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, 0);}// 只需要前序,前序中当前子树的左右范围,中序左右范围private TreeNode buildTree(int[] pre, int preL, int preR, int inL) {if (preL > preR)return null;// 当前子树的根TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[preL]);// 从中序中找出根的位置int inIndex = indexForInOrders.get(root.val);// 当前子树中左子树的节点数量int leftTreeSize = inIndex - inL;// 递归root.left = buildTree(pre, preL + 1, preL + leftTreeSize, inL);root.right = buildTree(pre, preL + leftTreeSize + 1, preR, inL + leftTreeSize + 1);return root;}
0106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.md
关键词 : 二叉树 重建 后序中序
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
// 缓存中序遍历数组每个值对应的索引HashMap<Integer,Integer> indexForInOrders = new HashMap<>();public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {// 存中序节点索引for(int i = 0;i < inorder.length; i++)indexForInOrders.put(inorder[i], i);return buildTree(postorder ,0, 0, postorder.length - 1);}public TreeNode buildTree(int[] postorder, int inL, int postL, int postR) {if(postR < postL) return null;// 当前子树的根TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postR]);// 从中序中找出根的位置int inIndex = indexForInOrders.get(root.val);root.left = buildTree(postorder ,inL, postL, postL + inIndex - inL - 1);root.right = buildTree(postorder ,inIndex + 1, postL + inIndex - inL, postR - 1);return root;}
0110. 平衡二叉树.md
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
思路 : 后序递归
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {int i = treeHeight(root);return i != -1;}private int treeHeight(TreeNode node){if (node == null) return 0;// 计算左子树的高度int leftHeight = treeHeight(node.left);// 如果左子树高度为-1, 说明左子树不平衡if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;// 计算右子树的高度int rightHeight = treeHeight(node.right);// 如果右子树高度为-1, 说明右子树不平衡if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;// 如果左子树右子树的高度差不超过1, 则返回最大高度, 超过1则返回-1表示不平衡return Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeight)<=1 ? Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight)+1 : -1;}
0111. 二叉树的最小深度.md
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
// BFSpublic int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();queue.addLast(root);// 初试深度设为1int depth = 1;while (!queue.isEmpty()){// 当前所在层有多少个节点int curLevelNodeNum = queue.size();;for (int i = 0; i < curLevelNodeNum; i++) { // 将一层节点全部出完之后, 深度+1TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst();if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return depth;if (node.left != null) queue.addLast(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.addLast(node.right);}// 出完一层, 深度++depth++;}return depth;}
0112.路径总和.md
关键字 : 二叉树 路径总和 递归
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum ,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {if (root == null) {return false;}if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {return sum == root.val;}return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);}
扩展, 找出所有路径总和=targetSum 的路径
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {dfs(root, targetSum);return ans;}public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return;}path.addLast(root.val);targetSum -= root.val; // targetSum - 当前节点值// 到达叶子结点, 且targetSum减到0, 添加一个答案if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0) {ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));}dfs(root.left, targetSum);dfs(root.right, targetSum);//path.removeLast();}
0121. 买卖股票的最佳时机.md
关键字 : 股票 最佳时机 买卖一次 最大收益 最大利润 动归
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
思路 : 使用一个变量记录 prices[i] 之前的最低价 minPrice, 每次使用 prices[i] - minPrice, 如果收益更多, 则更新收益
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {int ans = 0;int minPrice = prices[0];for(int i=1;i <prices.length;i++){ans = Math.max(ans, prices[i]-minPrice);minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, prices[i]);}return ans;}
0122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II.md
关键字 : 股票 最佳时机 买卖多次 最大收益 最大利润 贪心
给定一个数组 prices ,其中 prices[i] 是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {int ans = 0;int curMin = prices[0];for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {curMin = Math.min(curMin, prices[i]);// 只要赚钱就卖掉if (prices[i] > curMin){// 卖掉ans += prices[i] - curMin;curMin = prices[i];}}return ans;}
0124. 二叉树中的最大路径和.md
关键词 : 二叉树 最大路径和 关键路径 后序递归
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
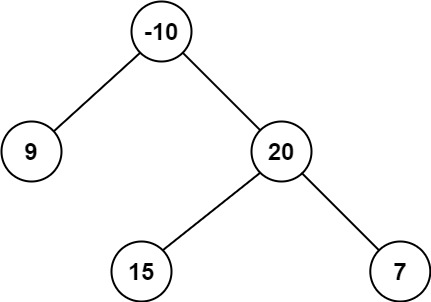
输入:root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:42
解释:最优路径是 15 -> 20 -> 7 ,路径和为 15 + 20 + 7 = 42思路, 后序递归, 将dfs(TreeNode node)定义为以node为根的二叉树且路径必须经过node节点的路径最大和
private int maxAns = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {dfs(root);return maxAns;}// 后序递归private int dfs(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) return 0;int left = Math.max(0, dfs(node.left));int right = Math.max(0, dfs(node.right));// 三种情况// 1. 路径为左边+当前节点// 2. 路径为右边+当前节点// 3. 路径为左边+当前节点+右边int sum = node.val + left + right;// 更新答案maxAns = Math.max(maxAns, sum);// 返回上一层的结果只能是选择当前节点左右两边的其中一边return node.val + Math.max(left, right);}
0129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和.md
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root,树中每个节点都存放有一个0到9之间的数字。每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
输入:root = [4,9,0,5,1]输出:495 + 491 + 40 = 1026
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {return dfs(root, 0);}public int dfs(TreeNode node, int prefix) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int newPrefix = prefix * 10 + node.val;if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {return newPrefix;} else {return dfs(node.left, newPrefix) + dfs(node.right, newPrefix);}}
0141. 环形链表.md
关键字 : 判断链表是否有环, 找链表入环节点
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
// 快慢指针public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return false;// 至少两个节点ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (true){if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null)return false;elsefast = fast.next.next;if (slow.val == fast.val)return true;elseslow = slow.next;}}
- 找出入环节点
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head, slow = head;while (true) {if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if (fast == slow) break;}fast = head;while (slow != fast) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return fast;}
公式推导
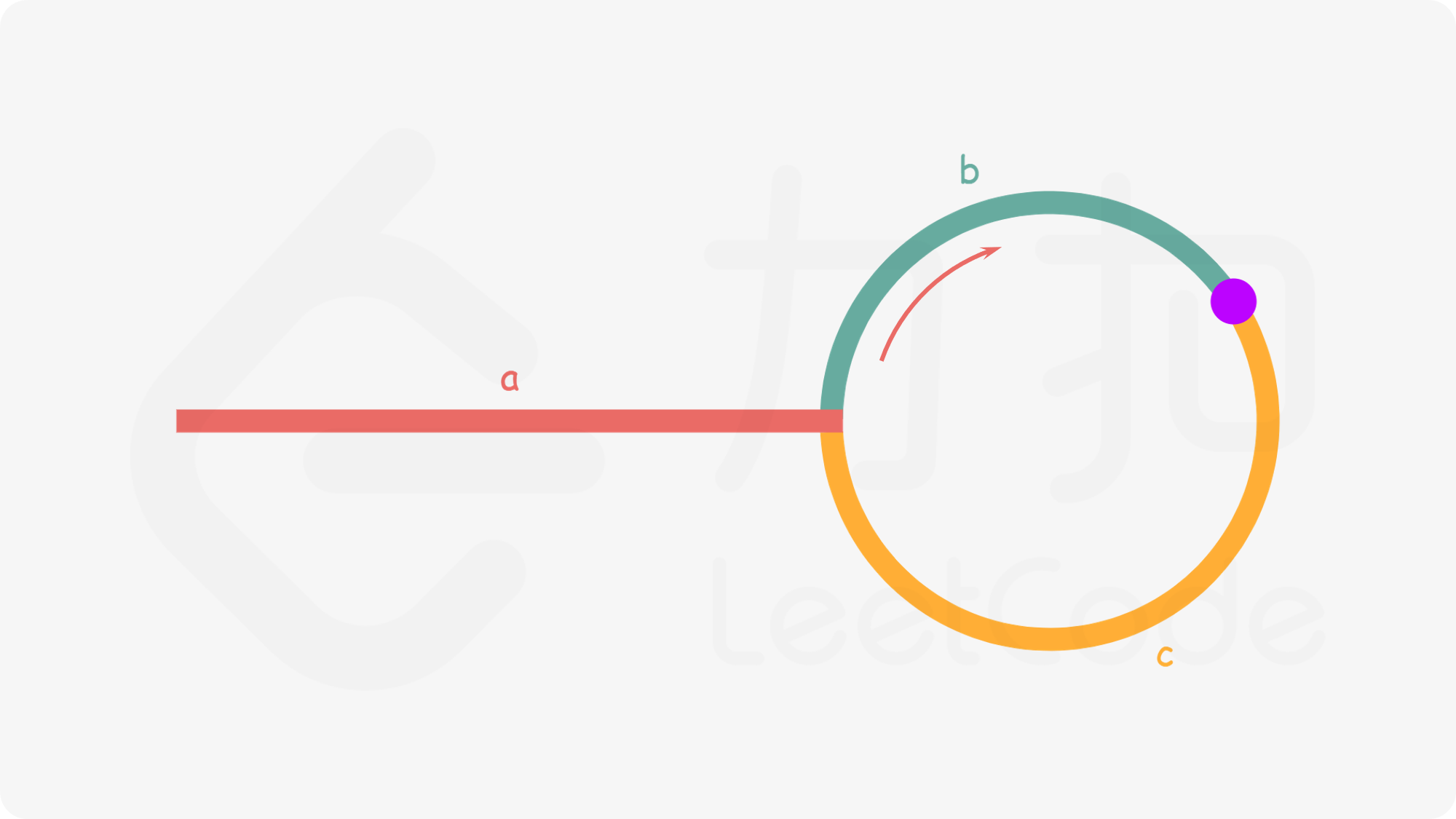
任意时刻,fast 指针走过的距离都为 slow 指针的 2 倍。因此,我们有
a+(n+1)b+nc=2(a+b) ⟹ a=c+(n-1)(b+c)
a+(n+1)b+nc=2(a+b) ⟹ a=c+(n−1)(b+c)
我们会发现:从相遇点到入环点的距离加上 n−1 圈的环长,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离。
因此,当发现slow 与 fast 相遇时,我们再额外使用一个指针 ptr。起始,它指向链表头部;随后,它和slow 每次向后移动一个位置。最终,它们会在入环点相遇。
0143. 重排链表.md
关键字 : 链表 重排序
对链表首尾重排
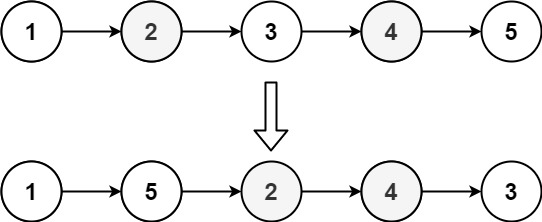
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]输出: [1,5,2,4,3]
方法一 : 使用List存下每一个节点, 按下标重新连接链表 空间O(n)
略
方法二 : 快慢指针找中点 + 反转后半段链表 + 合并前后两段链表 空间O(1)
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return;ListNode preSlow = new ListNode(-1, head);// 快慢指针找中点ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (fast != null && fast.next !=null){fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;preSlow = preSlow.next;}preSlow.next = null;// 反转链表后半段ListNode head2 = reverseList(slow);// 合并两条链表merge(head, head2);// System.out.println(head);}// 合并两条链表, 返回合并后的头结点private void merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){ListNode p = new ListNode(-1);ListNode x = p;while (head1 != null && head2 != null){p.next = head1;head1 = head1.next;p = p.next;p.next = head2;head2 = head2.next;p = p.next;}if (head1 != null){p.next = head1;}}// 非递归反转链表, 空间O(1)public ListNode reverseList(ListNode node) {if (node == null || node.next == null) return node;ListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = node;while (cur != null) {ListNode temp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}return pre;}// 递归反转链表,返回翻转后的头结点private ListNode reverseList(ListNode node){if (node == null || node.next == null) return node;ListNode node1 = reverseList(node.next);node.next.next = node;node.next = null;return node1;}
0146.手撕LRU.md
设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
实现 LRUCache 类:
- LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
- int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
- void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
要求:在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成 get() 和 put() 操作?
class LRUCache {// 使用双向链表记录头尾static class DLinkedNode {int key;int value;DLinkedNode prev;DLinkedNode next;public DLinkedNode() {}public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}}// 虚头虚尾DLinkedNode dummyHead;DLinkedNode dummyTail;// 为了快速查询,使用map去记录缓存中所有数据在链表中的位置Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> map;// 当前缓存中数据量int size;// 缓存容量int capacity;// 构造函数public LRUCache(int capacity) {// 初始化双向链表dummyHead = new DLinkedNode();dummyTail = new DLinkedNode();dummyHead.next = dummyTail;dummyTail.prev = dummyHead;size = 0;this.capacity = capacity;map = new HashMap<>(capacity);}// 访问缓存, 需要将被访问的元素移到队首public int get(int key) {if (map.containsKey(key)) {int ret = map.get(key).value;// 当前节点移到链首moveElementToFirst(map.get(key));return 1;}elsereturn -1;}// 添加元素到缓存public void put(int key, int value) {if (map.containsKey(key)){// 存在, 只修改值map.get(key).value = value;}else {// 不存在, 需新增if (size == capacity){ // 需要扩容// 移除链尾元素// 删除map中对应元素map.remove(dummyTail.prev.key);dummyTail.prev = dummyTail.prev.prev;dummyTail.prev.next = dummyTail;size--;}addElement(key, value);}}public void moveElementToFirst(DLinkedNode node){// 当前节点从链表上脱离node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;// 查到虚头节点后面node.next = dummyHead.next;dummyHead.next.prev = node;node.prev = dummyHead;dummyHead.next = node;}public void addElement(int key, int value){DLinkedNode node = new DLinkedNode(key, value);// 节点存入mapmap.put(key, node);// 将节点放到链表最前面node.next = dummyHead.next;dummyHead.next.prev = node;node.prev = dummyHead;dummyHead.next = node;size++;}}
0148.链表排序.md
关键字 : 链表排序 归并排序 堆排序 优先队列
给你链表的头结点
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。在
O(n log n)时间复杂度下,对链表进行排序
方法一 : 优先队列 堆排序
// 时间复杂度 O(n log n) 空间 O(n)public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> {return o1.val - o2.val;});while (head != null){priorityQueue.add(head);head = head.next;}ListNode p = dummyHead;while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){p.next = priorityQueue.remove();p = p.next;}p.next = null;return dummyHead.next;}
方法二 : 归并排序
// // 时间复杂度 O(n log n) 空间 O(log n) (递归栈的)private ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;//利用快慢指针来找到链表的中点ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}// 归并右边ListNode right = mergeSort(slow.next);slow.next = null; // 链表从中间断开// 归并左边ListNode left = mergeSort(head);return mergeTwoLists(left, right);}public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0), cur = dummyHead;while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {if(l1.val < l2.val) {cur.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;}else {cur.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}cur = cur.next;}cur.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;return dummyHead.next;}
0155. 最小栈.md
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。
pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。
top() —— 获取栈顶元素。
getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素
class MinStack {Deque<Integer> dataStack;Deque<Integer> minStack;/** initialize your data structure here. */public MinStack() {dataStack = new ArrayDeque<>();minStack = new ArrayDeque<>();}public void push(int x) {dataStack.addFirst(x);if (minStack.isEmpty() || minStack.peekFirst() >= x){minStack.addFirst(x);}}public void pop() {int popNum = dataStack.removeFirst();if (!minStack.isEmpty() && popNum == minStack.peekFirst()){minStack.removeFirst();}}public int top() {if (dataStack.isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("栈空");return dataStack.peekFirst();}public int min() {if (minStack.isEmpty())throw new RuntimeException("栈空");return minStack.peekFirst();}}
0160. 相交链表.md
关键字 : 链表 相交
找出链表相交的起始节点, 如果没有交点 返回null
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode A = headA, B = headB;while (A != B) {if( A != null) A = A.next; else A = headB;if( B != null) B = B.next; else B = headA;}return A;}
如果只要判断两链表是否相交, 只要判断最后一个尾结点地址是否相同即可
public boolean getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {while (headA.next != null){headA = headA.next;}while (headB.next != null){headB = headB.next;}return headA == headB;}
0162. 寻找峰值.md
关键字 : 数组 峰值
峰值元素是指其值大于左右相邻值的元素。
给你一个输入数组 nums,找到峰值元素并返回其索引。数组可能包含多个峰值,在这种情况下,返回 任何一个峰值 所在位置即可。
你可以实现时间复杂度为
O(logN)的解决方案吗?示例
输入:nums = [1,2,1,3,5,6,4]
输出:1 或 5
解释:你的函数可以返回索引 1,其峰值元素为 2;
或者返回索引 5, 其峰值元素为 6。
// 递归二分public class Solution {public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {return search(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);}public int search(int[] nums, int l, int r) {if (l == r)return l;int mid = (l + r) / 2;if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1])return search(nums, l, mid);return search(nums, mid + 1, r);}}
// 迭代二分public class Solution {public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {int l = 0, r = nums.length - 1;while (l < r) {int mid = (l + r) / 2;if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1])r = mid;elsel = mid + 1;}return l;}}
0199.二叉树的右视图.md
关键字 : 二叉树 右侧 层序遍历 BFS
给定一个二叉树的 根节点
root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。示例:
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return ans;Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.addLast(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst();if (i == size-1){// 当前层的最后一个ans.add(node.val);}if (node.left != null) queue.addLast(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.addLast(node.right);}}return ans;}
0200.岛屿数量.md
关键字 : 岛屿 二维数组 回溯
给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
输入:grid = [
[“1”,”1”,”0”,”0”,”0”],
[“1”,”1”,”0”,”0”,”0”],
[“0”,”0”,”1”,”0”,”0”],
[“0”,”0”,”0”,”1”,”1”]
]
输出:3
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {vis = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];// 以每一个坐标作为起点坐标for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !vis[i][j]){vis[i][j] = true;ans++;dfs(grid, i, j);}}}return ans;}// 访问数组public boolean[][] vis;// 行走方向public int[] xDirection = {1, 0, 0, -1};public int[] yDirection = {0, -1, 1, 0};public int ans = 0;public void dfs(char[][] grid, int row, int col){for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int nextX = row+xDirection[i];int nextY = col+yDirection[i];if (!(nextX >= grid.length || nextX < 0 || nextY >= grid[0].length || nextY < 0) && !vis[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] == '1') {vis[nextX][nextY] = true;dfs(grid, nextX, nextY);}}}
0206.反转链表.md
关键字 : 链表 反转
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
方法一 : 递归, 空间O(n)
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null){return head;}// 返回了以head.next为头结点的反转后的链表头ListNode rev = reverseList(head.next);// 对当前节点进行反转操作head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return rev;}
方法二 : 用三个指针, 空间O(1)
// 三指针public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode p1 = null;ListNode p2 = head;ListNode p3 = head.next;while (p3 != null){p2.next = p1;p1 = p2;p2 = p3;p3 =p3.next;}p2.next = p1;return p2;}
0208. 实现 Trie (前缀树).md
关键词 : 前缀树 字典树 数据结构 单词搜索 字典搜索
0221. 最大正方形.md
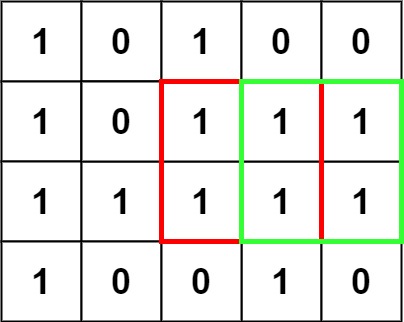
在一个由
'0'和'1'组成的二维矩阵内,找到只包含'1'的最大正方形,并返回其面积。
输入:matrix = [[“1”,”0”,”1”,”0”,”0”],[“1”,”0”,”1”,”1”,”1”],[“1”,”1”,”1”,”1”,”1”],[“1”,”0”,”0”,”1”,”0”]]
输出:4思路 : 动态规划
我们用 dp(i,j) 表示以 (i,j) 为右下角,且只包含 11 的正方形的边长最大值。如果我们能计算出所有 dp(i,j) 的值,那么其中的最大值即为矩阵中只包含 11 的正方形的边长最大值,其平方即为最大正方形的面积。
对于每个位置 (i,j),检查在矩阵中该位置的值:
- 如果该位置的值是 0,则 dp(i,j)=0,因为当前位置不可能在由 1 组成的正方形中;
- 如果该位置的值是 1,则 dp(i,j) 的值由其上方、左方和左上方的三个相邻位置的 dp 值决定。具体而言,当前位置的元素值等于三个相邻位置的元素中的最小值加 1,状态转移方程如下:dp(i,j)=m_in[ dp(_i−1,j), dp(i−1,j−1), dp(i,j−1) ]+1
public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {int maxSide = 0;if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {return maxSide;}int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;int[][] dp = new int[rows][columns];for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {if (i == 0 || j == 0) {dp[i][j] = 1;} else {dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;}maxSide = Math.max(maxSide, dp[i][j]);}}}int maxSquare = maxSide * maxSide;return maxSquare;}
0232. 使用栈实现队列.md
使用两个栈实现先入先出队列
class MyQueue {// 队列长度private int size;// 元素入队时入此栈private Stack<Integer> inQueue;// 元素出队时从此栈出private Stack<Integer> outQueue;public MyQueue() {inQueue = new Stack<>();outQueue = new Stack<>();size=0;}/** 将元素x放入队尾 */public void push(int x) {inQueue.push(x);size++;}/** 移除队头元素 */public int pop() {if (!outQueue.isEmpty()){size--;return outQueue.pop();}else {// 出栈空if (inQueue.isEmpty()) // 入栈也空return -1;else { // 入栈不空while (!inQueue.isEmpty()) {outQueue.push(inQueue.pop());}return pop();}}}/** 查看队头元素 */public int peek() {if (!outQueue.isEmpty()){return outQueue.peek();}else {// 出栈空if (inQueue.isEmpty()) // 入栈也空return -1;else { // 入栈不空while (!inQueue.isEmpty()) {outQueue.push(inQueue.pop());}return peek();}}}/** 判断队列是否为空 */public boolean empty() {return size == 0;}}
0236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先.md
关键字 : 二叉树 最近公共祖先 先序遍历 深度优先 DFS
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode node, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (node == null || node == p || node == q)return node;// 从左子树中找, 找到其中一个节点就返回, 没找到返回nullTreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(node.left, p, q);// 从右子树中找, 找到其中一个节点就返回, 没找到返回nullTreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(node.right, p, q);// 左右都没找到if (left == null && right == null)return null;// 左边和右边都有, 说明当前node左右各一个,就是祖先节点else if (left != null && right != null)return node;// 否则说明p或q其中一个就是公共祖先elsereturn left!=null?left:right;}
0260. 只出现一次的数字 III.md
关键词 数组 只出现一次的数 位运算 分组异或
给定一个整数数组
nums,其中恰好有两个元素只出现一次,其余所有元素均出现两次。 找出只出现一次的那两个元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
输入:nums = [1,2,1,3,2,5]输出:[3,5]解释:[5, 3] 也是有效的答案。
思路, 分组异或
public static int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {// 1. 先对数组所有数进行异或操作, 最终结果就是两个单独的数做异或的结果int temp = 0;for (int num : nums) {temp = temp ^ num;}// 2. 从右到左对异或结果temp找第一个不为0的位置int x = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {if ((temp>>i & 1) == 1){x = i;break;}}// 下面的x代表只有第x位不为0,其余位都是0的二进制数x = 1<<x;// 3. 将整个数组里的数分为第x位是0和第x位是1的两部分, 分别异或, 最终答案即为异或结果int num1 = 0, num2 = 0;for (int num : nums) {if ((num & x) == 0){num1 = num1 ^ num;}else {num2 = num2 ^ num;}}return new int[]{num1, num2};}
0300.最长递增序列.md
关键字 : 数组 最长不连续递增子序列 最长上升子序列 动归
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。
子序列是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序。例如,[3,6,2,7] 是数组 [0,3,1,6,2,2,7] 的子序列。
思路 : dp[i] 数组表示以 nums[i] 结尾的最长递增子序列
// 时间复杂度O(n^2)public static int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {int length = nums.length;int[] dp = new int[length];dp[0] = 1;int maxLen = 1;for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {dp[i] = 1; // 初始化为自己形成子序列// 遍历前面的,找到比自己小的, 更新dpfor (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (nums[i] > nums[j]){dp[i] = Math.max(dp[j]+1, dp[i]);}}maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, dp[i]);}return maxLen;}
0328. 奇偶链表.md
关键词 : 链表 奇偶 重排序
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起。请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性。
请尝试使用原地算法完成。你的算法的时间复杂度应为 O(n), 空间复杂度应为 O(1)
输入: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL输出: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return head;}// 偶数链表头ListNode head2 = head.next;// 奇数节点指针头ListNode odd = head;// 偶数节点指针ListNode even = head2;// 拆分成两个链表while (even != null && even.next != null) {odd.next = even.next;odd = odd.next;even.next = odd.next;even = even.next;}odd.next = head2;return head;}
0334.递增的三元子序列.md
关键字 : 数组 递增 三元 子序列
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断这个数组中是否存在长度为 3 的递增子序列。
如果存在这样的三元组下标 (i, j, k) 且满足 i < j < k ,使得 nums[i] < nums[j] < nums[k] ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
public boolean increasingTriplet(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;if (len < 3) return false;// 记录下遍历到的最小值和次小值int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, mid = Integer.MAX_VALUE;for (int num : nums) {if (num <= min) {min = num;} else if (num <= mid) { // 出现了比min大且比mid小的数,更新midmid = num;}else {// 一定出现了比mid更大的数return true;}}return false;}
0415.字符串相加.md
关键字 : 字符串 加法 相加 模拟 进位
给定两个字符串形式的非负整数
num1和num2,计算它们的和。提示:
- num1 和num2 的长度都小于 5100
- num1 和num2 都只包含数字 0-9
- num1 和num2 都不包含任何前导零
- 你不能使用任何內建 BigInteger 库, 也不能直接将输入的字符串转换为整数形式
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {int num1Len = num1.length();int num2Len = num2.length();int maxLen = Math.max(num1Len, num2Len);StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();// 进位标识boolean flag = false;for (int i = 0; i < maxLen; i++) {int n1 = 0;int n2 = 0;int curProd = 0;if (i < num1Len)n1 = num1.charAt(num1Len-i-1)-48;if (i < num2Len)n2 = num2.charAt(num2Len-i-1)-48;curProd = flag?n1+n2+1:n1+n2;flag = curProd >= 10;ans.insert(0,curProd%10);}// 需要判断一下最终flag是否还有进位,有则最前面插入一个1return flag?ans.insert(0,1).toString():ans.toString();}
0704.二分查找.md
给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;while (left <= right) {// 防止+操作溢出int mid = left + (right - left >> 1);if (nums[mid] == target)return mid;else if (nums[mid] < target) {left = mid + 1;}elseright = mid - 1;}return -1;}
0912. 快速排序.md
关键字 : 数组 排序 快排
给你一个整数数组
nums,请你将该数组升序排列。
public void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right){if (left >= right) return;int p = partition(arr, left, right);// 左边排序sort(arr, left, p-1);// 右边排序sort(arr, p+1, right);}// 对数组进行分区, 以枢纽为界, 左侧全部小于枢纽, 右侧全部大于枢纽, 返回枢纽最终所在位置private int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) {// 优化点 : 随机选取枢轴元素. 将选中的枢轴元素交换到最左边int p = left + (new Random()).nextInt(right-left+1);swap(arr, left, p);int i = left+1, j = right;while (true){// 从左往右找到第一个比枢纽元素大的, 注意循环条件while (i <= j && arr[i] < arr[left])i++;// 从右往左找到第一个比枢纽元素小的,注意循环条件while (i <= j && arr[j] > arr[left])j--;// 循环终止条件if (i >= j) break;// 交换两个位置的元素swap(arr, i, j);// i往后走一步, j往前走一步, 继续循环i++;j--;}// 最后交换枢纽元素和j停留的位置swap(arr, left, j);return j;}private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j){int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}
20. 有效的括号.md
关键词 括号匹配 栈
给定一个只包括
'(',')','{','}','[',']'的字符串s,判断字符串是否有效。思路 , 只要是左括号, 就入栈, 只要是右括号, 就出栈一个, 判断出栈的字符是否与有括号匹配
public boolean isValid(String s) {HashMap<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(')', '(');map.put(']', '[');map.put('}', '{');Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {Character c = s.charAt(i);if (c == '(' || c=='[' || c=='{'){stack.push(c);}else {if (stack.isEmpty()){return false;}else {Character popChar = stack.pop();if (map.get(c) != popChar){return false;}}}}if (!stack.isEmpty()){return false;}return true;}
234. 回文链表.md
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
要求用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题
思路 : 双指针 + 反转后半部分链表
public static boolean isPalindrome1(ListNode head) {if (head.next == null) return true;ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}// 退出while时, slow指向最中间或者中间左边ListNode reverseNode = slow.next;slow.next = null;ListNode reversedHead = reverse(reverseNode);while (reversedHead != null){if (reversedHead.val != head.val){return false;}reversedHead = reversedHead.next;head = head.next;}return true;}// 三指针反转链表, 空间O(1)public static ListNode reverse(ListNode head){if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = head;ListNode back = null;while (cur.next != null){back = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = back;}cur.next = pre;return cur;}
460. LFU 缓存.md
关键词 : 手撕LFU
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU) 缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
实现 LFUCache 类:
- LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象
- int get(int key) - 如果键存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回 -1。
- void put(int key, int value) - 如果键已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量时,则应该在插入新项之前,使最不经常使用的项无效。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最近最久未使用 的键。
思路, 使用两个HashMap, 一个存缓存(key为缓存的key, value为自定义缓存节点), 一个存频次链表(key为频次, value为该频次对应的双向链表), 然后还需要维护一个最低访问频次的int变量, 如果需要移除最低访问频次元素, 就从这个变量对应的频次链表中移除.
class LFUCache {class Node {int key;int value;int freq;Node pre;Node next;public Node() { }public Node(int key, int value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.freq = 1;}}class DLList {// 头尾伪结点Node head;Node tail;public DLList() {head = new Node();tail = new Node();head.next = tail;tail.pre = head;}void removeNode(Node node) {node.pre.next = node.next;node.next.pre = node.pre;}void addHead(Node node) {node.next = head.next;head.next.pre = node;head.next = node;node.pre = head;}}Map<Integer, Node> map; // 存储缓存, Map的key为缓存的keyMap<Integer, DLList> freqMap; // 每个频次维护一个双向链表int size; // 当前元素个数int capacity; // 允许存储的最大元素个数int minFreq; // 所有元素中的最小访问频次public LFUCache(int capacity) {map = new HashMap<>(capacity);freqMap = new HashMap<>();this.capacity = capacity;this.size = 0;}public int get(int key) {Node node = map.get(key);if (node == null) {return -1;}// 如果存在, 则对应元素访问频次++updateFreq(node);return node.value;}public void put(int key, int value) {if (capacity == 0) return;Node node = map.get(key);// 如果key已存在, 则更新value, 并更新其访问频次if (node != null) {node.value = value;updateFreq(node);} else { // key不存在, 则新增key到访问频次为1的链表中// 检查是否超出capacity, 超出则删除一个访问频次最低的if (size == capacity) {DLList minFreqLL = freqMap.get(minFreq);// 从缓存中删除map.remove(minFreqLL.tail.pre.key);// 从频次链表中删除minFreqLL.removeNode(minFreqLL.tail.pre); // 这里不需要维护min, 因为下面add了newNode后min肯定是1.size--;}// 将新节点插入访问频次为1的频次链表中node = new Node(key, value);map.put(key, node);DLList ll = freqMap.getOrDefault(1, new DLList());ll.addHead(node);freqMap.put(1, ll);size++;minFreq = 1;}}// node已存在,更新node的访问频次void updateFreq(Node node) {// 从原freq对应的链表里移除int preFreq = node.freq;DLList ll = freqMap.get(preFreq);ll.removeNode(node);// 如果当前频次链表为最低频次链表, 且从链表中删除node后链表为空时, 需要更新最小访问频次变量if (preFreq == minFreq && ll.head.next == ll.tail) {minFreq = preFreq + 1;}// 加入新freq对应的链表int curFreq = preFreq + 1;node.freq = curFreq;DLList curDLL = freqMap.getOrDefault(curFreq, new DLList());curDLL.addHead(node);freqMap.put(curFreq, curDLL);}}
470. 用 Rand7() 实现 Rand10().md
已有方法
rand7可生成 1 到 7 范围内的均匀随机整数,试写一个方法rand10生成 1 到 10 范围内的均匀随机整数。思路 :
执行一次 rand7() , 可得到均匀分布的 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
rand7() - 1, 得到均匀分布的 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
( rand7() - 1 ) * 7, 得到均匀分布的 0, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42
( rand7() - 1 ) * 7 + rand7(), 即( 0, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42 ) + ( 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ) 可以得到均匀分布的(1,2,3,4, … , 49)
对上面的式子产生的1 - 49 ,只取前40个, 即 1 - 40; 将得到的1 - 40 这个数X对10取模再减1, 即可得到rand10()
即, X % 10 + 1
public int rand10(){while (true){int num = (rand7() - 1) * 7 + rand7();if (num <= 40)return num % 10 + 1;rand10();}}public int rand7(){Random random = new Random();return random.nextInt(7) + 1;}
8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi).md
关键字 : 字符串转整数
函数
myAtoi(string s)的算法如下:
- 读入字符串并丢弃无用的前导空格
- 检查下一个字符(假设还未到字符末尾)为正还是负号,读取该字符(如果有)。 确定最终结果是负数还是正数。 如果两者都不存在,则假定结果为正。
- 读入下一个字符,直到到达下一个非数字字符或到达输入的结尾。字符串的其余部分将被忽略。
- 将前面步骤读入的这些数字转换为整数(即,”123” -> 123, “0032” -> 32)。如果没有读入数字,则整数为 0 。必要时更改符号(从步骤 2 开始)。
- 如果整数数超过 32 位有符号整数范围 [−231, 231 − 1] ,需要截断这个整数,使其保持在这个范围内。具体来说,小于 −231 的整数应该被固定为 −231 ,大于 231 − 1 的整数应该被固定为 231 − 1 。
返回整数作为最终结果。
public static int myAtoi(String s) {s = s.trim();if (s.length() == 0) return 0;boolean isNegative = false; // 负数标记if (s.charAt(0) == '-'){isNegative = true;}long ans = 0;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) {// 如果第一个字符是正负号,则跳过if (i == 0 && (s.charAt(0) == '-' || s.charAt(0) == '+')){continue;}// 判断当前字符是否是数字, 如果是, 则累加, 如果不是, 则结束遍历int cur = s.charAt(i) - '0';if (cur >= 0 && cur <= 9){ans = ans * 10 + cur;}else {break;}// 判断是否越界if (isNegative && ans > Integer.MAX_VALUE){return Integer.MIN_VALUE;}else if (ans > Integer.MAX_VALUE){return Integer.MAX_VALUE;}}return isNegative ? -(int) ans : (int) ans;}
剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数.md
编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数(以二进制串的形式),返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数
思路 : n&(n-1) 位运算可以将 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位 1 设置为 0。不断将 1 设置为 0,直到 n 为 0。
public int NumberOf1(int n) {int cnt = 0;while (n != 0) {cnt++;n &= (n - 1);}return cnt;}
剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数.md
如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
/* 大顶堆,存储左半边元素 */private PriorityQueue<Integer> left = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);/* 小顶堆,存储右半边元素,并且右半边元素都大于左半边 */private PriorityQueue<Integer> right = new PriorityQueue<>();/* 当前数据流读入的元素个数 */private int N = 0;public void Insert(Integer val) {/* 插入要保证两个堆存于平衡状态 */if (N % 2 == 0) {/* N 为偶数的情况下插入到右半边。* 因为右半边元素都要大于左半边,但是新插入的元素不一定比左半边元素来的大,* 因此需要先将元素插入左半边,然后利用左半边为大顶堆的特点,取出堆顶元素即为最大元素,此时插入右半边 */left.add(val);right.add(left.poll());} else {right.add(val);left.add(right.poll());}N++;}// 任意时刻获取中位数, 复杂度O(1)public Double GetMedian() {if (N % 2 == 0)return (left.peek() + right.peek()) / 2.0;elsereturn (double) right.peek();}
剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符.md
在字符串 s 中找出第一个只出现一次的字符。如果没有,返回一个单空格。 s 只包含小写字母。
ASCII 码只有 128 个字符,因此可以使用长度为 128 的整型数组来存储每个字符出现的次数。
注意最后遍历的是字符串, 而不是数组, 因为要保证找到的是第一个出现一次的字符
public static int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {// 128长度数组存储字符出现的次数int[] cnts = new int[128];// 计算每个字符出现的次数for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)cnts[str.charAt(i)]++;// 从头到尾再遍历一遍字符串, 看哪个字符的出现次数等于1for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)if (cnts[str.charAt(i)] == 1)return i;return -1;}
剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对.md
在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数。
思路 : 利用归并排序过程发现逆序对
// 答案private int res;public int reversePairs(int[] nums){res = 0;mergeSort(nums);return res;}public void mergeSort(int[] arr){int[] temp = new int[arr.length];sort(arr, 0, arr.length-1, temp);}public void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp){if (left>=right){return;}int mid = (left+right)/2;sort(arr, left, mid, temp);sort(arr, mid+1, right, temp);if (arr[mid] > arr[mid+1])merge(arr, left, mid, right, temp);}// 归并过程private void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {System.arraycopy(arr, left, temp, left, right-left+1);// 双指针比较并移动int i = left, j = mid+1;for (int k = left; k <= right; k++) {if (i > mid){arr[k] = temp[j];j++;}else if (j > right){arr[k] = temp[i];i++;}else if (temp[i] <= temp[j]){arr[k] = temp[i];i++;}else {arr[k] = temp[j];// 最关键的地方! 如果temp[i] > temp[j], 即左边指针位置元素大于右边, 则左边所有剩余元素都与右边指针位置元素形成逆序对res += (mid-i+1);j++;}}}
剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值.md
给定一个数组
nums和滑动窗口的大小k,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。
方法一 : 优先队列 大顶堆
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int[] num, int size) {ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();if (size > num.length || size < 1)return ans;// 大顶堆, 堆顶是最大值PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)heap.add(num[i]);ans.add(heap.peek());/* 维护一个大小为 size 的大顶堆 */for (int i = 0, j = i + size; j < num.length; i++, j++) {// 滑出窗口的数出堆, 新加入窗口的数入堆heap.remove(num[i]);heap.add(num[j]);// 取新窗口中的最大值ans.add(heap.peek());}return ans;}
方法二 : 单调队列
class Solution {public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {if(nums.length == 0 || k == 0) return new int[0];Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();int[] res = new int[nums.length - k + 1];for(int j = 0, i = 1 - k; j < nums.length; i++, j++) {// 删除 deque 中对应的 nums[i-1]if(i > 0 && deque.peekFirst() == nums[i - 1])deque.removeFirst();// 保持 deque 递减while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast() < nums[j])deque.removeLast();deque.addLast(nums[j]);// 记录窗口最大值if(i >= 0)res[i] = deque.peekFirst();}return res;}}
剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组.md
给定一个数组 A[0,1,…,n-1],请构建一个数组 B[0,1,…,n-1],其中 B[i] 的值是数组 A 中除了下标 i 以外的元素的积, 即 B[i]=A[0]×A[1]×…×A[i-1]×A[i+1]×…×A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
输入: [1,2,3,4,5]输出: [120,60,40,30,24]
public int[] constructArr(int[] a) {int len = a.length;if(len == 0) return new int[0];// 声明两个数组, 一个保存A[i]左边所有数的累乘和int[] dp1 = new int[len];// 一个保存A[i]右边所有数的累乘和int[] dp2 = new int[len];// 累乘A[i]左边的数dp1[0] = 1;for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {dp1[i] = dp1[i - 1] * a[i - 1];}// 累乘A[i]右边的数dp2[len - 1] = 1;for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {dp2[i] = dp2[i + 1] * a[i + 1];}// 求B[i] = 左边 * 右边for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {a[i] = dp1[i] * dp2[i];}return a;}
剑指 Offer II 001. 整数除法.md
给定两个整数
a和b,求它们的除法的商a/b,要求不得使用乘号'*'、除号'/'以及求余符号'%'。
示例:10 / 3 = 37 / -3 = -231 / 4 = 7
思路 :
( 7 / 3 = 2 ) ==> 7 = 3 * 2^1
( 10 / 3 = 3 ) ==> 10 = 3 2^1 + 3 2^0 = 3 * (2^1 + 2^0)
( 31/ 4 = 7 ) ==> 4 2^2 + 4 2^1 + 4 2^0 = 4 ( 2^2 + 2^1 + 2^0 )
public int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {// 特殊情况处理, 面试时先不写, 一般很难考虑到这一层if (dividend == Integer.MIN_VALUE && divisor == -1) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;// 将两数都转为正整数处理boolean isNegative = (dividend < 0 && divisor > 0) || (dividend > 0 && divisor < 0);long a = Math.abs((long) dividend);long b = Math.abs((long) divisor);int ans = 0;int shift = 31;// a 每次减去 b移shift位, 相当于 a - b * 2^shiftwhile (a >= b){while (a < b << shift){shift--;}a -= b << shift;ans += 1 << shift;}return isNegative ? -ans : ans;}
剑指 Offer II 002. 二进制加法.md
给定两个 01 字符串
a和b,请计算它们的和,并以二进制字符串的形式输出。输入为 非空 字符串且只包含数字
1和0。
输入: a = "1010", b = "1011"输出: "10101"
思路 : 模拟,设置是否要进位的标志变量flag
public static String addBinary(String a, String b) {// 模拟int aLen = a.length(), bLen = b.length();int maxLen = Math.max(aLen, bLen);boolean flag = false;StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < maxLen; i++) {char aChar = '0';char bChar = '0';if (aLen-i-1 >= 0) aChar=a.charAt(aLen-i-1);if (bLen-i-1 >= 0) bChar=b.charAt(bLen-i-1);int cur = aChar - '0' + bChar - '0';if (flag) cur++;if (cur > 1){ // 要进位了flag = true;cur = cur % 2;}else {flag = false;}ans.insert(0, cur);}if (flag) ans.insert(0, '1');return ans.toString();}
剑指 Offer II 003. 前 n 个数字二进制中 1 的个数.md
关键词 : 二进制 动态规划
给定一个非负整数
n,请计算0到n之间的每个数字的二进制表示中 1 的个数,并输出一个数组。每次计算一个数包含多少个1时,只需要将该数往右移动一位(等价于除2),此时有两种情况:
如果计算的是偶数,1的个数 = 移位后的数中1的个数
如果计算的是奇数,1的个数 = 移位后的数中1的个数 + 1 (因为移位前末尾有个1)
public int[] countBits(int n) {int[] ret = new int[n+1];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {ret[i] = ret[i>>1];if (i % 2 == 1) ret[i]++;}return ret;}
func countBits(n int) []int {ret := make([]int, n+1)for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {ret[i] = ret[i>>1]if i%2 == 1 {ret[i]++}}return ret}
剑指 Offer II 004. 只出现一次的数字 .md
关键词 : 数组 只出现一次的数 位运算
给你一个整数数组
nums,除某个元素仅出现 一次 外,其余每个元素都恰出现 三次 。请你找出并返回那个只出现了一次的元素。思路 : 累加每个数字每一个bit位上的1, 最后对每一位上1的个数对3取余数, 就得到了目标答案在这一位上是0还是1
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {int[] bitCounts = new int[32];// 对每个数字进行位移, 累加每一位上的1for (int num : nums) {for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {if ((num & 1) == 1) {bitCounts[i]++;}num = num >> 1;}}// 遍历记录数组, 每一位对3取余, 得到目标值每一位上的值int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {ans = ans<<1;ans += bitCounts[i] % 3;}return ans;}
剑指 Offer II 005. 单词长度的最大乘积.md
给定一个字符串数组 words,请计算当两个字符串 words[i] 和 words[j] 不包含相同字符时,它们长度的乘积的最大值。假设字符串中只包含英语的小写字母。如果没有不包含相同字符的一对字符串,返回 0。
输入: words = ["abcw","baz","foo","bar","fxyz","abcdef"]输出: 16解释: 这两个单词为 "abcw", "fxyz"。它们不包含相同字符,且长度的乘积最大。输入: words = ["a","aa","aaa","aaaa"]输出: 0解释: 不存在这样的两个单词。
思路,比较挫,暴力遍历每一个字符串,比较是否有相同字符,如果没有则更新maxProd
时间复杂度 O(n^2 + L1+L2)
public int maxProduct(String[] words) {int maxProd = 0;for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {for (int j = i+1; j < words.length; j++) {if (!containSameChar(words[i], words[j])){maxProd = Math.max(maxProd, words[i].length() * words[j].length());}}}return maxProd;}public boolean containSameChar(String word1, String word2){boolean[] arr = new boolean[26];for (int i = 0; i < word1.length(); i++) {arr[word1.charAt(i)-'a'] = true;}for (int i = 0; i < word2.length(); i++) {if (arr[word2.charAt(i) - 'a'])return true;}return false;}
剑指 Offer II 006. 排序数组中两个数字之和.md
给定一个已按照 升序排列 的整数数组
numbers,请你从数组中找出两个数满足相加之和等于目标数target。假设数组中存在且只存在一对符合条件的数字,同时一个数字不能使用两次。
输入:numbers = [1,2,4,6,10], target = 8
输出:[1,3]
解释:2 与 6 之和等于目标数 8 。因此 index1 = 1, index2 = 3 。思路 : 双指针, 一头一尾,慢慢向中间靠拢
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {int index1 = 0, index2 = numbers.length-1;while (true){int curSum = numbers[index1] + numbers[index2];if (curSum == target){return new int[]{index1 , index2};}else if (curSum < target){index1++;}else {index2--;}}}
剑指 Offer II 008. 和大于等于 target 的最短子数组.md
关键词 数组 连续子数组 最小长度 滑动窗口
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target 。
找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [numsl, numsl+1, …, numsr-1, numsr] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0 。
思路, 滑动窗口
public int minSubArrayLen1(int s, int[] nums) {int left = 0, right = 0;int curSum = 0, ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;while (right < nums.length) {curSum += nums[right++];while (curSum >= s) {ans = Math.min(ans, right - left);curSum -= nums[left++];}}return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : ans;}
多线程交替打印.md
public class 多线程交替输出 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 推荐使用方法一和三,最简单method3();}// 方法一public static void method1(){WaitNotify waitNotify = new WaitNotify(1, 5);new Thread(()->waitNotify.print("hello1", 1, 2),"t1").start();new Thread(()->waitNotify.print("hello2", 2, 3),"t2").start();new Thread(()->waitNotify.print("hello3", 3, 1),"t3").start();}// 方法二public static void method2(){AwaitSignal awaitSignal = new AwaitSignal(5);Condition t1 = awaitSignal.newCondition();Condition t2 = awaitSignal.newCondition();Condition t3 = awaitSignal.newCondition();new Thread(()->awaitSignal.print("hello1", t1, t2), "t1").start();new Thread(()->awaitSignal.print("hello2", t2, t3), "t2").start();new Thread(()->awaitSignal.print("hello3", t3, t1), "t3").start();awaitSignal.lock();try {t1.signal();} finally {awaitSignal.unlock();}}// 方法三static Thread t1;static Thread t2;static Thread t3;public static void method3(){ParkUnpark parkUnpark = new ParkUnpark(5);t1 = new Thread(() -> parkUnpark.print("hello1", t2));t2 = new Thread(() -> parkUnpark.print("hello2", t3));t3 = new Thread(() -> parkUnpark.print("hello3", t1));t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();LockSupport.unpark(t1);}}// 第一种方法, 使用Wait() NotifyAll()class WaitNotify{private int flag;private int loopNumber;public void print(String str, int flag, int nextFlag){for (int i = 0; i < this.loopNumber; i++) {synchronized (this){while (this.flag != flag){try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + str);this.flag = nextFlag;this.notifyAll();}}}public WaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber) {this.flag = flag;this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}}// 方法二 : 使用ReentrantLock的Await 和 Signalclass AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock{private int loopNumber;public AwaitSignal(int loopNumber) {this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}public void print(String str, Condition current, Condition next){for (int i = 0; i < this.loopNumber; i++) {this.lock();try {// 一上来先进阻塞队列current.await();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + str);// 打印完,唤醒下一个next.signal();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {this.unlock();}}}}// 方法三 : 使用Park Unparkclass ParkUnpark{private int loopNumber;public void print(String str, Thread next){for (int i = 0; i < this.loopNumber; i++) {LockSupport.park();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + str);LockSupport.unpark(next);}}public ParkUnpark(int loopNumber) {this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}}
奇升偶降链表.md
字节跳动高频题——排序奇升偶降链表
给定一个奇数位升序,偶数位降序的链表,将其重新排序。
输入: 1->8->3->6->5->4->7->2->NULL输出: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL
思路 :
- 按奇偶位置拆分链表, 得1->3->5->7->NULL和8->6->4->2->NULL
- 反转偶链表,得1->3->5->7->NULL和2->4->6->8->NULL
- 合并两个有序链表,得1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL
时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度O(1)。
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return head;}// 偶数链表头ListNode head2 = head.next;// 奇数节点指针头ListNode odd = head;// 偶数节点指针ListNode even = head2;// 拆分成两个链表while (even != null && even.next != null) {odd.next = even.next;odd = odd.next;even.next = odd.next;even = even.next;}odd.next = null;// 反转偶数链表ListNode newHead2 = reverse(head2);// 链表合并return mergeTwoLists(head, newHead2);}// 合并两个有序链表public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);// p指针指向合并后的最后一个节点ListNode p = dummyHead;while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {if (head1.val <= head2.val) {p.next = head1;head1 = head1.next;} else {p.next = head2;head2 = head2.next;}p = p.next;}// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可p.next = head1 == null ? head2 : head1;return dummyHead.next;}// 迭代反转链表private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode temp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}return pre;}
手撕单例模式.md
懒汉式(DCL : double check lock)
class LazySingleton{private static volatile LazySingleton instance;private LazySingleton(){}public static LazySingleton getInstance() {if (instance == null){synchronized (LazySingleton.class){if (instance == null)instance = new LazySingleton();}}return instance;}}
饿汉式
class HungrySingleton{private static HungrySingletonTest instance = new HungrySingletonTest();private HungrySingleton(){}public static HungrySingletonTest getInstance() {return instance;}}
手撕归并排序.md
public void mergeSort(int[] arr){// temp是一个辅助归并的空数组int[] temp = new int[arr.length];sort(arr, 0, arr.length-1, temp);}public void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp){if (left>=right){return;}int mid = (left+right)/2;sort(arr, left, mid, temp);sort(arr, mid+1, right, temp);// 优化点, 面试中可以后面补充, 如果左边最后一个小于或等于右边第一个则不用归并if (arr[mid] > arr[mid+1])merge(arr, left, mid, right, temp);}// 归并过程private void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {// 归并时, 将原数组中需要归并的部分复制到辅助数组中System.arraycopy(arr, left, temp, left, right-left+1); // 优化点// 双指针比较并移动int i = left, j = mid+1;for (int k = left; k <= right; k++) {// 如果左边归并完了, 直接放入右边的元素即可if (i > mid){arr[k] = temp[j];j++;}else if (j > right){ // 如果右边归并完了, 直接放入左边的元素即可arr[k] = temp[i];i++;}else if (temp[i] <= temp[j]){ // 取二者之中较小arr[k] = temp[i];i++;}else {arr[k] = temp[j];j++;}}}
手撕线程池.md
关键在阻塞队列
class ThreadPool{// 核心线程数private int coreSize;// 阻塞队列(任务集合)private BlockingDeque<Runnable> taskQueue;private int queueCapacity;// 线程集合private HashSet<Worker> workers;public ThreadPool(int coreSize, int queueCapacity) {this.coreSize = coreSize;this.taskQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(queueCapacity);this.queueCapacity = queueCapacity;this.workers = new HashSet<>();}// 执行任务public void execute(Runnable task){synchronized (workers) {// 1. 判断当前线程数是否等于coreSizeif (workers.size() < coreSize){// 若小于, 则创建新线程执行任务Worker worker = new Worker(task);worker.start();// worker 加入线程集合workers.add(worker);}else{// 若等于,则放入阻塞队列// 情况一: 阻塞队列不满, 直接添加if (taskQueue.size() < queueCapacity) {System.out.println("加入任务队列");taskQueue.add(task);}else {System.out.println("任务被抛弃...");}// 情况二: 阻塞队列满, 拒绝策略(啥也不做)}}}// 线程包装类class Worker extends Thread{private Runnable task;public Worker(Runnable task) {this.task = task;}@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行任务// task 任务执行完毕后, 或者task为空时, 从任务队列中取出任务执行while (task != null || !taskQueue.isEmpty()){try {if (task == null)task = taskQueue.take();task.run();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {task = null;}}// 任务队列中没有任务, 则销毁当前workersynchronized (workers) {workers.remove(this);}}}}