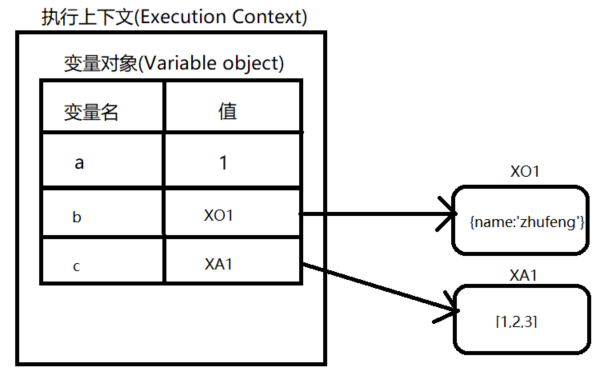
JavaScript 代码执行一段可执行代码(executable code)时,会创建对应的执行环境,这个执行环境就叫做执行上下文(Execution Context);上下文又分为全局上下文和函数上下文
每个执行上下文会有三个重要的属性:
- 变量对象(Variable object,VO),基础数据类型就保存在这个变量中
- 作用域链(Scope chain)
- this
引用类型的值保存在堆里,我们通过引用地址来操作对象
function task(){var a = 1;var b = {name:'zhufeng'}var c = [1,2,3];}
let ExecutionContext{VO:{a:1,b:'X01'c:'XA1'}}
复制
基本数据类型
- 基本数据类型复制的是值本身
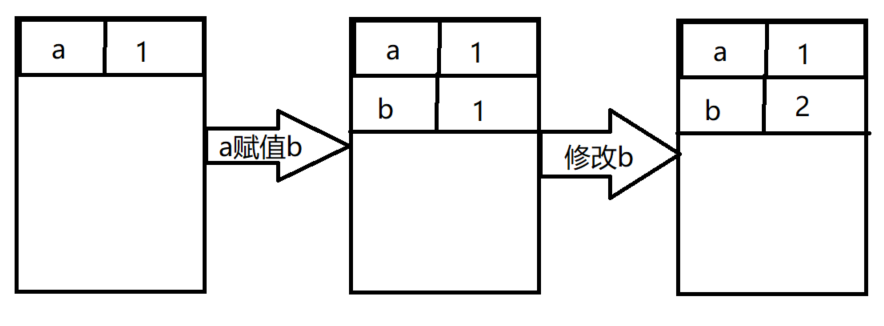
```javascript var ExecuteContext = { VO: { a: 1 } };var a = 1;var b = a;b = 2;console.log(a);1
ExecuteContext.VO.b = ExecuteContext.VO.a; ExecuteContext.VO.b = 2; console.log(ExecuteContext.VO.a);
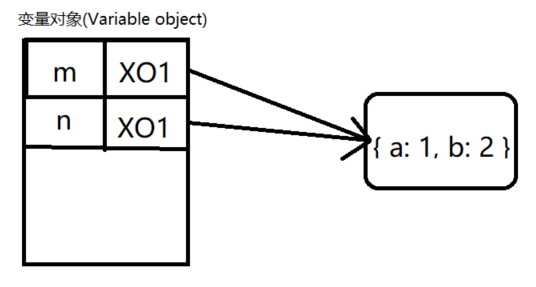
<a name="q1z5n"></a>## 引用类型- 引用数据类型复制的是引用地址指针```javascriptvar m = { a: 1, b: 2 };var n = m;n.a = 10;console.log(m.a);// 10
var ExecuteContext = {VO: { m: { a: 1, b: 2 } }};ExecuteContext.VO.b = ExecuteContext.VO.a;ExecuteContext.VO.a = 10;console.log(ExecuteContext.VO.a);
执行上下文周期
- 分为编译阶段
- 创建变量VO:
- 处理参数,把参数放入vo
- 扫描代码,找出function声明,从上往下依次执行,在编译阶段,会处理所有的函数声明,如果有重复的函数声明,后面的会覆盖前面的声明。
- 扫描var关键字,var是不赋值的,只声明,值是undefined
- 在编译阶段是不会扫描let的,也不会将let声明的变量放在VO上
- 确定作用域链
- 当前执行上下文的所有父级的vo对象[oneVO,globalVO]
- 确定this指向
- 创建变量VO:
- 执行阶段
- 变量赋值
- 函数赋值
- 代码执行
执行栈(多执行上下文栈)
执行上下文的分类
- js代码在执行的时候会进去一个执行上下文,可以理解为当前代码的运行环境
在js运行环境主要分为全局执行上下文和函数执行上下文
js在执行的时候创建多个执行上下文,js引擎会通过栈来管理这些上下文
- 执行上下文栈,简称调用栈,执行栈用于存储代码在执行期间的上下文,具有LIFO(Last in First Output),后进先出
- 栈底永远是全局上下文,栈顶为当前执行上下文
- 当开启一个函数执行时会创建一个执行上下文存储在调用栈中,执行完毕后会自动出栈
作用域链
作用域链是当前执行环境与上层执行环境的一系列变量对象组成,它保证了当前执行环境对符合访问权限的变量和函数的有序访问
```javascript var globalExecuteContext = { VO: { setTimeout: ‘setTimeout’ }, scopeChain:[globalExecuteContextVo] //作用域链 } var executeContextStack = [globalExecuteContext]; var oneExecuteContext = { VO: { a: 1 }, /// 作用域链创建时机是在上层执行上下来创建的时候就确定了 scopeChain:[oneExecuteContextVO,globalExecuteContextVo] //作用域链 } executeContextStack.push(oneExecuteContext); var twoExecuteContext = { VO: { b: 2 }, scopeChain:[twoExecuteContextVO,oneExecuteContextVO,globalExecuteContextVo] //作用域链 } executeContextStack.push(twoExecuteContext); var threeExecuteContext = { VO: { c: 3 }, scopeChain:[threeExecuteContextVO,twoExecuteContextVO,oneExecuteContextVO,globalExecuteContextVo] //作用域链 } executeContextStack.push(threeExecuteContext); console.log(executeContextStack);function one() {var a = 1;debugger;function two() {var b = 1;debugger;function three() {var c = 1;debugger;}three();debugger;}two();debugger;}one();
executeContextStack.pop(); executeContextStack.pop(); executeContextStack.pop();
<a name="cvwMa"></a># 思考题以下两段代码执行的结果一样,但是两段代码究竟有哪些不同呢?```javascriptvar scope = "global scope";function checkscope(){var scope = "local scope";function f(){return scope;}return f();}checkscope();
var scope = "global scope";function checkscope(){var scope = "local scope";function f(){return scope;}return f;}checkscope()();
答:执行上下文栈的变化不一样
第一段代码
ECStack.push(<checkscope> functionContext);ECStack.push(<f> functionContext);ECStack.pop();ECStack.pop();
第二段代码
ECStack.push(<checkscope> functionContext);ECStack.pop();ECStack.push(<f> functionContext);ECStack.pop();