[open()](https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/functions.html#open)
Python open() 方法用于打开一个文件,并返回文件对象,在对文件进行处理过程都需要使用到这个函数,如果该文件无法被打开,会抛出 OSError
[open()](https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/functions.html#open) 最常用的有两个参数: open(filename, mode)。
filename:第一个参数是包含文件名的字符串mode:
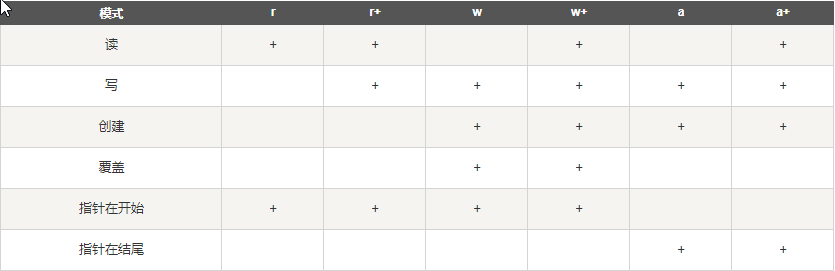
注意:使用 open() 方法一定要保证关闭文件对象,即调用 close() 方法。
open()案例
# f为文件对象# workfile:包含文件名称和路径的文件全称,可以是绝对或者相对路径# w:文件的读取模式f = open('workfile', 'w').... #文件对象的操作f.close() #文件对象操作完成后,必须关闭文件对象
[with](https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/reference/compound_stmts.html#with) open()在处理文件对象时,最好使用
with关键字。 优点是当子句体结束后文件会自动正确关闭,即使在某个时刻引发了异常。 而且使用with相比等效的try-finally代码块要简短得多
[with](https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/reference/compound_stmts.html#with) open()案例
# f是文件对象with open('workfile') as f:# 通过文件对象方法读取数据read_data = f.read()
open()完整的语法格式为:
open(file, mode=’r’, buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True,opener=None)
参数说明:
- file: 必需,文件路径(相对或者绝对路径)。
- mode: 可选,文件打开模式
- buffering: 设置缓冲
- encoding: 一般使用utf8
- errors: 报错级别
- newline: 区分换行符
- closefd: 传入的file参数类型
- opener:
文件对象方法
file.close()
| file.close()
关闭文件。关闭后文件不能再进行读写操作。 | | —- |
文件读方法
file.read([size])
| file.read([size]) 从文件读取指定的字节数,如果未给定或为负则读取所有。 |
|---|
file.readline([size])
| file.readline([size]) 读取整行,包括 “\n” 字符。 |
|---|
file.readline()案例
# 文件 runoob.txt 的内容如下:# 1:www.runoob.com# 2:www.runoob.com# 3:www.runoob.com# 4:www.runoob.com# 5:www.runoob.com# 读取文件的内容:# 实例:file_readline.py#!/usr/bin/python3# 打开文件fo = open("runoob.txt", "r+") #r+ 表示从头开始以读写的方式打开文件print ("文件名为: ", fo.name)line = fo.readline() #读取第一行print ("读取第一行 %s" % (line))line = fo.readline(5) # 读取第一行的前五个字符print ("读取的字符串为: %s" % (line))# 关闭文件fo.close()以上实例输出结果为:文件名为: runoob.txt读取第一行 1:www.runoob.com读取的字符串为: 2:www
file.readlines([sizeint])
| file.readlines([sizeint]) 读取所有行并返回列表,若给定sizeint>0,返回总和大约为sizeint字节的行, 实际读取值可能比 sizeint 较大, 因为需要填充缓冲区。 |
|---|
file.readlines()案例
# 文件 runoob.txt 的内容如下:# 1:www.runoob.com# 2:www.runoob.com# 3:www.runoob.com# 4:www.runoob.com# 5:www.runoob.com# 循环读取文件的内容:#!/usr/bin/python3# 打开文件fo = open("runoob.txt", "r")print ("文件名为: ", fo.name)for line in fo.readlines(): #依次读取每行line = line.strip() #去掉每行头尾空白print ("读取的数据为: %s" % (line))# 关闭文件fo.close()# 以上实例输出结果为:文件名为: runoob.txt读取的数据为: 1:www.runoob.com读取的数据为: 2:www.runoob.com读取的数据为: 3:www.runoob.com读取的数据为: 4:www.runoob.com读取的数据为: 5:www.runoob.com
文件写方法
file.write(str)
| file.write(str) 参数 str — 要写入文件的字符串。返回值 返回的是写入的字符长度。 |
|---|
file.write(str)案例
# 文件runoob.txt的内容如下:## 1: www.runoob.com# 2: www.runoob.com# 3: www.runoob.com# 4: www.runoob.com# 5: www.runoob.com## 以下实例演示了write()方法的使用:#!/usr/bin/python3# 打开文件fo = open("runoob.txt", "r+")str = "6:www.runoob.com"# 在文件末尾写入一行fo.seek(0, 2)line = fo.write( str )# 查看文件内容:$ cat runoob.txt1:www.runoob.com2:www.runoob.com3:www.runoob.com4:www.runoob.com5:www.runoob.com6:www.runoob.com # 新写入的一行文本
file.writelines(sequence)
| file.writelines(sequence)
向文件写入一个序列字符串列表,如果需要换行则要自己加入每行的换行符。
- 参数
str — 要写入文件的字符串序列。
- 返回值
该方法没有返回值 |
| —- |
| |
file.writelines()案例
#!/usr/bin/python3# 打开文件fo = open("test.txt", "w")print ("文件名为: ", fo.name)seq = ["菜鸟教程 1\n", "菜鸟教程 2"]fo.writelines( seq )# 关闭文件fo.close()# 查看文件内容:$ cat test.txt菜鸟教程 1菜鸟教程 2

