简单讲其实就两步:
1、引入 starter
2、开启所有 endpoint
1、引入 starter
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>
2、测试
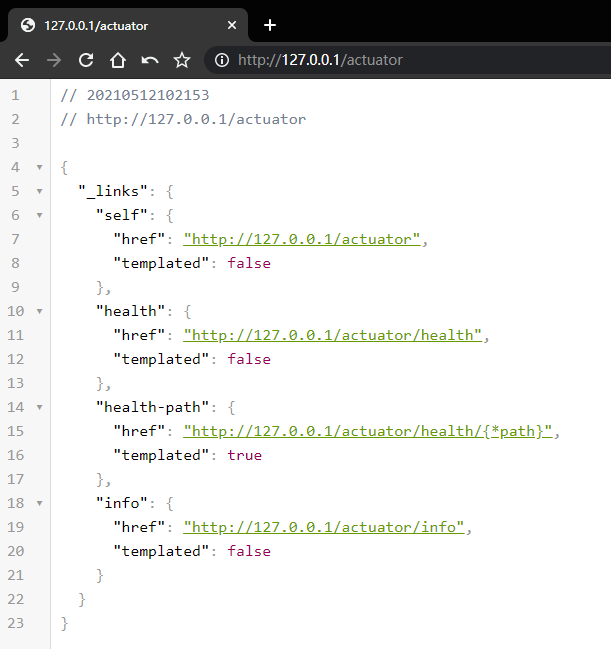
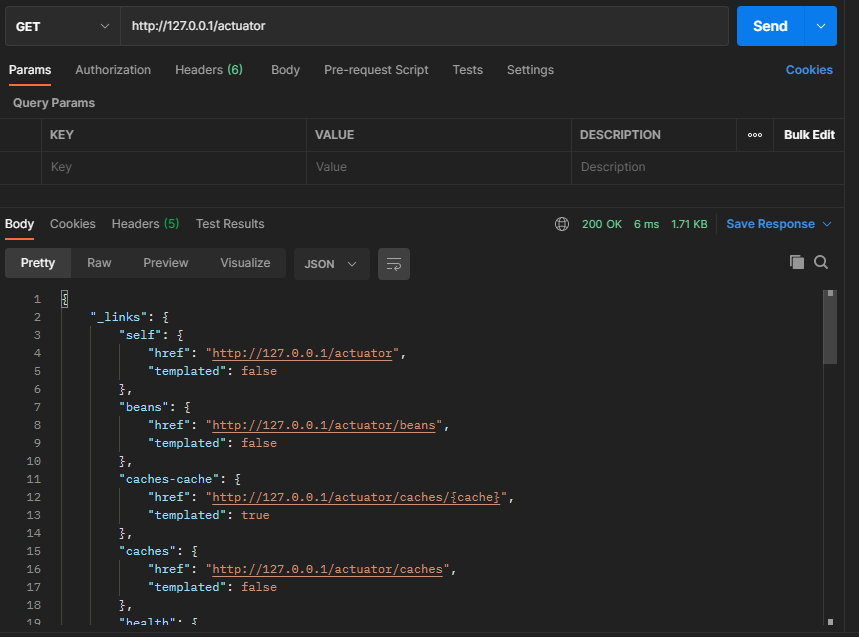
2.1、目前可用的指标
2.2、当前应用的健康状况
http://127.0.0.1/actuator/health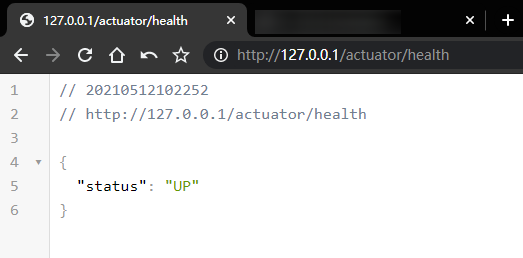
2.3、当前应用的详细信息
http://127.0.0.1/actuator/info
3、endpoint
3.1、概述
例如:http://127.0.0.1/actuator/info
我们把 actuator 后面的 info 称为一个 endpoint。
spring 官方有非常多的 endpoint:
文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/production-ready-features.html#production-ready-endpoints
这些 endpoint 都是我们可以监控的端点,但不是全部都默认开启的。
3.2、最常使用的端点
| ID | 描述 |
|---|---|
auditevents |
暴露当前应用程序的审核事件信息。需要一个AuditEventRepository组件。 |
beans |
显示应用程序中所有Spring Bean的完整列表。 |
caches |
暴露可用的缓存。 |
conditions |
显示自动配置的所有条件信息,包括匹配或不匹配的原因。 |
configprops |
显示所有@ConfigurationProperties。 |
env |
暴露Spring的属性ConfigurableEnvironment |
flyway |
显示已应用的所有Flyway数据库迁移。 需要一个或多个 Flyway组件。 |
health |
显示应用程序运行状况信息。 |
httptrace |
显示HTTP跟踪信息(默认情况下,最近100个HTTP请求-响应)。需要一个HttpTraceRepository组件。 |
info |
显示应用程序信息。 |
integrationgraph |
显示Spring integrationgraph 。需要依赖spring-integration-core。 |
loggers |
显示和修改应用程序中日志的配置。 |
liquibase |
显示已应用的所有Liquibase数据库迁移。需要一个或多个Liquibase组件。 |
metrics |
显示当前应用程序的“指标”信息。 |
mappings |
显示所有@RequestMapping路径列表。 |
scheduledtasks |
显示应用程序中的计划任务。 |
sessions |
允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。需要使用Spring Session的基于Servlet的Web应用程序。 |
shutdown |
使应用程序正常关闭。默认禁用。 |
startup |
显示由ApplicationStartup收集的启动步骤数据。需要使用SpringApplication进行配置BufferingApplicationStartup。 |
threaddump |
执行线程转储。 |
如果您的应用程序是Web应用程序(Spring MVC,Spring WebFlux或Jersey),则可以使用以下附加端点:
| ID | 描述 |
|---|---|
heapdump |
返回hprof堆转储文件。 |
jolokia |
通过HTTP暴露JMX bean(需要引入Jolokia,不适用于WebFlux)。需要引入依赖jolokia-core。 |
logfile |
返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置logging.file.name或logging.file.path属性)。支持使用HTTPRange标头来检索部分日志文件的内容。 |
prometheus |
以Prometheus服务器可以抓取的格式公开指标。需要依赖micrometer-registry-prometheus。 |
最常用的Endpoint
- Health:监控状况
- Metrics:运行时指标
- Loggers:日志记录
3.3、两种监控方式
Spring Boot 底层有两种监控模式:
JMX:默认暴露所有 EndPoint ( jconsole )
HTTP:默认只暴露部分 EndPoint
可以查看两种监控方式默认暴露的对比表格。
3.4、以 Web 方式开启所有 endpoint
修改配置,以 application.yml 方式为例:
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: true # 默认开启所有监控端点web:exposure:include: '*' # 以 Web 方式暴露所有端点
3.5、常用的 metrics endpoint
查看有哪些具体指标:http://127.0.0.1/actuator/metrics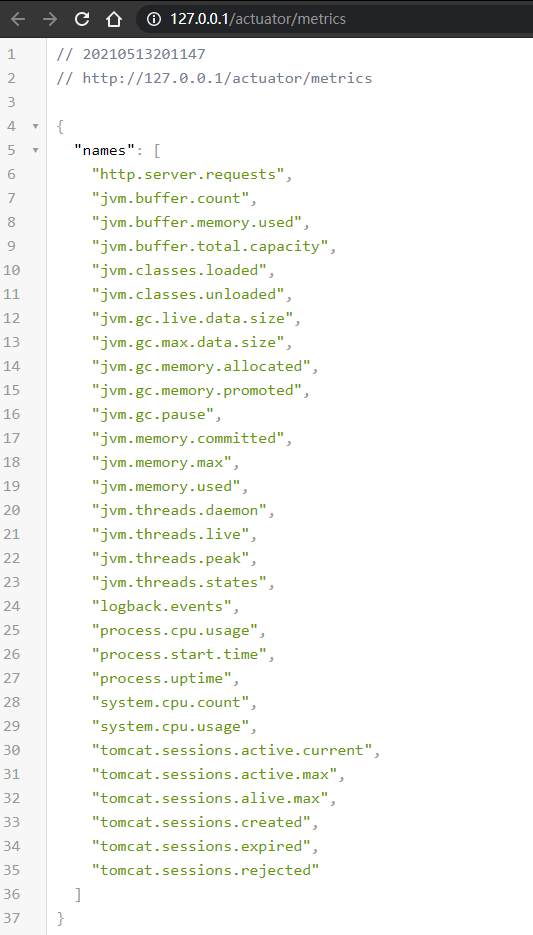
根据需求,根据 names 里的各个指标名访问,例如:
http://127.0.0.1/actuator/metrics/http.server.requests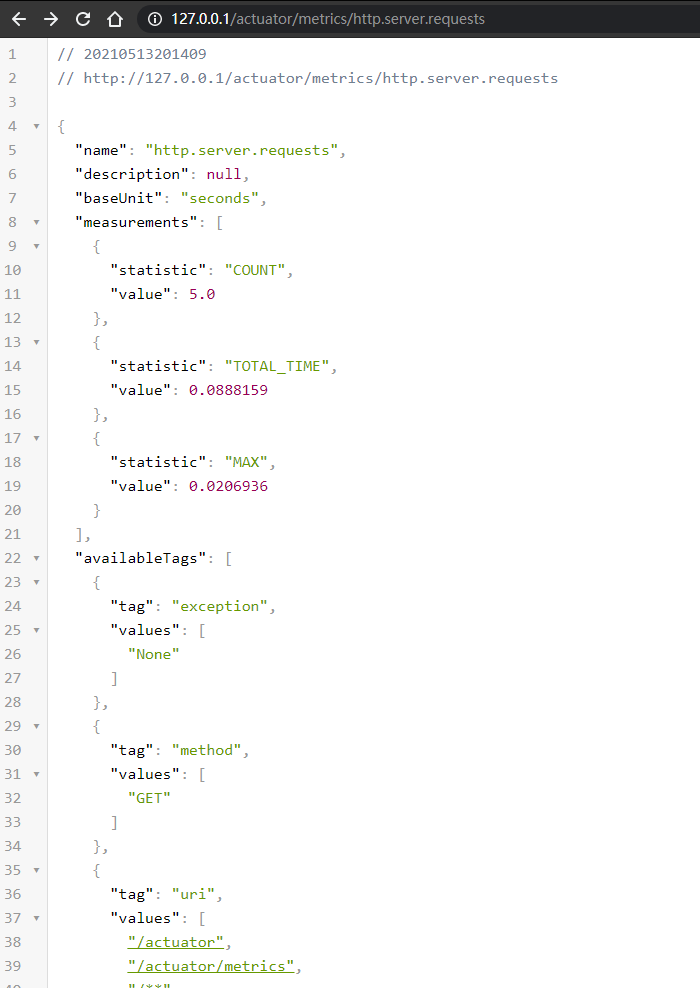
http://127.0.0.1/actuator/metrics/jvm.gc.memory.allocated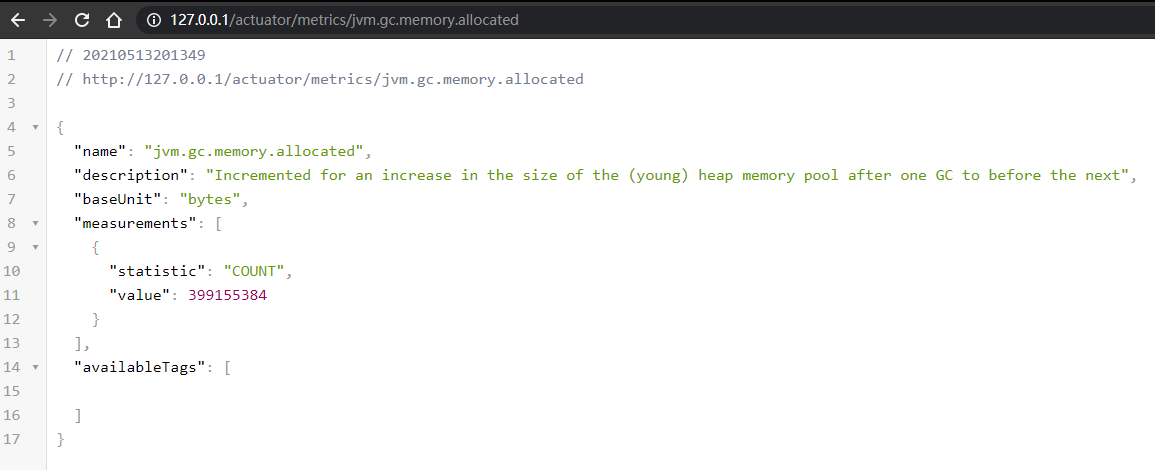
4、管理 Endpoints
4.1、开启与禁用Endpoints
- 默认所有的Endpoint除过shutdown都是开启的。
需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint。配置模式为 management.endpoint.
.enabled = true management:endpoint:beans:enabled: true
或者禁用所有的Endpoint然后手动开启指定的Endpoint
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: falseendpoint:beans:enabled: truehealth:enabled: true
4.2、定制 Endpoint
定制化一个我们自己的 endpoint
@Component@Endpoint(id = "container")public class DockerEndpoint {@ReadOperationpublic Map getDockerInfo(){return Collections.singletonMap("info","docker started...");}@WriteOperationprivate void restartDocker(){System.out.println("docker restarted....");}}
场景:开发ReadinessEndpoint来管理程序是否就绪,或者LivenessEndpoint来管理程序是否存活;
当然,这个也可以直接使用 https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/production-ready-features.html#production-ready-kubernetes-probes