服务端渲染 SSR
import Support from ‘../../../src/components/Support’
icejs 支持服务端渲染(即 SSR)能力,开发者可以按需一键开启 SSR 的模式,相比于传统的客户端渲染,SSR 常用于两个场景:1. 有 SEO 诉求;2. 对首屏渲染速度要求比较高。相比于传统的 SSR 方案,icejs 提供的 SSR 能力具有以下特性:
- 支持一键开启/关闭 SSR 能力
- 与服务端低耦合,无论是传统的 Nodejs 应用还是 Serverless 模式,都可以非常简单的集成
- 支持页面级服务端加载数据
开启 SSR
在工程配置文件 build.json 中开启 SSR:
{"ssr": true}
配置完之后即可启用 SSR,同理置为 false 即可关闭 SSR 功能。此时重新执行 npm run start 即可看到页面中直出的 HTML:
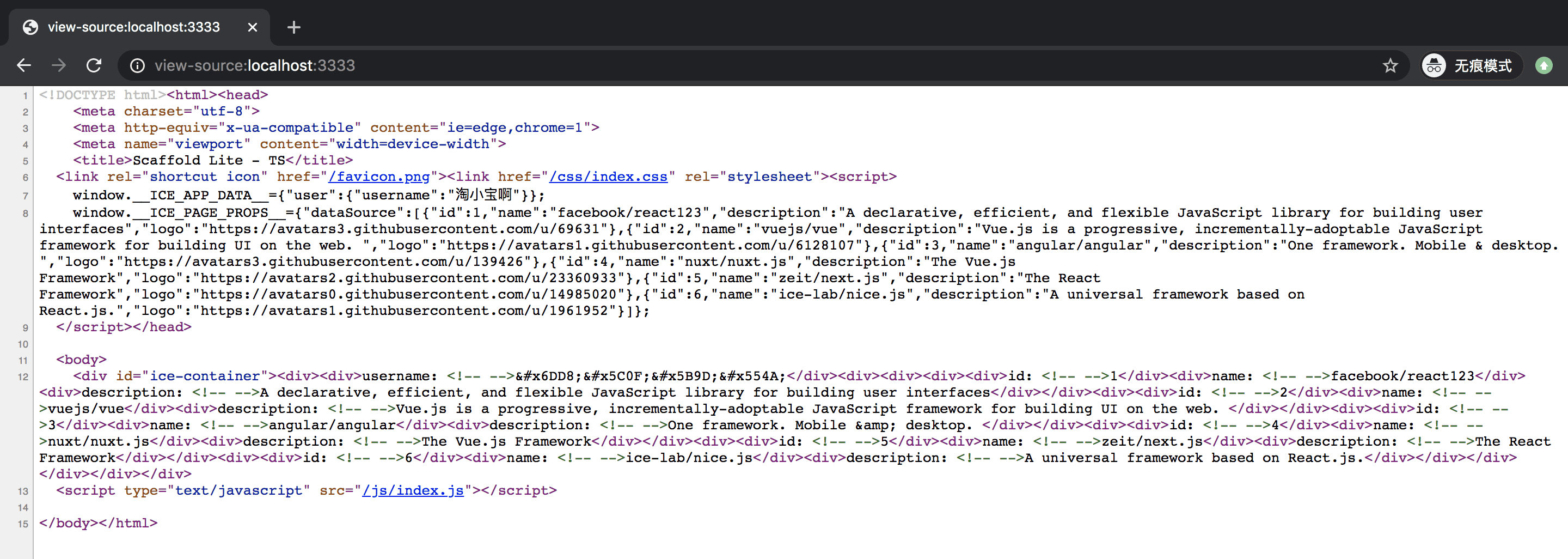
应用级数据
获取应用初始化数据
在 src/app.ts 中通过声明 app.getInitialData 获取全局数据,同时支持通过 API 在 View 中消费该数据,具体请参考 app.getInitialData 。
开启了 SSR 的行为说明:
- 服务端渲染时直接调用
app.getInitialData()获取数据并渲染应用,同时将数据注入到 HTML 的全局变量中 - 浏览器端渲染(hydrate)时直接通过全局变量获取初始数据,不再调用
app.getInitialData()
未开启 SSR 的行为说明:
- 浏览器端会同步调用
app.getInitialData() - 调用完成后执行页面 render 逻辑
页面级数据
SEO 场景下,需要访问每个页面时都能够返回实际的 DOM 节点,此时如果把数据放到全局的 initialData 里管理成本会非常高,因此 icejs 支持页面级通过 getInitialProps 来获取自身需要的数据。
注意:如果只是追求首屏加载速度,不推荐使用页面级的 getInitialProps,因为这在一定程度上会延长服务端渲染直出 HTML 的时间。
在页面级组件中通过 Component.getInitialProps 来获取页面初始数据:
import { request } from 'ice';function Home({ stars }) {return <div>icejs stars: {stars}</div>;}+ Home.getInitialProps = async (ctx) => {+ const res = await request.get('https://api.github.com/repos/alibaba/ice');+ return { stars: res.data.stargazers_count };+ }export default Home;
开启了 SSR 的行为说明:
- 服务端渲染时调用对应页面的
getInitialProps,然后在渲染页面组件时将数据作为 props 传递给页面组件,同时将数据注入到 HTML 全局变量上 - 浏览器端渲染(hydrate)时不再调用
getInitialProps,会直接通过全局变量获取初始数据并作为组件的 props
未开启 SSR 的行为说明:
- 浏览器端渲染时,先进行组件渲染(render),然后在
useEffect(() => {}, [])中调用Component.getInitialProps - getInitialProps 执行完成后,触发组件 rerender 此时拿到的新的 props 数据
:::caution
页面组件中需要兼容好 getInitialProps() 未执行时 props 取不到对应数据(比如上述的 props.stars)的情况
:::
构建产物
当应用开发完成时,通过运行 npm run build 默认构建后的文件如下:
.├── build│ ├── index.html│ ├── css/index.css│ ├── js/index.js│ ├── loadable-stats.json+ | ├── server+ | │ ├── chunk1.js+ | │ ├── chunk2.js+ | │ └── index.js
服务端集成
本地开发时 icejs 通过内置的 dev-server 做服务端渲染,应用发布后则需要对应的服务端自行渲染。首先建议将整个 build 产物复制到服务端指定目录:
.├── build/│ ├── loadable-stats.json // 可选,仅在 webpack 模式下存在| └── server/└── app.js // 服务端应用入口
app.js 核心逻辑如下:
const path = require('path');const Koa = require('koa');const Router = require('@koa/router');const app = new Koa();const router = new Router();router.get('/', (ctx, next) => {const buildDir = path.join(__dirname, './build');const serverBundlePath = path.resolve(buildDir, 'server/index.js');// vite 模式下不存在 loadable-stats.json,loadableStatsPath 传入 false 即可const webStatsPath = path.resolve(buildDir, 'loadable-stats.json');const serverRender = require(serverBundlePath);const { html, error, redirectUrl } = await serverRender.default(ctx,{loadableStatsPath: webStatsPath,},);if (redirectUrl) {console.log('[SSR Redirect]', `Redirect to the new path ${redirectUrl}`);// 重定向ctx.res.redirect(302, redirectUrl);} else {if (error) {console.log('[SSR ERROR]', 'serverRender error', error);}ctx.res.body = html;}});app.use(router.routes())app.listen(3000);
icejs 构建出来的 server/index.js 会暴露出 render 方法供服务端调用,该方法提供以下参数:
- ctx: 必填,当前请求上下文,ctx 的格式如下:
ctx.req:HTTP request 对象(仅在 server 端输出)ctx.res:HTTP response 对象(仅在 server 端输出)ctx.pathname:当前路由路径ctx.query:请求参数对象ctx.path:URL 路径(包括请求参数)ctx.ssrError:服务端渲染时错误信息(仅在 client 端输出)
- options:
- loadableStatsPath: 必填,loadable-stats.json 本地路径
- htmlTemplate: 选填,html 模板内容
- initialData: 选填,如果不填写,服务端则会调用前端声明的
app.getInitialData()方法,但如果对性能追求比较极致,服务端则可以自行获取对应数据并通过initialData传入。(调用前端的 getInitialData 一般会发起 HTTP 请求,但是服务端有可能通过缓存/数据库来查询,速度会快一点)
高阶用法
动态设置页面 Meta 标签
在 SEO 场景下,往往需要动态设置每个页面的标题和 Meta 标签,以更好地让搜索引擎抓取页面内容。使用步骤如下:
// pages/Home/index.jsximport React from 'react';import { Head } from 'ice';const Home = (props) => {const { title, description } = props;return (<div><Head><title>{title}</title><meta name="description" content={description} /><meta name="keywords" content="Home Keywords" /></Head></div>);};Home.getInitialProps = async () => {// 模拟服务端返回 title 和 description 数据const res = await request('/detail');return {title: res.data.title,description: res.data.description,};};
服务端请求必须使用绝对的 URL 路径
开启了 SSR 之后,app.getInitialData 以及 Home.getInitialProps 都会在服务端下执行,服务端发请求必须用绝对路径不能用相对路径,因此这两个方法里如果出现异步请求,请务必使用绝对路径,或者正确设置 request.baseURL。推荐做法:
src/config.js 中动态区分环境并配置 baseURL:
if (process.env.__IS_SERVER__) {// 动态扩展环境:服务端通过环境变量区分,此处以 Midway 为例globalThis.__app_mode__ = process.env.MIDWAY_SERVER_ENV;} else {// 动态扩展环境globalThis.__app_mode__ = globalThis.__env__;}export default {local: {baseURL: `http://localhost:${process.env.SERVER_PORT}`,},daily: {baseURL: 'https://ice-ssr.daily.fx.net',},prod: {baseURL: 'https://ice-ssr.fx.com',},};
然后在 src/app.js 中设置 request.baseURL:
import { runApp, IAppConfig } from 'ice';const appConfig: IAppConfig = {+ request: {+ baseURL: config.baseURL+ }};runApp(appConfig);

