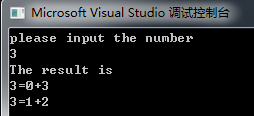
1.输出和为一个给定整数的所有组合,例如 n=5 ;5=1+4;5=2+3(相加的数不能重复);则输出 1,4;2,3。
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(void){unsigned long int i,j,k;cout << "please input the number" << endl;cin >> i;if( i % 2 == 0)j = i / 2;elsej = i / 2 + 1;cout << "The result is" << endl;for(k = 0; k < j; k++)cout << i << "=" << k << "+" << i-k << endl;return 0;}
2.递规反向输出字符串的例子,可谓是反序的经典例程
#include<iostream>void inverse(char *p){if (*p == '\0')return;inverse(p+1);printf("%c", *p);}int main(int argc, char *argv[]){inverse("abc\0");return 0;}
3、写一段程序,找出数组第K大小的数,输出数所在的位置。例如{2,4,3,4,7}中,第一大的数是7,位置在4。第二大、第三大的数都是4,位置在1、3随便输出哪一个均可。
函数接口为:int find_orderk(const int* narry,const int n,const int k)
要求算法复杂度不能是 O(n^2)
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int Partition(int*L, int low, int high){int temp = L[low];int pt = L[low];while (low < high){while (low < high && L[high] >= pt)--high;L[low] = L[high];while (low < high && L[low] <= pt)++low;L[low] = temp;}L[low] = temp;return low;}void QSort(int*L, int low, int high){if (low < high){int pl = Partition(L, low, high);QSort(L, low, pl - 1);QSort(L, pl + 1, high);}}int main(){int narry[100], addr[100];int sum = 1, t;cout << "Input number:" << endl;cin >> t;while (t != -1){narry[sum] = t;addr[sum - 1] = t;sum++;cin >> t;}sum -= 1;QSort(narry, 1, sum);for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)cout << narry[i] << '\t';cout << endl;int k;cout << "Please input place you want:" << endl;cin >> k;int aa = 1;int kk = 0;for (;;){if (aa == k)break;if (narry[kk] != narry[kk + 1]){aa += 1;kk++;}}cout << "The NO." << k << "number is:" << narry[sum - kk] << endl;cout << "And it's place is:";for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++){if (addr[i] == narry[sum - kk])cout << i << '\t';}return 0;}