回溯是一种渐进式寻找并构建问题解决方式的策略。我们从一个可能的动作开始并试着用这个动作解决问题。如果不能解决,就回溯并选择另-个动作直到将问题解决。根据这种行为,回溯算法会尝试所有可能的动作(如果更快找到了解决办法就尝试较少的次数)来解决问题。
有一些可用回溯解决的著名问题:
- 骑士巡逻问题.
- N皇后问题
- 迷宫老鼠问题
- 数独解题器
骑士周游问题

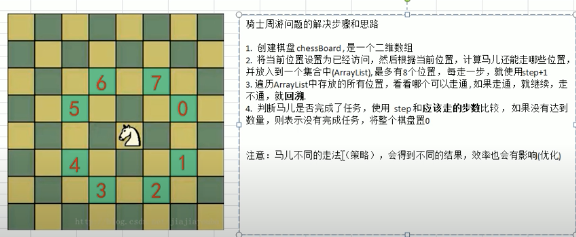
console.log(run(3, 4, 0, 0))// X、Y表示棋盘X轴、Y轴大小 ,x、y 表示马儿起始位置所在X、Y轴的坐标function run (X, Y, x, y) {// 标记马儿所有走的路径const visited = Array.from({length: X * Y}, () => false)let finished = false // 标记马儿是否走完所有方格const chessBoard = new Array(Y) // 创建一个棋盘for(let i = 0; i < chessBoard.length; i++){chessBoard[i] = Array.from({length: X}, () => 0)}return traversalChessBoard(chessBoard, x, y)// chessBoard [][] 棋盘 x, y起始位置, step走了多少步,step等于棋盘大小时即成功走完所有棋盘function traversalChessBoard(chessBoard, x, y, step = 1) {chessBoard[x][y] = step // 标记棋盘走了一步visited[x * X + y] = trueconst nextSteps = next({y, x}, X, Y) // 下一步马儿能走哪些点// 这里体现了贪心算法nextSteps.sort((p1, p2) => next(p1, X, Y).length - next(p2, X, Y).length)while (nextSteps.length) {const p = nextSteps.shift()if(!visited[p.x * X + p.y]) {traversalChessBoard(chessBoard, p.x, p.y, step + 1)}}if (step < X * Y) {if (!finished) { // 只能走这么多步,没能走完,只好回退了, 这里体现了回溯算法chessBoard[x][y] = 0visited[x * X + y] = false}} else {finished = true}return chessBoard}}function next(currPoint, X, Y) {const nextSteps = []let y, x// 0if ((y = currPoint.y + 2) < X && (x = currPoint.x - 1) >= 0 ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 1if ((y = currPoint.y + 2) < X && (x = currPoint.x + 1) < Y) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 2if ((y = currPoint.y + 1) < X && (x = currPoint.x + 2) < Y ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 3if ((y = currPoint.y - 1) >= 0 && (x = currPoint.x + 2) < Y ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 4if ((y = currPoint.y - 2) >= 0 && (x = currPoint.x + 1) < Y ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 5if ((y = currPoint.y - 2) >= 0 && (x = currPoint.x - 1) >= 0 ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 6if ((y = currPoint.y - 1) >= 0 && (x = currPoint.x - 2) >= 0 ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}// 7if ((y = currPoint.y + 1) < X && (x = currPoint.x - 2) >= 0 ) {nextSteps.push({y, x})}return nextSteps}
老鼠迷宫
只能走简单的迷宫
console.log(ratInAMaze([[1, 0, 0, 0],[1, 1, 1, 1],[0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 1, 1, 1]]))function ratInAMaze(maze) {const solution = [];for (let i = 0; i < maze.length; i++) {solution[i] = [];for (let j = 0; j < maze[i].length; j++) {solution[i][j] = 0;}}if (findPath(maze, 0, 0, solution) === true) {return solution;}return 'NO PATH FOUND';}function findPath(maze, x, y, solution) {const n = maze.length;if (x === n - 1 && y === n - 1) {solution[x][y] = 1;return true;}if (isSafe(maze, x, y) === true) {solution[x][y] = 1;if (findPath(maze, x + 1, y, solution)) {return true;}if (findPath(maze, x, y + 1, solution)) {return true;}solution[x][y] = 0;return false;}return false;}function isSafe(maze, x, y) {const n = maze.length;if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < n && maze[x][y] !== 0) {return true;}return false;}
复原ip
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。
有效的 IP 地址正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成),整数之间用 ‘.’ 分隔。
function run (str) {const list = []figureItOut(str, [])return listfunction figureItOut (str, arr) {if (!str.length && arr.length == 4) {list.push(arr.join('.'))return}if (arr.length == 4 ) {return}let tp = '', tps = str.split('')for (let i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {tp = tps.pop() + tpif (legal(tp)) {let tpa = arr.slice()tpa.unshift(tp)figureItOut(tps.join(''), tpa)}}}function legal(num) {if (Number(num) < 256 && Number(num).toString() == num) {return true}return false}}console.log(run('25525511135'))

