- RandomErasing">1. RandomErasing
- CutOut">2. CutOut
- MixUp">3. MixUp
- CutMix">4. CutMix
- AugMix">5. AugMix
- DropBlock">6. DropBlock
- References
1. RandomErasing
Random Erasing randomly
selects a rectangle region in an image and erases its pixels with random values(随机选择一个方形区域填充一个随机值)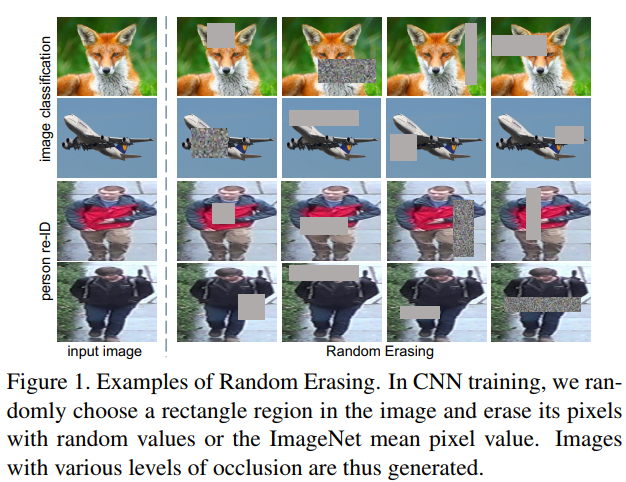
code
2. CutOut
随机的将样本中的部分区域cut掉,并且填充0像素值
CutOut和Random Erasing最主要的区别在于在CutOut中,擦除矩形区域存在一定概率不完全在原图像中的。而在Random Erasing中,擦除矩形区域一定在原图像内。
class Cutout(object):"""Randomly mask out one or more patches from an image.Args:n_holes (int): Number of patches to cut out of each image.length (int): The length (in pixels) of each square patch."""def __init__(self, n_holes, length):self.n_holes = n_holesself.length = lengthdef __call__(self, img):"""Args:img (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W).Returns:Tensor: Image with n_holes of dimension length x length cut out of it."""h = img.size(1)w = img.size(2)mask = np.ones((h, w), np.float32)for n in range(self.n_holes):y = np.random.randint(h)x = np.random.randint(w)y1 = np.clip(y - self.length // 2, 0, h)y2 = np.clip(y + self.length // 2, 0, h)x1 = np.clip(x - self.length // 2, 0, w)x2 = np.clip(x + self.length // 2, 0, w)mask[y1: y2, x1: x2] = 0.mask = torch.from_numpy(mask)mask = mask.expand_as(img)img = img * maskreturn img
3. MixUp
对于图像分类:
分类代码:
def mixup_data(x, y, alpha=1.0, use_cuda=True):'''Returns mixed inputs, pairs of targets, and lambda'''if alpha > 0:lam = np.random.beta(alpha, alpha)else:lam = 1batch_size = x.size()[0]if use_cuda:index = torch.randperm(batch_size).cuda()else:index = torch.randperm(batch_size)mixed_x = lam * x + (1 - lam) * x[index, :]y_a, y_b = y, y[index]return mixed_x, y_a, y_b, lamdef mixup_criterion(criterion, pred, y_a, y_b, lam):return lam * criterion(pred, y_a) + (1 - lam) * criterion(pred, y_b)
对于目标检测,mixup为如下图操作:
输出图像尺寸为较大w和较大h组合,新增区域填0即可。
4. CutMix
将一幅图像某块区域剪切贴到另一幅图上。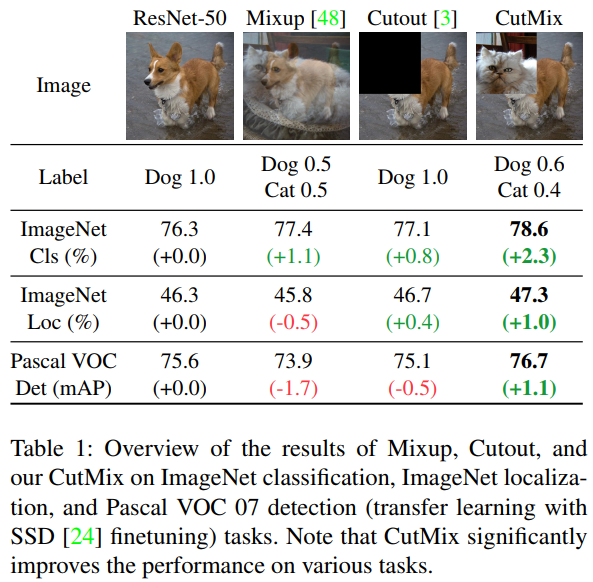
def cutmix(batch, alpha):data, targets = batchindices = torch.randperm(data.size(0))shuffled_data = data[indices]shuffled_targets = targets[indices]lam = np.random.beta(alpha, alpha)image_h, image_w = data.shape[2:]cx = np.random.uniform(0, image_w)cy = np.random.uniform(0, image_h)w = image_w * np.sqrt(1 - lam)h = image_h * np.sqrt(1 - lam)x0 = int(np.round(max(cx - w / 2, 0)))x1 = int(np.round(min(cx + w / 2, image_w)))y0 = int(np.round(max(cy - h / 2, 0)))y1 = int(np.round(min(cy + h / 2, image_h)))data[:, :, y0:y1, x0:x1] = shuffled_data[:, :, y0:y1, x0:x1]targets = (targets, shuffled_targets, lam)return data, targetsclass CutMixCollator:def __init__(self, alpha):self.alpha = alphadef __call__(self, batch):batch = torch.utils.data.dataloader.default_collate(batch)batch = cutmix(batch, self.alpha)return batchclass CutMixCriterion:def __init__(self, reduction):self.criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction=reduction)def __call__(self, preds, targets):targets1, targets2, lam = targetsreturn lam * self.criterion(preds, targets1) + (1 - lam) * self.criterion(preds, targets2)
5. AugMix
augmix伪代码: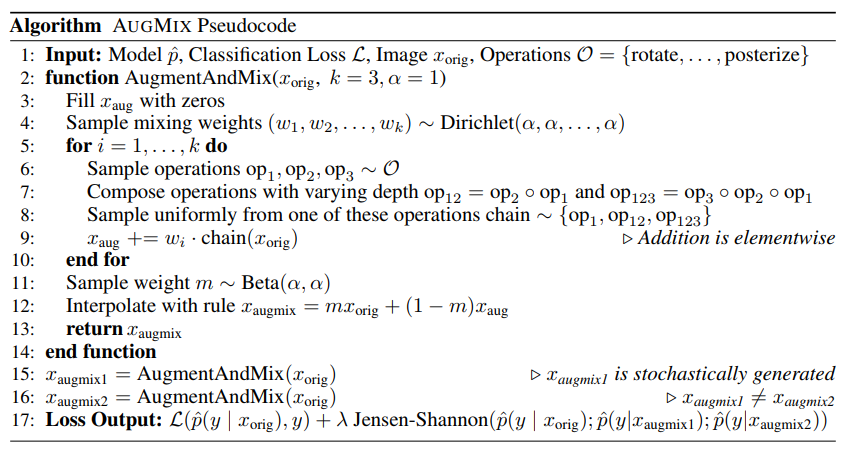


AugMix包含增强和混合两个部分:
- 增强(利用一些不对图像做对比度改变、颜色改变、亮度改变、锐化改变、切块操作这些导致明显视觉变化的操作,例如小角度旋转对图像进行一系列变换)
- 融合:此过程则是,先使用
分布随机抽取3个权值
,根据Dirichlet分布的性质,权值和
。之后按照权值
将三条链按权相加得到
。同时原图
会跨接到最后一步与
按权相加,权值来自从
分布中取样,相加后得到最后的新样本
,至此所有步骤完成。
为了使模型的输出更平滑更稳定,同时由于从同一个原始样本中使用AugMix得到的不同的新样本具有相似的语义,假设对做了两次AugMix,得到
,
这三个样本输入模型后得到的结果的分布理应是相似,所以作者在损失函数中引入了
散度,具体为:
"""Reference implementation of AugMix's data augmentation method in numpy."""import augmentationsimport numpy as npfrom PIL import Image# CIFAR-10 constantsMEAN = [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465]STD = [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010]def normalize(image):"""Normalize input image channel-wise to zero mean and unit variance."""image = image.transpose(2, 0, 1) # Switch to channel-firstmean, std = np.array(MEAN), np.array(STD)image = (image - mean[:, None, None]) / std[:, None, None]return image.transpose(1, 2, 0)def apply_op(image, op, severity):image = np.clip(image * 255., 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)pil_img = Image.fromarray(image) # Convert to PIL.Imagepil_img = op(pil_img, severity)return np.asarray(pil_img) / 255.def augment_and_mix(image, severity=3, width=3, depth=-1, alpha=1.):"""Perform AugMix augmentations and compute mixture.Args:image: Raw input image as float32 np.ndarray of shape (h, w, c)severity: Severity of underlying augmentation operators (between 1 to 10).width: Width of augmentation chaindepth: Depth of augmentation chain. -1 enables stochastic depth uniformlyfrom [1, 3]alpha: Probability coefficient for Beta and Dirichlet distributions.Returns:mixed: Augmented and mixed image."""ws = np.float32(np.random.dirichlet([alpha] * width))m = np.float32(np.random.beta(alpha, alpha))mix = np.zeros_like(image)for i in range(width):image_aug = image.copy()depth = depth if depth > 0 else np.random.randint(1, 4)for _ in range(depth):op = np.random.choice(augmentations.augmentations)image_aug = apply_op(image_aug, op, severity)# Preprocessing commutes since all coefficients are convexmix += ws[i] * normalize(image_aug)mixed = (1 - m) * normalize(image) + m * mixreturn mixed
6. DropBlock
References
Random Erasing&Cutout——两种相似的数据增强方式 目标检测中图像增强,mixup 如何操作? 【论文阅读笔记】CutMix:数据增强 google-research/augmix https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/101432423 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100960934

