标准模板库(STL)向程序员提供了一个用于字符串操作的容器类。string 类不仅能够根据应用程 序的需求动态调整大小,还提供了很有用的辅助函数(方法),可帮助操作字符串,这让程序员能够在 应用程序中使用标准的、经过测试的可移植功能,并将其主要精力放在开发应用程序的重要功能上。
在 C++中,字符串是一个字符数组。简单的字符数组可这样定义:
char staticName [20];
为了避开 上面所示 静态数组的长度 限制,C++支持动态分配内存,因此可以如下定义更 动态的字符数组:
char* dynamicName = new char [arrayLen];
这定义了一个动态分配的字符数组,其长度由变量 arrayLen 的值指定,而这种值是在运行阶段确 定的,因此该数组的长度是可变的。然而,如果要在运行阶段改变数组的长度,必须首先释放以前分配给它的内存,再重新分配内存来存储数据。 这样往往会带来很多复杂和麻烦,实例化并初始化 string 对象时,无需关心字符串长度和内存分配细节。STL string 类的构造 函数将自动完成这些工作
用法
std::string str2 ("Hello String!");// 同样,可使用一个 string 对象来初始化另一个:std::string str2Copy (str2);// 可让 string 的构造函数只接受输入字符串的前 n 个字符std::string strPartialCopy (constCStyleString, 5);// 使其包含指定数量的特定字符来初始化std::string strRepeatChars (10, 'a');
#include <string>#include <iostream>int main(){using namespace std;const char* constCStyleString = "Hello String!";cout << "Constant string is: " << constCStyleString << endl;std::string strFromConst (constCStyleString); // constructorcout << "strFromConst is: " << strFromConst << endl;std::string str2 ("Hello String!");std::string str2Copy (str2);cout << "str2Copy is: " << str2Copy << endl;// Initialize a string to the first 5 characters of anotherstd::string strPartialCopy (constCStyleString, 5);cout << "strPartialCopy is: " << strPartialCopy << endl;// Initialize a string object to contain 10 'a'sstd::string strRepeatChars (10, 'a');cout << "strRepeatChars is: " << strRepeatChars << endl;return 0;}
Constant string is: Hello String!
strFromConst is: Hello String!
str2Copy is: Hello String!
strPartialCopy is: Hello
strRepeatChars is: aaaaaaaaa
访问 std::string 的字符内容
#include <string>#include <iostream>int main (){using namespace std;string stlString ("Hello String");// Access the contents of the string using array syntaxcout << "Dispaly elements in string using array-syntax: " << endl;for (size_t charCounter = 0; charCounter < stlString.length(); ++ charCounter){cout << "Character [" << charCounter << " ] is : ";cout << stlString [charCounter] << endl;}cout << endl;// Access the contents of a string using iteratorscout << "Display elements in string using iterators: " << endl;int charOffset = 0;string::const_iterator charLocator;for (auto charLocator = stlString.cbegin(); charLocator != stlString.cend(); ++ charLocator){cout << "Character [" << charOffset ++ << "] is : ";cout << *charLocator << endl;}cout << endl;// Access contents as a const char*cout << "The char* representation of the string is: ";cout << stlString.c_str () << endl;cout << endl;}
要访问 STL string 的字符内容,可使用迭代器,也可采用类似于数组的语法并使用下标运算符([]) 提供偏移量
拼接字符串
要拼接字符串,可使用运算符+=,也可使用成员函数 append():
string sampleStr1 ("Hello");string sampleStr2 (" String! ");sampleStr1 += sampleStr2; // use std::string::operator+=// alternatively use std::string::append()sampleStr1.append (sampleStr2); // (overloaded for char* too)
使用加法赋值运算符(+=)或 append( )拼接字符串
#include <string>#include <iostream>int main(){using namespace std;string sampleStr1 ("Hello");string sampleStr2 (" String!");// ConcatenatesampleStr1 += sampleStr2;cout << sampleStr1 << endl << endl;string sampleStr3 (" Fun is not needing to use pointers!");sampleStr1.append (sampleStr3);cout << sampleStr1 << endl << endl;const char* constCStyleString = " You however still can!";sampleStr1.append (constCStyleString);cout << sampleStr1 << endl;return 0;}
Hello String!
Hello String! Fun is not needing to use pointers!
Hello String! Fun is not needing to use pointers! You however still can!
在 string 中查找字符或子字符串
STL string 类提供了成员函数 find(),该函数有多个重载版本,可在给定 string 对象中查找字符或 子字符串
#include <string>#include <iostream>int main(){using namespace std;string sampleStr1 ("Hello");string sampleStr2 (" String!");// ConcatenatesampleStr1 += sampleStr2;cout << sampleStr1 << endl << endl;string sampleStr3 (" Fun is not needing to use pointers!");sampleStr1.append (sampleStr3);cout << sampleStr1 << endl << endl;const char* constCStyleString = " You however still can! Fun Fun Fun";sampleStr1.append (constCStyleString);cout << sampleStr1 << endl << endl;size_t charPos = sampleStr1.find("Fun", 0); // 查找第一个出现 "day" 字符或者子字符串// size_t 类型名称非常直观,它的含义就是“size type”,大小的类型,也直接意味着它是sizeof运算符结果的类型if (charPos != string::npos) //npos是一个常数,表示size_t的最大值(Maximum value for size_t){cout << "First instance of \"Fun\" was found at position " << charPos << endl << endl;}else{cout << "Substring not found." << endl << endl;}// 查找所有的 "Fun" 子串cout << "Locating all instances of substring \"Fun\" " << endl;size_t subStrPos = sampleStr1.find ("Fun", 0);while (subStrPos != string::npos){cout << "\"Fun\" found at position " << subStrPos << endl;size_t searchOffset = subStrPos + 1;subStrPos = sampleStr1.find("Fun", searchOffset); // 通过 searchOffset查找}return 0;}
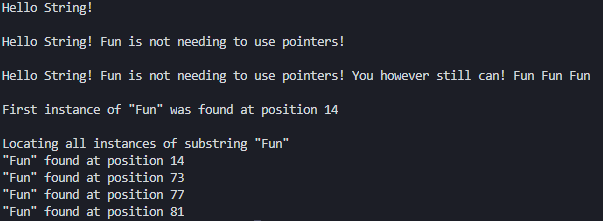
我们就通过指定偏移量,让 find()搜索下一个指定的子字符串
截短 STL string
STL string 类提供了 erase()函数,具有以下用途。
• 在给定偏移位置和字符数时删除指定数目的字符。
string sampleStr ("Hello String! Wake up to a beautiful day!");sampleStr.erase (13, 28); // Hello String!
• 在给定指向字符的迭代器时删除该字符
sampleStr.erase (iCharS); // iterator points to a specific character
字符串反转
假设要判断用户输入的字符串是否为回文,方法之一是将其反转, 再与原来的字符串进行比较。反转 STL string 很容易,只需使用泛型算法 std::reverse()
string sampleStr (“Hello String! We will reverse you!”);
reverse (sampleStr.begin (), sampleStr.end ());
#include <string>#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>// reverse 是 <algorithm> 的实现int main(){using namespace std;string samplestr ("Hello String! we will reverse you!");cout << "the original sample string is: " << endl;cout << samplestr << endl << endl;reverse (samplestr.begin(), samplestr.end());cout << "After applying the std::reverse algorithm: " << endl;cout << samplestr << endl;return 0;}
the original sample string is:
Hello String! we will reverse you!
After applying the std::reverse algorithm:
!uoy esrever lliw ew !gnirtS olleH

