反射机制概述
关于反射的理解
Reflection(反射)是Java被视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期借助于反射API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作任意对象的内部属性及方法。
- 加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。
反射机制提供的功能
- 在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
- 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
- 在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时获取泛型信息
- 在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时处理注解
-
相关API
java.lang.Class:代表一个类
- java.lang.reflect.Method:代表类的方法
- java.lang.reflect.Field:代表类的成员变量
- java.lang.reflect.Constructor:代表类的构造器
- … …
代码举例
public class ReflectionTest {//反射之前,对于Person的操作@Testpublic void test1() {//1.创建Person类的对象Person p1 = new Person("Tom", 12);//2.通过对象,调用其内部的属性、方法p1.age = 10;System.out.println(p1.toString());p1.show();//在Person类外部,不可以通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有结构。//比如:name、showNation()以及私有的构造器}//反射之后,对于Person的操作@Testpublic void test2() throws Exception{Class clazz = Person.class;//1.通过反射,创建Person类的对象Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);Object obj = cons.newInstance("Tom", 12);Person p = (Person) obj;System.out.println(p.toString());//2.通过反射,调用对象指定的属性、方法//调用属性Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");age.set(p,10);System.out.println(p.toString());//调用方法Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");show.invoke(p);System.out.println("*******************************");//通过反射,可以调用Person类的私有结构的。比如:私有的构造器、方法、属性//调用私有的构造器Constructor cons1 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);cons1.setAccessible(true);Person p1 = (Person) cons1.newInstance("Jerry");System.out.println(p1);//调用私有的属性Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");name.setAccessible(true);name.set(p1,"HanMeimei");System.out.println(p1);//调用私有的方法Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class);showNation.setAccessible(true);String nation = (String) showNation.invoke(p1,"中国");//相当于String nation = p1.showNation("中国")System.out.println(nation);}//疑问1:通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以调用公共的结构,开发中到底用那个?//建议:直接new的方式。//什么时候会使用:反射的方式。 反射的特征:动态性//疑问2:反射机制与面向对象中的封装性是不是矛盾的?如何看待两个技术?//不矛盾。}
Class类的理解及获取Class的实例
Class类的理解
- 一个Class对象包含了某个特定结构(class/interface/…)的有关信息
- Class本身也是一个类,只能由系统建立对象
- 一个加载的类在JVM中只会有一个Class实例
- 一个Class对象对应的是一个加载到JVM中的一个.class文件
- 每个类的实例都会记得自己是由哪个Class实例所生成
- 通过Class可以完整地得到一个类中的所有被加载的结构
Class类是Reflection的根源,针对任何你想动态加载、运行的类,唯有先获得相应的Class对象
获取Class类实例的四种方式
public void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException {//方式一:调用运行时类的属性:.class,该方法最为安全可靠,性能最高Class clazz1 = Person.class;System.out.println(clazz1);//方式二:通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()Person p1 = new Person();Class clazz2 = p1.getClass();System.out.println(clazz2);//方式三:调用Class的静态方法:forName(String classPath),可能抛出异常Class clazz3 = Class.forName("com.atguigu.java.Person");System.out.println(clazz3);System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz2);System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz3);//方式四:使用类的加载器:ClassLoaderClassLoader classLoader = ReflectionTest.class.getClassLoader();Class clazz4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.atguigu.java.Person");System.out.println(clazz4);System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz4);}
有Class对象的类型
class:外部类,成员(成员内部类,静态内部类),局部内部类,匿名内部类
- interface:接口
- []数组
- enum:枚举
- annotation:注解@interface
- primitive type:基本数据类型
- void
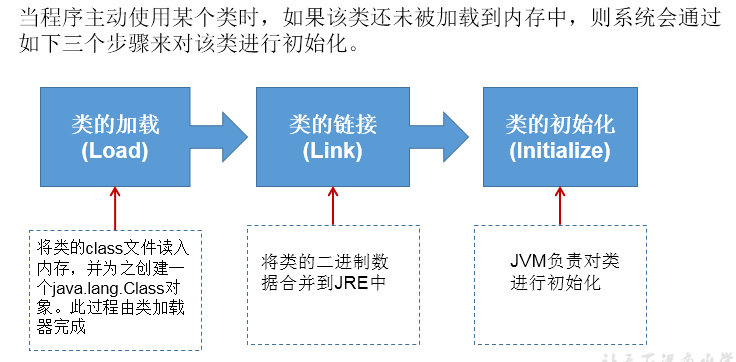
类的加载与ClassLoader
类的加载过程
类加载的作用
- 类加载的作用:将class文件字节码内容加载到内存中,并将这些静态数据转换成方法区的运行时数据结构,然后在堆中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区中类数据的访问入口。
- 类缓存:标准的SE类加载器可以按要求查找类,但一旦某个类被加载到类加载器中,它将维持加载(缓存)一段时间。不过JVM垃圾回收机制可以回收这些Class对象。
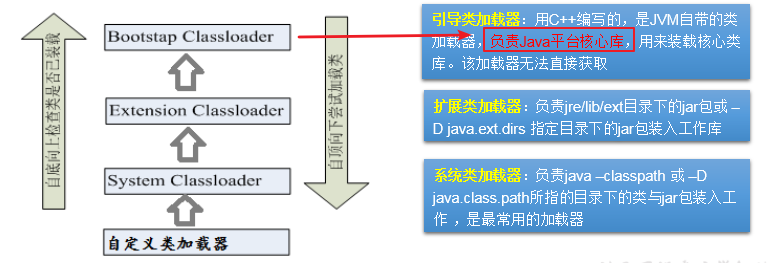
类加载器的分类
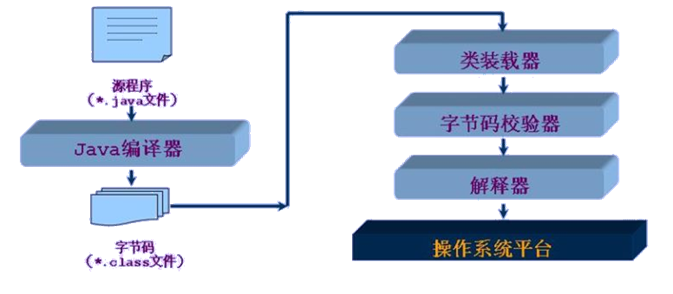
Java类编译、运行、执行的流程
获取类加载器
public void test() {//对于自定义类,使用系统类加载器进行加载ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();System.out.println(classLoader);//调用系统类加载器的getParent():获取扩展类加载器ClassLoader classLoader1 = classLoader.getParent();System.out.println(classLoader1);//调用扩展类加载器的getParent():无法获取引导类加载器//引导类加载器主要负责加载java的核心类库,无法加载自定义类的。ClassLoader classLoader2 = classLoader1.getParent();System.out.println(classLoader2);ClassLoader classLoader3 = String.class.getClassLoader();System.out.println(classLoader3);}
使用ClassLoader加载配置文件
Properties pros = new Properties();//此时的文件默认在当前的module下。//读取配置文件的方式一:// FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");// FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\jdbc1.properties");// pros.load(fis);//读取配置文件的方式二:使用ClassLoader//配置文件默认识别为:当前module的src下ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("jdbc1.properties");pros.load(is);String user = pros.getProperty("user");String password = pros.getProperty("password");System.out.println("user = " + user + ",password = " + password);
应用一:创建运行时类的对象
代码举例
Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Person obj = clazz.newInstance();System.out.println(obj);
说明
newInstance():调用此方法,创建对应的运行时类的对象。内部调用了运行时类的空参的构造器。
想要此方法正常的运行创建运行时类的对象,要求:
- 运行时类必须提供空参构造器
- 空参构造器需要具备足够的访问权限,通常设为public
在javabean中通常要求提供一个public的空参构造器。原因:
- 便于通过反射创建运行时类的对象
- 便于子类运行此运行时类时,默认调用super()时,保证父类有此构造器
应用二:获取运行时类的完整结构
通过反射可以获取对应的运行时类中所有的属性、方法、构造器、父类、接口、父类的泛型、包、注解、异常等。
获取属性
public void test1(){Class clazz = Person.class;//getFields():获取当前运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();for(Field f : fields){System.out.println(f);}System.out.println();//getDeclaredFields():获取当前运行时类中声明的所属性。(不包含父类中声明的属性Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();for(Field f : declaredFields){System.out.println(f);}}
获取方法
public void test1(){Class clazz = Person.class;//getMethods():获取当前运行时类及其所父类中声明为public权限的方法Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();for(Method m : methods){System.out.println(m);}System.out.println();//getDeclaredMethods():获取当前运行时类中声明的所方法。(不包含父类中声明的方法Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();for(Method m : declaredMethods){System.out.println(m);}}
获取构造器
public void test1(){Class clazz = Person.class;//getConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明为public的构造器Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();for(Constructor c : constructors){System.out.println(c);}System.out.println();//getDeclaredConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明的所的构造器Constructor[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();for(Constructor c : declaredConstructors){System.out.println(c);}}
获取运行时类的父类
public void test2(){Class clazz = Person.class;Class superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();System.out.println(superclass);}
获取运行时类的带泛型的父类
public void test3(){Class clazz = Person.class;Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();System.out.println(genericSuperclass);}
获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型
public void test4(){Class clazz = Person.class;Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;//获取泛型类型Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments();//System.out.println(actualTypeArguments[0].getTypeName());System.out.println(((Class)actualTypeArguments[0]).getName());}
获取运行时类实现的接口
public void test5(){Class clazz = Person.class;Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();for(Class c : interfaces){System.out.println(c);}System.out.println();//获取运行时类的父类实现的接口Class[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces();for(Class c : interfaces1){System.out.println(c);}}
获取运行时类所在的包
public void test6(){Class clazz = Person.class;Package pack = clazz.getPackage();System.out.println(pack);}
获取运行时类声明的注解
public void test7(){Class clazz = Person.class;Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();for(Annotation annos : annotations){System.out.println(annos);}}
应用三:获取运行时类的指定结构
**
public void testField1() throws Exception {Class clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();//1. getDeclaredField(String fieldName):获取运行时类中指定变量名的属性Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");//2.保证当前属性是可访问的name.setAccessible(true);//3.获取、设置指定对象的此属性值name.set(p,"Tom");System.out.println(name.get(p));}
调用指定的方法:
public void testMethod() throws Exception {Class clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();/*1.获取指定的某个方法getDeclaredMethod():参数1 :指明获取的方法的名称参数2:指明获取的方法的形参列表*/Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class);//2.保证当前方法是可访问的show.setAccessible(true);/*3. 调用方法的invoke():参数1:方法的调用者 参数2:给方法形参赋值的实参invoke()的返回值即为对应类中调用的方法的返回值。*/Object returnValue = show.invoke(p,"CHN"); //String nation = p.show("CHN");System.out.println(returnValue);System.out.println("*************如何调用静态方法*****************");// private static void showDesc()Method showDesc = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showDesc");showDesc.setAccessible(true);//如果调用的运行时类中的方法没返回值,则此invoke()返回null//Object returnVal = showDesc.invoke(null);Object returnVal = showDesc.invoke(Person.class);System.out.println(returnVal);//null}
调用指定的构造器:
public void testConstructor() throws Exception {Class clazz = Person.class;//private Person(String name)/*1.获取指定的构造器getDeclaredConstructor():参数:指明构造器的参数列表*/Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);//2.保证此构造器是可访问的constructor.setAccessible(true);//3.调用此构造器创建运行时类的对象Person per = (Person) constructor.newInstance("Tom");System.out.println(per);}