Encapsulation in Java
Encapsulation is one of the four fundamental OOP concepts. The other three are- Inheritance, Polymorphism, Abstraction
What is Encapsulation
The concept of Encapsulation is to keep together the implementation (code) and the data it manipulates (variables). Having proper encapsulation ensures that the code and data both are safe from misuse by outside entity.
Encapsulation also helps in maintaining code as the implementation that may change and evolve is kept at one place which makes it easy to change with out impacting other classes in application.
Encapsulation in Java
Foundation of encapsulation in Java is a Java class which encapsulates both methods and instance variables. Since it’s the code in the method that operates on the variables, in a properly encapsulated Java class, method should define how member variables can be used. That access control to the methods and the variables is achieved through access modifiers (public, private, default & protected).
Each method or variable in the class may be marked public or private in order to ensure access control.
- A method or variable marked as public is accessible to other classes.
- A method or variable marked as private is internal to the class.
In a properly encapsulated Java class you mark only those methods as public that should be accessed by the other classes. Complete encapsulation in java is achieved by making variables of a class private and access to them, outside the class, is provided only through public methods with in the same class. Any method having logic that is specific only to that class and used only by other methods of that class should be marked private.
Since the private members (variables or methods) of a class may only be accessed with in the class, no improper outside access is possible.
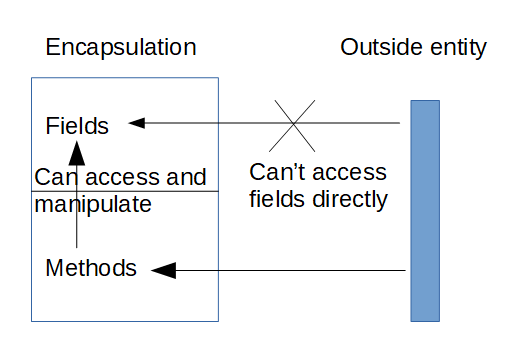
Following image shows the concept of encapsulation. Fields and methods are encapsulated with in the class and the methods of the class can access and manipulate fields. Outside entity can’t access fields directly but need to call methods which in turn can access data.
Encapsulation Java Example code
Lets assume there is a class Employee which gets data of the employee from the DB. in the Java class there is a getEmployeeData() method marked as public which can be accessed from outside.
Let’s assume when you get data from DB there are separate lastName and firstName fields but the user wants it concatenated as full name. Since that logic of concatenating the lastName and firstName fields is specific to the class, so you can have a private method getFullName() which will concatenate them.
There will be another EmployeeBean class with the fields, you can notice that all the fields are marked private and getters and setters are used to access those fields.
Let’s go through the code to make it clear -
In class Employee there is getEmployeeData() method which can be accessed from outside. Since getFullName() has some logic specific to the class so that is made private.
public class Employee {public EmployeeBean getEmployeeData(String empId){System.out.println("Going to DB to get employee Data");// goes to the stub method rather than going to DBEmployeeBean employeeBean = getData();//Will give Compilation error, data can be set only through setters method//employeeBean.age = 10;String name = getFullName(employeeBean.getFirstName(), employeeBean.getLastName());employeeBean.setFullName(name);System.out.println("Employee bean - " + "Age - " + employeeBean.getAge() +" Name - " + employeeBean.getFullName() + " Emp ID - " + employeeBean.getEmpId());return employeeBean;}// private method to concatenate first and last nameprivate String getFullName(String firstName, String lastName){return firstName + " " + lastName;}// Stub methodprivate EmployeeBean getData(){EmployeeBean employeeBean = new EmployeeBean();employeeBean.setEmpId("E001");employeeBean.setLastName("Mishra");employeeBean.setFirstName("Pyaremohan");employeeBean.setAge(35);return employeeBean;}}
Employee Bean Class
It can be seen how in EmployeeBean all the variables are private and access is provided through setters and getters methods.
public class EmployeeBean {
private String lastName;
private String firstName;
private String fullName;
private String empId;
private int age;
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getEmpId() {
return empId;
}
public void setEmpId(String empId) {
this.empId = empId;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public void setFullName(String fullName) {
this.fullName = fullName;
}
}
Test Class
public class EmployeeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
//employee.getData(); // WILL GIVE COMPILATION ERROR
employee.getEmployeeData("E001");
}
}
Encapsulate what varies
Encapsulate what varies is one of the design principle centered around the concept of encapsulation.
By encapsulating method and fields that are required for that method you also get the advantage of making it easy to maintain and evolve your code.
As an example consider the scenario where you have to calculate tax by using the prevailing tax rate (which may keep on changing). What is the best design strategy for such scenario-
Hard coding the tax rate wherever it is used or having a single method with a access to taxRate field with in the same class?
Of course by having a single method calculateTax(person) and all the other classes accessing this method is better as any change in the logic requires change just in the encapsulated method calculateTax() making it easy to maintain.
Benefits of Encapsulation
- Encapsulation helps to maintain code that is changed frequently by keeping that in one place thus providing maintainability and flexibility.
- Encapsulation allows you to control the access to the class.
Points to note-
- Encapsulation is one of the four fundamental OOPS concept. Other being, inheritance, polymorphism and abstraction.
- Encapsulation means keeping code and data together in a class.
- An encapsulated class will have private instance variable and only the methods within that class can access those variables.
- Outside classes will be given access to any particular class through one or more public methods only.
- Encapsulation in Java is achieved through the access modifiers- public, private, protected and default.
That’s all for this topic Encapsulation in Java. If you have any doubt or any suggestions to make please drop a comment. Thanks!