01、面向过程与面向对象
何谓“面向对象”的编程思想?
首先解释一下“思想”。
先问你个问题:你想做个怎样的人?
可能你会回答:我想做个好人,孝敬父母,尊重长辈,关爱亲朋…
你看,这就是思想。这是你做人的思想,或者说,是你做人的原则。做人有做人的原则,编程也有编程的原则。这些编程的原则呢,就是编程思想
面向过程(POP) 与面向对象(OOP)
- 面向对象:Object Oriented Programming
- 面向过程:Procedure Oriented Programming
```java
/*
- 一、学习面向对象内容的三条主线
- 1.Java 类及类的成员:属性、方法、构造器、代码块、内部类
- 2.面向对象的三大特征:封装、继承、多态性、(抽象性)
- 3.其它关键字:this、super、static、final、abstract、interface、package、import 等
- 二、人把大象装进冰箱
- 1.面向过程:强调的是功能行为,以函数为最小单位,考虑怎么做。
- ① 打开冰箱
- ② 把大象装进冰箱
- ③ 把冰箱门关住
- 2.面向对象:强调具备了功能的对象,以类/对象为最小单位,考虑谁来做。
- 人{
- 打开(冰箱){
- 冰箱.开门();
- }操作(大象){
- 大象.进入(冰箱);
- }关闭(冰箱){
- 冰箱.关门();
- }
- }
- 冰箱{
- 开门(){
- }
- 关门(){
- }
- }
- 大象{
- 进入(冰箱){
- }
- } */
面向对象的思想概述<br />程序员从面向过程的执行者转化成了面向对象的指挥者<br />面向对象分析方法分析问题的思路和步骤:- 根据问题需要,选择问题所针对的现实世界中的实体。- 从实体中寻找解决问题相关的属性和功能,这些属性和功能就形成了概念世界中的类。- 把抽象的实体用计算机语言进行描述,形成计算机世界中类的定义。即借助某种程序语言,把类构造成计算机能够识别和处理的数据结构。- 将类实例化成计算机世界中的对象。对象是计算机世界中解决问题的最终工具。[](https://blog.csdn.net/PorkBird/article/details/113694493)<a name="nRIPW"></a># 02、 类和对象```java/** 三、面向对象的两个要素:* 类:对一类事物的描述,是抽象的、概念上的定义* 对象:是实际存在的该类事物的每个个体,因而也称为实 例(instance)。* 可以理解为:类= 抽象概念的人;对象= 实实在在的某个人* 面向对象程序设计的重点是类的设计;* 设计类,其实就是设计类的成员。*/
2.1、Java 类及类的成员
现实世界的生物体,大到鲸鱼,小到蚂蚁,都是由最基本的细胞构成的。同理,Java 代码世界是由诸多个不同功能的类构成的。
现实生物世界中的细胞又是由什么构成的呢?细胞核、细胞质、… 那么,Java 中用类 class 来描述事物也是如此。常见的类的成员有:
- 属性:对应类中的成员变量
- 行为:对应类中的成员方法
2.2、类与对象的创建及使用
/** 一、设计类、其实就是设计类的成员* Field = 属性 = 成员变量 = 域、字段* Method = (成员)方法 = 函数* 创建类 = 类的实例化 = 实例化类* 二.类和对象的使用(面向对象思想落地的实现)* 1.创建类,设计类的成员* 2.创建类的对象* 3.通过“对象.属性”或“对象.方法”调用对象的结构* 三、如果创建类一个类的多个对象,则每个对象都独立的拥有一套类的属性。(非 static 的)* 意味着:如果我们修改一个对象的属性 a,则不影响另外一个对象属性 a 的值。(重点)*///测试类public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//2.创建 Person 类的对象//创建对象语法:类名对象名= new 类名();Person p1 = new Person();//Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);//调用类的结构:属性、方法//调用属性:“对象.属性”p1.name = "Tom";p1.age = 25;p1.isMale = true;System.out.println(p1.name);//调用方法:“对象.方法”p1.eat();p1.sleep();p1.talk("chinese");//**********************Person p2 = new Person();System.out.println(p2.name); //nullSystem.out.println(p2.isMale);//**********************//将 p1 变量保存的对象地址值赋给 p3,导致 p1 和 p3 指向了堆空间中的一个对象实体。Person p3 = p1;System.out.println(p3.name);//Tomp3.age = 10;System.out.println(p1.age); //10}}/** 类的语法格式:* 修饰符 class 类名{* 属性声明;* 方法声明;* }* 说明:修饰符 public:类可以被任意访问类的正文要用{ }括起来*///1.创建类,设计类的成员class Person{//属性:对应类中的成员变量String name;int age;boolean isMale;//方法:对应类中的成员方法public void eat(){System.out.println("吃饭");}public void sleep(){System.out.println("睡觉");}public void talk(String language){System.out.println("人可以说话,使用的是:" + language);}}
重点:
Person p3 = p1;
//将 p1 变量保存的对象地址值赋给 p3,导致 p1 和 p3 指向了堆空间中的一个对象实体。
2.3、对象的创建和使用:内存解析
堆(Heap),此内存区域的唯一目的就是存放对象实例,几乎所有的对象实例都在这里分配内存。这一点在 Java 虚拟机规范中的描述是:所有的对象实例以及数组都要在堆上分配。
通常所说的栈(Stack),是指虚拟机栈。虚拟机栈用于存储局部变量等。局部变量表存放了编译期可知长度的各种基本数据类型(boolean、byte、char、short、int、float、long、double)、对象引用(reference 类型,它不等同于对象本身,是对象在堆内存的首地址)。方法执行完,自动释放。
方法区(MethodArea),用于存储已被虚拟机加载的类信息、常量、静态变量、即时编译器编译后的代码等数据。
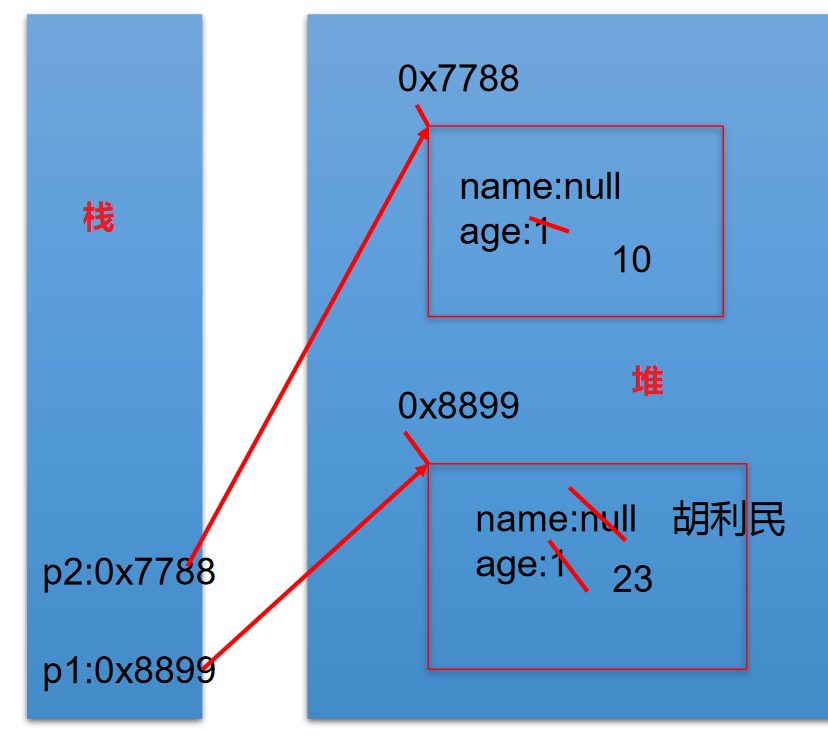
1、案例 1
Person p1= newPerson();p1.name = "Tom";p1.isMale = true;Person p2 = new Person();sysout(p2.name);//nullPerson p3 = p1;p3.age = 10;
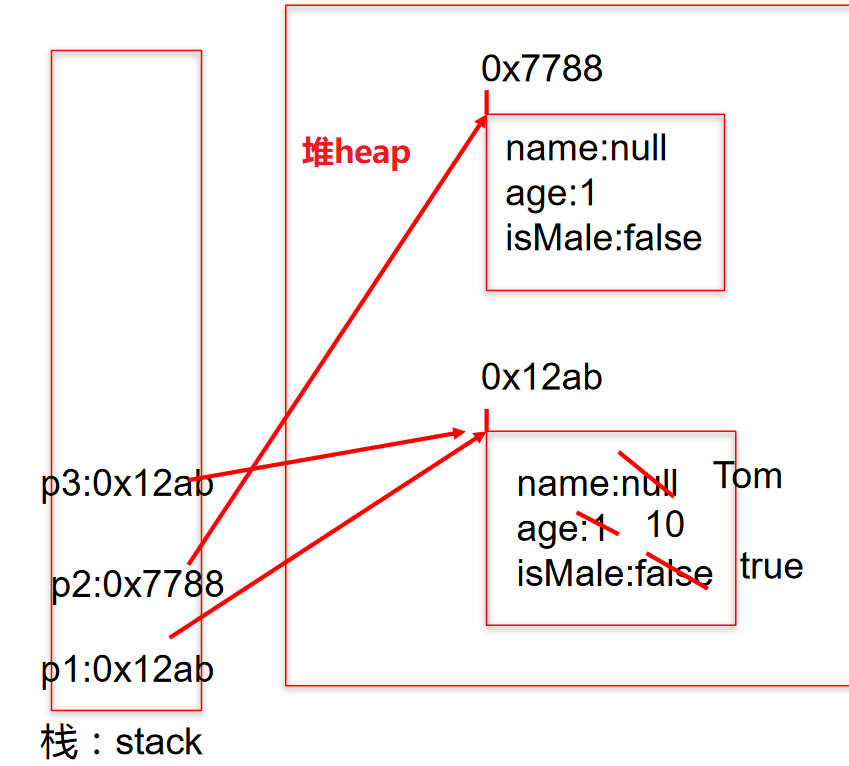
2、案例 2
Person p1= newPerson();p1.name = "胡利民";p1.age = 23;Person p2 = new Person();p2.age = 10;
03、类的成员之一:属性
/** 类中属性的使用** 属性(成员变量) vs 局部变量* 1.相同点:* 1.1 定义变量的格式:数据类型 变量名 = 变量值* 1.2 先声明,后使用* 1.3 变量都有其对应的作用域** 2.不同点:* 2.1 在类中声明的位置不同* 属性:直接定义在类的一对{}内* 局部变量:声明在方法内、方法形参、构造器形参、构造器内部的变量** 2.2 关于权限修饰符的不同* 属性:可以在声明属性时,指明其权限,使用权限修饰符。* 常用的权限修饰符:private、public、缺省、protected* 目前声明属性时,都使用缺省即可。* 局部变量:不可以使用权限修饰符。** 2.3 默认初始化值的情况:* 属性:类的属性,根据其类型,都有默认初始化值。* 整型(byte、short、int、long):0* 浮点型(float、double):0.0* 字符型(char):0(或‘\u0000’)* 布尔型(boolean):false** 引用数据类型(类、数组、接口):null** 局部变量:没有默认初始化值* 意味着:在调用局部变量之前,一定要显式赋值。* 特别地:形参在调用时,赋值即可。例,45 行** 2.4 在内存中加载的位置,亦各不相同。* 属性:加载到堆空间中(非 static)跟着对象走* 局部变量:加载到栈空间*/public class UserTest {public static void main(String[] args) {User u1 = new User();System.out.println(u1.name);System.out.println(u1.age);System.out.println(u1.isMale);u1.talk("俄语");}}class User{//属性(或成员变量)String name; //不加 private 即为缺省public int age; //不加 public 即为缺省boolean isMale;public void talk(String language){//language:形参,也是局部变量System.out.println("我们使用" + language + "进行交流。");}public void eat(){String food = "石头饼"; //石头饼:局部变量System.out.println("北方人喜欢吃:" + food);}}
1、练习1
/*编写教师类和学生类,并通过测试类创建对象进行测试Student类属性:name:String age:int major:String interests:String方法:say() 返回学生的个人信息Teacher类属性:name:String age:int teachAge:int course:String方法:say() 输出教师的个人信息*/public class School {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu = new Student();stu.name = "小明";stu.age = 16;Teacher tea = new Teacher();tea.name = "王老师";tea.age = 27;tea.say(stu.name,stu.age);stu.say(tea.name, tea.age);}}class Student{String name;int age;String major;String interests;void say(String name, int age){System.out.println("这个学生是:"+name+"年龄是:"+age); }}class Teacher{String name;int age;String teachAge;String course;void say(String name, int age){System.out.println("这个老师是:"+name+"年龄是:"+age);}}
04、 类的成员之二:方法
4.1、类中方法的声明和使用
/** 类中方法的声明和使用** 方法:描述类应该具有的功能。* 比如:Math类:sqrt()\random() \...* Scanner类:nextXxx() ...* Arrays类:sort() \ binarySearch() \ toString() \ equals() \ ...** 1.举例:* public void eat(){}* public void sleep(int hour){}* public String getName(){}* public String getNation(String nation){}** 2. 方法的声明:权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(形参列表){* 方法体* }* 注意:static、final、abstract 来修饰的方法,后面再讲。** 3. 说明:* 3.1 关于权限修饰符:默认方法的权限修饰符先都使用public* Java规定的4种权限修饰符:private、public、缺省、protected -->封装性再细说** 3.2 返回值类型: 有返回值 vs 没有返回值* 3.2.1 如果方法有返回值,则必须在方法声明时,指定返回值的类型。同时,方法中,需要使用* return关键字来返回指定类型的变量或常量:“return 数据”。* 如果方法没有返回值,则方法声明时,使用void来表示。通常,没有返回值的方法中,就不需要* 使用return.但是,如果使用的话,只能“return;”表示结束此方法的意思。** 3.2.2 我们定义方法该不该有返回值?* ① 题目要求* ② 凭经验:具体问题具体分析** 3.3 方法名:属于标识符,遵循标识符的规则和规范,“见名知意”* 3.4 形参列表:方法名可以声明0个、1个,或多个形参。* 3.4.1 格式:数据类型1 形参1,数据类型2 形参2,...** 3.4.2 我们定义方法时,该不该定义形参?* ① 题目要求* ② 凭经验,具体问题具体分析* 3.5 方法体:方法功能的体现。* 4. return关键字的使用:* 1.使用范围:使用在方法体中* 2.作业:① 结束方法* ② 针对于有返回值类型的方法,使用"return 数据"方法返回所要的数据。* 3.注意点:return关键字后不可声明执行语句。* 5. 方法的使用中,可以调用当前类的属性或方法。* 特殊的:方法A中又调用了方法A:递归方法。* 方法中不能定义其他方法。*/public class CustomerTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Customer cust1 = new Customer();cust1.eat();//测试形参是否需要设置的问题// int[] arr = new int[]{3,4,5,2,5};// cust1.sort();cust1.sleep(8);}}//客户类class Customer{//属性String name;int age;boolean isMale;//方法public void eat(){System.out.println("客户吃饭");return;//return后不可以声明表达式// System.out.println("hello");}public void sleep(int hour){System.out.println("休息了" + hour + "个小时");eat();// sleep(10);}public String getName(){if(age > 18){return name;}else{return "Tom";}}public String getNation(String nation){String info = "我的国籍是:" + nation;return info;}//体会形参是否需要设置的问题// public void sort(int[] arr){//// }// public void sort(){// int[] arr = new int[]{3,4,5,2,5,63,2,5};// //。。。。// }public void info(){//错误的// public void swim(){//// }}}
1、练习1
创建一个Person类,其定义如下:
public class Person {String name;int age;/** sex:1表示为男性* sex:0表示为女性*/int sex;public void study(){System.out.println("studying");}public void showAge(){System.out.println("age:" + age);}public int addAge(int i){age += i;return age;}}
测试类
/** 要求:* (1)创建Person类的对象,设置该对象的name、age和sex属性,* 调用study方法,输出字符串“studying”,* 调用showAge()方法显示age值,* 调用addAge()方法给对象的age属性值增加2岁。* (2)创建第二个对象,执行上述操作,体会同一个类的不同对象之间的关系。**/public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person();p1.name = "Tom";p1.age = 18;p1.sex = 1;p1.study();p1.showAge();int newAge = p1.addAge(2);System.out.println(p1.name + "的年龄为" + newAge);System.out.println(p1.age); //20//*******************************Person p2 = new Person();p2.showAge(); //0p2.addAge(10);p2.showAge(); //10p1.showAge(); //20}}
2、练习2
/** 2.利用面向对象的编程方法,设计类Circle计算圆的面积。*///测试类public class CircleTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Circle c1 = new Circle();c1.radius = 2.1;//对应方式一:// double area = c1.findArea();// System.out.println(area);//对应方式二:c1.findArea();//错误的调用double area = c1.findArea(3.4);System.out.println(area);}}//圆:3.14*r*rclass Circle{//属性double radius;//圆的面积方法//方法1:// public double findArea(){// double area = 3.14 * radius * radius;// return area;// }//方法2:public void findArea(){double area = Math.PI * radius * radius;System.out.println("面积为:" + area);}//错误情况:public double findArea(Double r){double area = 3.14 * r * r;return area;}}
3、练习3
/** 3.1 编写程序,声明一个method方法,在方法中打印一个10*8的*型矩形,在main方法中调用该方法。* 3.2修改上一个程序,在method方法中,除打印一个10*8的*型矩形外,再计算该矩形的面积,* 并将其作为方法返回值。在main方法中调用该方法,接收返回的面积值并打印。** 3.3 修改上一个程序,在method方法提供m和n两个参数,方法中打印一个m*n的*型矩形,* 并计算该矩形的面积,将其作为方法返回值。在main方法中调用该方法,接收返回的面积值并打印。**/public class ExerTest {public static void main(String[] args) {ExerTest esr = new ExerTest();//3.1测试// esr.method();//3.2测试//方式一:// int area = esr.method();// System.out.println("面积为:" + area);//方式二:// System.out.println("面积为:" + esr.method());//3.3测试System.out.println("面积为:" + esr.method(6,5));}//3.1// public void method(){// for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){// for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++){// System.out.print("* ");// }// System.out.println();// }// }//3.2// public int method(){// for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){// for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++){// System.out.print("* ");// }// System.out.println();// }// return 10 * 8;// }//3.3public int method(int m,int n){for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){System.out.print("* ");}System.out.println();}return m * n;}}
4、练习四
/** 4. 对象数组题目:定义类Student,包含三个属性:* 学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。* 创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。* 问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。* 问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息* 提示: 1) 生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double;* 2) 四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。**/public class StudentTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//声明一个Student类型的数组Student[] stu = new Student[20];for(int i = 0;i <stu.length;i++){//给数组元素赋值stu[i] = new Student();//给Student的对象的属性赋值stu[i].number = i + 1;//年级:[1,6]stu[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1);//成绩:[0,100]stu[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * (100 - 0 + 1));}//遍历学生数组for(int i = 0;i < stu.length;i++){// System.out.println(stu[i].number + "," + stu[i].state// + "," + stu[i].score);System.out.println(stu[i].info());}System.out.println("*********以下是问题1*********");//问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。for(int i = 0;i < stu.length;i++){if(stu[i].state == 3){System.out.println(stu[i].info());}}System.out.println("********以下是问题2**********");//问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息。for(int i = 0;i < stu.length - 1;i++){for(int j = 0;j <stu.length - 1 - i;j++){if(stu[j].score >stu[j+1].score){//如果需要换序,交换的是数组的元素,Student对象!!!Student temp = stu[j];stu[j] = stu[j+1];stu[j+1] = temp;}}}//遍历学生数组for(int i = 0;i < stu.length;i++){System.out.println(stu[i].info());}}}class Student{int number; //学号int state; //年级int score; //成绩//显示学生信息的方法public String info(){return "学号:" + number + ",年级:" + state + ",成绩:" + score;}}
4-1、练习四优化
/** 4. 对象数组题目:定义类Student,包含三个属性:* 学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。* 创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。* 问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。* 问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息* 提示: 1) 生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double;* 2) 四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。** 此代码是对StudentTest.java的改进,将操作数组的功能封装到方法中。*/public class StudentTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//声明一个Student类型的数组Student2[] stu = new Student2[20];for(int i = 0;i <stu.length;i++){//给数组元素赋值stu[i] = new Student2();//给Student的对象的属性赋值stu[i].number = i + 1;//年级:[1,6]stu[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1);//成绩:[0,100]stu[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * (100 - 0 + 1));}StudentTest2 test = new StudentTest2();//遍历学生数组test.print(stu);System.out.println("*********以下是问题1*********");//问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。test.searchState(stu, 3);System.out.println("********以下是问题2**********");//问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息。test.sort(stu);//遍历学生数组for(int i = 0;i < stu.length;i++){System.out.println(stu[i].info());}}/**** @Description 遍历Student[]数组的操作*/public void print(Student2[] stu){for(int i = 0;i < stu.length;i++){System.out.println(stu[i].info());}}/**** @Description 查找Student数组中指定年级的学习信息*/public void searchState(Student2[] stu,int state){for(int i = 0;i < stu.length;i++){if(stu[i].state == state){System.out.println(stu[i].info());}}}/**** @Description 给Student数组排序*/public void sort(Student2[] stu){for(int i = 0;i < stu.length - 1;i++){for(int j = 0;j <stu.length - 1 - i;j++){if(stu[j].score >stu[j+1].score){//如果需要换序,交换的是数组的元素,Student对象!!!Student2 temp = stu[j];stu[j] = stu[j+1];stu[j+1] = temp;}}}}}class Student2{int number; //学号int state; //年级int score; //成绩//显示学生信息的方法public String info(){return "学号:" + number + ",年级:" + state + ",成绩:" + score;}}
4.2、理解“万事万物皆对象”
/* 1.在Java语言范畴中,我们都将功能、结构等封装到类中,通过类的实例化,来调用具体的功能结构。* 》Scanner,String等* 》文件:File* 》网络资源:URL* 2.涉及到Java语言与前端html、后端的数据库交互时,前后端的结构在Java层面交互时,都体现为类、对象。*/
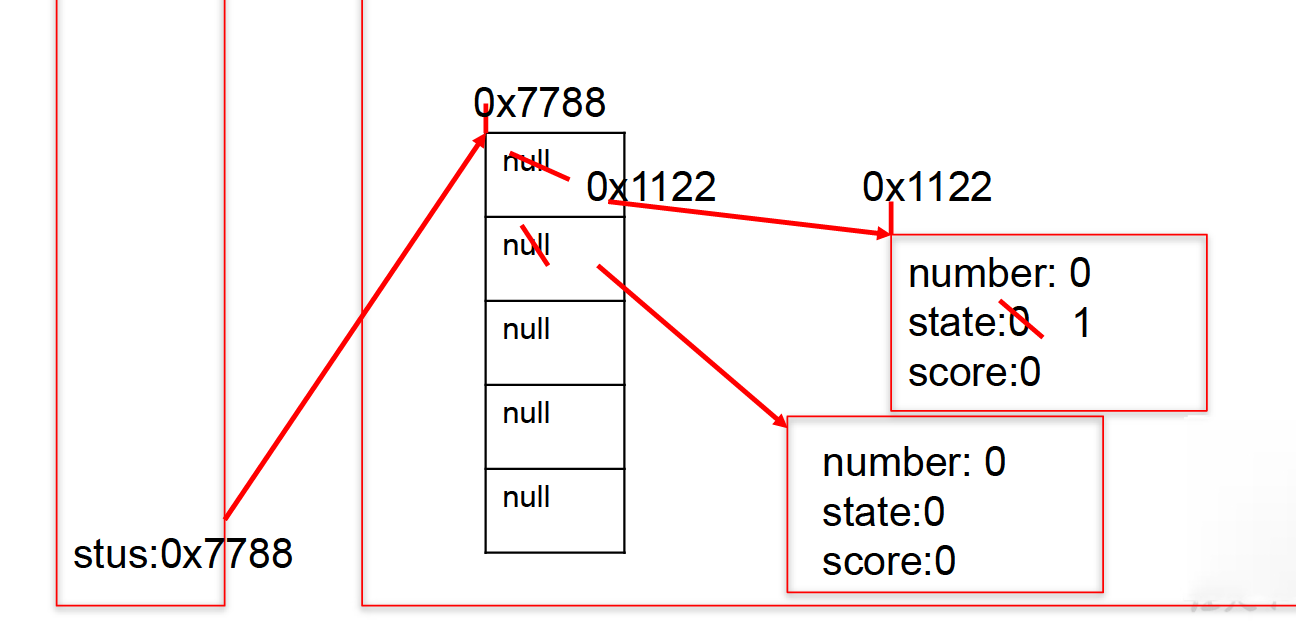
4.3、对象数组的内存解析
/*引用类型的变量,只可能存储量两类值:null或地址值(含变量类型)*/Student[] stus= newStudent[5];stus[0] = new Student();sysout(stus[0].state);//1sysout(stus[1]);//nullsysout(stus[1].number);//异常stus[1] = new Student();sysout(stus[1].number);//0class Student{int number;//学号int state = 1;//年级int score;//成绩}
4.4、匿名对象的使用
/** 三、匿名对象的使用* 1.理解:我们创建的对象,没有显示的赋值给一个变量名。即为匿名对象。* 2.特征:匿名对象只能调用一次。* 3.使用:如下*/public class InstanceTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Phone p = new Phone();// p = null;System.out.println(p);p.sendEmail();p.playGame();//匿名对象// new Phone().sendEmail();// new Phone().playGame();new Phone().price = 1999;new Phone().showPrice(); //0.0//*******************************PhoneMall mall = new PhoneMall();// mall.show(p);//匿名对象的使用mall.show(new Phone());}}class PhoneMall{public void show(Phone phone){phone.sendEmail();phone.playGame();}}class Phone{double price; //价格public void sendEmail(){System.out.println("发邮件");}public void playGame(){System.out.println("打游戏");}public void showPrice(){System.out.println("手机价格为:" + price);}}
4.5、自定义数组的工具类
1、工具类
/** 自定义数组工具类*/public class ArrayUtil {// 求数组的最大值public int getMax(int[] arr) {int maxValue = arr[0];for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {if (maxValue < arr[i]) {maxValue = arr[i];}}return maxValue;}// 求数组的最小值public int getMin(int[] arr) {int minValue = arr[0];for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {if (minValue > arr[i]) {minValue = arr[i];}}return minValue;}// 求数组总和public int getSum(int[] arr) {int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {sum += arr[i];}return sum;}// 求数组平均值public int getAvg(int[] arr) {int avgValue = getSum(arr) / arr.length;return avgValue;}// 反转数组public void reverse(int[] arr) {for (int i = 0; i < arr.length / 2; i++) {int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[arr.length - i - 1];arr[arr.length - i - 1] = temp;}}// 复制数组public int[] copy(int[] arr) {int[] arr1 = new int[arr.length];for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {arr1[i] = arr[i];}return null;}// 数组排序public void sort(int[] arr) {for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j + 1];arr[j + 1] = temp;}}}}// 遍历数组public void print(int[] arr) {System.out.print("[");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.print(arr[i] + ",");}System.out.println("]");}// 查找指定元素public int getIndex(int[] arr, int dest) {//线性查找for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if (dest==arr[i]) {return i;}}return -1;}}
2、测试类
/*** @Description 测试类**/public class ArrayUtilTest {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayUtil util = new ArrayUtil();int[] arr = new int[]{32,5,26,74,0,96,14,-98,25};int max = util.getMax(arr);System.out.println("最大值为:" + max);// System.out.print("排序前:");// util.print(arr);//// util.sort(arr);// System.out.print("排序后:");// util.print(arr);System.out.println("查找:");int index = util.getIndex(arr, 5);if(index > 0){System.out.println("找到了,索引地址:" + index);}else{System.out.println("没找到");}}}
4.6、方法的重载(overload)
/** 方法的重载(overload) loading...** 1.定义:在同一个类中,允许存在一个以上的同名方法,只要它们的参数个数或者参数类型不同即可。** “两同一不同”:同一个类、相同方法名* 参数列表不同:参数个数不同,参数类型不同** 2.举例:* Arrays类中重载的sort() / binarySearch()** 3.判断是否重载* 与方法的返回值类型、权限修饰符、形参变量名、方法体都无关。** 4.在通过对象调用方法时,如何确定某一个指定的方法:* 方法名---》参数列表*/public class OverLoadTest {public static void main(String[] args) {OverLoadTest test = new OverLoadTest();test.getSum(1, 2); //调用的第一个,输出1}//如下的四个方法构成了重载public void getSum(int i,int j){System.out.println("1");}public void getSum(double d1,double d2){System.out.println("2");}public void getSum(String s,int i){System.out.println("3");}public void getSum(int i,String s){}//以下3个是错误的重载// public int getSum(int i,int j){// return 0;// }// public void getSum(int m,int n){//// }// private void getSum(int i,int j){//// }}
1、举例
1.判断:与void show(int a,char b,double c){}构成重载的有:a)void show(int x,char y,double z){} // nob)int show(int a,double c,char b){} // yesc) void show(int a,double c,char b){} // yesd) boolean show(int c,char b){} // yese) void show(double c){} // yesf) double show(int x,char y,double z){} // nog) void shows(){double c} // no
2、编程
/** 1.编写程序,定义三个重载方法并调用。方法名为mOL。* 三个方法分别接收一个int参数、两个int参数、一个字符串参数。* 分别执行平方运算并输出结果,相乘并输出结果,输出字符串信息。* 在主类的main ()方法中分别用参数区别调用三个方法。* 2.定义三个重载方法max(),* 第一个方法求两个int值中的最大值,* 第二个方法求两个double值中的最大值,* 第三个方法求三个double值中的最大值,并分别调用三个方法。**/public class OverLoadever {public static void main(String[] args) {OverLoadever test = new OverLoadever();//1.调用3个方法test.mOL(5);test.mOL(6, 4);test.mOL("fg");//2.调用3个方法int num1 = test.max(18, 452);System.out.println(num1);double num2 = test.max(5.6, -78.6);System.out.println(num2);double num3 = test.max(15, 52, 42);System.out.println(num3);}//1.如下三个方法构成重载public void mOL(int i){System.out.println(i*i);}public void mOL(int i,int j){System.out.println(i*j);}public void mOL(String s){System.out.println(s);}//2.如下三个方法构成重载public int max(int i,int j){return (i > j) ? i : j;}public double max(double i,double j){return (i > j) ? i : j;}public double max(double d1,double d2,double d3){double max = (d1 > d2) ? d1 : d2;return (max > d3) ? max : d3;}}
4.7、可变个数的形参
JavaSE 5.0 中提供了Varargs(variable number of arguments)机制,允许直接定义能和多个实参相匹配的形参。从而,可以用一种更简单的方式,来传递个数可变的实参。
/** 可变个数形参的方法* 1.jdk 5.0新增的内容* 2.具体使用:* 2.1 可变个数形参的格式:数据类型 ... 变量名* 2.2 当调用可变个数形参的方法时,传入的参数的个数可以是:0个,1个,2个...* 2.3可变个数形参的方法与本类中方法名相同,形参不同的方法之间构成重载。* 2.4可变个数形参的方法与本类中方法名相同,形参类型也相同的数组之间不构成重载。即二者不可共存。* 2.5可变个数形参在方法中的形参中,必须声明在末尾。* 2.6可变个数形参在方法中的形参中,最多只能声明一个可变形参。*/public class MethodArgs {public static void main(String[] args) {MethodArgs test = new MethodArgs();test.show(12);// test.show("hell0");// test.show("hello","world");// test.show();test.show(new String[] { "AA", "BB", "CC" });}public void show(int i) {}// public void show(String s){// System.out.println("show(String)");// }public void show(String... strs) {System.out.println("show(String ...strs)");for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {System.out.println(strs[i]);}}// 此方法与上一方法不可共存// public void show(String[] strs){//// }public void show(int i, String... strs) {}//The variable argument type String of the method show must be the last parameter// public void show(String... strs,int i,) {//// }}
4.8、方法参数的值传递机制(重点!!!)
关于变量的赋值
* 如果变量是基本数据类型,此时赋值的是变量所保存的数据值。
* 如果变量是引用数据类型,此时赋值的是变量所保存的数据的地址值。
public class ValueTransferTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("**********基本数据类型:***********");int m = 10;int n = m;System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);n = 20;System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);System.out.println("***********引用数据类型:********");Order o1 = new Order();o1.orderId = 1001;Order o2 = o1; //赋值后,o1和o2的地址值相同,都指向了堆空间中同一个对象实体System.out.println("o1.orderId = " + o1.orderId + ",o2.orderId = " + o2.orderId);o2.orderId = 1002;System.out.println("o1.orderId = " + o1.orderId + ",o2.orderId = " + o2.orderId);}}class Order{int orderId;}
4.8.1、针对基本数据类型
/** 方法的形参的传递机制:值传递** 1.形参:方法定义时,声明的小括号内的参数* 实参:方法调用时,实际传递给形参的数据** 2.值传递机制:* 如果参数是基本数据类型,此时实参赋值给形参的是实参真是存储的数据值。*/public class ValueTransferTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {int m = 10;int n = 20;System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);//交换两个变量的值的操作// int temp = m;// m = n;// n = temp;ValueTransferTest1 test = new ValueTransferTest1();test.swap(m, n);System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);/****m = 10, n = 20m = 10, n = 20**/}public void swap(int m,int n){int temp = m;m = n;n = temp;}}
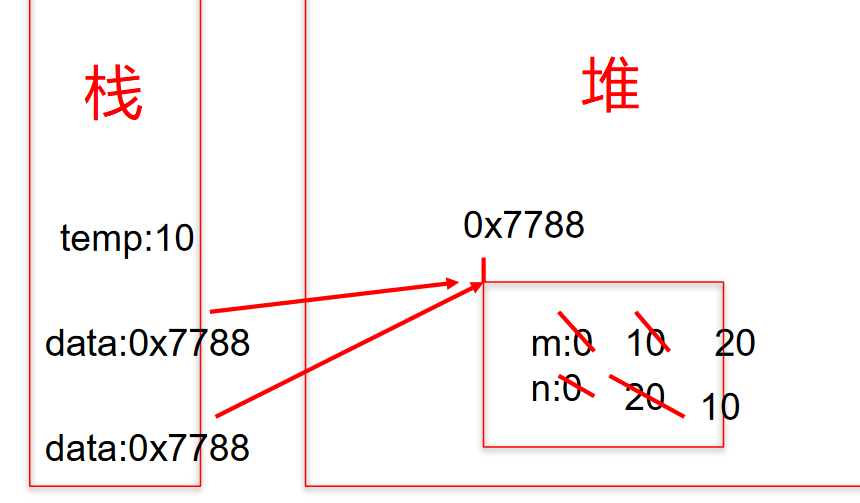
4.8.2、针对引用数据类型
如果参数是引用数据类型,此时实参赋值给形参的是实参存储数据的地址值。
public class ValueTransferTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Data data = new Data();data.m = 10;data.n = 20;System.out.println("m = " + data.m + ", n = " + data.n);//交换m和n的值// int temp = data.m;// data.m = data.n;// data.n = temp;ValueTransferTest2 test = new ValueTransferTest2();test.swap(data);System.out.println("m = " + data.m + ", n = " + data.n);}public void swap(Data data){int temp = data.m;data.m = data.n;data.n = temp;}}class Data{int m;int n;}
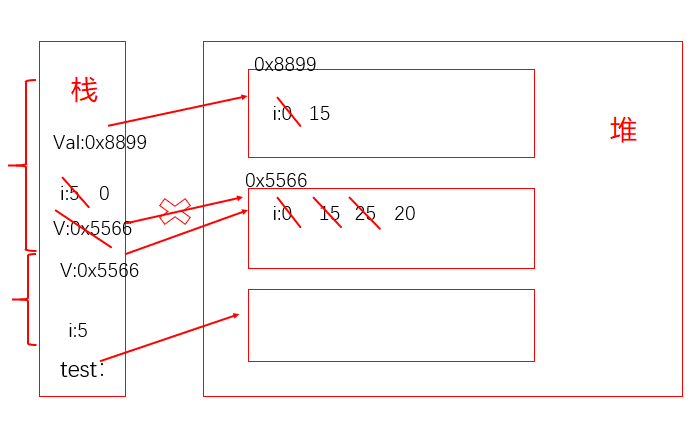
4.8.3、练习1
public class TransferTest3{public static void main(String args[]){TransferTest3 test=new TransferTest3();test.first();}public void first(){int i=5;Value v=new Value();v.i=25;second(v,i);System.out.println(v.i); //20}public void second(Value v,int i){i=0;v.i=20;Value val=new Value();v=val;System.out.println(v.i+" "+i);//15 0}}class Value {int i= 15;}//15 020
4.8.4、练习2

public static void method(int a,int b){a = a * 10;b = b * 20;System.out.println(a);System.out.println(b);System.exit(0);}
4.8.5、练习3
/** 微软:* 定义一个int型的数组:int[] arr = new int[]{12,3,3,34,56,77,432};* 让数组的每个位置上的值去除以首位置的元素,得到的结果,作为该位置上的新值。遍历新的数组。*///错误写法for(int i= 0;i < arr.length;i++){arr[i] = arr[i] / arr[0];}//正确写法1for(int i = arr.length –1;i >= 0;i--){arr[i] = arr[i] / arr[0];}//正确写法2int temp = arr[0];for(int i= 0;i < arr.length;i++){arr[i] = arr[i] / temp;}
4.8.6、练习4
/** int[] arr = new int[10];* System.out.println(arr);//地址值?** char[] arr1 = new char[10];* System.out.println(arr1);//地址值?*/public class ArrayPrint {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3};//传进去的是一个Object的对象System.out.println(arr);//地址值char[] arr1 = new char[]{'a','b','c'};//传进去的是一个数组,里面遍历数据了System.out.println(arr1);//abc}}
4.8.7、练习5:将对象作为参数传递给方法
/** 练习5:将对象作为参数传递给方法* (1)定义一个Circle类,包含一个double型的radius属性代表圆的半径,一个findArea()方法返回圆的面积。** (2)定义一个类PassObject,在类中定义一个方法printAreas(),该方法的定义如下:* public void printAreas(Circle c,int time)* 在printAreas方法中打印输出1到time之间的每个整数半径值,以及对应的面积。* 例如,times为5,则输出半径1,2,3,4,5,以及对应的圆面积。** (3)在main方法中调用printAreas()方法,调用完毕后输出当前半径值。**/public class Circle {double radius; //半径//返回圆的面积public double findArea(){return radius * radius * Math.PI;}}
PassObject类
public class PassObject {public static void main(String[] args) {PassObject test = new PassObject();Circle c = new Circle();test.printAreas(c, 5);System.out.println("no radius is:" + c.radius);}public void printAreas(Circle c,int time){System.out.println("Radius\t\tAreas");//设置圆的半径for(int i = 1;i <= time ;i++){c.radius = i;System.out.println(c.radius + "\t\t" + c.findArea());}//重新赋值c.radius = time + 1;}}
4.9、递归(recursion)方法
/** 递归方法的使用(了解)* 1.递归方法:一个方法体内调用它自身。* 2.方法递归包含了一种隐式的循环,它会重复执行某段代码,但这种重复执行无须循环控制。** 3.递归一定要向已知方向递归,否则这种递归就变成了无穷递归,类似于死循环。**/public class RecursionTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 例1:计算1-100之间所有自然数的和// 方法1:int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {sum += i;}System.out.println("sum = " + sum);// 方法2:RecursionTest test = new RecursionTest();int sum1 = test.getSum(100);System.out.println("sum1 = " + sum1);}// 例1:计算1-n之间所有自然数的和public int getSum(int n) {if (n == 1) {return 1;} else {return n + getSum(n - 1);}}// 例2:计算1-n之间所有自然数的乘积//归求阶乘(n!)的算法public int getSum1(int n) {if (n == 1) {return 1;} else {return n * getSum1(n - 1);}}}
1、练习1
public class RecursionTest {public static void main(String[] args) {int value = test.f(10);System.out.println(value);}//例3:已知有一个数列:f(0) = 1,f(1) = 4,f(n+2)=2*f(n+1) + f(n),//其中n是大于0的整数,求f(10)的值。public int f(int n){if(n == 0){return 1;}else if(n == 1){return 4;}else{return 2*f(n-1) + f(n-2);}}//例4:已知一个数列:f(20) = 1,f(21) = 4,f(n+2) = 2*f(n+1)+f(n),//其中n是大于0的整数,求f(10)的值。public int f1(int n){if(n == 20){return 1;}else if(n == 21){return 4;}else{return 2*f1(n-1) + f1(n-2);}}}
2、练习2
/** 输入一个数据n,计算斐波那契数列(Fibonacci)的第n个值* 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55* 规律:一个数等于前两个数之和* 要求:计算斐波那契数列(Fibonacci)的第n个值,并将整个数列打印出来**/public class Recursion2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Recursion2 test = new Recursion2();int value = test.f(10);System.out.println(value);}public int f(int n) {if (n == 1 || n == 2) {return 1;} else {return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);}}}
05、面向对象特征之一:封装与隐藏
1、封装性的引入与体现
为什么需要封装?封装的作用和含义?
我要用洗衣机,只需要按一下开关和洗涤模式就可以了。有必要了解洗衣机内部的结构吗?有必要碰电动机吗?
我要开车,…
2、我们程序设计追求“高内聚,低耦合”。
高内聚:类的内部数据操作细节自己完成,不允许外部干涉;
低耦合:仅对外暴露少量的方法用于使用。
3、隐藏对象内部的复杂性,只对外公开简单的接口。
便于外界调用,从而提高系统的可扩展性、可维护性。通俗的说,把该隐藏的隐藏起来,该暴露的暴露出来。这就是封装性的设计思想。
/** 面向对象的特征一:封装与隐藏* 一、问题的引入:* 当我们创建一个类的对象以后,我们可以通过"对象.属性"的方式,对对象的属性进行赋值。这里,赋值操作要受到* 属性的数据类型和存储范围的制约。但除此之外,没有其他制约条件。但是,实际问题中,我们往往需要给属性赋值* 加入额外限制条件。这个条件就不能在属性声明时体现,我们只能通过方法进行条件的添加。比如说,setLegs* 同时,我们需要避免用户再使用“对象.属性”的方式对属性进行赋值。则需要将属性声明为私有的(private)* --》此时,针对于属性就体现了封装性。** 二、封装性的体现:* 我们将类的属性私有化(private),同时,提供公共的(public)方法来获取(getXxx)和设置(setXxx)** 拓展:封装性的体现:① 如上 ② 单例模式 ③ 不对外暴露的私有方法**/public class AnimalTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Animal a = new Animal();a.name = "大黄";// a.age = 1;// a.legs = 4;//The field Animal.legs is not visiblea.show();// a.legs = -4;// a.setLegs(6);a.setLegs(-6);// a.legs = -4;//The field Animal.legs is not visiblea.show();System.out.println(a.name);System.out.println(a.getLegs());}}class Animal{String name;private int age;private int legs; //腿的个数//对于属性的设置public void setLegs(int l){if(l >= 0 && l % 2 == 0){legs = l;}else{legs = 0;}}//对于属性的获取public int getLegs(){return legs;}public void eat(){System.out.println("动物进食");}public void show(){System.out.println("name = " + name + ",age = " + age + ",legs = " + legs);}//提供关于属性 age 的 get 和 set 方法public int getAge(){return age;}public void setAge(int a){age = a;}}
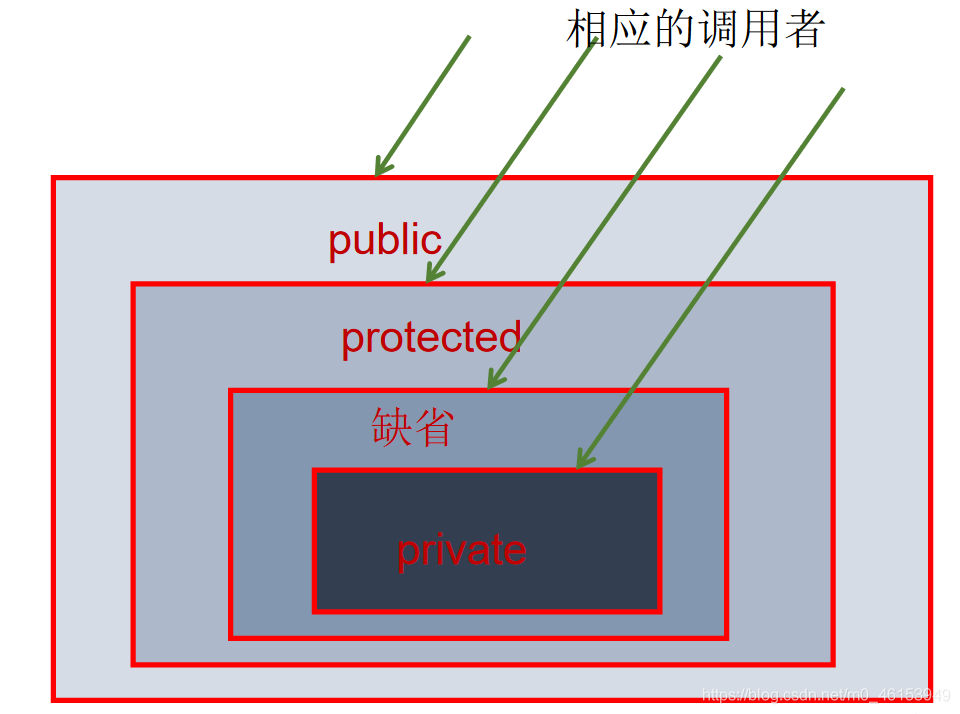
5.1、四种权限修饰符的理解与测试
Java 权限修饰符public、protected、default(缺省)、private 置于类的成员定义前,用来限定对象对该类成员的访问权限。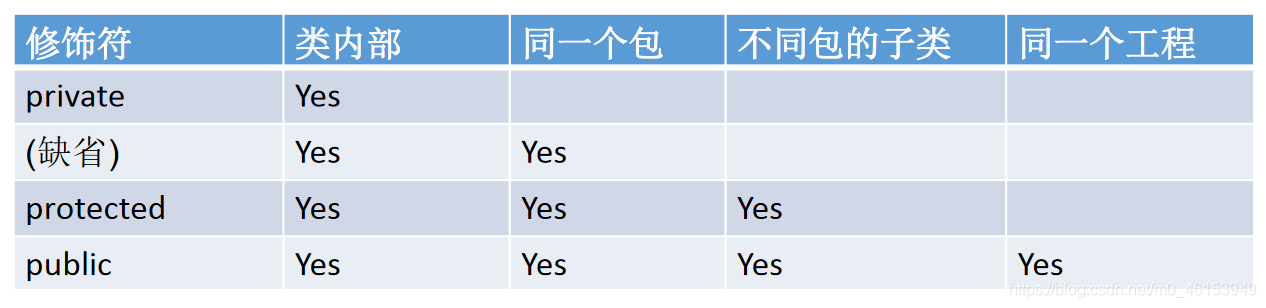
对于 class 的权限修饰只可以用 public 和 default(缺省)。
- public 类可以在任意地方被访问。
- default 类只可以被同一个包内部的类访问。
1、Order 类
/** 三、封装性的体现,需要权限修饰符来配合。* 1.Java 规定的 4 种权限:(从小到大排序)private、缺省、protected、public* 2.4 种权限用来修饰类及类的内部结构:属性、方法、构造器、内部类* 3.具体的,4 种权限都可以用来修饰类的内部结构:属性、方法、构造器、内部类* 修饰类的话,只能使用:缺省、public* 总结封装性:Java 提供了 4 中权限修饰符来修饰类积累的内部结构,体现类及类的内部结构的可见性的方法。**/public class Order {private int orderPrivate;int orderDefault;public int orderPublic;private void methodPrivate(){orderPrivate = 1;orderDefault = 2;orderPublic = 3;}void methodDefault(){orderPrivate = 1;orderDefault = 2;orderPublic = 3;}public void methodPublic(){orderPrivate = 1;orderDefault = 2;orderPublic = 3;}}
2、OrderTest 类
public class OrderTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Order order = new Order();order.orderDefault = 1;order.orderPublic = 2;//出了 Order 类之后,私有的结构就不可调用了// order.orderPrivate = 3;//The field Order.orderPrivate is not visibleorder.methodDefault();order.methodPublic();//出了 Order 类之后,私有的结构就不可调用了// order.methodPrivate();//The method methodPrivate() from the type Order is not visible}}
相同项目不同包的 OrderTest 类
import github.Order;public class OrderTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Order order = new Order();order.orderPublic = 2;//出了 Order 类之后,私有的结构、缺省的声明结构就不可调用了// order.orderDefault = 1;// order.orderPrivate = 3;//The field Order.orderPrivate is not visibleorder.methodPublic();//出了 Order 类之后,私有的结构、缺省的声明结构就不可调用了// order.methodDefault();// order.methodPrivate();//The method methodPrivate() from the type Order is not visible}}
5.2、封装性的练习

/** 1.创建程序,在其中定义两个类:Person 和 PersonTest 类。* 定义如下:用 setAge()设置人的合法年龄(0~130),用 getAge()返回人的年龄。**/public class Person {private int age;public void setAge(int a){if(a < 0 || a > 130){// throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据据非法");System.out.println("传入的数据据非法");return;}age = a;}public int getAge(){return age;}//绝对不能这样写!!!public int doAge(int a){age = a;return age;}}
3、测试类
/** 在 PersonTest 类中实例化 Person 类的对象 b,* 调用 setAge()和 getAge()方法,体会 Java 的封装性。*/public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person();// p1.age = 1; //编译不通过p1.setAge(12);System.out.println("年龄为:" + p1.getAge());}}
06、 构造器(构造方法)
6.1、构造器的理解
/** 类的结构之三:构造器(构造方法、constructor)的使用* constructor:** 一、构造器的作用:* 1.创建对象* 2.初始化对象的属性** 二、说明* 1.如果没有显示的定义类的构造器的话,则系统默认提供一个空参的构造器。* 2.定义构造器的格式:* 权限修饰符 类名(形参列表) { }* 3.一个类中定义的多个构造器,彼此构成重载。* 4.一旦显示的定义了类的构造器之后,系统不再提供默认的空参构造器。* 5.一个类中,至少会有一个构造器*/public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建类的对象:new + 构造器Person p = new Person(); //Person()这就是构造器p.eat();Person p1 = new Person("Tom");System.out.println(p1.name);}}class Person{//属性String name;int age;//构造器public Person(){System.out.println("Person()......");}public Person(String n){name = n;}public Person(String n,int a){name = n;age = a;}//方法public void eat(){System.out.println("人吃饭");}public void study(){System.out.println("人学习");}}
1、练习 1
/* 2.在前面定义的 Person 类中添加构造器,* 利用构造器设置所有人的 age 属性初始值都为 18。**/public class Person {private int age;public Person(){age = 18;}}public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person();System.out.println("年龄为:" + p1.getAge());}}
2、练习 2
/* 3.修改上题中类和构造器,增加 name 属性,* 使得每次创建 Person 对象的同时初始化对象的 age 属性值和 name 属性值。*/public class Person {private int age;private String name;public Person(){age = 18;}public Person(String n,int a){name = n;age = a;}public void setName(String n){name = n;}public String getName(){return name;}public void setAge(int a){if(a < 0 || a > 130){// throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据据非法");System.out.println("传入的数据据非法");return;}age = a;}public int getAge(){return age;}}public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Person p2 = new Person("Tom",21);System.out.println("name = " + p2.getName() + ",age = " + p2.getAge());}}
3、练习 3
/** 编写两个类,TriAngle 和 TriAngleTest,* 其中 TriAngle 类中声明私有的底边长 base 和高 height,同时声明公共方法访问私有变量。* 此外,提供类必要的构造器。另一个类中使用这些公共方法,计算三角形的面积。**/public class TriAngle {private double base;//底边长private double height;//高public TriAngle(){}public TriAngle(double b,double h){base = b;height = h;}public void setBase(double b){base = b;}public double getBase(){return base;}public void setHeight(double h){height = h;}public double getHeight(){return height;}}public class TriAngleTest {public static void main(String[] args) {TriAngle t1 = new TriAngle();t1.setBase(2.0);t1.setHeight(2.5);// t1.base = 2.5;//The field TriAngle.base is not visible// t1.height = 4.3;System.out.println("base : " + t1.getBase() + ",height : " + t1.getHeight());TriAngle t2 = new TriAngle(5.1,5.6);System.out.println("面积 : " + t2.getBase() * t2.getHeight() / 2);}}
6.2、总结属性赋值的过程
* 总结:属性赋值的先后顺序
*
* ① 默认初始化值
* ② 显式初始化
* ③ 构造器中赋值
* ④ 通过”对象.方法” 或 “对象.属性”的方式,赋值
*
* 以上操作的先后顺序:① - ② - ③ - ④
public class UserTest {public static void main(String[] args) {User u = new User();System.out.println(u.age);User u1 = new User(2);u1.setAge(3);System.out.println(u1.age);}}class User{String name;int age = 1;public User(){}public User(int a){age = a;}public void setAge(int a){age = a;}}
6.3、JavaBean 的使用
/** JavaBean 是一种 Java 语言写成的可重用组件。* 所谓 javaBean,是指符合如下标准的 Java 类:* > 类是公共的* > 有一个无参的公共的构造器* > 有属性,且有对应的 get、set 方法**/public class Customer {private int id;private String name;public Customer(){}public void setId(int i){id = i;}public int getId(){return id;}public void setName(String n){name = n;}public String getName(){return name;}}
6.4、UML 类图
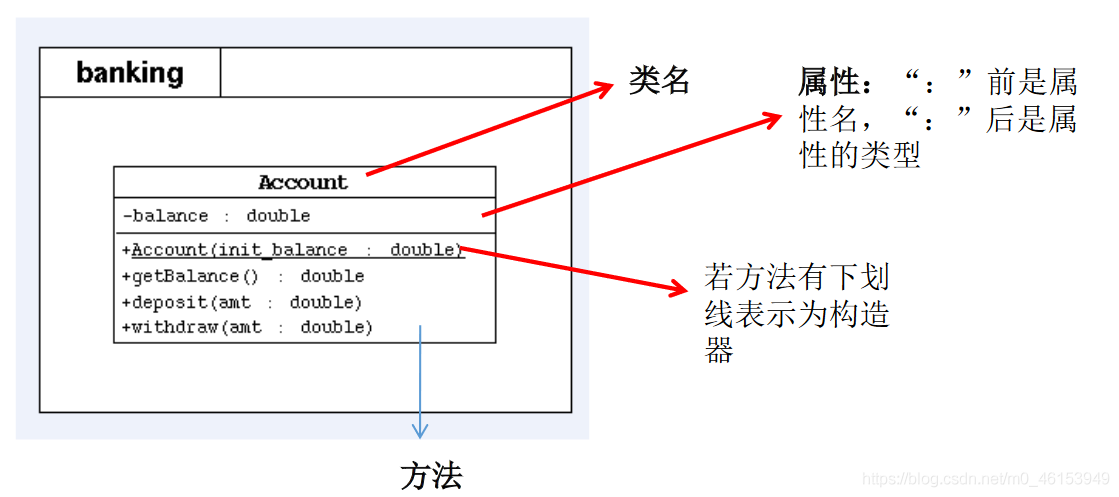
- 表示 public 类型,-表示 private 类型,#表示 protected 类型
- 方法的写法: 方法的类型(+、-) 方法名(参数名:参数类型):返回值类型
07、关键字:this 的使用
7.1、this 调用属性、方法、构造器
/** this 关键字的使用* 1.this 用来修饰、调用:属性、方法、构造器** 2.this 修饰属性和方法:* this 理解为:当前对象,或当前正在创建的对象。** 2.1 在类的方法中,我们可以使用"this.属性"或"this.方法"的方式,调用当前对象属性和方法。* 通常情况下,我们都选择省略“this.”。特殊情况下,如果方法的形参和类的属性同名,我们必须显式* 的使用"this.变量"的方式,表明此变量是属性,而非形参。** 2.2 在类的构造器中,我们可以使用"this.属性"或"this.方法"的方式,调用正在创建的对象属性和方法。* 但是,通常情况下,我们都选择省略“this.”。特殊情况下,如果构造器的形参和类的属性同名,我们必须显式* 的使用"this.变量"的方式,表明此变量是属性,而非形参。** 3.this 调用构造器* ① 我们可以在类的构造器中,显式的使用"this(形参列表)"的方式,调用本类中重载的其他的构造器!* ② 构造器中不能通过"this(形参列表)"的方式调用自己。* ③ 如果一个类中声明了n个构造器,则最多有n -1个构造器中使用了"this(形参列表)"。* ④ "this(形参列表)"必须声明在类的构造器的首行!* ⑤ 在类的一个构造器中,最多只能声明一个"this(形参列表)"。*/public class PersonTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person();p1.setAge(1);System.out.println(p1.getAge());p1.eat();System.out.println();Person p2 = new Person("jerry" ,20);System.out.println(p2.getAge());}}class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person(){this.eat();String info = "Person 初始化时,需要考虑如下的 1,2,3,4...(共 40 行代码)";System.out.println(info);}public Person(String name){this();this.name = name;}public Person(int age){this();this.age = age;}public Person(String name,int age){this(age); //调用构造器的一种方式this.name = name;// this.age = age;}public void setNmea(String name){this.name = name;}public String getName(){return this.name;}public void setAge(int age){this.age = age;}public int getAge(){return this.age;}public void eat(){System.out.println("人吃饭");this.study();}public void study(){System.out.println("学习");}}
7.2、this 的练习
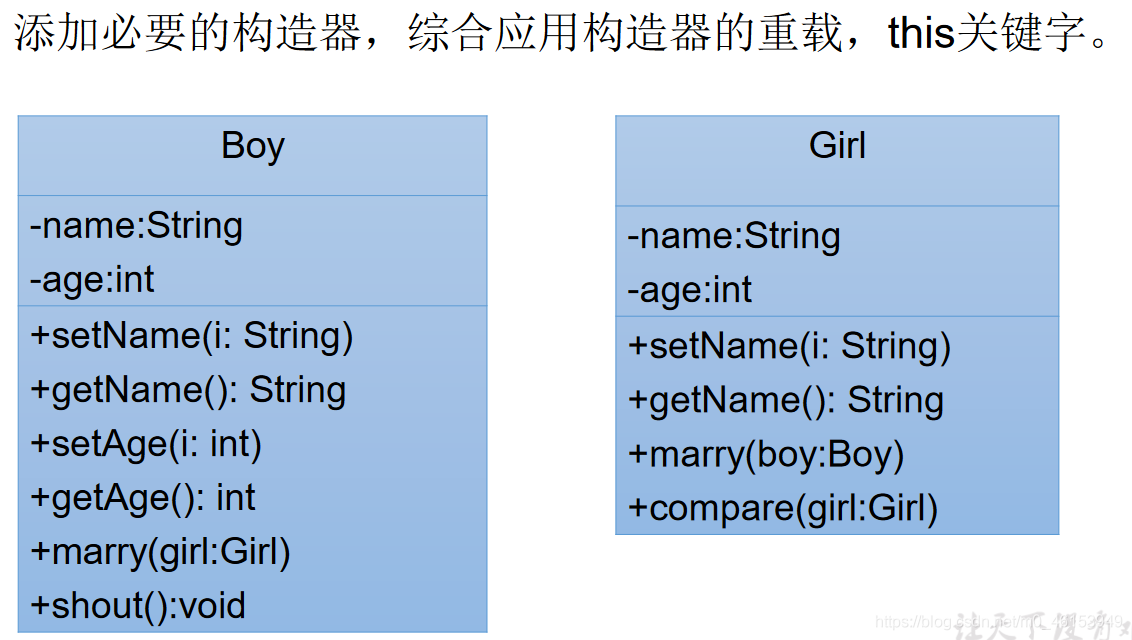
1、Boy 类
public class Boy {private String name;private int age;public void setName(String name){this.name = name;}public String getName(){return name;}public void setAge(int ahe){this.age = age;}public int getAge(){return age;}public Boy(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public void marry(Girl girl){System.out.println("我想娶" + girl.getName());}public void shout(){if(this.age >= 22){System.out.println("可以考虑结婚");}else{System.out.println("好好学习");}}}
2、Girl 类
public class Girl {private String name;private int age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Girl(){}public Girl(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public void marry(Boy boy){System.out.println("我想嫁给" + boy.getName());}/**** @Description 比较两个对象的大小* @author subei* @date 2020 年 4 月 21 日上午 9:17:35* @param girl* @return*/public int compare(Girl girl){// if(this.age >girl.age){// return 1;// }else if(this.age < girl.age){// return -1;// }else{// return 0;// }return this.age - girl.age;}}
3、测试类
public class BoyGirlTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Boy boy = new Boy("罗密欧",21);boy.shout();Girl girl = new Girl("朱丽叶", 18);girl.marry(boy);Girl girl1 = new Girl("祝英台", 19);int compare = girl.compare(girl1);if(compare > 0){System.out.println(girl.getName() + "大");}else if(compare < 0){System.out.println(girl1.getName() + "大");}else{System.out.println("一样的");}}}
2、练习2
Account 类
public class Account {private int id; // 账号private double balance; // 余额private double annualInterestRate; // 年利率public void setId(int id) {}public double getBalance() {return balance;}public void setBalance(double balance) {this.balance = balance;}public double getAnnualInterestRate() {return annualInterestRate;}public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;}public int getId() {return id;}public void withdraw(double amount) { // 取钱if(balance < amount){System.out.println("余额不足,取款失败");return;}balance -= amount;System.out.println("成功取出" + amount);}public void deposit(double amount) { // 存钱if(amount > 0){balance += amount;System.out.println("成功存入" + amount);}}public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate) {this.id = id;this.balance = balance;this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;}}
Customer 类
public class Customer {private String firstName;private String lastName;private Account account;public Customer(String f, String l) {this.firstName = f;this.lastName = l;}public String getFirstName() {return firstName;}public String getLastName() {return lastName;}public Account getAccount() {return account;}public void setAccount(Account account) {this.account = account;}}
CustomerTest 类
/** 写一个测试程序。* (1)创建一个 Customer,名字叫 Jane Smith, 他有一个账号为 1000,* 余额为 2000 元,年利率为 1.23%的账户。* (2)对 Jane Smith 操作。存入 100 元,再取出 960 元。再取出 2000 元。* 打印出 Jane Smith 的基本信息** 成功存入:100.0* 成功取出:960.0* 余额不足,取款失败* Customer [Smith, Jane] has a account: id is 1000,* annualInterestRate is 1.23%, balance is 1140.0**/public class CustomerTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Customer cust = new Customer("Jane" , "Smith");Account acct = new Account(1000,2000,0.0123);cust.setAccount(acct);cust.getAccount().deposit(100); //存入 100cust.getAccount().withdraw(960); //取钱 960cust.getAccount().withdraw(2000); //取钱 2000System.out.println("Customer[" + cust.getLastName() + cust.getFirstName() + "] has a account: id is "+ cust.getAccount().getId() + ",annualInterestRate is " + cust.getAccount().getAnnualInterestRate() * 100 + "%, balance is "+ cust.getAccount().getBalance());}}
3、练习3
Account 类
public class Account {private double balance;public double getBalance() {return balance;}public Account(double init_balance){this.balance = init_balance;}//存钱操作public void deposit(double amt){if(amt > 0){balance += amt;System.out.println("存钱成功");}}//取钱操作public void withdraw(double amt){if(balance >= amt){balance -= amt;System.out.println("取钱成功");}else{System.out.println("余额不足");}}}
Customer 类
public class Customer {private String firstName;private String lastName;private Account account;public String getFirstName() {return firstName;}public String getLastName() {return lastName;}public Account getAccount() {return account;}public void setAccount(Account account) {this.account = account;}public Customer(String f, String l) {this.firstName = f;this.lastName = l;}}
Bank 类
public class Bank {private int numberOfCustomers; //记录客户的个数private Customer[] customers; //存放多个客户的数组public Bank(){customers = new Customer[10];}//添加客户public void addCustomer(String f,String l){Customer cust = new Customer(f,l);// customers[numberOfCustomers] = cust;// numberOfCustomers++;customers[numberOfCustomers++] = cust;}//获取客户的个数public int getNumberOfCustomers() {return numberOfCustomers;}//获取指定位置上的客户public Customer getCustomers(int index) {// return customers; //可能报异常if(index >= 0 && index < numberOfCustomers){return customers[index];}return null;}}
BankTest 类
public class BankTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Bank bank = new Bank();bank.addCustomer("Jane", "Smith");bank.getCustomers(0).setAccount(new Account(2000));bank.getCustomers(0).getAccount().withdraw(500);double balance = bank.getCustomers(0).getAccount().getBalance();System.out.println("客户: " + bank.getCustomers(0).getFirstName() + "的账户余额为:" + balance);System.out.println("***************************");bank.addCustomer("万里", "杨");System.out.println("银行客户的个数为: " + bank.getNumberOfCustomers());}}
8、 关键字:package、import 的使用
8.1、关键字—package
/** 一、package 关键字的使用* 1.为了更好的实现项目中类的管理,提供包的概念* 2.使用 package 声明类或接口所属的包,声明在源文件的首行* 3.包,属于标识符,遵循标识符的命名规则、规范"见名知意"* 4.每“.”一次,就代表一层文件目录。** 补充:同一个包下,不能命名同名接口或同名类* 不同包下,可以命名同名的接口、类。**/public class PackageImportTest {}
JDK 中主要的包介绍
1.java.lang----包含一些 Java 语言的核心类,如 String、Math、Integer、System 和 Thread,提供常用功能2.java.net----包含执行与网络相关的操作的类和接口。3.java.io----包含能提供多种输入/输出功能的类。4.java.util----包含一些实用工具类,如定义系统特性、接口的集合框架类、使用与日期日历相关的函数。5.java.text----包含了一些 java 格式化相关的类6.java.sql----包含了 java 进行 JDBC 数据库编程的相关类/接口7.java.awt----包含了构成抽象窗口工具集(abstractwindowtoolkits)的多个类,这些类被用来构建和管理应用程序的图形用户界面(GUI)。B/S C/S
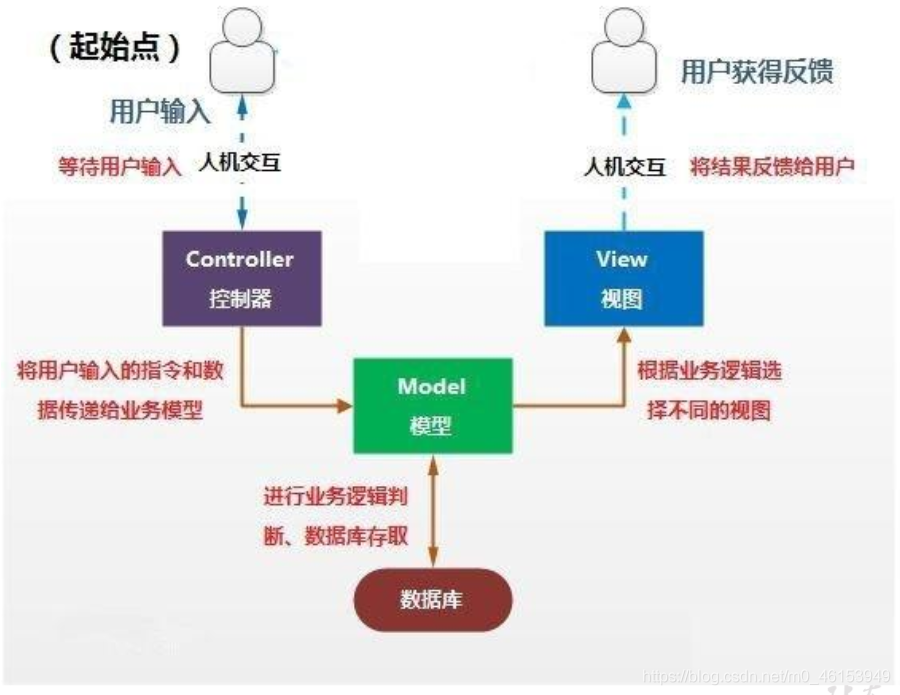
8.2、MVC 设计模式
MVC 是常用的设计模式之一,将整个程序分为三个层次:视图模型层,控制器层,数据模型层。这种将程序输入输出、数据处理,以及数据的展示分离开来的设计模式使程序结构变的灵活而且清晰,同时也描述了程序各个对象间的通信方式,降低了程序的耦合性。
8.3、关键字—import
import java.util.*;import account2.Bank;/** 二、import关键字的使用* import:导入* 1.在源文件中显式的使用import结构导入指定包下的类、接口* 2.声明在包的声明和类的声明之间* 3.如果需要导入多个结构,则并列写出即可* 4.可以使用"xxx.*"的方式,表示可以导入xxx包下的所有结构。* 5.如果导入的类或接口是java.lang包下的,或者是当前包下的,则可以省略此import语句。* 6.如果在代码中使用不同包下的同名的类。那么就需要使用类的全类名的方式指明调用的是哪个类。* 7.如果已经导入java.a包下的类。那么如果需要使用a包的子包下的类的话,仍然需要导入。* 8.import static组合的使用:调用指定类或接口下的静态的属性或方法.**/public class PackageImportTest {public static void main(String[] args) {String info = Arrays.toString(new int[]{1,2,3});Bank bank = new Bank();ArrayList list = new ArrayList();HashMap map = new HashMap();Scanner s = null;System.out.println("hello");UserTest us = new UserTest();}}