数据结构KMP算法配图详解
解决问题类型
KMP算法的作用是在一个已知字符串中查找子串的位置,也叫做串的模式匹配。
:::info
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置(下标从 0 开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1 。
输入:haystack = “hello”, needle = “ll” 输出:2
:::
操作流程
- 假设现在文本串 S 匹配到 i 位置,模式串 P 匹配到 j 位置
- 如果 j = -1,或者当前字符匹配成功(即 S[i] == P[j] ),都令 i++,j++,继续匹配下一个字符;
- 如果 j != -1,且当前字符匹配失败(即 S[i] != P[j] ),则令 i 不变,j = next[j]。此举意味着失配时,模式串 P相对于文本串 S 向右移动了 j - next [j] 位
- 换言之,将模式串 P 失配位置的 next 数组的值对应的模式串 P 的索引位置移动到失配处
算法内容概念
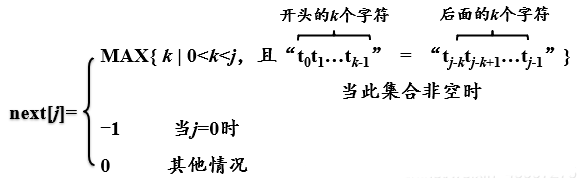
next数组
用一个next数组存储子串的最长相等前后缀的长度。而且next数组的数值只与子串本身有关。
所以next[i]=j,含义是:下标为i 的字符前的字符串最长相等前后缀的长度为j。
:::warning
子串t= “abcabcmn”的next数组为next[0]=-1(前面没有字符串单独处理)
next[1]=0;next[2]=0;next[3]=0;next[4]=1;next[5]=2;next[6]=3;next[7]=0;
:::
“提示”示例代码
public class Solution{public int StrStr(string haystack, string needle){// 排除子串为空if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(needle)){return 0;}// 排除子串字长大于匹配字符串以及匹配字符串为空if (needle.Length > haystack.Length || string.IsNullOrEmpty(haystack)){return -1;}// 调用KMP算法return KMP( haystack, needle);}}private static int KMP(string haystack, string needle){// 创建 next数组:最长匹配长度+1int[] next = GetNext(needle);// 字符串下标int i = 0;int j = 0;// KMP判断循环while (i < haystack.Length){if (haystack[i] == needle[j]) // 字符相等,两者各进一步{j++;i++;}if (j == needle.Length){return i - j;}else if (i < haystack.Length && haystack[i] != needle[j]){if (j != 0)j = next[j - 1];elsei++;}}return -1;}// 计算获取next数组内的值private static int[] GetNext(string str){int[] next = new int[str.Length];//数组内元素个数等于子串字符数next[0] = 0;int i = 1;// 指针初始位int j = 0;// 元素值while (i < str.Length){if (str[i] == str[j]){j++;next[i] = j;i++;}else{if (j == 0){next[i] = 0;i++;}// 回溯else{j = next[j - 1];}}}return next;}