Pythond 是定时触发用户自定义 Python 采集脚本的一整套方案。本文以 “获取每个小时登录的用户数”作为指标上报给中心为例。
1.1. 业务演示介绍
业务流程大致如下: 从数据库中采集数据 (Python 脚本) -> pythond 采集器定时触发该脚本上报数据(datakit) -> 从中心可看到指标(web)。
数据库现在有一张表叫 customers, 表中有如下字段:
- name: 姓名 (字符串)
- last_logined_time : 登录时间 (时间戳)
建表语句如下:
create table customers(`id` BIGINT(20) not null AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增 ID',`last_logined_time` BIGINT(20) not null DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '登录时间 (时间戳)',`name` VARCHAR(48) not null DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名',primary key(`id`),key idx_last_logined_time(last_logined_time)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
往上面的表中插入测试数据:
INSERT INTO customers (id, last_logined_time, name) VALUES (1, 1645600127, 'zhangsan');INSERT INTO customers (id, last_logined_time, name) VALUES (2, 1645600127, 'lisi');INSERT INTO customers (id, last_logined_time, name) VALUES (3, 1645600127, 'wangwu');
使用以下 SQL 语句来获取 “获取每个小时登录的用户数”:
select count(1) from customers where last_logined_time>=(unix_timestamp()-3600);
把上面的数据以指标形式上报给中心。
下面详细讲述实现上述业务的具体步骤。
1.2. 前置条件
1.2.1. Python 环境
需要安装 Python,目前 Pythond 采集器处于 alpha 阶段,同时兼容 Python 2.7+ 和 Python 3+。但为了以后的兼容性,强烈建议使用 Python 3,毕竟 Python 2 官方已经不作支持了。下面的演示也是使用 Python 3。
1.2.2. Python 依赖库
需要安装以下依赖库:
- requests(操作网络,用于上报指标)
- pymysql(操作 MySQL 数据库,用于连接数据库获取业务数据)
安装方法如下:
# python3python3 -m pip install requestspython3 -m pip install pymysql
上述的安装需要安装 pip,如果你没有,可以参考以下方法(源自: 这里):
# Linux/MacOSpython3 -m ensurepip --upgrade# Windowspy -m ensurepip --upgrade
1.3. 编写用户自定义脚本
需要用户继承 DataKitFramework 类,然后对 run 方法进行改写。DataKitFramework 类源代码文件是 datakit_framework.py,路径是 datakit/python.d/core/datakit_framework.py。
具体的使用可以参见源代码文件 datakit/python.d/core/demo.py。
我们这里根据上述需求,写成如下的 Python 脚本,命名为 hellopythond.py:
from datakit_framework import DataKitFrameworkimport pymysqlimport reimport loggingclass MysqlConn():def __init__(self, logger, config):self.logger = loggerself.config = configself.re_errno = re.compile(r'^\((\d+),')try:self.conn = pymysql.Connect(**self.config)self.logger.info("pymysql.Connect() ok, {0}".format(id(self.conn)))except Exception as e:raise edef __del__(self):self.close()def close(self):if self.conn:self.logger.info("conn.close() {0}".format(id(self.conn)))self.conn.close()def execute_query(self, sql_str, sql_params=(), first=True):res_list = Nonecur = Nonetry:cur = self.conn.cursor()cur.execute(sql_str, sql_params)res_list = cur.fetchall()except Exception as e:err = str(e)self.logger.error('execute_query: {0}'.format(err))if first:retry = self._deal_with_network_exception(err)if retry:return self.execute_query(sql_str, sql_params, False)finally:if cur is not None:cur.close()return res_listdef execute_write(self, sql_str, sql_params=(), first=True):cur = Nonen = Noneerr = Nonetry:cur = self.conn.cursor()n = cur.execute(sql_str, sql_params)except Exception as e:err = str(e)self.logger.error('execute_query: {0}'.format(err))if first:retry = self._deal_with_network_exception(err)if retry:return self.execute_write(sql_str, sql_params, False)finally:if cur is not None:cur.close()return n, errdef _deal_with_network_exception(self, stre):errno_str = self._get_errorno_str(stre)if errno_str != '2006' and errno_str != '2013' and errno_str != '0':return Falsetry:self.conn.ping()except Exception as e:return Falsereturn Truedef _get_errorno_str(self, stre):searchObj = self.re_errno.search(stre)if searchObj:errno_str = searchObj.group(1)else:errno_str = '-1'return errno_strdef _is_duplicated(self, stre):errno_str = self._get_errorno_str(stre)# 1062:字段值重复,入库失败# 1169:字段值重复,更新记录失败if errno_str == "1062" or errno_str == "1169":return Truereturn Falseclass HelloPythond(DataKitFramework):__name = 'HelloPythond'interval = 10 # 每 10 秒钟采集上报一次。这个根据实际业务进行调节,这里仅作演示。# if your datakit ip is 127.0.0.1 and port is 9529, you won't need use this,# just comment it.# def __init__(self, **kwargs):# super().__init__(ip = '127.0.0.1', port = 9529)def run(self):config = {"host": "172.16.2.203","port": 30080,"user": "root","password": "Kx2ADer7","db": "df_core","autocommit": True,# "cursorclass": pymysql.cursors.DictCursor,"charset": "utf8mb4"}mysql_conn = MysqlConn(logging.getLogger(''), config)query_str = "select count(1) from customers where last_logined_time>=(unix_timestamp()-%s)"sql_params = ('3600')n = mysql_conn.execute_query(query_str, sql_params)data = [{"measurement": "hour_logined_customers_count", # 指标名称。"tags": {"tag_name": "tag_value", # 自定义 tag,根据自己想要标记的填写,我这里是随便写的},"fields": {"count": n[0][0], # 指标,这里是每个小时登录的用户数},},]in_data = {'M':data,'input': "pyfromgit"}return self.report(in_data) # you must call self.report here
1.4. 将自定义脚本放入正确的位置
在 Datakit 安装目录的 python.d 目录下新建一个文件夹,并命名为 hellopythond,这个文件夹名称要与上面编写的类名相同,即为 hellopythond。
然后将上面写好的脚本 hellopythond.py 放入此文件夹下,即最后的目录结构如下:
├── ...├── datakit└── python.d├── core│ ├── datakit_framework.py│ └── demo.py└── hellopythond└── hellopythond.py
上面的 core 文件夹是 Pythond 的核心文件夹,不要动。
上面是在没有开启 gitrepos 功能的情况下,如果是开启了 gitrepos 功能,那么路径结构就是这样的:
├── ...├── datakit├── python.d├── gitrepos│ └── yourproject│ ├── conf.d│ ├── pipeline│ └── python.d│ └── hellopythond│ └── hellopythond.py
1.5. 开启 pythond 配置文件
将 Pythond 配置文件复制出来。在 conf.d/pythond 目录下复制 pythond.conf.sample 为 pythond.conf,然后将配置成如下形式:
[[inputs.pythond]]# Python 采集器名称name = 'some-python-inputs' # required# 运行 Python 采集器所需的环境变量#envs = ['LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH',]# Python 采集器可执行程序路径(尽可能写绝对路径)cmd = "python3" # required. python3 is recommended.# 用户脚本的相对路径(填写文件夹,填好后该文件夹下一级目录的模块和 py 文件都将得到应用)dirs = ["hellopythond"] # 这里填的是文件夹名,即类名
1.6. 重启 Datakit
sudo datakit --restart
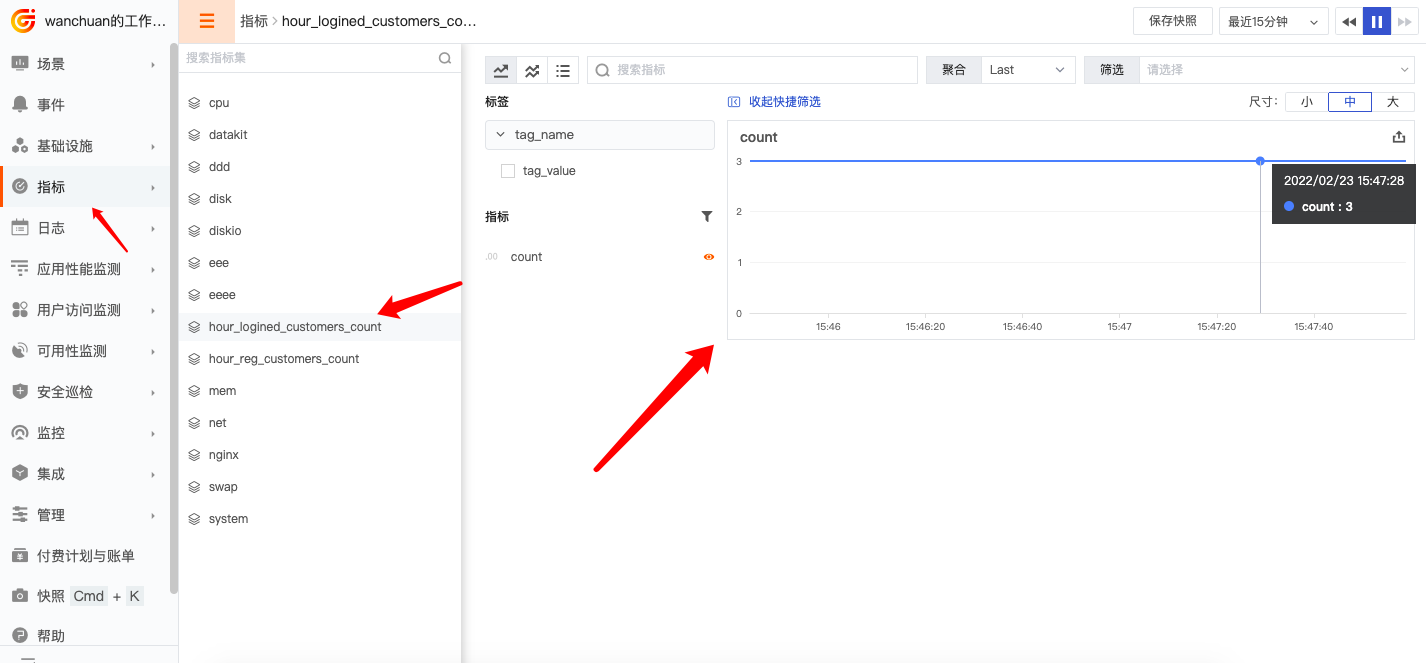
1.7. 效果图
如果一切顺利的话,大概 1 分钟内我们就能在中心看到指标图。