1 Spring Boot 主要特点是:
- 创建独立的Spring应用,为所有 Spring 的开发者提供一个非常快速的、广泛接受的入门体验
- 直接嵌入应用服务器,如tomcat、jetty、undertow等;不需要去部署war包
- 提供固定的启动器依赖去简化组件配置;实现开箱即用(启动器starter-其实就是Spring Boot提供的一个jar
包),通过自己设置参数(.properties或.yml的配置文件),即可快速使用。
- 自动地配置Spring和其它有需要的第三方依赖
- 提供了一些大型项目中常见的非功能性特性,如内嵌服务器、安全、指标,健康检测、外部化配置等
- 绝对没有代码生成,也无需 XML 配置。
2 创建工程
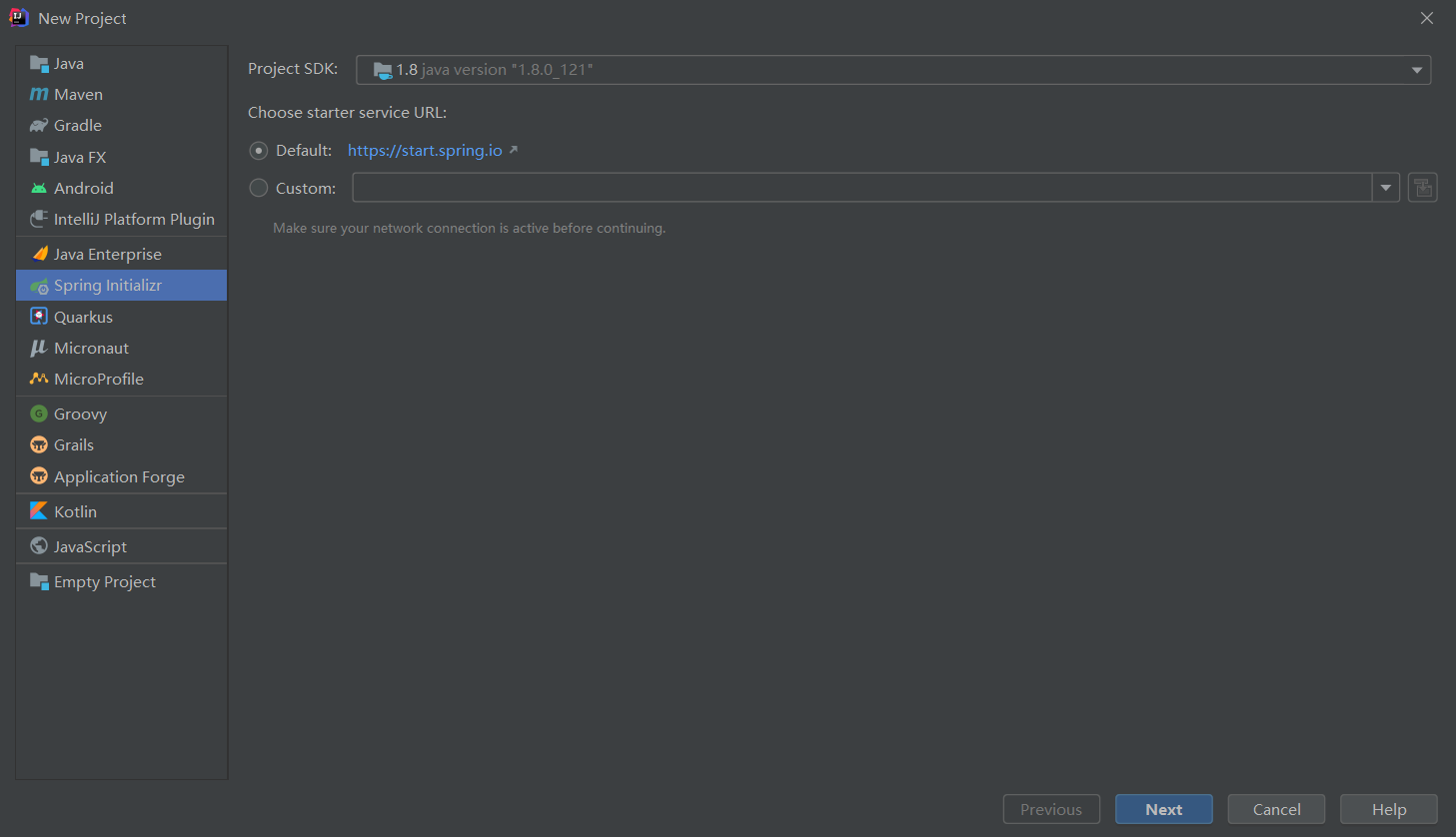
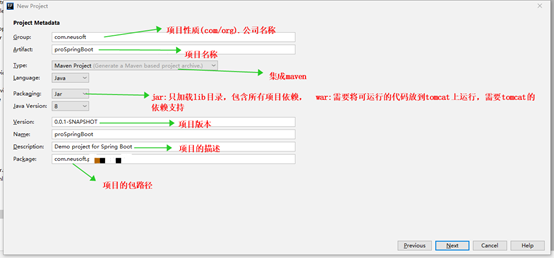
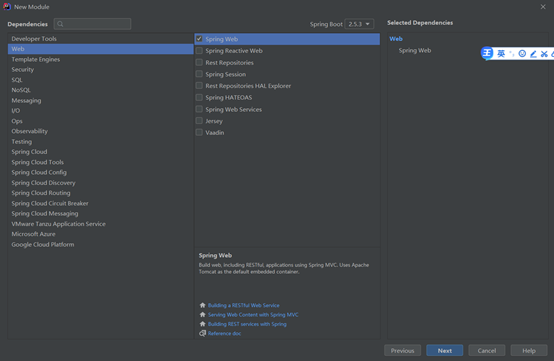
创建完成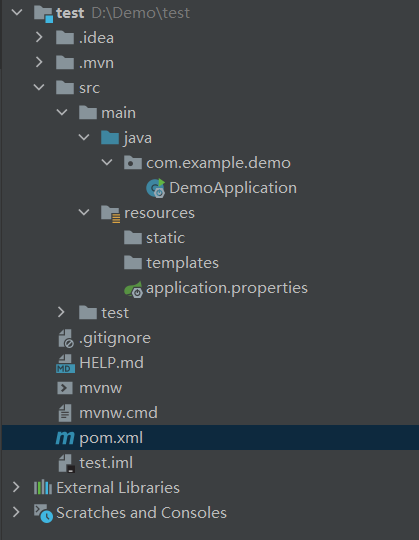
DemoApplication是启动类
3 配置
3.1 Java配置
@Configuration :声明一个类作为配置类,代替xml文件
@Bean :声明在方法上,将方法的返回值加入Bean容器,代替
@Value :属性注入
@PropertySource :指定外部属性文件
3.1.1 配置pom.xml
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.1.6</version></dependency>
3.1.2 配置jdbc.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot_test
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
3.1.3 JdbcConfig.java
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
String driverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}
3.1.4 测试
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@GetMapping("hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("dataSource = " + dataSource);
return "hello, spring boot!";
}
}
3.2 spring boot 属性注入
默认的文件名必须是:application.properties或application.yml
3.2.1 JdbcProperties.java
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "jdbc")
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
String driverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}
- 在类上通过@ConfigurationProperties注解声明当前类为属性读取类
- prefix=”jdbc” 读取属性文件中,前缀为jdbc的值。
- 在类上定义各个属性,名称必须与属性文件中 jdbc. 后面部分一致
- 需要注意的是,这里我们并没有指定属性文件的地址,所以我们需要把jdbc.properties名称改为
application.properties,这是Spring Boot默认读取的属性文件名
3.2.2 JdbcConfig.java
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}
通过 @EnableConfigurationProperties(JdbcProperties.class) 来声明要使用 JdbcProperties 这个类的
对象。然后要使用配置的话;可以通过以下方式注入JdbcProperties(三种):
@Autowired注入
@Autowired
private JdbcProperties prop;
构造函数注入
private JdbcProperties prop;
public JdbcConfig(Jdbcproperties prop){
this.prop = prop;
}
声明有@Bean的方法参数注入
@Bean
public Datasource dataSource(JdbcProperties prop){
// ...
}
3.3 yaml配置
3.3.1 单个yaml配置
配置文件除了可以使用application.properties类型,还可以使用后缀名为:.yml或者.yaml的类型
jdbc:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springboot_test
username: root
password: root
3.3.2 多个yaml配置
当一个项目中有多个yml配置文件的时候,可以以application-**.yml命名;在application.yml中配置项目使用激活
这些配置文件即可。
创建 application-abc.yml 文件
创建 application-def.yml 文件
在 application.yml 文件中添加如下配置:
#加载其它配置文件
spring:
profiles:
active: abc,def
多个文件名只需要写application-之后的名称,在多个文件之间使用,隔开。
4 自动配置原理
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 注解:@SpringBootApplication
- run方法:SpringApplication.run()
4.1 @SpringBootApplication 声明当前类是SpringBoot应用的配置类
源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackages"
)
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackageClasses"
)
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "nameGenerator"
)
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
4.1.1 @SpringBootConfiguration
源码
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Indexed;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
@Indexed
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
通过这段我们可以看出,在这个注解上面,又有一个 @Configuration 注解。通过上面的注释阅读我们知道:这个注解的作用就是声明当前类是一个配置类,然后Spring会自动扫描到添加了 @Configuration 的类,并且读取其中的配置信息。而 @SpringBootConfiguration 是来声明当前类是SpringBoot应用的配置类,项目中只能有一个。所以一般我们无需自己添加。
4.1.2 @EnableAutoConfiguration
第二级的注解 @EnableAutoConfiguration ,告诉Spring Boot基于你所添加的依赖,去“猜测”你想要如何配
置Spring。
比如我们引入了 spring-boot-starter-web ,而这个启动器中帮我们添加了 tomcat 、 SpringMVC的依赖。此时自动配置就知道你是要开发一个web应用,所以就帮你完成了web及SpringMVC的默认配置了!
4.1.3 @ComponentScan main函数所在的启动类
源码
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class;
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT;
String resourcePattern() default "**/*.class";
boolean useDefaultFilters() default true;
ComponentScan.Filter[] includeFilters() default {};
ComponentScan.Filter[] excludeFilters() default {};
boolean lazyInit() default false;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Filter {
FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION;
@AliasFor("classes")
Class<?>[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
Class<?>[] classes() default {};
String[] pattern() default {};
}
}
@SpringBootApplication注解声明的类就是main函数所在的启动类,因此扫描的包是该类所在包及其子
包。因此,一般启动类会放在一个比较前的包目录中。
4.2 默认配置原理
SpringBoot为我们提供了默认配置,而默认配置生效的步骤:
- @EnableAutoConfiguration注解会去寻找 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,读取其中以EnableAutoConfiguration 为key的所有类的名称,这些类就是提前写好的自动配置类
- 这些类都声明了 @Configuration 注解,并且通过 @Bean 注解提前配置了我们所需要的一切实例
- 但是,这些配置不一定生效,因为有 @ConditionalOn 注解,满足一定条件才会生效。比如条件之一: 是一些相关的类要存在类要存在,我们只需要引入了相关依赖(启动器),依赖有了条件成立,自动配置生效。
- 如果我们自己配置了相关Bean,那么会覆盖默认的自动配置的Bean
- 我们还可以通过配置application.yml文件,来覆盖自动配置中的属性
5 应用
5.1. Lombok
我们编写pojo时,经常需要编写构造函数和getter、setter方法,属性多的时候,就非常浪费时间,使用lombok插件可以解决这个问题:
安装插件
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Data : 注在类上,提供类的get、set、equals、hashCode、canEqual、toString方法
@AllArgsConstructor : 注在类上,提供类的全参构造
@NoArgsConstructor : 注在类上,提供类的无参构造
@Setter : 注在属性上,提供 set 方法
@Getter : 注在属性上,提供 get 方法
@EqualsAndHashCode : 注在类上,提供对应的 equals 和 hashCode 方法
@Log4j/@Slf4j : 注在类上,提供对应的 Logger 对象,变量名为 log
5.2 整合ssm
5.2.1 端口
server:
port: 80
5.2.2 静态资源
默认静态资源路径
classpath:/META-INF/resources/ classpath:/resources/ classpath:/static/ classpath:/public
5.2.3 拦截器
通过实现 WebMvcConfigurer 并添加 @Configuration 注解来实现自定义部分SpringMvc配置
创建拦截器
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Slf4j
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
log.debug("这是MyInterceptor拦截器的preHandle方法");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
log.debug("这是MyInterceptor拦截器的postHandle方法");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
log.debug("这是MyInterceptor拦截器的afterCompletion方法");
}
}
注册拦截器
import com.itheima.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 将拦截器注册到spring ioc容器
* @return myInterceptor
*/
@Bean
public MyInterceptor myInterceptor(){
return new MyInterceptor();
}
/**
* 重写该方法;往拦截器链添加自定义拦截器
* @param registry 拦截器链
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//通过registry添加myInterceptor拦截器,并设置拦截器路径为 /*
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/*");
}
}
5.2.4 整合jdbc和事务
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
事务:SpringBoot中通过注解来控制 @Transactional
5.2.5 整合连接池
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_test
username: root
password: root
5.2.6 整合mybatis
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
# mybatis配置
mybatis:
# 实体类别名包路径
type-aliases-package: com.itheima.pojo
# 映射文件路径
# mapper-locations: classpath:mappers/*.xml
configuration:
# 控制台输出执行sql
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
要给每一个Mapper接口添加 @Mapper 注解,才能被识别
或者,可以不加注解,而是在启动类上添加扫描包注解(推荐):
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.itheima.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 启动代码
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
@Data
@Table(name = "tb_user")
public class User{
// id
@Id
//开启主键自动回填
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
// 用户名
private String userName;
// 密码
private String password;
}
5.2.7 junit测试
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
在测试类上面必须要添加@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest 注解。
5.2.8 整合redis
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379

