https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Zy4y1K7SH?p=1
Vue核心
Vue特点:
- 遵循MVVM模式
- 代码简洁体积小,运行效率高,适合移动/PC端开发
- 只关注UI,可以轻松引入vue插件或其他第三库开发项目
与其他JS框架关联:
- 借鉴Angular的结构模板和数据绑定技术
- 借鉴React组件化和虚拟DOM技术
扩展插件:
- vue-cli:脚手架
- vue-resource、axios:ajax请求
- vue-router:路由
- vuex:状态管理
- mint-ui:基于vue的ui库(移动端)
- element-ui:基于vue的ui组件库(PC端)
初识Vue
初始Vue.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>初识Vue</title><script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script></head><body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h1>Hello,{{school.name.toUpperCase()}}</h1><h1>学校坐落在:{{school.address}}</h1><h1>我学的是:{{school.subject()}}</h1></div><script type="text/javascript">//创建一个Vue的实例对象,并传入配置对象new Vue({el:'#root',//用于指定当前Vue实例为哪个容器服务,值是选择器字符串,选择器写法类似于jquerydata:{//data是存储数据的地方,为root容器提供数据,值为一个对象,相当于React中的stateschool:{name:'atguigu',address:'鸿福科技园综合楼',subject:()=>'前端'}}})</script></body></html>
效果图:
总结:
补充小知识:JavaScript逻辑与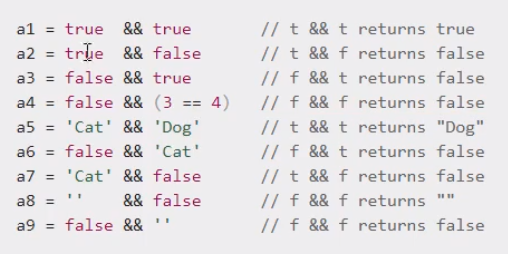
Vue的模板语法
语法分为两种
- 插值语法(双大括号表达式),用于解析标签体内容
- 指令(以v-开头),用于解析标签(包括:标签属性、标签内容、绑定事件…)
ps:v-bind:可以简写为:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>模板语法</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>插值语法</h2>
<h4>你好,{{msg}}</h4>
<hr/>
<h2>指令语法</h2>
<a v-bind:href="url">点我去学习</a>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
msg:'atguigu',
url:'http://www.atguigu.com'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
Vue的数据绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>数据绑定</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
单向数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="msg"><br/><br/>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model="msg">
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: '尚硅谷'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
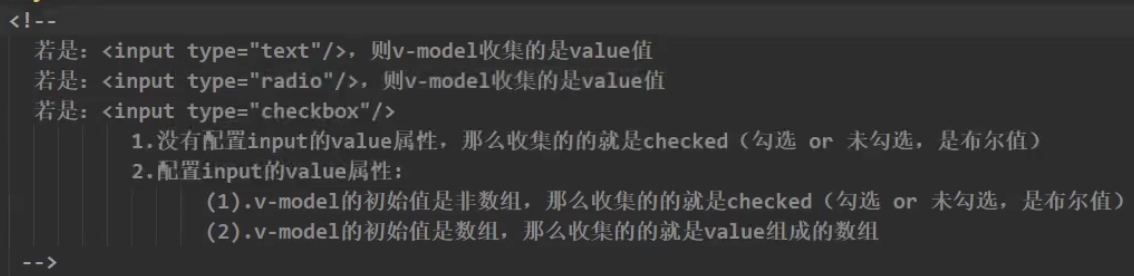
v-bind单向绑定,v-model双向绑定
v-model自动收集value值,可以省略:value,只支持输入类DOM
MVVM模型
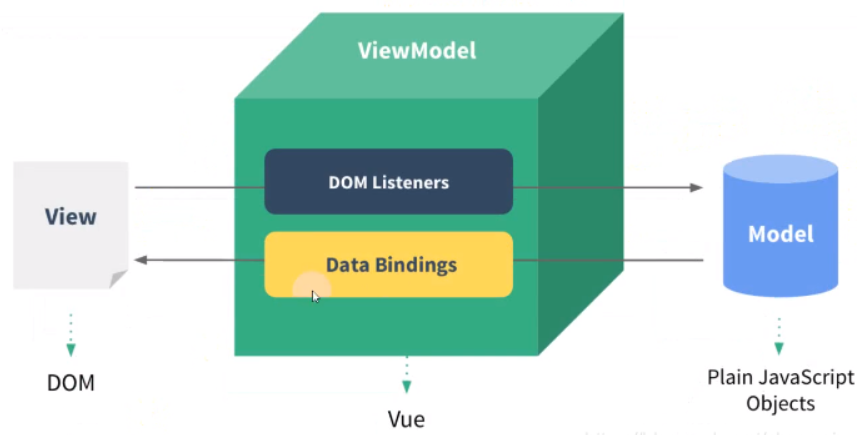
VM为视图模型,即new Vue({…})
Data与El的写法
el两种写法
- new Vue时候直接传递el属性
- 先new Vue再通过vm.$mount(‘#root’)指定el属性
data两种写法
- 对象式:非组件编码时可写对象,也可写函数
- 函数式:组件化编码必须使用函数式data
重要原则:由Vue所管理的函数,都不要写成箭头函数,一旦写了箭头函数,this就不对了(undefined或window)
Vue数据代理*
通过一个对象代理对另一个对象中属性的操作(读/写)
作用:更加方便读取到数据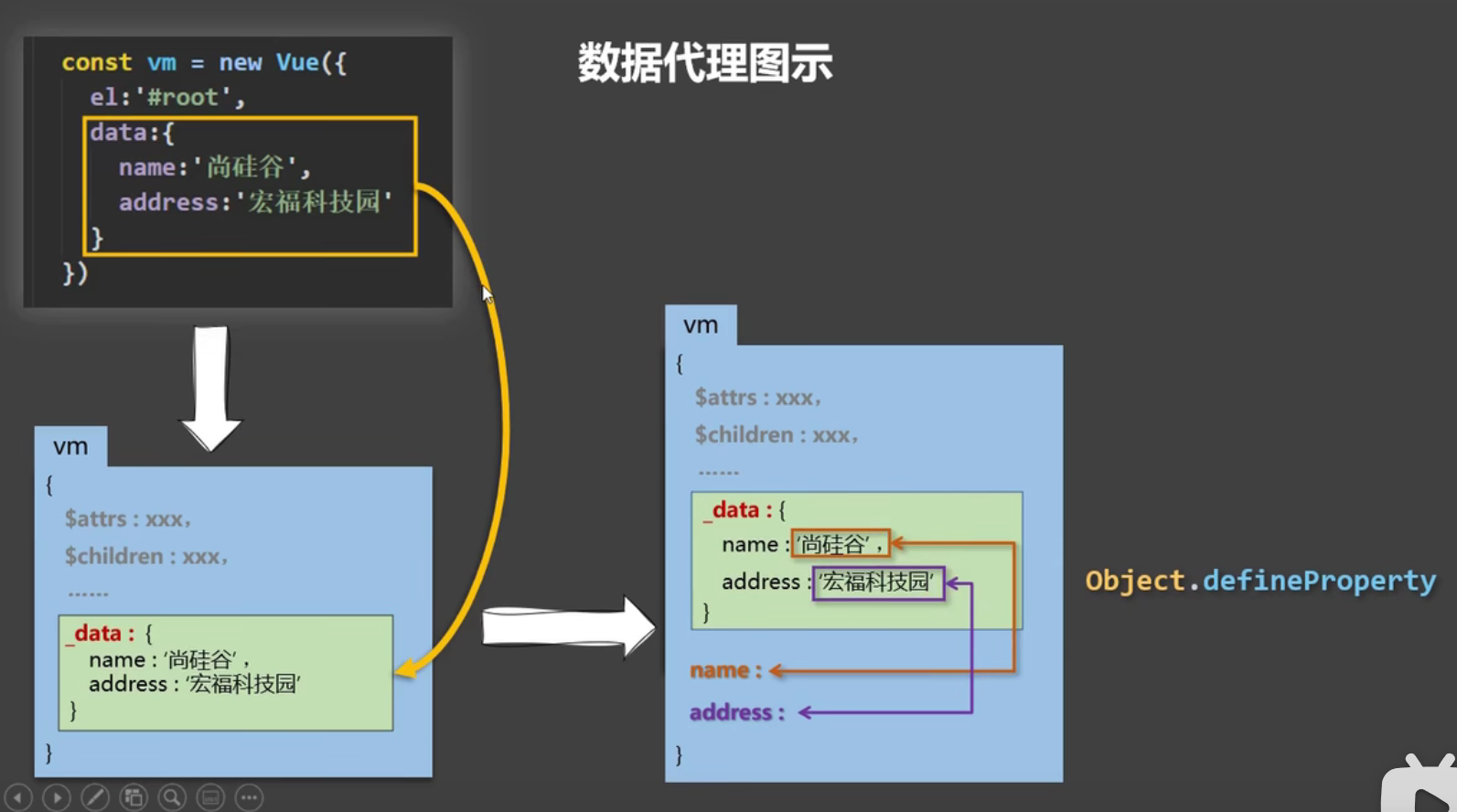
Q1:数据定义在data里面,为什么可以通过vm直接进行读写操作?
A1:vue对象对data里的数据进行代理操作,所有数据获取和设置由vue实例操作
Q2:vm.$data vs vm.data?
A2:vm.$data读取属性列表(第一层),vm.data读取属性中的数据(第二层),等价于vm.$data.data
Q3:为什么使用_data?
A4:取别名用于区分,避免data中含有data属性时,vm.data = vm.data.data混淆(个人理解)
官方说明↓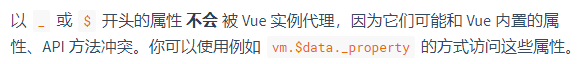
事件处理
<button v-on:click="show1">...</button>
<button @click="show1">...</button>
<button @click.once="show1">...</button>
<button @click="show2($event,666)">...</button>
计算属性
用于简单计算
computed:{
//简写,只有读
fullName(){
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
}
//完整写法
fullName:{
set(value){
const arr = value.split('-')
this.firstName = arr[0]
this.lastName = arr[1]
}
get(){
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
}
}
}
数据监视
warch:{
number(newValue,oldValue){
console.log('number变了',newValue,oldValue)
}
}
绑定样式
<!-- class字符串写法,适用类名不确定,需要动态获取 -->
<h2 class="atguigu" :class="myStyle">{{title}}</h2>
<!-- class对象写法,适用于类名确定,但不确定用不用 -->
<h2 class="atguigu" :class="{classB:hasB,classC:hasC}">{{title}}</h2>
<!-- class三元表达式写法,适用于类名确定,但不确定用不用 -->
<h2 class="atguigu" :class="hasB ? 'classB" : ''>{{title}}</h2>
<!-- class数组写法,适用于同时应用多个class -->
<h2 class="atguigu" :class="[a,b,c]">{{title}}</h2>
<!-- 绑定style -->
<h2 class="atguigu" :class="[a,b,c]" :style="{fontSize:size+'px'}">{{title}}</h2>
条件渲染
v-show
v-if,v-else-if,v-else
列表渲染
v-for指令:
- 用于展示列表数据
- 语法:v-for=”(item,index) in arr” :key=”item.id”
- 可遍历:数组、对象、字符串
ps:key为数据的唯一标识,无:key属性时,状态默认绑定的是位置;有:key属性时,状态根据key的属性值绑定到了相应的数组元素。
列表过滤
computed:{
fmtPersons(){
return persons.filter(p => p.name.indexOf(keyWord) !== -1)
}
}
列表排序
computed:{
fmtPersons(){
let arr = persons.filter(p => p.name.indexOf(keyWord) !== -1)
if(sortType){
arr.sort((a,b)=>{
if(sortType === 1)return a.age - b.age
else return b.age - a.age
})
}
return arr;
}
}
列表更新
methods:{
updateMei(){
this.persons[0].name = '小佩奇' //代码奏效
this.persons[0] = {name:'小佩奇',age:99}//不奏效,用push
}
}
收集表单数据
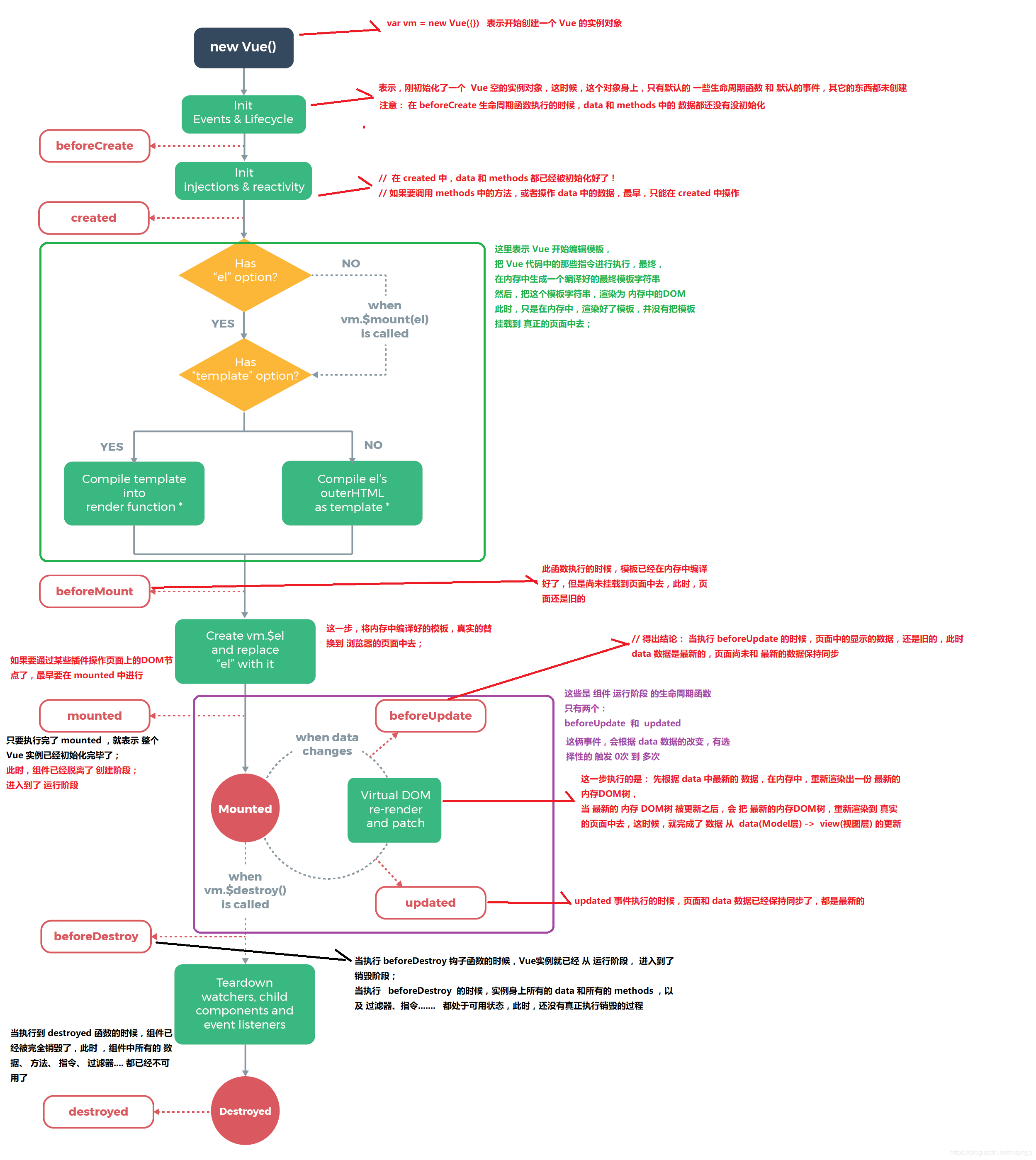
Vue实例的生命周期*
Vue组件化编程
概念
模块
向外提供特定功能的js程序,一般是一个js文件
组件
实现局部功能效果的代码集合
传统方式
组件方式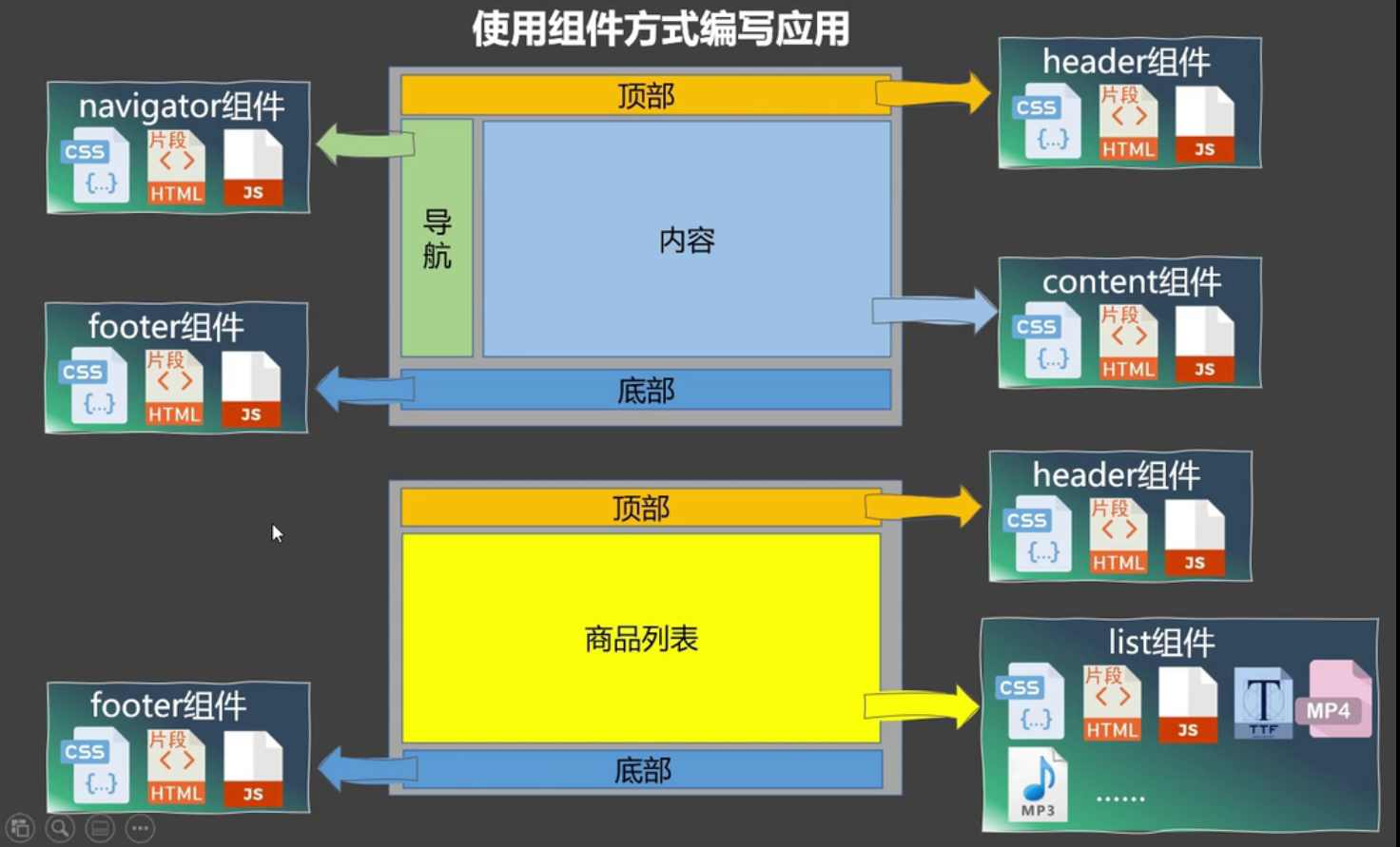
组件_非单文件
组件_单文件
使用Vue脚手架
…
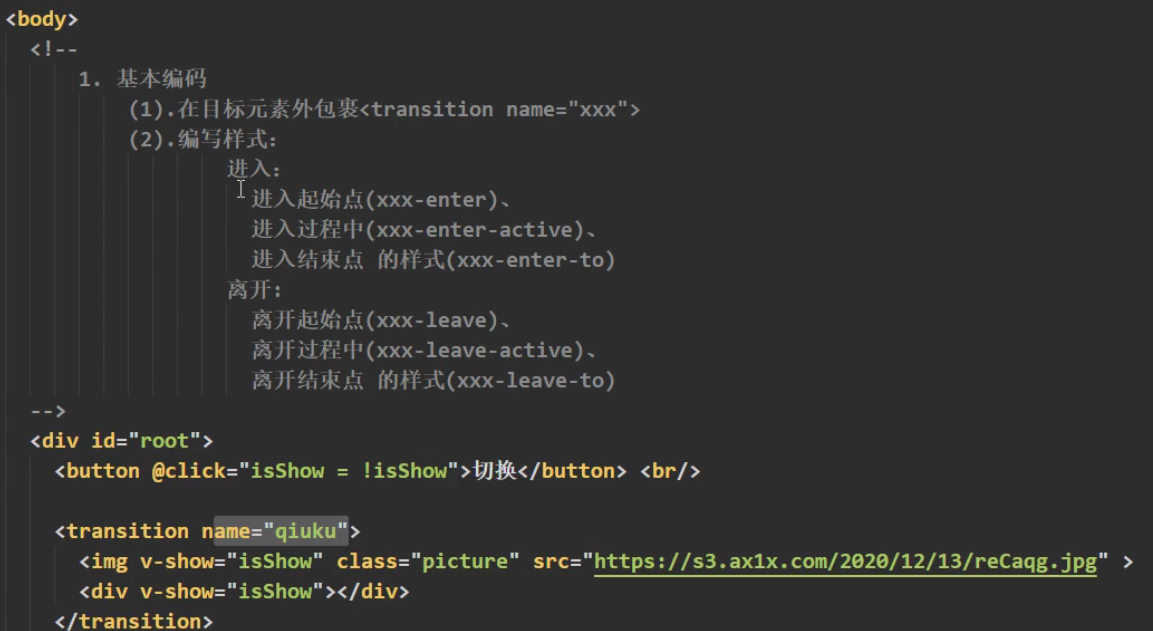
过度与动画
过滤器
指令
v-text,v-html,v-if,v-else
v-show,v-for,v-on,v-bind:xx,v-model
自定义指令
<h2 v-upper-text="name"></h2>
...
Vue.directive('upper-text',function(el,binding){
el.innerText = binding.value.toUpperCase()
}
)
new Vue({
..
directives:{
'lower-text'(el,binding){
el.innerText = binding.value.toUpperCase()
}
}
..
})
插件
const atguigu = {}
atguigu.install = funcion(Vue.option){
}
挂载?
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create vue-demo
npm run serve
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
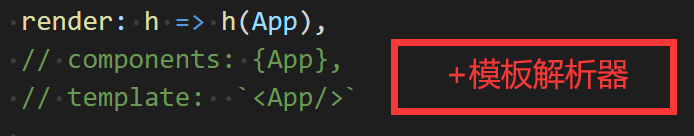
vue.runtime.common.js:
- 不包含模板解析器,打包后体积小
- 配置项中不能写template,要用render: h => h(App)
ref与props
ref用来给元素注册引用信息,通俗说就是获取DOM节点,相当于document.querySelector(”.xxx”)
ref的使用:
- 标签中直接编写ref=””
- 通过this.$refs.xxx获取
- 备注:若给html内置标签打ref,则获取真实DOM节点。若给组件标签打ref,则获取到组件实例对象
<button ref="btn" @click="showData">点我获取焦点</button> <input type="text" ref="keyWord"></input> <!-- School标签的ref,通过this.$refs.xuexiao获取的是组件实例 --> <School ref="xuehao"/> ... import School from './components/School' ... methods:{ showData(){ this.$refs.keyWord.focus() } }
props是子组件访问父组件数据的唯一接口
父组件App.vue中:
...
<School ref="xuehao" :username="username"/>
...
data(){
return {
username:"老刘"
}
},
//注册组件--局部注册
components:{School}
子组件components/School.vue中:
//声明接收props,限制类型、必要性、指定默认值
props:{
username:{
type:String,
required:true,
default:'老王'
}
}
//精简写法,啥都不限制
props:['username']
todoList案例
全局事件总线
组件间通信的一种方式,适用于任意组件间通信
(1)安装全局事件总线,在main.js中配置
new Vue({
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
},
el:'#app',
render:h => h(App)
})
(2)需要接收数据的组件给$bus绑定自定义事件
mounted(){
this.$bus.$on('xxx',this.yyy)
}
备注:上方的yyy一定要配置在当前组件的methods,this为当前组件vc。最好不要直接写一个function,否则会造成this的指向问题,此时this是$bus。
(3)要提供数据的组件中触发事件
this.$bus.$emit('xxx',数据)
Vue中的ajax
slot插槽
插槽:挖个坑,等组件的使用者进行填充
原生写法
<ul v-show="title ==='游戏'">
<li v-for="game in gameArr" :key="game.id">
{{game.name}}--{{game.price}}
</li>
</ul>
<img v-show="title === '美食'" :src="foodUrl" alt="">
默认插槽
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<Category title="游戏" :gameArr="gameArr">
<ul>
<li v-for="game in gameArr" :key="game.id">
{{game.name}}--{{game.price}}
</li>
</ul>
</Category>
<Category title="美食">
<img :src="foodUrl" alt="">
</Category>
<Category title="视频">
<video controls :src="videoUrl"></video>
</Category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from './components/Category.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Category
},
data(){
return {
gameArr:[
{id:'001',name:'王者荣耀',price:100},
{id:'002',name:'绝地求生',price:200},
{id:'003',name:'使命召唤',price:300},
{id:'004',name:'穿越火线',price:400},
],
foodUrl:'https://i3.meishichina.com/attachment/recipe/2021/07/05/2021070516254630835928197577.jpg?x-oss-process=style/c320',
videoUrl:'https://v-cdn.zjol.com.cn/276984.mp4'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.app{
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
video{
width: 100%;
}
</style>
Category.vue
<template>
<div class="cate">
<h3 class="bt">{{title}}分类</h3>
<!-- 默认插槽 -->
<slot></slot>
<!-- 命名插槽 -->
<slot name="game"></slot>
<slot name="food"></slot>
<slot name="movie"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Category',
props: ['gameArr','title','foodUrl']
}
</script>
<style>
.cate{
width: 240px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.bt{
text-align: center;
}
img{
width: 100%;
}
</style>
命名插槽
App.vue
<Category title="游戏" :gameArr="gameArr">
<template slot="game">
<ul>
<li v-for="game in gameArr" :key="game.id">
{{game.name}}--{{game.price}}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
</Category>
Github搜索案例*
- 全局事件总线
- 消息订阅与发布
Vuex
理解Vuex
集中式状态管理,也可以理解成任意组件间的通信方式
应用场景
- 多个组件依赖同一状态
- 来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态
- 多个组件要共享状态
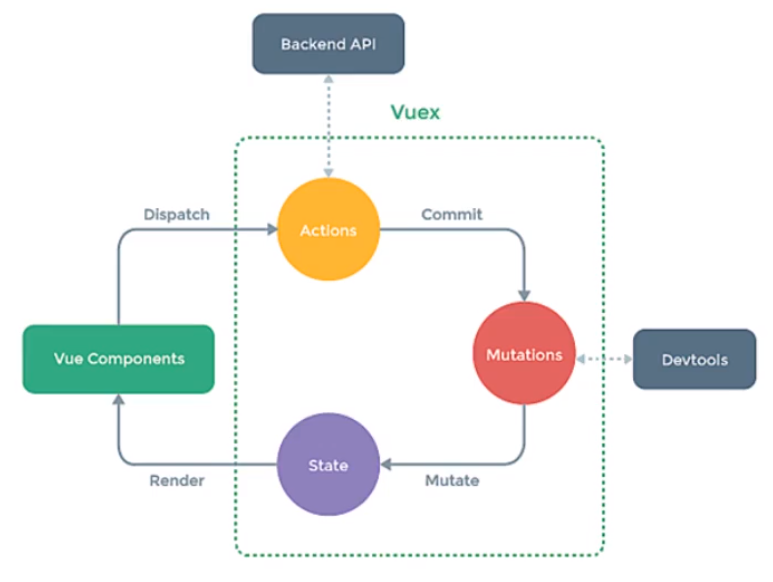
Actions:用于响应组件的动作
Mutations:用于操作数据(state)
State:用于存储数据
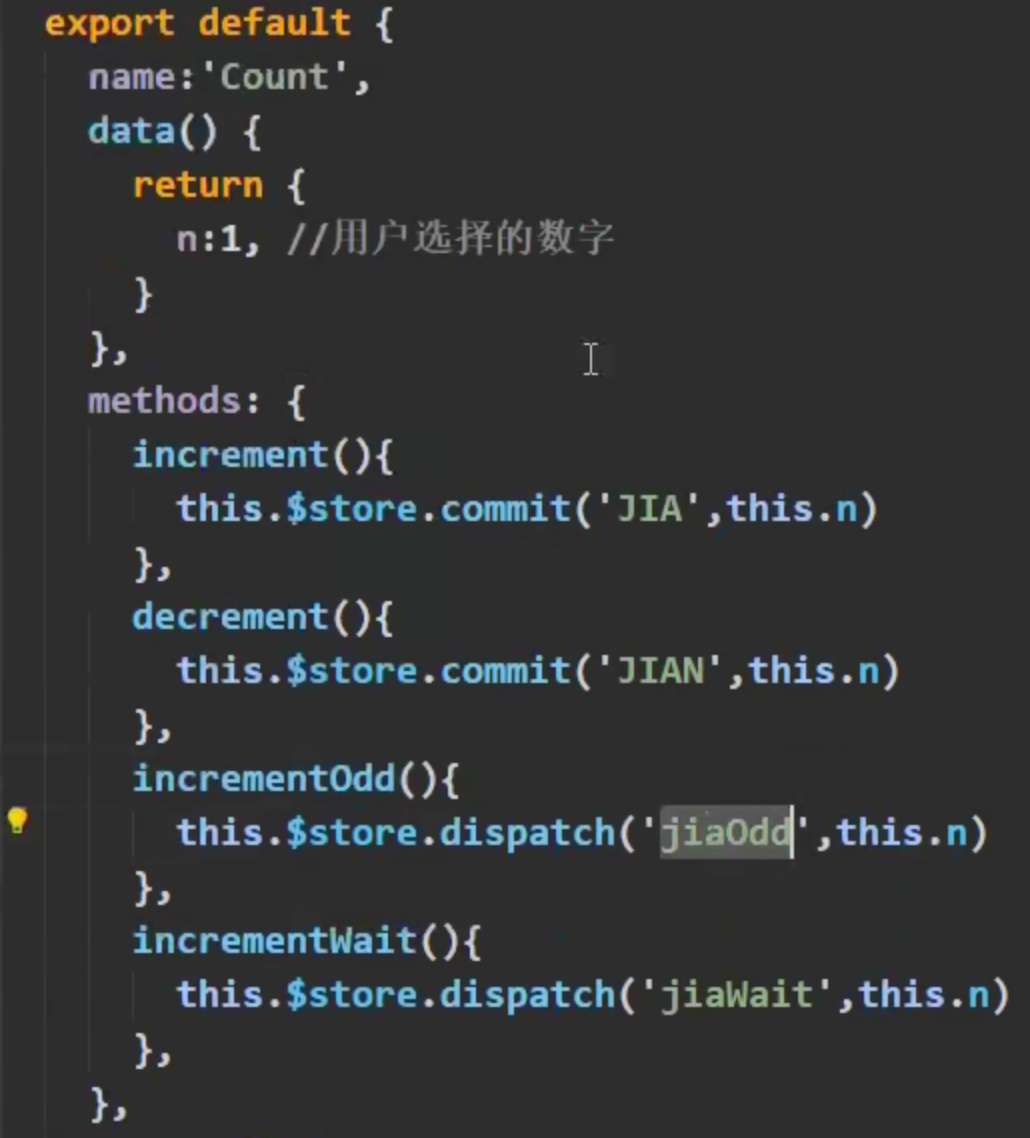

Q:为什么需要Action和Mutation两层?为什么不在Actions中直接对state进行操作?
A:开发者工具失效,只对Mutation进行监控。
Q:为什么需要Actions?不在vue中直接写逻辑操作Actions进行commit?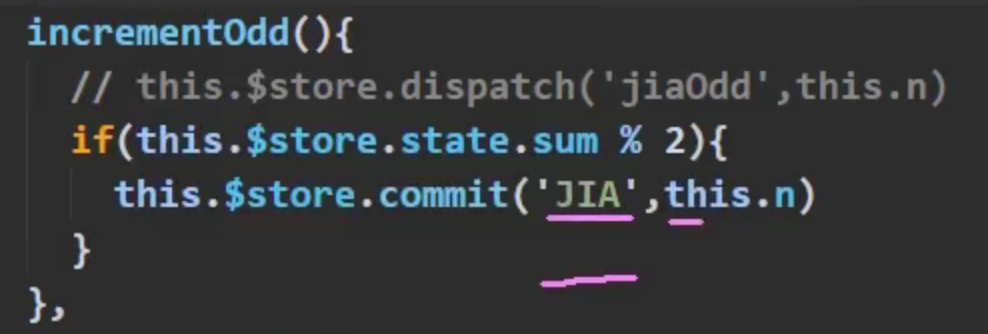
A:减少代码冗余
为什么这么设计?详见视频P110:20mins
Vuex开发者工具
getters配置项
const getters = {
bigSum(state){
return state.sum*10;
}
}
用于对state数据进行加工
mapState 优化
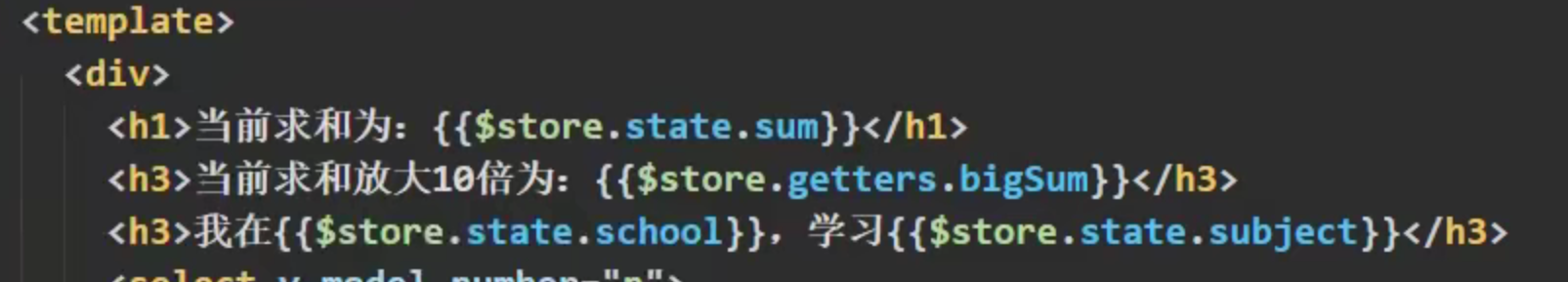
...
computed:{
he(){
return this.$store.state.sum
}
xuexiao(){
return this.$store.state.school
}
xueke(){
return this.$store.state.subject
}
}
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
...
computed(){
//对象写法
...mapState({he:'sum',xuexiao:'school',xueke:'subject'})
//数组写法
...mapState(['sum','school','subject'])
}
mapActions与mapMutations
methods: {
increment(){
this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n);
}
decrement(){
this.$store.commit('JIAN',this.n);
}
}
mapActions:包含$store.dispatch(xxx)的函数
mapMutations:包含$store.commit(xxx)的函数
methods: {
...mapActions(['jiaOdd','jiaWait'])
...mapMutations({increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'})
}
ps:在使用时如果需要传递参数,在模板中绑定事件时传递好参数,否则参数是事件对象
多组件共享数据
放在vuex中的东西可以在任意组件内使用
使用方式:
- 传统方式
- mapState
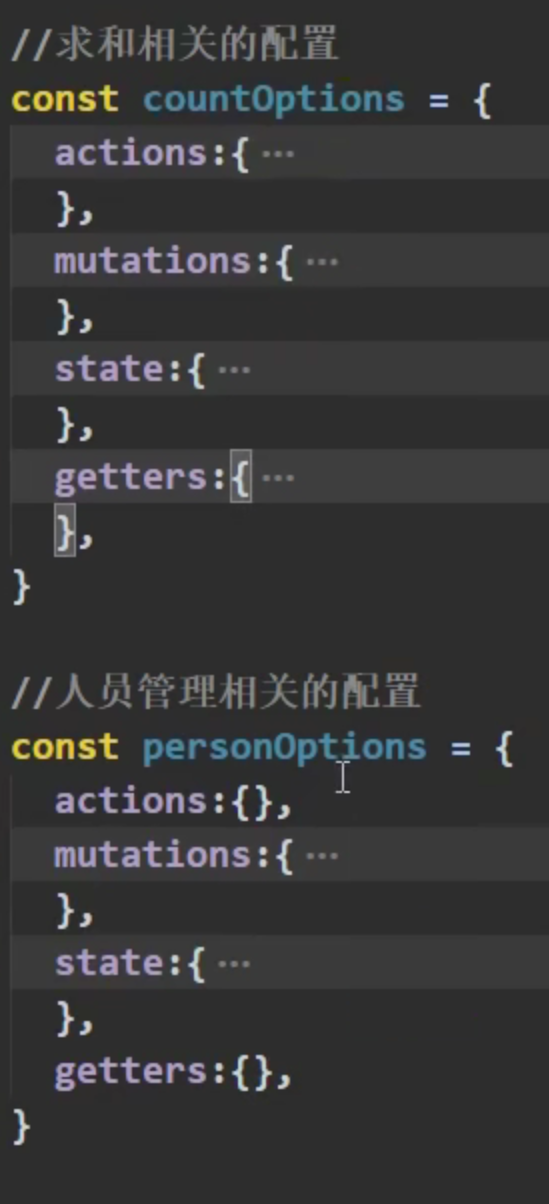
vuex模块化编码
根据功能划分