7.1if语句
if语句称为分支语句,相当于一个分叉点;
if语句只能执行或测试一次;
C缩进有助于识别语句的所属和结构;
if和else之前只能有一个语句,多一个语句则要加钱(使用花括号构成代码块);
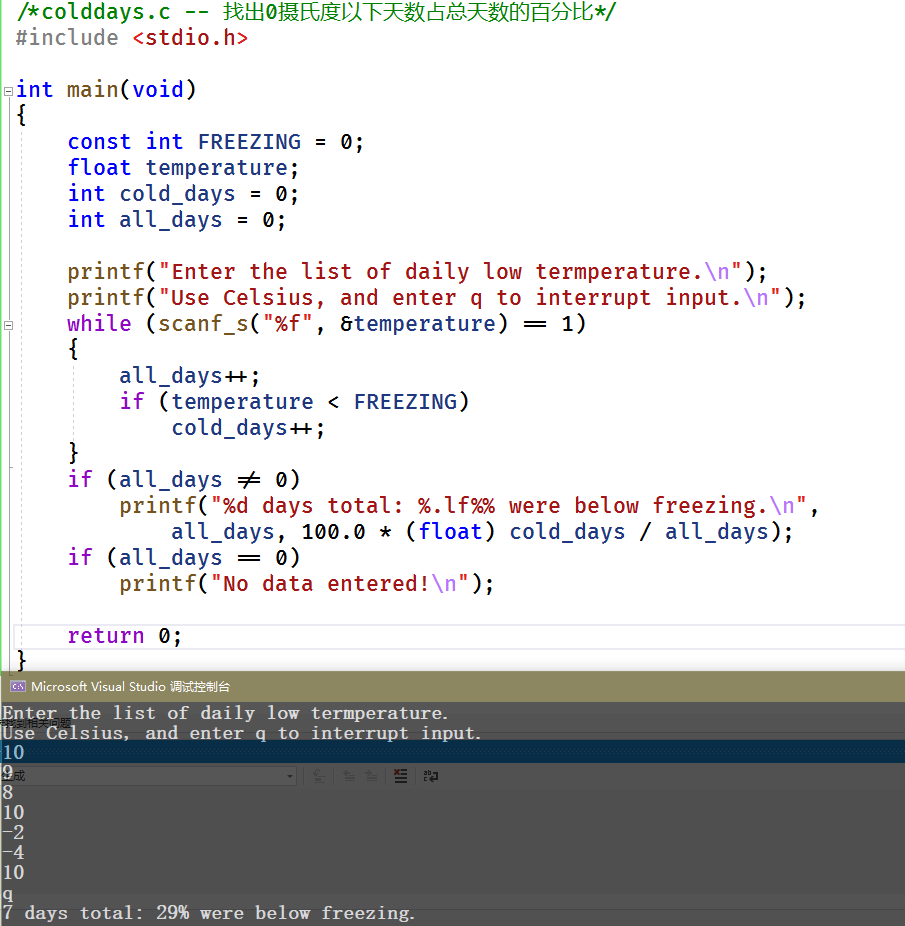
/*colddays.c -- 找出0摄氏度以下天数占总天数的百分比*/#include <stdio.h>int main(void){const int FREEZING = 0;float temperature;int cold_days = 0;int all_days = 0;// 提示输入printf("Enter the list of daily low termperature.\n");printf("Use Celsius, and enter q to interrupt input.\n");// 循环获取输入while (scanf_s("%f", &temperature) == 1){all_days++;if (temperature < FREEZING)cold_days++;}// 计算输出结果if (all_days != 0)printf("%d days total: %.lf%% were below freezing.\n",all_days, 100.0 * (float) cold_days / all_days);// 判断是否为空if (all_days == 0)printf("No data entered!\n");return 0;}
7.21 putchar() & getchar()
注意循环语句中,处理数据分类之后,还需要获取下一次的输入,while循环是入口条件语句
通常使用getchar()语句会比scanf_s(“%c”, &object)更加高效
#include <stdio.h>#define SPACE ' ' // SPACE 表示单引号 - 空格 - 单引号int main(void){char ch;ch = getchar();// 读取字符while (ch != '\n') // 进行判断, 当一行未结束的时候{if (ch == SPACE) // 留下空格putchar(ch); // 该字符不变,直接输出elseputchar(ch + 1); // 不是空格就加1再输出,查询ASCⅡch = getchar(); // 获取下一个字符}putchar(ch); // 打印换行符return 0;}
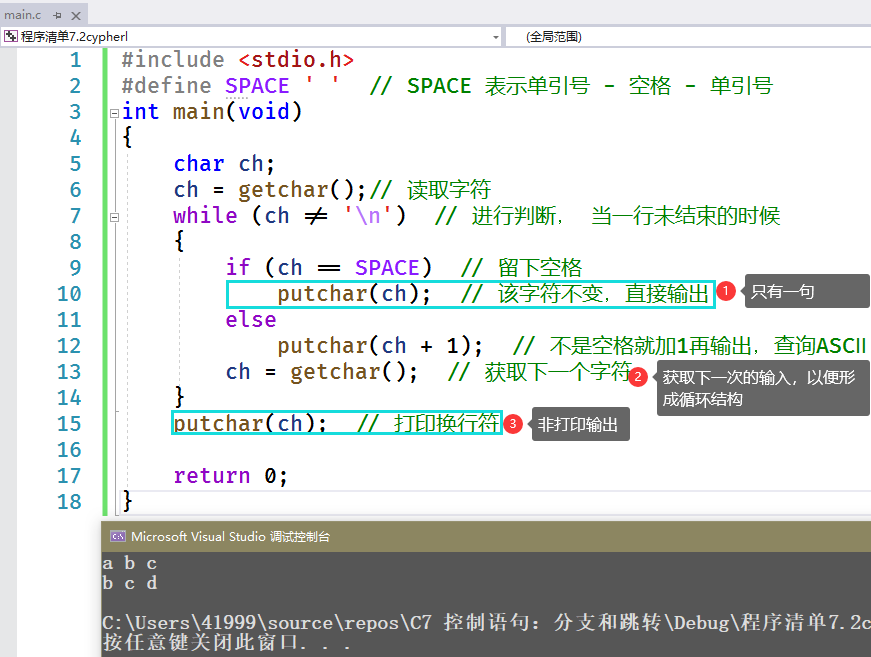
圆括号修改优先级—-两份代码的比较
运算顺序是:先获取输入字符,然后赋值给变量ch,最后判断输入符号时候为换行符
造成的问题是:输出的结果失去了空格。
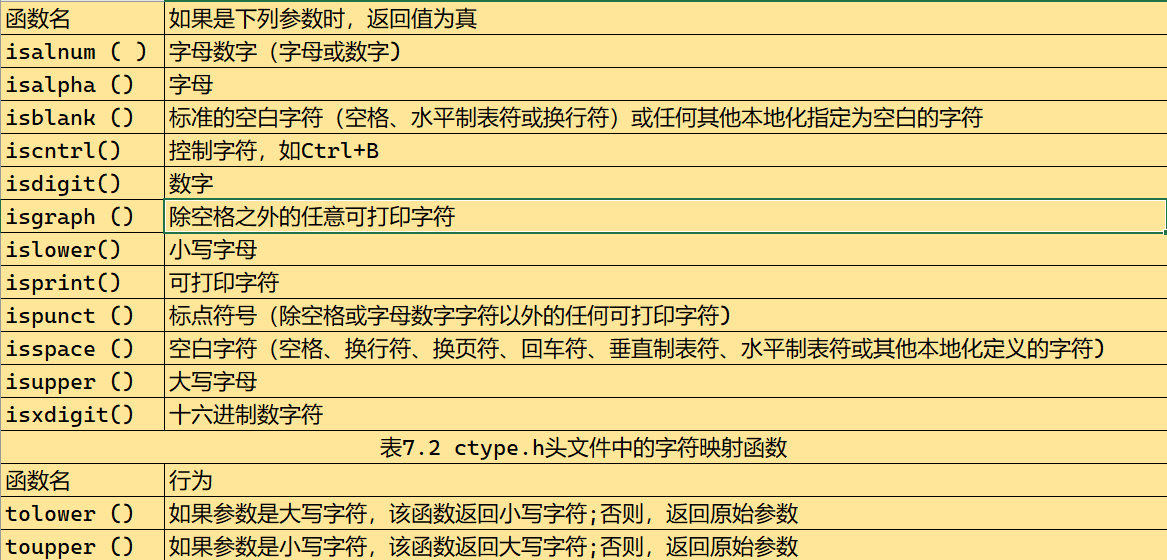
7.2.2 ctype.h系列的字符函数
引入新的函数用于做字符判断。
ctype.h头文件解析
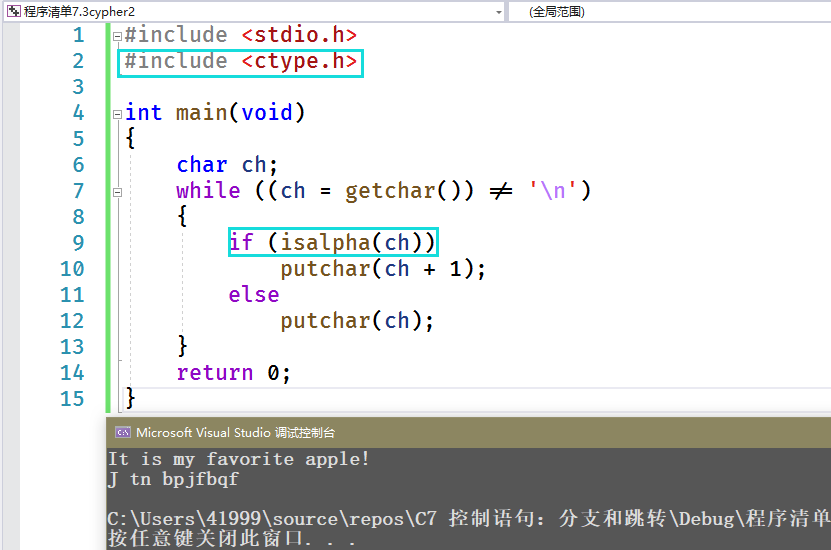
#include <stdio.h>#include <ctype.h>int main(void){char ch;while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n'){if (isalpha(ch))putchar(ch + 1);elseputchar(ch);}return 0;}

7.2.4else与if配对(20210312)
语法
如果没有花括号,if与最近的else匹配,除非最近的if被花括号包含在内;
原理:编译器忽略缩进(这是C语言和Python不同的一点)
技巧
if else是单独的语句,无需使用花括号,但语句太长可以使用,提高代码的可读性,同时避免漏掉花括号;
代码
注意循环语句之外再次获取输入,这也是构成循环的一个条件;
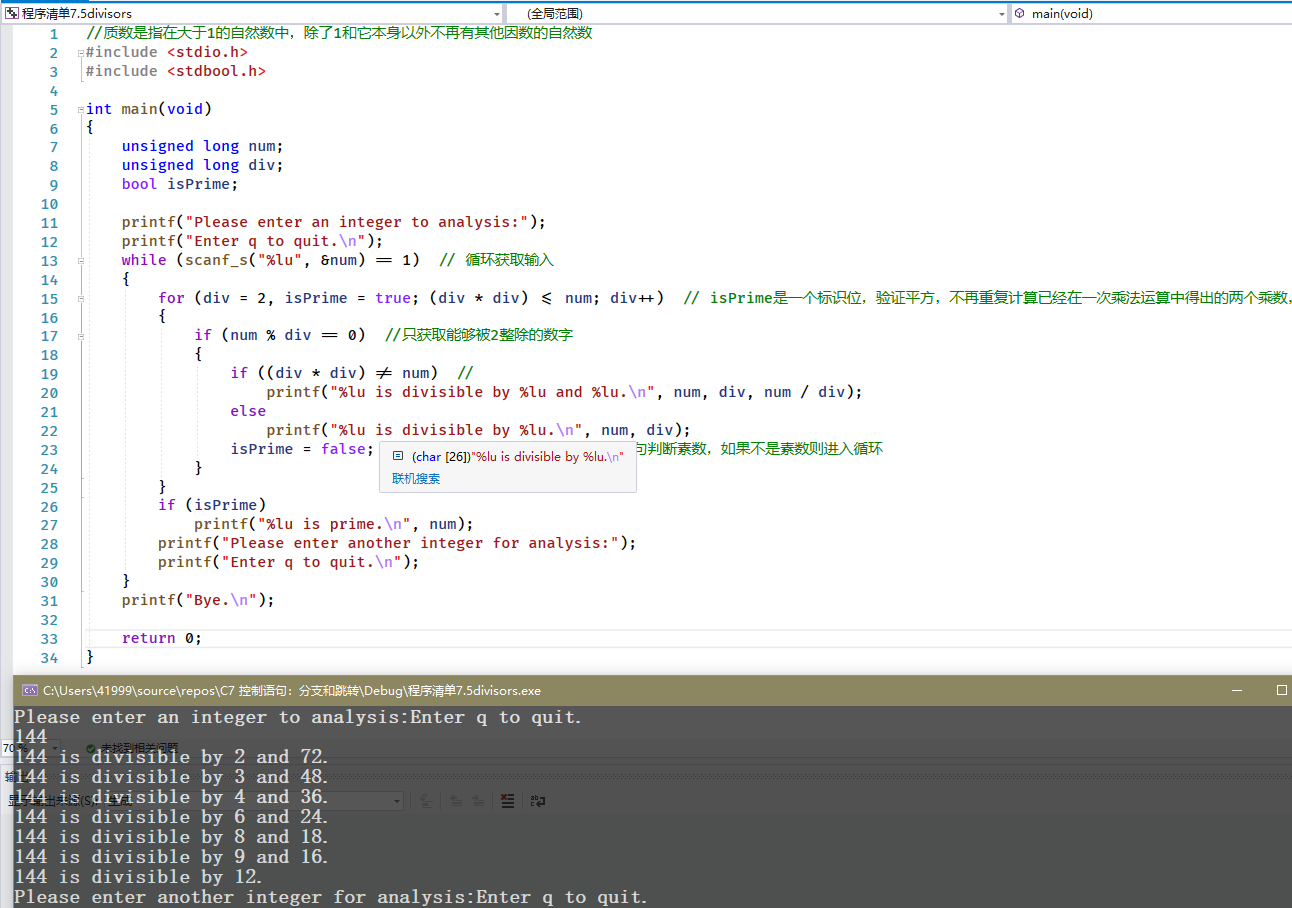
通过乘方而不是开方减少重复计算(一次运算就可以得出的两个乘数);
什么是素数(质数)?标识位用来判断是否未素数,进入即改变标识位;
//质数是指在大于1的自然数中,除了1和它本身以外不再有其他因数的自然数#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h>int main(void){unsigned long num;unsigned long div;bool isPrime;printf("Please enter an integer to analysis:");printf("Enter q to quit.\n");while (scanf_s("%lu", &num) == 1) // 循环获取输入{for (div = 2, isPrime = true; (div * div) <= num; div++) // isPrime是一个标识位,验证平方,不再重复计算已经在一次乘法运算中得出的两个乘数,{if (num % div == 0) //只获取能够被2整除的数字{if ((div * div) != num) //printf("%lu is divisible by %lu and %lu.\n", num, div, num / div);elseprintf("%lu is divisible by %lu.\n", num, div);isPrime = false; // 进入if语句才修改标识位,if语句判断素数,如果不是素数则进入循环}}if (isPrime)printf("%lu is prime.\n", num);printf("Please enter another integer for analysis:");printf("Enter q to quit.\n");}printf("Bye.\n");return 0;}
7.3逻辑运算符
语法
逻辑运算符比关系运算符的优先级低,所以无需再之表达式两侧加圆括号;
iso646.h头文件可以替换这些逻辑运算符为and or not
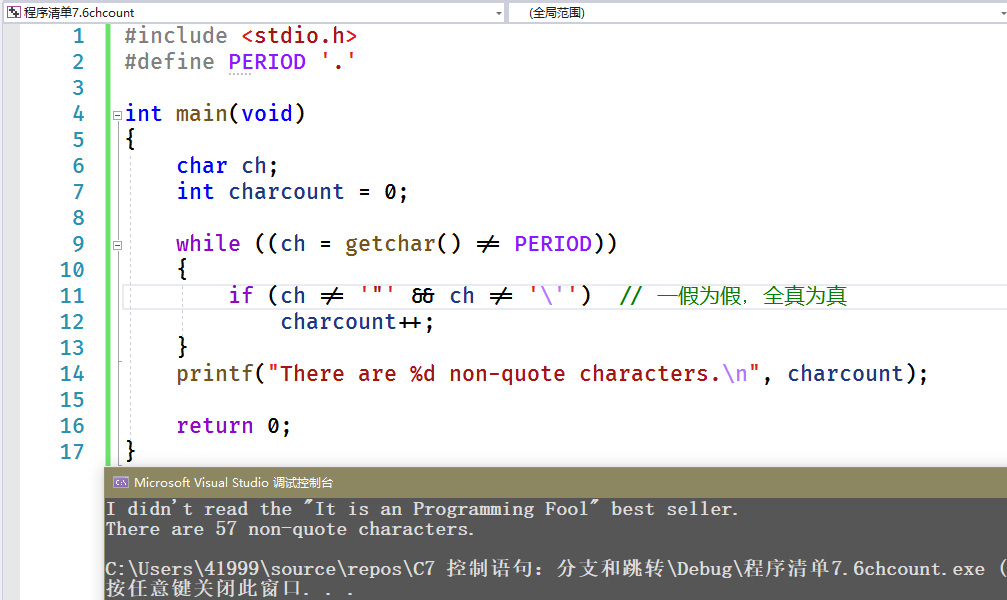
#include <stdio.h>#define PERIOD '.'int main(void){char ch;int charcount = 0;while ((ch = getchar() != PERIOD)){if (ch != '"' && ch != '\'') // 一假为假,全真为真charcount++;}printf("There are %d non-quote characters.\n", charcount);return 0;}
7.4一个统计单词的程序
程序设计
如何标记输出的结束?
|
如何定义一个单词?
不包含空白字符,回车符,换行符,制表符
如何判断空白字符?
ctype.h中的isspace()函数
语句转换
!=inword // inword == false
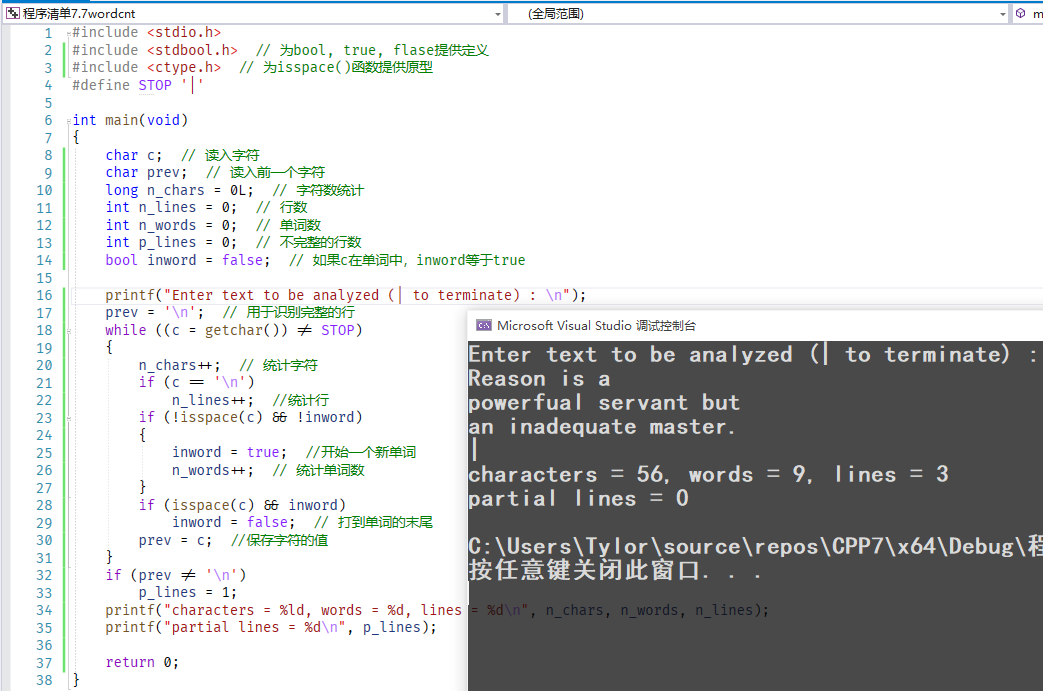
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h> // 为bool, true, flase提供定义#include <ctype.h> // 为isspace()函数提供原型#define STOP '|'int main(void){char c; // 读入字符char prev; // 读入前一个字符long n_chars = 0L; // 字符数统计int n_lines = 0; // 行数int n_words = 0; // 单词数int p_lines = 0; // 不完整的行数bool inword = false; // 如果c在单词中,inword等于trueprintf("Enter text to be analyzed (| to terminate) : \n");prev = '\n'; // 用于识别完整的行while ((c = getchar()) != STOP){n_chars++; // 统计字符if (c == '\n')n_lines++; //统计行if (!isspace(c) && !inword){inword = true; //开始一个新单词n_words++; // 统计单词数}if (isspace(c) && inword)inword = false; // 打到单词的末尾prev = c; //保存字符的值}if (prev != '\n')p_lines = 1;printf("characters = %ld, words = %d, lines = %d\n", n_chars, n_words, n_lines);printf("partial lines = %d\n", p_lines);return 0;}
7.5条件运算符
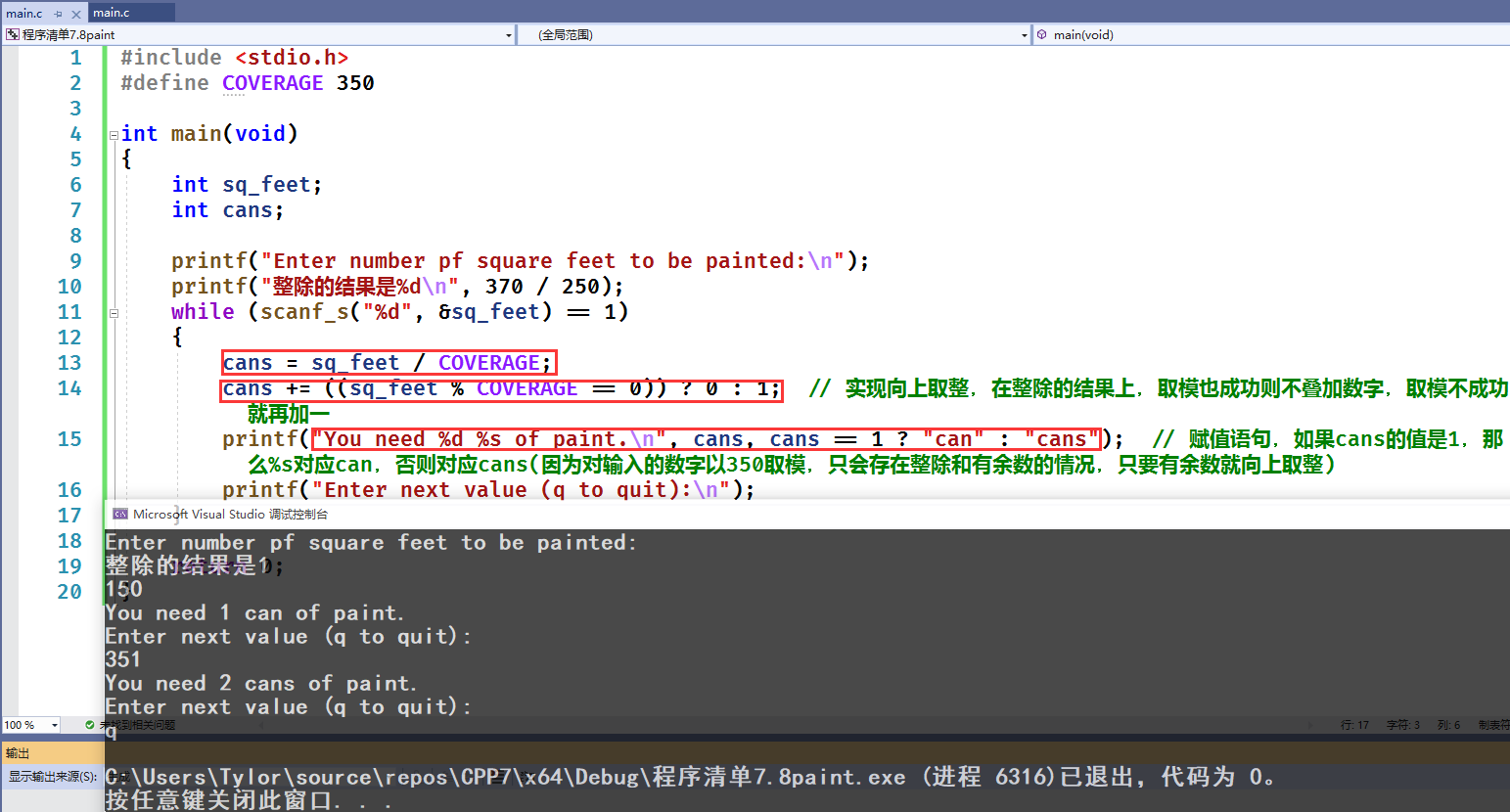
程序如何实现向上取整?
首先整除得到一个值,然后求模运算,求模成功说明完全整除不必加一。求模失败说明又余数,自动加一
#include <stdio.h>#define COVERAGE 350int main(void){int sq_feet;int cans;printf("Enter number pf square feet to be painted:\n");printf("整除的结果是%d\n", 370 / 250);while (scanf_s("%d", &sq_feet) == 1){cans = sq_feet / COVERAGE;cans += ((sq_feet % COVERAGE == 0)) ? 0 : 1; // 实现向上取整,在整除的结果上,取模也成功则不叠加数字,取模不成功就再加一printf("You need %d %s of paint.\n", cans, cans == 1 ? "can" : "cans"); // 赋值语句,如果cans的值是1,那么%s对应can,否则对应cans(因为对输入的数字以350取模,只会存在整除和有余数的情况,只要有余数就向上取整)printf("Enter next value (q to quit):\n");}return 0;}
7.6辅助循环:continue 和 break
continue和break语句都只对当前语句有效(也就是内循环)
continue等于你想要的条件取相反的时候,用于继续执行程序
使用continue语句可以减少主语句中的一级缩进,但语句很长或者嵌套多的时候,使得语句更加紧凑,提高了代码
#include <stdio.h>// 20210315int main(void){const float MIN = 0.0f;const float MAX = 100.0f;float score;float total = 0.0f; //前一个零指的是最小宽度,第二个零指的是精度int n = 0;float min = MAX;float max = MIN;printf("Enter the first score(q to quit):");while (scanf_s("%f", &score) == 1) // 输入的内容必须是数字{if (score < MIN || score > MAX){printf("%0.1f is an invalid value.Try again: ", score);continue;}// MIN<=socre <= MAXprintf("Accepting %0.1f:\n", score);min = (score < min) ? score : min; // 如果在输入的数字小于最小值,则将值传递给便俩个:最小值max = (score > max) ? score : max; // 如果在输入的数字中出现大于最小值,则将值传递给变量:最大值total += score;n++;printf("Enter next score (q to quit) : ");}if (n > 0){printf("Average of %d score is %0.1f.\n", n, total / n);printf("Low = %0.1f, high = %0.1f\n", min, max);}elseprintf("No valid scores were entered.\n");return 0;}
7.6.2break语句
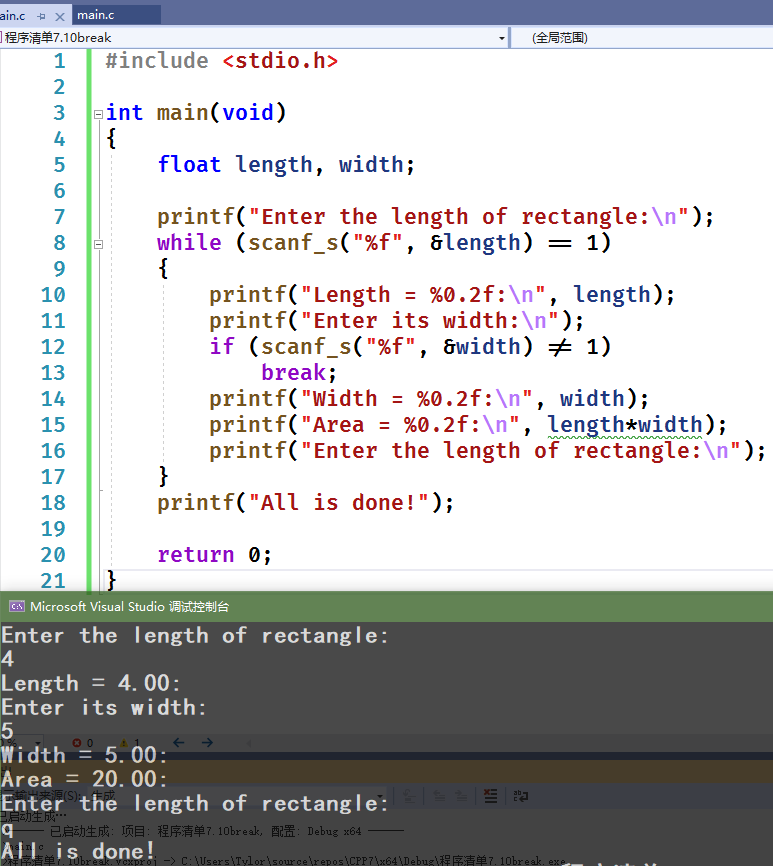
#include <stdio.h>int main(void){float length, width;printf("Enter the length of rectangle:\n");while (scanf_s("%f", &length) == 1){printf("Length = %0.2f:\n", length);printf("Enter its width:\n");if (scanf_s("%f", &width) != 1)break;printf("Width = %0.2f:\n", width);printf("Area = %0.2f:\n", length * width);printf("Enter the length of rectangle:\n");}printf("All is done!");return 0;}
7.7 多重选择: switch 和break
#include <stdio.h>#include <ctype.h>int main(void){char ch;printf("Give me a letter of the alphabet, and I will give ");printf("an animal name\nbeginning with that letter.\n");printf("Please type in a letter; type # to end my act.\n");while ((ch = getchar()) != '#') // 仅仅读取首字母{if ('\n' == ch) // 如果输入为回车符,那么循环获取输入continue;if (islower(ch)) // 只接受小写字母switch (ch){case 'a':printf("argali, a wild sheep of Asia\n");break;case 'b':printf("babirusa, a wild pig of Malay\n");break;case 'c':printf("coati, recoonlike mammal\n");break;case 'd':printf("desman, aquatic, molelike critter\n");break;case 'e':printf("echidna, the spiny anteater\n");break;case 'f':printf("fisher, brownish marten\n");break;default:printf("That's a stumper!\n"); // switch结束}elseprintf("I recognize only lowcase letters.\n");while (getchar() != '\n')continue;printf("Please type another letter or a #.\n"); // while循环结束}printf("Bye!\n");return 0;}
7.7.3多重标签
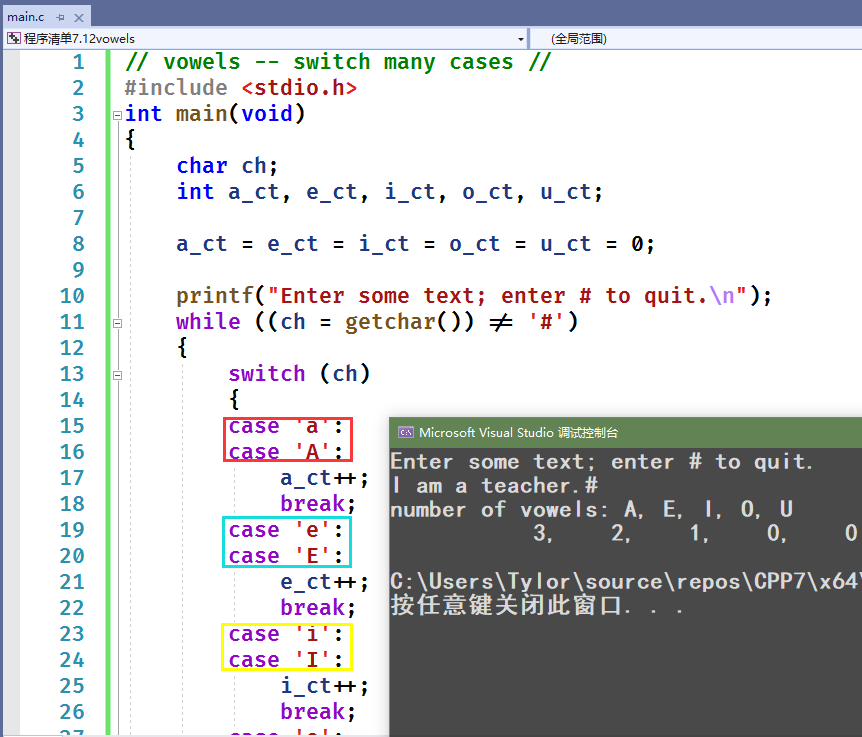
// vowels -- switch many cases //#include <stdio.h>int main(void){char ch;int a_ct, e_ct, i_ct, o_ct, u_ct;a_ct = e_ct = i_ct = o_ct = u_ct = 0;printf("Enter some text; enter # to quit.\n");while ((ch = getchar()) != '#'){switch (ch){case 'a':case 'A':a_ct++;break;case 'e':case 'E':e_ct++;break;case 'i':case 'I':i_ct++;break;case 'o':case 'O':o_ct++;break;case 'u':u_ct++;break;default:break;} // switch结束}printf("number of vowels: A, E, I, O, U\n");printf(" %4d, %4d, %4d, %4d, %4d\n", a_ct, e_ct, i_ct, o_ct, u_ct);return 0;}
7.7.4 switch & if else语句的比较
适用于那种情况呢?观察代码可以知道,if else可以用在表示范围的的条件中,浮点变量或者表达式都可以。但是switch case用于确定的选项。
7.8 goto语句
为何避免使用goto语句?
goto语句在程序执行中跳来跳去,一般程序都是顺序执行,该语句可能会打乱程序的执行;
其次该语句只能标识该语句的功能,但不具备准确的意义,比如continue和break语句都可以跳出内部循环
章末总结
所有的循环和switch语句都可以使用break语句,所有的循环都可以使用continue语句,但是switch语句不行;
条件运算符;
关系表达式,满足条件执行的时问号前面的语句;
ctype.h是字符函数;
switch用整数作为标签语句的条件用于匹配输入;
break, continue, goto都可以作为跳转语句;