本章介绍
- 关键字:return
-
- 运算符: *(一元), &(一元)
-
- 函数及其定义方式
-
- 如何使用参数和返回值
-
- 如何把指针变量用作函数参数
-
- 函数类型
-
- ANSI C原型
-
- 递归
章末小结
9.1.2 分析程序
函数原型指明函数的返回值类型和函数可以接受的参数类型。这些信息统称为函数的签名(signature)
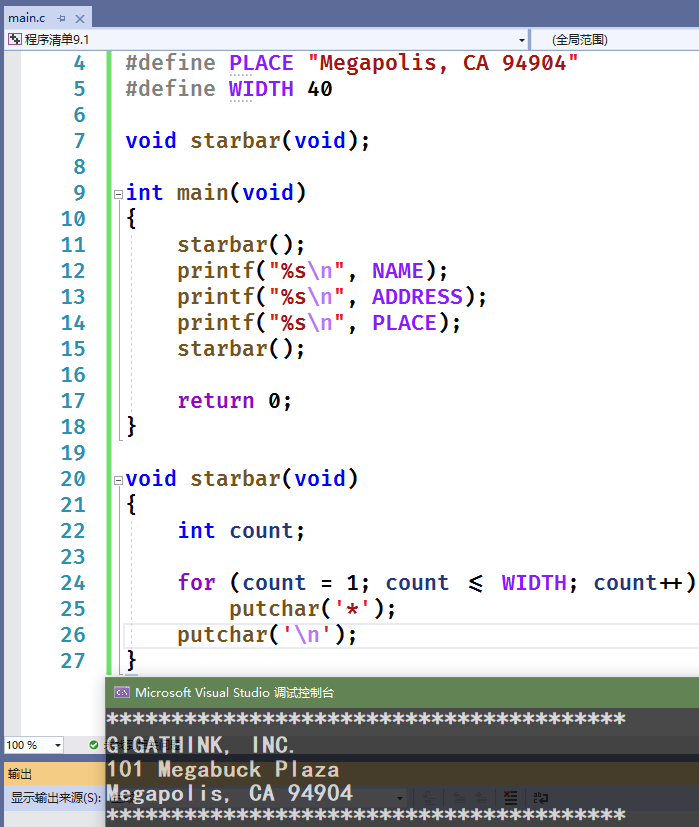
#include <stdio.h>#define NAME "GIGATHINK, INC."#define ADDRESS "101 Megabuck Plaza"#define PLACE "Megapolis, CA 94904"#define WIDTH 40void starbar(void); // ANSI C 函数原型int main(void){starbar(); // 该函数的作用就是打印四十个星号,调用函数printf("%s\n", NAME);printf("%s\n", ADDRESS);printf("%s\n", PLACE);starbar(); // 该函数的作用就是打印四十个星号,调用函数return 0;}void starbar(void) // 函数准确的定义{int count;for (count = 1; count <= WIDTH; count++)putchar('*');putchar('\n');}
9.1.13 函数参数
函数参数的书写格式
void dibs(int x, y, z) /* 无效的函数头 */void dubs(int x, int y, int z) /* 有效的函数头 */void dibs(x, y, z)int x, y, z; /* 有效 */
/* lethead2.c*//*20210315 20:11*/#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#define NAME "GIGATHINK, INC."#define ADDRESS "101 Megabuck Plaza"#define PLACE "Megapolis, CA 94904"#define WIDTH 40#define SPACE ' 'void show_n_char(char ch, int num);int main(void){int spaces;show_n_char('*', WIDTH); // 第一行putchar('\n'); // 手动换行show_n_char(SPACE, 12); // 12个空格printf("%s\n", NAME); //打印NAME并且换行spaces = (WIDTH - strlen(ADDRESS)) / 2;show_n_char(SPACE, spaces);printf("%s\n", ADDRESS); // 打印第二行的文字: ADDRESSshow_n_char(SPACE, (WIDTH - strlen(PLACE)) / 2);printf("%s\n", PLACE);show_n_char('*', WIDTH);putchar('\n'); //换行return 0;}void show_n_char(char ch, int num){int count;for (count = 1; count <= num; count++)putchar(ch);}
9.1.8 return返回
返回值不仅可以赋值给变量,还可以用作表达式的一部分;
返回值不一定是变量的值,也可以是任意表达式;
return语句可以融入花括号里面;
#include <stdio.h>int imin(int, int);int main(void){int evill, evil2;printf("Enter a pair of integers(q to quit): \n");while (scanf_s("%d %d", &evill, &evil2) == 2){printf("The lesser of %d and %d is %d.\n", evill, evil2, imin(evill, evil2));printf("Enter a pair of integers (q to quit):\n");}printf("Bye.\n");return 0;}int imin(int n, int m){int min;if (n < m)min = n;elsemin = m;return min;}
9.2ANSI 函数原型
/* misuse.c -- 错误使用函数*/// 20210315 23:15#include <stdio.h>int imax();int main(void){printf("The maximum of %d and %d is %d\n", 3, 5, imax(3));printf("The maximum of %d and %d is %d\n", 3, 5, imax(3.0, 5.0));return 0;}int imax(n, m)int n, m;{return (n > m ? n : m);}
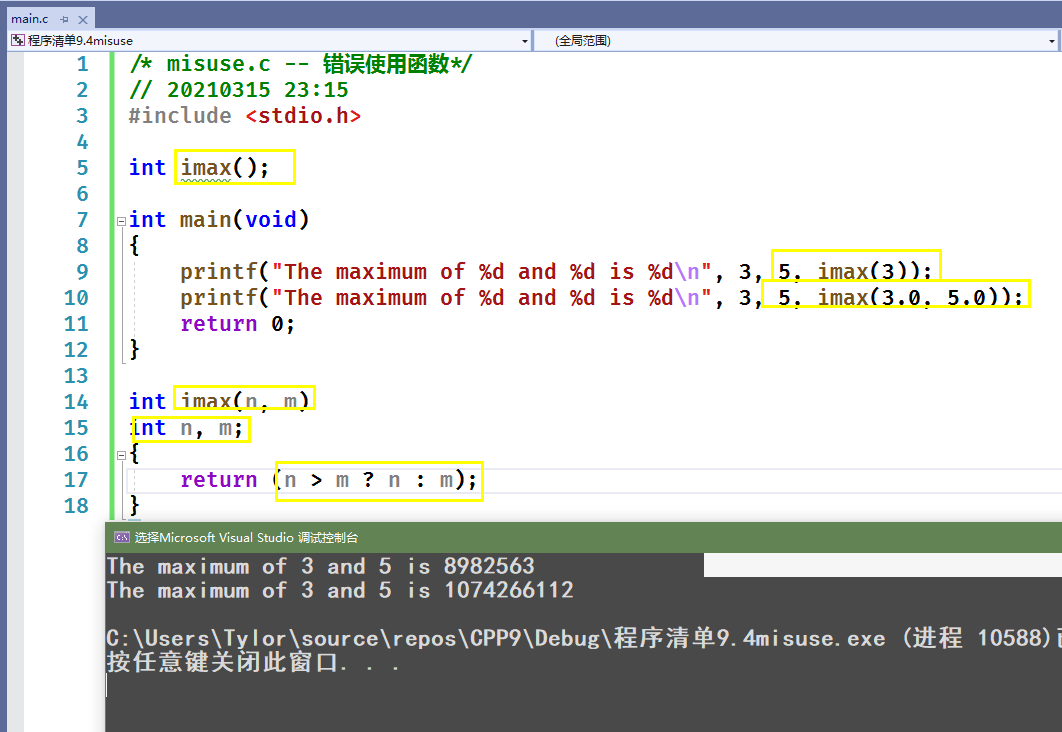
9.2.2 ANSI 的解决方案
由代码可见,函数原型中,个数对应的形式参数数据类型是必须的,而变量是选配;
函数原型可以去掉,直接把自定义函数放在主调函数之前,完整声明,然后在主调函数中调用即可;
printf()的参数是不确定的,可以是多个。
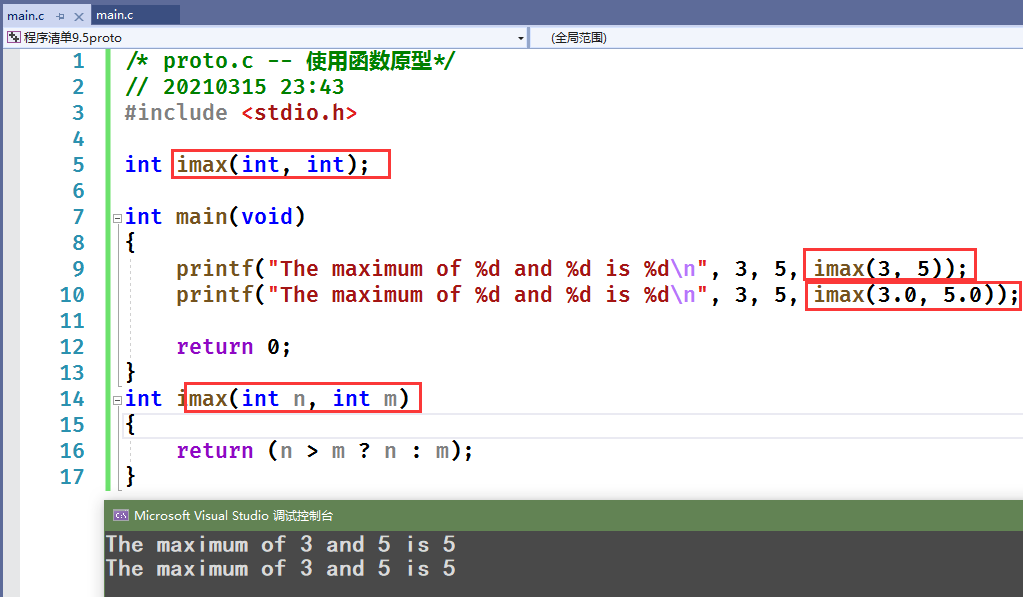
/* proto.c -- 使用函数原型*/// 20210315 23:43#include <stdio.h>int imax(int, int);int main(void){printf("The maximum of %d and %d is %d\n", 3, 5, imax(3, 5));printf("The maximum of %d and %d is %d\n", 3, 5, imax(3.0, 5.0));return 0;}int imax(int n, int m){return (n > m ? n : m);}
9.3 递归
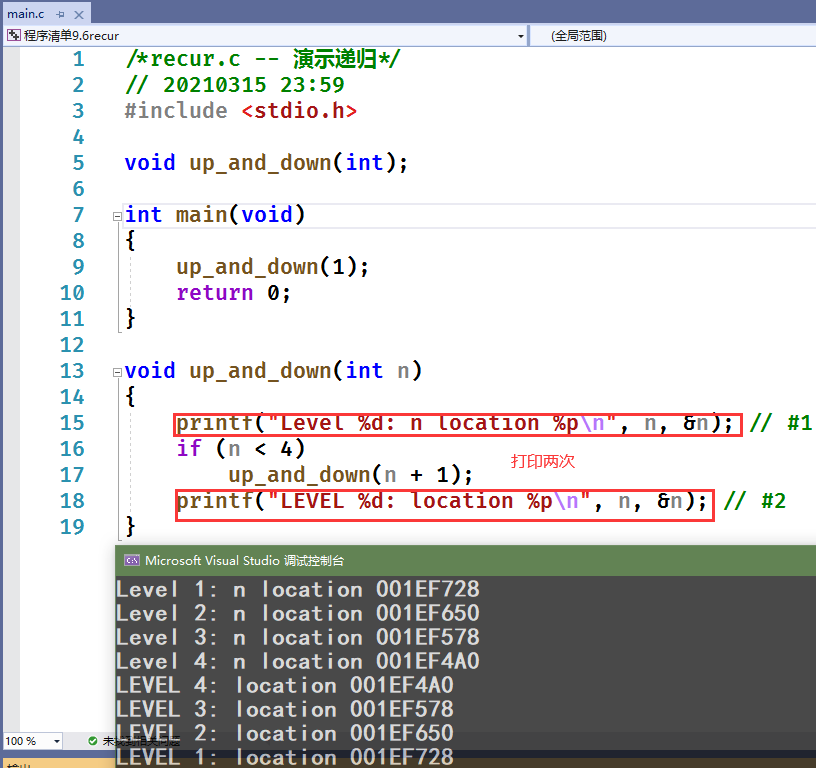
代码解析:但n的值小于四的时候进入循环,资质进入第四层,因为每一层都只执行到第一句打印语句;
所以但第四层循环退出之后,首先进行的是重复当前循环的打印语句,也就是第二个打印语句,然后逐次退出第三层,第二层和第一层;
递归和循环,条件下可以相互转换;
可在调试模式下观察代码执行过程。
/*recur.c -- 演示递归*/// 20210315 23:59#include <stdio.h>void up_and_down(int);int main(void){up_and_down(1);return 0;}void up_and_down(int n){printf("Level %d: n location %p\n", n, &n); // #1if (n < 4)up_and_down(n + 1);printf("LEVEL %d: location %p\n", n, &n); // #2}
9.3.3尾递归
把递归调用置于函数末尾,return语句之前,相当于循环;
每次递归都会创造一组变量,所以占用的内存更多;
递归调用的数量受限于内存空间;
// factor.c -- 使用循环和递归计算阶乘// 20210317 14:13#include <stdio.h>long fact(int n);long rfact(int n);int main(void){int num;printf("This program calculates factorials.\n");printf("Enter a value in the range 0-12(q to quit):\n");while (scanf_s("%d", &num) == 1){if (num < 0)printf("No negative numbers, please.\n");else if (num > 12)printf("Keep input under 13.\n");else{printf("loop: %d factorial = %ld\n", num, fact(num));printf("recursion: %d factorial = %ld\n", num, rfact(num));}printf("Enter a value in the range 0-12 (q to quit):\n");}printf("Bye!\n");return 0;}long fact(int n){long ans;for (ans = 1; n > 1; n--)ans *= n;return ans;}long rfact(int n){long ans;if (n > 0)ans = n * rfact(n - 1);elseans = 1;return ans;}
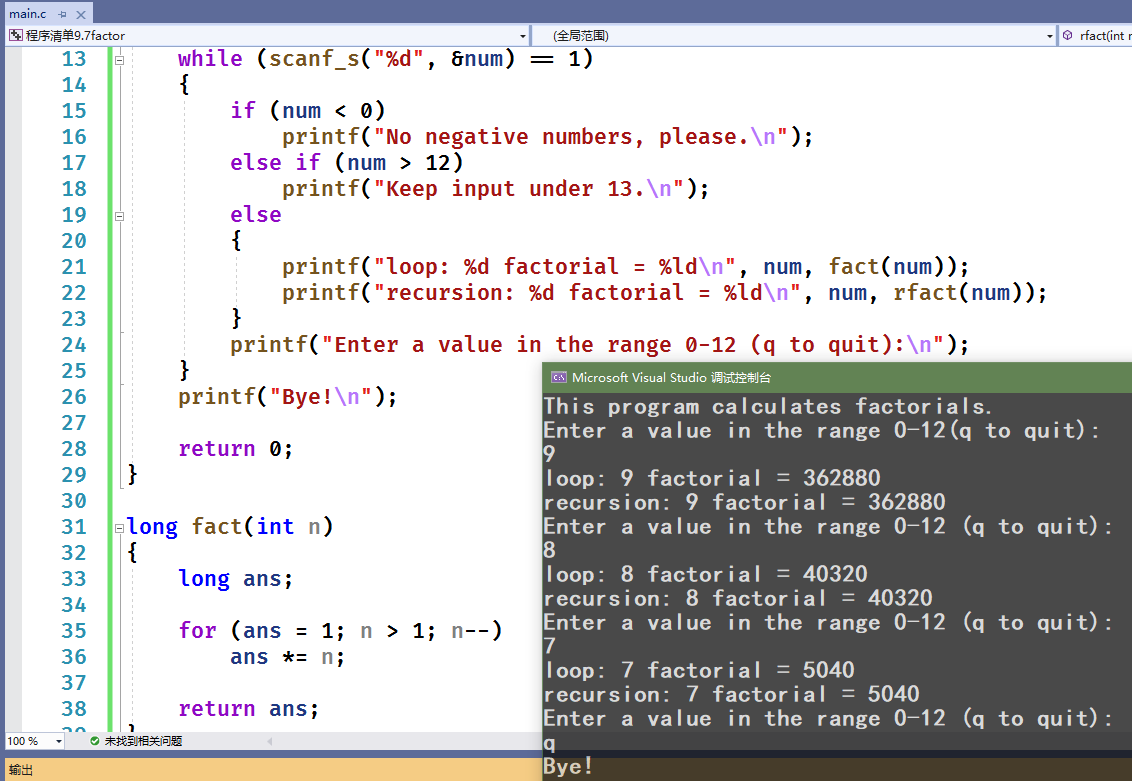
9.3.5 递归的优缺点
为编程问题提供了简单的解决方案,但会快速消耗计算机内存;
递归通过创造指数级变量快速占有大量内存空间,类似于fork()函数创建多线程;
9.4.5 使用头文件(构建文件项目)
1,文件结构
2,hotel.h
/*hotel.h -- 符号常量和hotel.c中的所有函数原型*///20210319 08:42#include <stdio.h>#define QUIT 5#define HOTEL1 180.00#define HOTEL2 225.00#define HOTEL3 255.00#define HOTEL4 355.00#define DISCOUNT 0.95#define STARS "****************************"//显示选择列表int menu(void);//返回预定天数int getnights(void);//根据费率,入住天数计算费用//并显示结果void showprice(double rate, int nights);
3 hotel.c
/*hotel.c -- 酒店管理函数*///20210319 0851#include <stdio.h>#include "hotel.h"int menu(void){int code, status;printf("\n%s%s\n", STARS, STARS);printf("Enter the number of the desired hotel:\n");printf("1) Fairfield Arms 2) Hotel Olympic\n");printf("3) Cherworthy Plaza 4) The Stockon\n");printf("5) quit\n");printf("%s%s\n", STARS, STARS);while ((status = scanf_s("%d", &code) != 1) || (code < 1 || code > 5)){if (status != 1)scanf_s("%*s");printf("Enter an integer form 1 to 5, please.\n");}return code;}int getnights(void){int nights;printf("How many nights are needed?");while (scanf_s("%d", &nights) != 1){scanf_s("%*s");printf("Please enter an integer, such as 2.\n");}return nights;}void showprice(double rate, int nights){int n;double total = 0.0;double factor = 1.0;for (n = 1; n <= nights; n++, factor *= DISCOUNT)total += rate * factor;printf("The total cost will be $%0.2f.\n", total);}
3 main.c
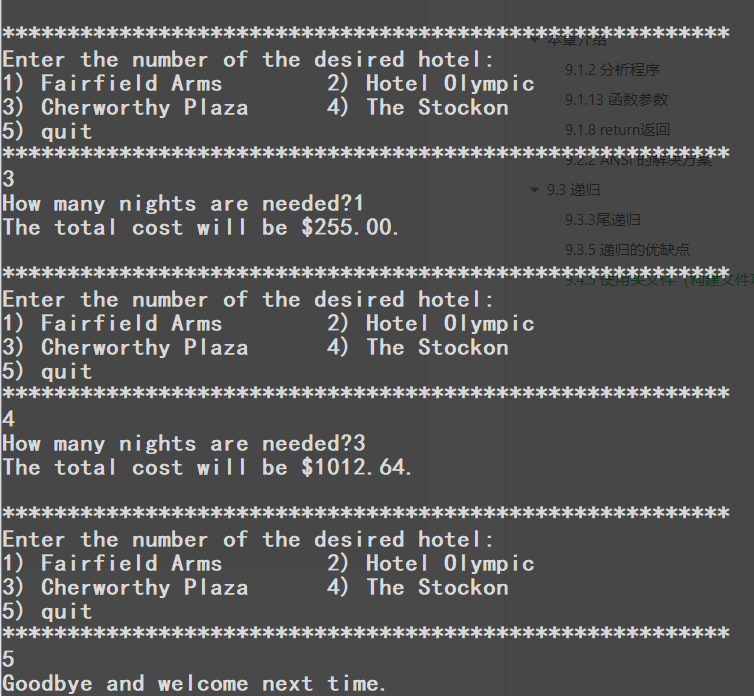
/*usehotel.c -- 房间汇率程序*//*与程序清单9.10一起编译*///20210319 09:23#include <stdio.h>#include "hotel.h"int main(void){int nights;double hotel_rate;int code;while ((code = menu()) != QUIT){switch (code){case 1:hotel_rate = HOTEL1;break;case 2:hotel_rate = HOTEL2;break;case 3:hotel_rate = HOTEL3;break;case 4:hotel_rate = HOTEL4;break;default:hotel_rate = 0.0;printf("Oops!\n");break;}nights = getnights();showprice(hotel_rate, nights);}printf("Goodbye and welcome next time.\n");return 0;}
4,测试输出
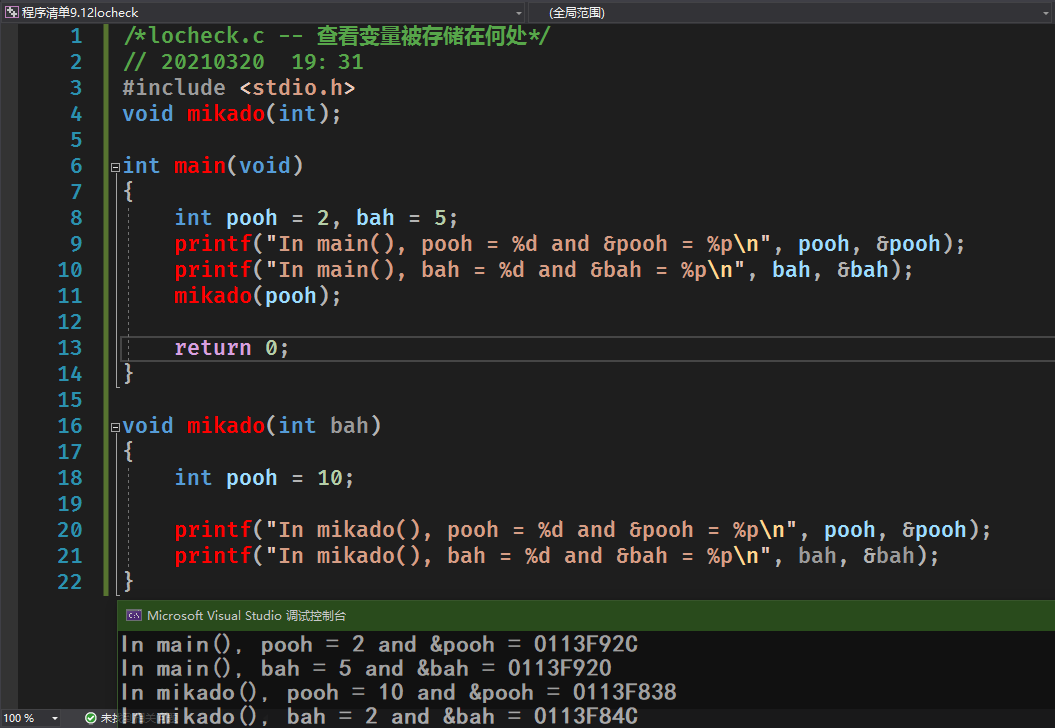
9.5 查找地址:&运算符
取地址运算符也是一元运算符;
子函数共享主调函数的变量;
/*locheck.c -- 查看变量被存储在何处*/// 20210320 19:31#include <stdio.h>void mikado(int);int main(void){int pooh = 2, bah = 5;printf("In main(), pooh = %d and &pooh = %p\n", pooh, &pooh);printf("In main(), bah = %d and &bah = %p\n", bah, &bah);mikado(pooh);return 0;}void mikado(int bah){int pooh = 10;printf("In mikado(), pooh = %d and &pooh = %p\n", pooh, &pooh);printf("In mikado(), bah = %d and &bah = %p\n", bah, &bah);}
9.6更改主调函数的变量
失败截图
/*swap1.c -- 第一个版本的交换函数*/// 20210320 19:53#include <stdio.h>void interchange(int u, int y);int main(void){int x = 5, y = 10;printf("Originally x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);interchange(x, y);printf("Now x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);return 0;}void interchange(int u, int v){int temp;temp = u;u = v;v = temp;}

对代码的改进
使用printf()语句,检查程序运行过程
/*swap1.c -- 第一个版本的交换函数*/// 20210320 20:19#include <stdio.h>void interchange(int u, int y);int main(void){int x = 5, y = 10;printf("Originally x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);interchange(x, y);printf("Now x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);return 0;}void interchange(int u, int v){int temp;printf("Originally u = %d and v = %d.\n", u, v);temp = u;u = v;v = temp;printf("Now u = %d and v = %d.\n", u, v);}
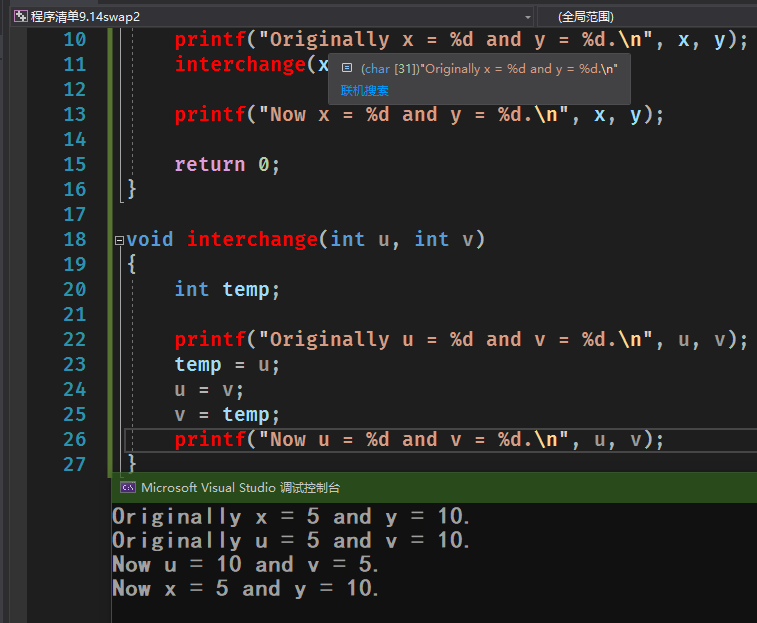
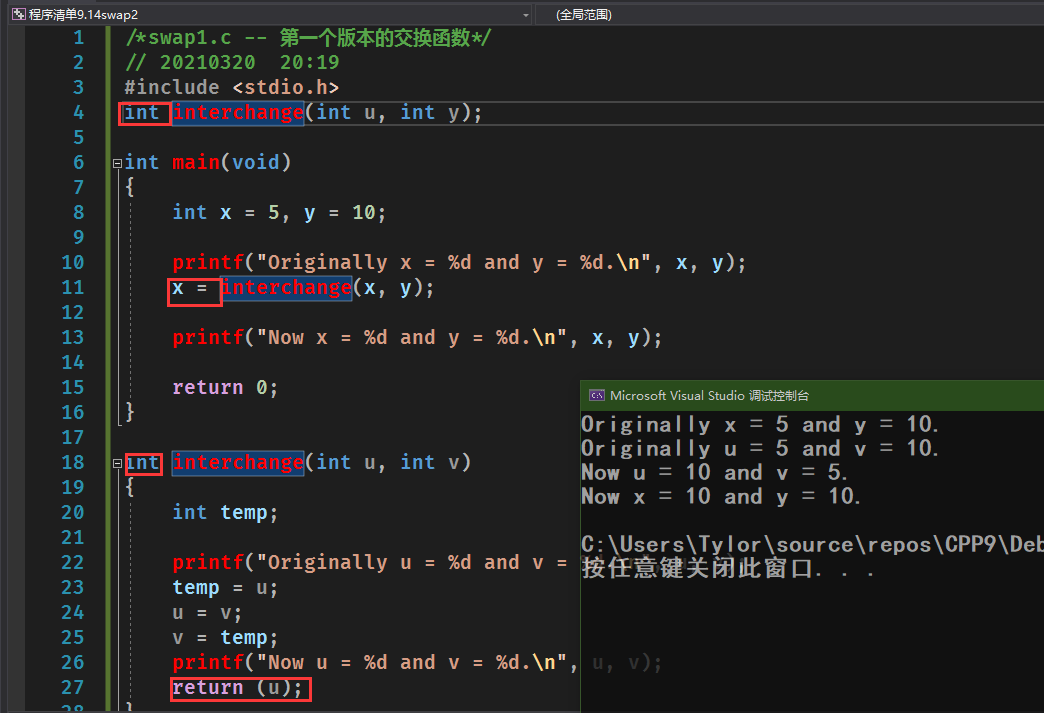
修改函数调用方式,传递参数返回主调函数,交换子函数的值会传递给主调函数,但缺点也是明显的。
首先需要修改函数原型声明,其次只能返回一个值
/*swap1.c -- 第一个版本的交换函数*/// 20210320 20:19#include <stdio.h>int interchange(int u, int y);int main(void){int x = 5, y = 10;printf("Originally x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);x = interchange(x, y);printf("Now x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);return 0;}int interchange(int u, int v){int temp;printf("Originally u = %d and v = %d.\n", u, v);temp = u;u = v;v = temp;printf("Now u = %d and v = %d.\n", u, v);return (u);}
9.7 指针简介
使用指针也需要声明指针的数据类型;
&将变量指向该变量的内存地址, *解析该内存地址存储的值;
val = *ptr;ptr = &bah;val = *ptr;// 等价于 val = bah
9.7.2 声明指针
必须指明指针指向变量的数据类型;
程序员在声明指针数据类型时在* 和数据类型之间保留一个空格,但是解引用变量时忽略空格;
指针指向的是一个新的数据类型,不要对它做整数的一些操作;
%p用于printf()语句中指针的转义声明;
9.7.3 使用指针在函数间通信
传入的是指向该变量的内存地址,但是函数内部完成交换是通过解析引用运算符
// 第一种声明方式,形式参数必须是一个与调入值数据类型相同void interchange(int u, int v);// 第二种声明方式, 形式参数必须是一个指向正确类型的指针void interchange(int * u, int * v);
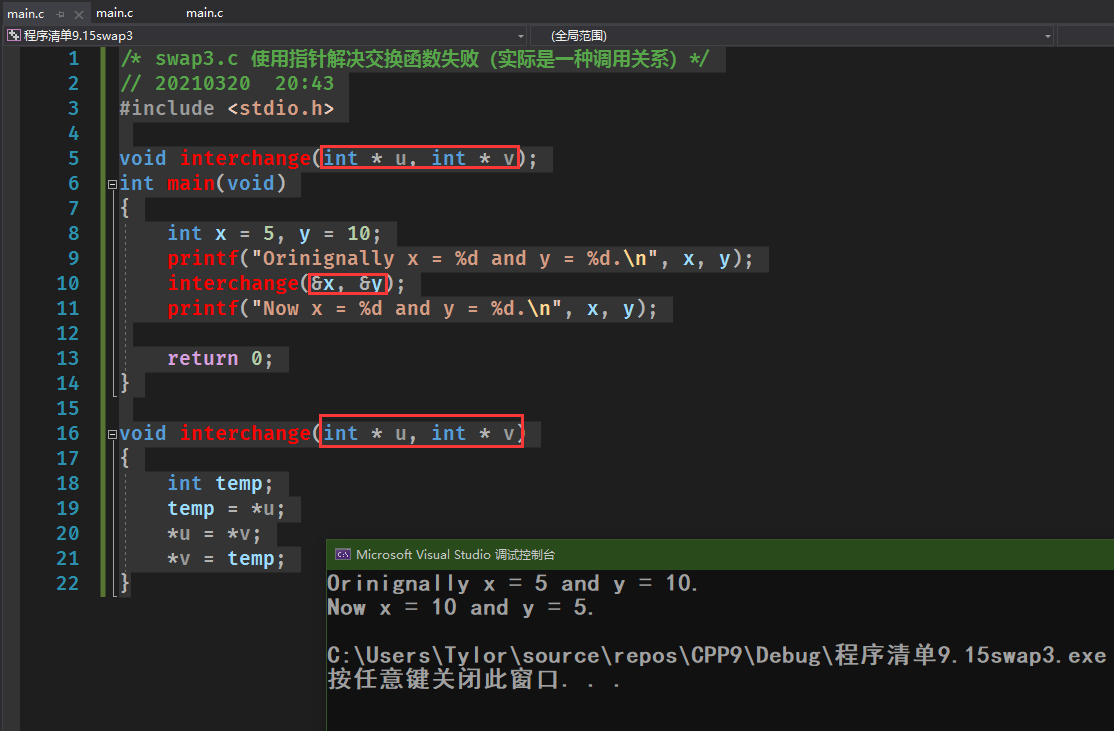
/* swap3.c 使用指针解决交换函数失败(实际是一种调用关系)*/// 20210320 20:43#include <stdio.h>void interchange(int * u, int * v);int main(void){int x = 5, y = 10;printf("Orinignally x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);interchange(&x, &y);printf("Now x = %d and y = %d.\n", x, y);return 0;}void interchange(int * u, int * v){int temp;temp = *u;*u = *v;*v = temp;}