React 处理事件的方法是事件委托。无论子元素有多少相同事件,在doc上只挂载一次,且挂载的是一个 dispatch 方法。
事件概览
先来看下react 的事件系统.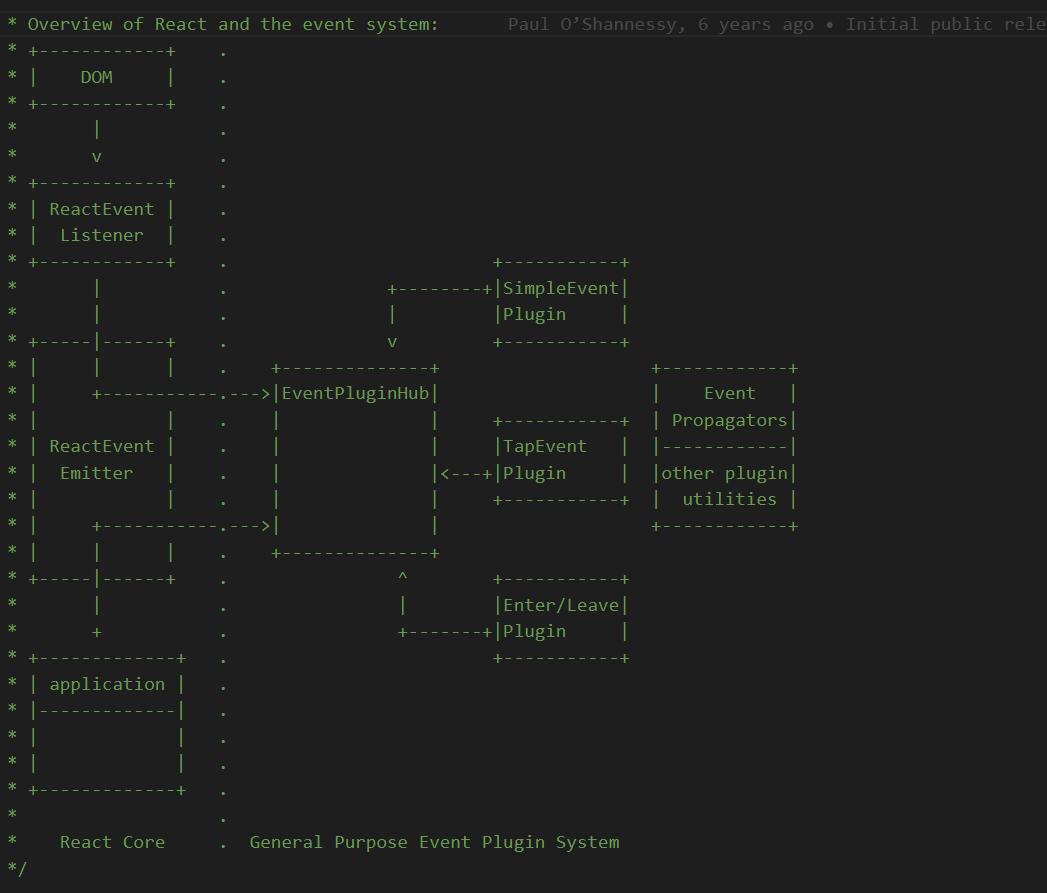
这是React Event源码中介绍的插件,具体的插件和上图有些差异。event 在不同端实现的方式不同。
import BeforeInputEventPlugin from '../events/BeforeInputEventPlugin';import ChangeEventPlugin from '../events/ChangeEventPlugin';import DOMEventPluginOrder from '../events/DOMEventPluginOrder';import EnterLeaveEventPlugin from '../events/EnterLeaveEventPlugin';import SelectEventPlugin from '../events/SelectEventPlugin';import SimpleEventPlugin from '../events/SimpleEventPlugin';//插件是React-dom/events 实现部分功能。EventPluginHubInjection.injectEventPluginsByName({SimpleEventPlugin: SimpleEventPlugin,EnterLeaveEventPlugin: EnterLeaveEventPlugin,ChangeEventPlugin: ChangeEventPlugin,SelectEventPlugin: SelectEventPlugin,BeforeInputEventPlugin: BeforeInputEventPlugin,//beforeInput 是规范,但没有在任何浏览器中实现});
在初始React-dom时,会注入写 DOMEventPlugin,这些插件注入是有一定顺序的。具体如下:
//packages\react-dom\src\events\DOMEventPluginOrder.jsconst DOMEventPluginOrder = ['ResponderEventPlugin','SimpleEventPlugin','EnterLeaveEventPlugin','ChangeEventPlugin','SelectEventPlugin','BeforeInputEventPlugin',];export default DOMEventPluginOrder;
react中的事件机制是按w3c实现的,有些浏览器不支持的事件,react是支持的。例如“beforeInput”是规范的事件,但没有在任何浏览器中实现。在react中之所以可不考虑事件的兼容性,并且可以按照w3c中的规范进行操作,其原因就是这些插件。
扩展event方法
在解析 react-dom.js文件时会修改event的方法,例如对preventDefault、stopPropagation的修改。
_assign(SyntheticEvent.prototype, {preventDefault: function preventDefault() {this.defaultPrevented = true;var event = this.nativeEvent;if (!event) { return; }if (event.preventDefault) {event.preventDefault();} else if (typeof event.returnValue !== 'unknown') {event.returnValue = false;}this.isDefaultPrevented = functionThatReturnsTrue;},stopPropagation: function stopPropagation() {var event = this.nativeEvent;if (!event) {return;}if (event.stopPropagation) {event.stopPropagation();} else if (typeof event.cancelBubble !== 'unknown') {// IE specificevent.cancelBubble = true;}this.isPropagationStopped = functionThatReturnsTrue;},persist: function persist() {this.isPersistent = functionThatReturnsTrue;}//...省略代码});function functionThatReturnsTrue() {return true;}function functionThatReturnsFalse() {return false;}
触发事件
class App extends Component {render() {return <div onClick={ ()=>{ console.log('被点击了') }}>Hello World!</div>}}
运行例子,并点击div触发onClick,其调用栈如下: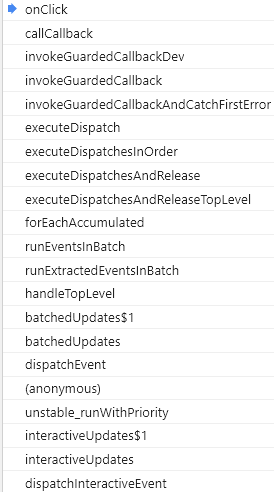
在绑定事件 trapBubbledEvent 绑定事件时,绑定的监听方法是 dispatchInteractiveEvent 和 dispatchEvent中的一个。dispatchInteractiveEvent 间接调用的是dispatchEvent。
点击click触发 dispatch 事件,此处派发的方法是 dispatchInteractiveEvent ,其调用方法如下:
function dispatchInteractiveEvent(topLevelType, nativeEvent) {interactiveUpdates(dispatchEvent, topLevelType, nativeEvent);}function interactiveUpdates(fn, a, b) {return _interactiveUpdatesImpl(fn, a, b);}
在 interactiveUpdates$1 开启批处理:isBatchingUpdates=true。
function interactiveUpdates$1(fn, a, b) {if (!isBatchingUpdates && !isRendering &&lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime !== NoWork) {// Synchronously flush pending interactive updates.performWork(lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime, false);lowestPriorityPendingInteractiveExpirationTime = NoWork;}var previousIsBatchingUpdates = isBatchingUpdates;isBatchingUpdates = true;try {//unstable标志着这些代码不稳定,可能被修改。return scheduler.unstable_runWithPriority(scheduler.unstable_UserBlockingPriority,function () { return fn(a, b); }//执行事件方法);} finally {isBatchingUpdates = previousIsBatchingUpdates;if (!isBatchingUpdates && !isRendering) {performSyncWork(); //开始更新}}}
react是函数编程,在函数调用时,将相应功能组合。在 interactiveUpdates$1 中可知道,执行完事件方法才会调用performSyncWork。
dispatchEvent
由 dispatchInteractiveEvent 中可以知道 scheduler.unstable_runWithPriority中 fn 是dispatchEvent,a是topLevelType,b是nativeEvent。
function dispatchEvent(topLevelType, nativeEvent) {if (!_enabled) { return; }var nativeEventTarget = getEventTarget(nativeEvent);var targetInst = getClosestInstanceFromNode(nativeEventTarget);if (targetInst !== null && typeof targetInst.tag === 'number'&& !isFiberMounted(targetInst)) {targetInst = null;}var bookKeeping = getTopLevelCallbackBookKeeping(topLevelType, nativeEvent, targetInst);try {// 在同一个循环中处理事件队列允许使用“preventDefault”。batchedUpdates(handleTopLevel, bookKeeping);} finally {releaseTopLevelCallbackBookKeeping(bookKeeping);}}var CALLBACK_BOOKKEEPING_POOL_SIZE = 10;var callbackBookkeepingPool = [];//callbackBookkeepingPool.pop;function getTopLevelCallbackBookKeeping(topLevelType, nativeEvent, targetInst) {if (callbackBookkeepingPool.length) {var instance = callbackBookkeepingPool.pop();//instance.topLevelType = topLevelType;instance.nativeEvent = nativeEvent;instance.targetInst = targetInst;return instance;}return {topLevelType: topLevelType,nativeEvent: nativeEvent,targetInst: targetInst,ancestors: []};}// callbackBookkeepingPool.pushfunction releaseTopLevelCallbackBookKeeping(instance) {instance.topLevelType = null;instance.nativeEvent = null;instance.targetInst = null;instance.ancestors.length = 0;if (callbackBookkeepingPool.length < CALLBACK_BOOKKEEPING_POOL_SIZE) {callbackBookkeepingPool.push(instance);}}
batchedUpdates
由上面可知道fn是handleTopLevel;_batchedUpdatesImpl 是batchedUpdates$1,编译命名的问题(忽略)。
var isBatching = false;function batchedUpdates(fn, bookkeeping) {//fn 是 handleTopLevelif (isBatching) { //如果当前在另一个批处理中,则需要等到它完全完成后才能恢复状态return fn(bookkeeping);}isBatching = true;try {return _batchedUpdatesImpl(fn, bookkeeping);} finally {isBatching = false;var controlledComponentsHavePendingUpdates = needsStateRestore();if (controlledComponentsHavePendingUpdates) {_flushInteractiveUpdatesImpl();restoreStateIfNeeded();}}}function batchedUpdates$1(fn, a) {var previousIsBatchingUpdates = isBatchingUpdates;isBatchingUpdates = true;try {return fn(a);// 等于 handleTopLevel(bookKeeping)} finally {isBatchingUpdates = previousIsBatchingUpdates;if (!isBatchingUpdates && !isRendering) {// 使用原生事件更新sateperformSyncWork();}}}function handleTopLevel(bookKeeping) {var targetInst = bookKeeping.targetInst; //遍历层次结构,以防有嵌套组件var ancestor = targetInst;do {if (!ancestor) {bookKeeping.ancestors.push(ancestor);break;}var root = findRootContainerNode(ancestor);if (!root) { break; }bookKeeping.ancestors.push(ancestor);ancestor = getClosestInstanceFromNode(root);} while (ancestor);for (var i = 0; i < bookKeeping.ancestors.length; i++) {// ancestors-->上代targetInst = bookKeeping.ancestors[i];runExtractedEventsInBatch(bookKeeping.topLevelType, targetInst,bookKeeping.nativeEvent,getEventTarget(bookKeeping.nativeEvent));}}//返回的是HostRootfunction findRootContainerNode(inst) {while (inst.return) { inst = inst.return; }if (inst.tag !== HostRoot) { return null; }return inst.stateNode.containerInfo;}
执行到此基本上是包装,为后续的执行设定条件。在handleTopLevel中执行runExtractedEventsInBatch。
runExtractedEventsInBatch
runExtractedEventsInBatch用于提取组件中的事件,形成捕获和冒泡队列。
function runExtractedEventsInBatch(topLevelType, targetInst,nativeEvent, nativeEventTarget) {var events = extractEvents(topLevelType, targetInst, nativeEvent, nativeEventTarget);runEventsInBatch(events);}
extractEvents
plugins的值是[null, ‘SimpleEventPlugin’,’EnterLeaveEventPlugin’,’ChangeEventPlugin’,
‘SelectEventPlugin’, ‘BeforeInputEventPlugin’]。这些事件都有 extractEvents 接口,但仅 SimpleEventPlugin 返回extractedEvents值。
//packages\events\EventPluginHub.jsfunction extractEvents(topLevelType, targetInst, nativeEvent, nativeEventTarget) {var events = null;for (var i = 0; i < plugins.length; i++) {// 并不是所有的插件都可以在运行时加载.var possiblePlugin = plugins[i];if (possiblePlugin) {var extractedEvents = possiblePlugin.extractEvents(topLevelType,targetInst, nativeEvent,nativeEventTarget);if (extractedEvents) {events = accumulateInto(events, extractedEvents);}}}return events;}
在SimpleEventPlugin 会处理event的信息并收集事件信息.
var SimpleEventPlugin = {extractEvents: function extractEvents(topLevelType, targetInst,nativeEvent, nativeEventTarget) {var dispatchConfig = topLevelEventsToDispatchConfig[topLevelType];if (!dispatchConfig) { return null; }//....省略。var event = EventConstructor.getPooled(dispatchConfig, targetInst,nativeEvent, nativeEventTarget);accumulateTwoPhaseDispatches(event);return event;}}function accumulateTwoPhaseDispatches(events) {forEachAccumulated(events, accumulateTwoPhaseDispatchesSingle);//forEachAccumulated 在后面}function accumulateTwoPhaseDispatchesSingle(event) {if (event && event.dispatchConfig.phasedRegistrationNames) {traverseTwoPhase(event._targetInst, accumulateDirectionalDispatches, event);}}// fn 是 accumulateDirectionalDispatches;inst是实例function traverseTwoPhase(inst, fn, arg) {var path = [];while (inst) {// 收集当前inst 和 父级 instpath.push(inst);inst = getParent(inst);}var i = void 0;for (i = path.length; i-- > 0;) {fn(path[i], 'captured', arg);}for (i = 0; i < path.length; i++) {fn(path[i], 'bubbled', arg);}}
traverseTwoPhase 中 path是当前dom到根节点的目录。traverseTwoPhase中的 fn 是 accumulateDirectionalDispatches,在for循环中依次执行 fn 收集 path 到dom上的事件,这和冒泡和捕获机制一样。
function accumulateDirectionalDispatches(inst, phase, event) {const listener = listenerAtPhase(inst, event, phase);if (listener) {event._dispatchListeners = accumulateInto(event._dispatchListeners,listener);//此处事件数组event._dispatchInstances = accumulateInto(event._dispatchInstances, inst);//此处实例数组}}
event._dispatchListeners 保存整棵树的事件。event._dispatchInstances 保存对应的dom 实例。
listenerAtPhase
event.dispatchConfig.phasedRegistrationNames 中存放当前事件名称,以onClick为例,此时它的值为 {bubbled: “onClick”, captured: “onClickCapture”}。在traverseTwoPhase中传入的phase值依次为captured、bubbled,就可收集 path(树) 上的onClickCapture、onClick 事件。
function listenerAtPhase(inst, event, propagationPhase) {// registrationName 为事件的名称,例如 onClickconst registrationName = event.dispatchConfig.phasedRegistrationNames[propagationPhase];return getListener(inst, registrationName);}//获得事件方法export function getListener(inst: Fiber, registrationName: string) {let listener;const stateNode = inst.stateNode;if (!stateNode) {return null;}const props = getFiberCurrentPropsFromNode(stateNode);if (!props) {// Work in progress.return null;}listener = props[registrationName]; // 实例上的方法if (shouldPreventMouseEvent(registrationName, inst.type, props)) {return null;}return listener;}
accumulateInto
traverseTwoPhase 是在for循环中执行accumulateDirectionalDispatches,也就是说 listenerAtPhase是逐级收集的。accumulateInto 会将传入的值转为数组,形成相应的队列并返回。
function accumulateInto(current, next) {if (current == null) {return next;}if (Array.isArray(current)) {if (Array.isArray(next)) {current.push.apply(current, next);return current;}current.push(next);return current;}if (Array.isArray(next)) {return [current].concat(next);}return [current, next];}
runEventsInBatch
开始运行批处理事件。
var eventQueue = null;export function runEventsInBatch(events) {if (events !== null) { eventQueue = accumulateInto(eventQueue, events); }const processingEventQueue = eventQueue;eventQueue = null;if (!processingEventQueue) { return; }forEachAccumulated(processingEventQueue, executeDispatchesAndReleaseTopLevel);invariant(!eventQueue,'processEventQueue(): Additional events were enqueued while processing ' +'an event queue. Support for this has not yet been implemented.',);rethrowCaughtError();}
forEachAccumulated
若传入是数组则遍历执行;若传入是方法则执行方法;
function forEachAccumulated(arr, cb, scope) {if (Array.isArray(arr)) {arr.forEach(cb, scope);} else if (arr) {cb.call(scope, arr);}}
executeDispatchesAndReleaseTopLevel
executeDispatchesInOrder按队列执行方法,先执行captured事件,接着执行bubbled事件。若其中一个事件stopPropagation则isPropagationStopped返回true,不再执行后续事件。
var executeDispatchesAndReleaseTopLevel = function executeDispatchesAndReleaseTopLevel(e) {return executeDispatchesAndRelease(e);};var executeDispatchesAndRelease = function executeDispatchesAndRelease(event) {if (event) {executeDispatchesInOrder(event);if (!event.isPersistent()) {event.constructor.release(event);}}};function executeDispatchesInOrder(event) {var dispatchListeners = event._dispatchListeners;var dispatchInstances = event._dispatchInstances;//包括captured 和 bubbledif (Array.isArray(dispatchListeners)) {for (var i = 0; i < dispatchListeners.length; i++) {if (event.isPropagationStopped()) {//是否终止冒泡break;}//Listeners 和 Instances是两个总是同步的并行数组executeDispatch(event, dispatchListeners[i], dispatchInstances[i]);}} else if (dispatchListeners) {executeDispatch(event, dispatchListeners, dispatchInstances);}event._dispatchListeners = null;event._dispatchInstances = null;}function executeDispatch(event, listener, inst) {const type = event.type || 'unknown-event';event.currentTarget = getNodeFromInstance(inst);// 当前事件中的实例invokeGuardedCallbackAndCatchFirstError(type, listener, undefined, event);//执行方法event.currentTarget = null;}function getNodeFromInstance$1(inst) {if (inst.tag === HostComponent || inst.tag === HostText) {return inst.stateNode;}invariant(false, 'getNodeFromInstance: Invalid argument.');}
执行调用listener
在执行事件时需要 捕获异常 和处理异常,invokeGuardedCallbackAndCatchFirstError 就是创建这些环节的方法。
function invokeGuardedCallbackAndCatchFirstError(name, func, context, a, b, c, d, e, f) {invokeGuardedCallback.apply(this, arguments);if (hasError) {var error = clearCaughtError();if (!hasRethrowError) { hasRethrowError = true; rethrowError = error; }}}var reporter = {onError: function onError(error) { hasError = true; caughtError = error; }};// context 是undefinedfunction invokeGuardedCallback(name, func, context, a, b, c, d, e, f) {hasError = false;caughtError = null;invokeGuardedCallbackImpl$1.apply(reporter, arguments);}// funcArgs是 listenervar invokeGuardedCallbackImpl = function invokeGuardedCallbackImpl(name, func, context,a, b, c, d, e, f) {var funcArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 3);try {func.apply(context, funcArgs);//执行dom上的事件} catch (error) {this.onError(error);//this => reporter}};
批处理
处理 原生事件和 react 事件 是不一样的,react是批处理事件。例如,在react组件中使用setState设置state,代码如下:
class App extends Component {state = { val: 0 }batchUpdates = () => {this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 });console.log(this.state.val);this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 });console.log(this.state.val);this.setState({ val: this.state.val + 1 });console.log(this.state.val);//this.state.val的值为多少呢?}render() {return (<div onClick={this.batchUpdates}>{`Counter is ${this.state.val}`} </div>)}}
此时的console.log(this.state.val)输出的为0,组件中的this.state.val为 1。更新过程如下: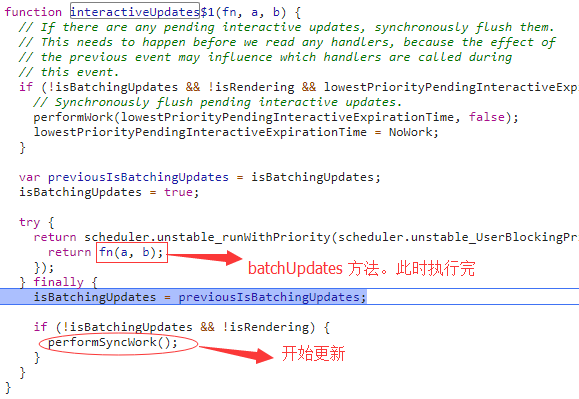
先执行完事件方法,然后调用preformSyncWork进行reconciliation。

