队列(Queue)是一种先进先出(FIFO,First-In-First-Out)的线性表。
在具体应用中通常用链表或者数组来实现。队列只允许在后端(称为 rear)进行插入操作,在前端(称为 front)进行删除操作。
队列的操作方式和堆栈类似,唯一的区别在于队列只允许新数据在后端进行添加。
队列常用的方法有:add、remove、element、offer、poll、peek、put、take。
原理: 栈,后进先出, LIFO, last in first out,
方法:
- 创建/销毁
- 是否空/是否满
- 清空
- 统计长度
- 入栈push/出栈pop
- 遍历
私有:
- 指针
- 容量
- 栈顶指针
经典:
20. 有效的括号
function isValid(s: string): boolean {// 栈, 先进后出let hashTable = new Map([['(', ')'],['{', '}'],['[', ']']]);let stack = [];for (let char of s) {let last = stack[stack.length - 1];if (stack.length > 0 && char == hashTable.get(last)) {stack.pop();} else {stack.push(char);}}return stack.length === 0;};
剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。
pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。
top() —— 获取栈顶元素。
getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素。
辅助栈存放当前位置的最小值
MinStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
let index = this.size - 1;
this.stack.push(x);
this.minStack.push(index > -1 ? Math.min(this.minStack[index], x) : x);
this.size++;
};
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
辅助栈存放后入数据
CQueue.prototype.appendTail = function(value) {
while (this.stack2.length > 0) {
this.stack1.push(this.stack2.pop())
}
this.stack1.push(value)
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
CQueue.prototype.deleteHead = function() {
while (this.stack1.length > 0) {
this.stack2.push(this.stack1.pop());
}
return this.stack2.pop() || -1;
};
剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值
- max_value 队列头部的最大值
- push_back 队列尾部添加
- pop_front 队列头部移除
入队时, 把辅助队列中不小于当前元素, 否则移除。
MaxQueue.prototype.push_back = function(value) {
this.queue.push(value);
while (this.maxQueue.some(d => d < value)) {
this.maxQueue.pop()
}
this.maxQueue.push(value)
};
Hard
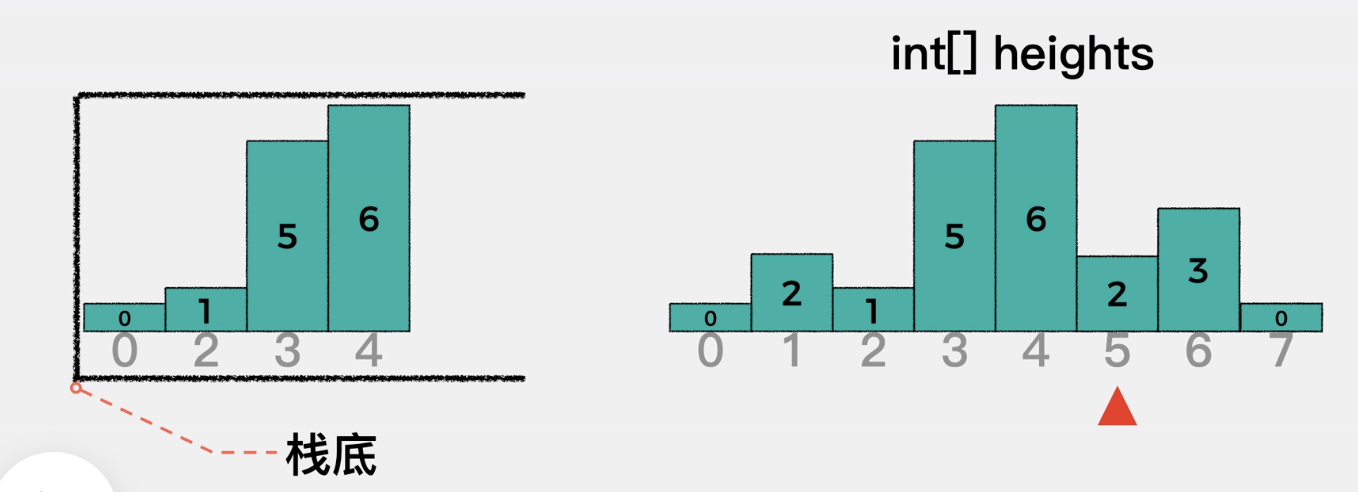
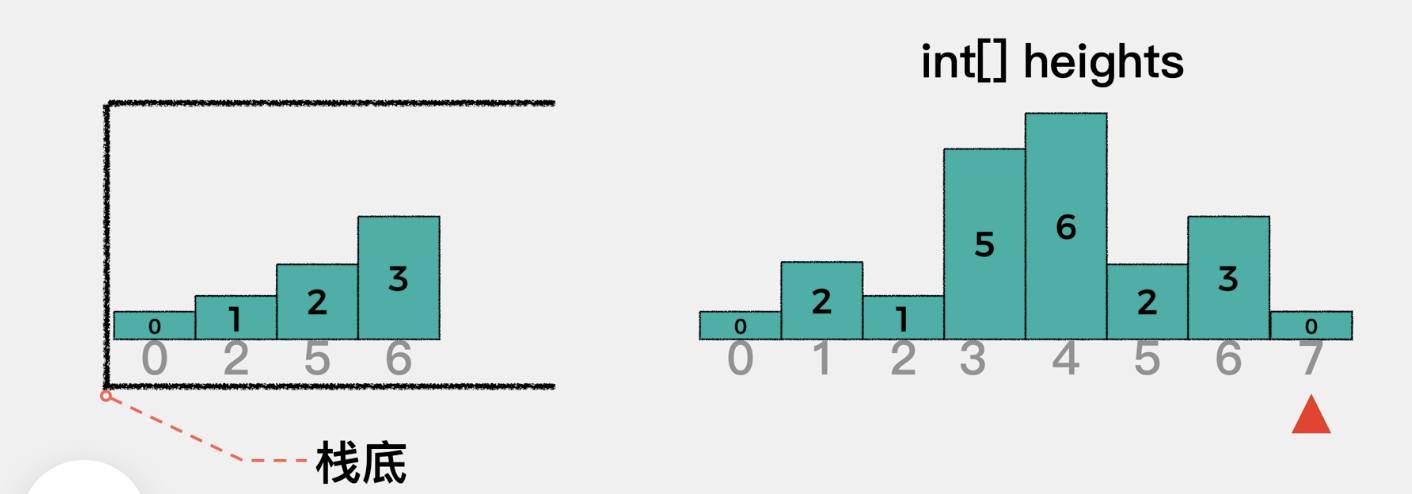
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形[字节]
[2,1,5,6,2,3]
10
2 [ 0, 1 ]
5 [ 0, 2, 3, 4 ]
5 [ 0, 2, 3 ]
7 [ 0, 2, 5, 6 ]
7 [ 0, 2, 5 ]
7 [ 0, 2 ]
实现
var largestRectangleArea = function(heights) {
let max=0;
let stack = []; // 下标
let arr = [0, ...heights, 0]
for (let i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
// 出现下滑式, 出站栈,寻找最大矩形
while (stack.length > 0 && arr[i] < arr[stack[stack.length-1]]) {
console.log(i, stack);
let lastIndex = stack.pop();
let curArea = arr[lastIndex] * (i - stack[stack.length-1]-1);
max = Math.max(max, curArea);
}
// 递增状态下,入栈
stack.push(i);
}
return max;
};
LC3:
496. 下一个更大元素 I
右边的第一个比 x 大的元素
case:
nums1 = [4,1,2], nums2 = [1,3,4,2] => [-1,3,-1]
nums1 = [2,4], nums2 = [1,2,3,4] => [3,-1]
📢 数组中的整数互不相同
var nextGreaterElement = function(nums1, nums2) {
let stack = [];
let nextBigger = {};
for (let num of nums2) {
while(stack.length > 0 && stack[stack.length-1] < num) {
nextBigger[stack.pop()] = num;
}
stack.push(num);
}
let res = nums1.map(d => nextBigger[d] || -1);
return res;
};
503. 下一个更大元素 II
[1,2,1] => [2,-1,2]
stack维护的是下标, 栈底到栈顶的下标在数组 nums 中对应的值是单调不升的
| i, num, stack | stack, stack[-1], res |
|---|---|
| 0 1 [] | |
| 1 2 [ 0 ] | [ 0 ] 0 [ 2, -1, -1 ] |
| 2 1 [ 1 ] | |
| 3 1 [ 1, 2 ] | |
| 4 2 [ 1, 2, 0 ] | [ 1, 2, 0 ] 0 [ 2, -1, -1 ] [ 1, 2 ] 2 [2,-1,2] |
| 5 1 [ 1, 1 ] |
var nextGreaterElements = function(nums) {
let n = nums.length;
let stack = [];
let res = new Array(n).fill(-1);
for (let i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) {
let cur = nums[i % n];
while(stack.length > 0 && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] < cur) {
res[stack.pop()] = cur;
}
stack.push(i % n);
}
return res;
};
1019. 链表中的下一个更大节点
链表+栈
栈存放下标
var nextLargerNodes = function(head) {
let nums = [];
let larger = [];
let stack = [];
let i = 0;
while (head != null) {
let val = head.val;
while (stack.length > 0 && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] < val) {
larger[stack.pop()] = val;
}
nums.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
stack.push(i);
larger[i] = 0;
i++;
}
return larger;
};
LC4:
1190. 反转每对括号间的子串
var reverseParentheses = function(s) {
let stack = [];
let hashMap = {};
const n = s.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let cur = s.charAt(i);
if (cur == '(') {
stack.push(i);
} else if (cur == ')') {
let left = stack.pop();
hashMap[left] = i;
hashMap[i] = left;
}
}
// console.log(hashMap)
let res = [];
let i = 0;
let step = 1; // 1向右,-1向左
while (i > -1 && i < n) {
let cur = s.charAt(i);
if (cur == '(' || cur == ')') {
step = -step;
i = hashMap[i];
} else {
res.push(cur);
}
i += step;
}
// console.log(res)
return res.join('');
};