使用 interface 定义接口 对象类型接口和函数类型接口 接口可以约束对象,函数,类的结构和类型,是一种代码协作必须遵守的契约
接口事列
interface List {id: number;name: string;}interface Result {data: List[];}function render(result: Result) {result.data.forEach((value) => {console.log(value.id, value.name);});}let result = {data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS" },{ id: 2, name: "TS" }],};render(result);
额外属性
在接口的实际调用中,后端也经常会传递约定之外的字段,如
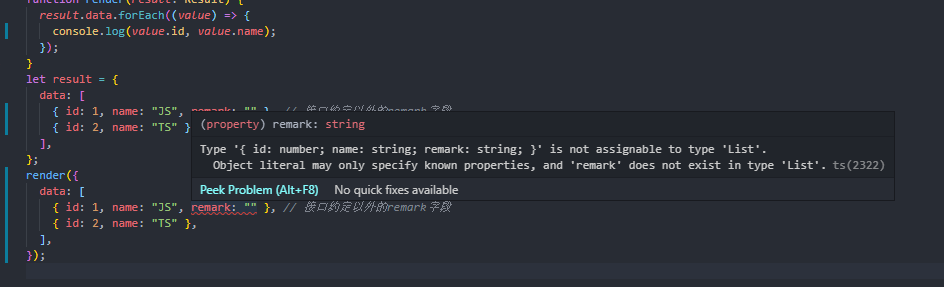
interface List {id: number;name: string;}interface Result {data: List[];}function render(result: Result) {result.data.forEach((value) => {console.log(value.id, value.name);});}let result = {data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark:"" }, // 接口约定以外的remark字段{ id: 2, name: "TS" }],};render(result);
传入接口以外的字段remark是并没有报错,ts允许这种情况的发生
只要传入的对象满足接口的必要条件就可以被允许,即使传入多余的字段也可以通过类型检查
但也有例外,如果直接传入对象字面量,TS就会对额外的字段进行类型检查,如下:
render({data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark:"" }, // 接口约定以外的remark字段{ id: 2, name: "TS" }],});
绕过检查的方法有3种
- 将对象字面量赋值给一个变量
```typescript
let result = {
data: [
], }; render(result);{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark:"" }, // 接口约定以外的remark字段{ id: 2, name: "TS" }
2. 使用类型断言```typescript// onerender({data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark: "" }, // 接口约定以外的remark字段{ id: 2, name: "TS" },],} as Result);// tworender(<Result>{data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark: "" }, // 接口约定以外的remark字段{ id: 2, name: "TS" },],});
- 使用字符串索引签名
表示用任意字符串去索引List,可得到任意结果,此时List可以实现支持多个属性
interface List {id: number;name: string;[remark: string]: any;}
接口成员
可选属性
对于一个约定好的接口类型,其中有些字段并不是一定会存在的,是可选属性 而之前在接口中声明的字段,是必须要满足的字段,不可以缺少
声明方式:
接口属性? 类型注解
interface List {id: number;name: string;// [x: string]: any;age?: number;}interface Result {data: List[];}function render(result: Result) {result.data.forEach((value) => {console.log(value.id, value.name); // 1 "JS" 2 "TS"if (value.age) {console.log(value.age); // 10}});}let result = {data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark: "" }, // 接口约定以外的remark字段{ id: 2, name: "TS", age:10 },],};render(result);
只读属性
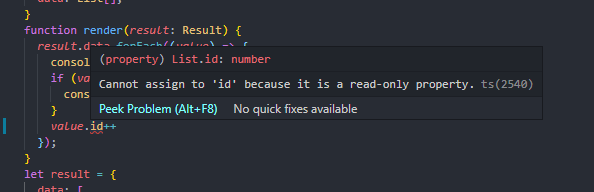
有时候我们希望对象中的一些字段只能在创建的时候被赋值,那么可以用 readonly 定义只读属性
interface List {readonly id: number; // 只读属性name: string;// [x: string]: any;age?: number;}interface Result {data: List[];}function render(result: Result) {result.data.forEach((value) => {console.log(value.id, value.name); // 1 JS" 2 "TS"if (value.age) {console.log(value.age); // 10}value.id++; // 修改只读属性});}let result = {data: [{ id: 1, name: "JS", remark: "" },{ id: 2, name: "TS", age:10 },],};render(result);
可索引类型的接口
数字索引接口
声明一个数字索引类型的接口 表示用任意数字去索引 number Index都会得到一个 string
interface StringArray {[index: number]: string;}// 相当于声明了一个字符串类型的数组let chars: StringArray = ["A", "B"];
字符串索引接口
声明一个字符串索引类型的接口 表示用任意的字符串去索引 string Index 得到的结果都是 string
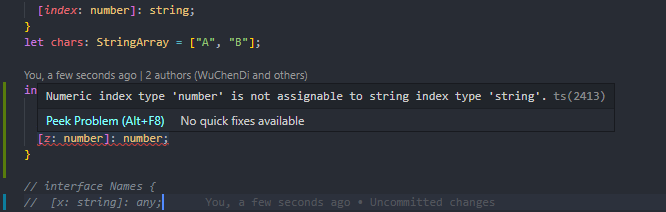
interface stringIndex {[x: string]: string;}// 这样声明后,就不能声明 number 类型的成员了,会报错interface stringIndex {[x: string]: string;y: number; // Property 'y' of type 'number' is not assignable to string index type 'string'.}
两种索引签名混用
注: 数字索引的返回值,一定要是字符串返回类型的子类型 这是因为JS会进行类型转换,将number转换成string,这样就能保证类型的兼容性
// 在上边的字符串索引接口stringIndex中,添加数字索引签名interface stringIndex {[x: string]: string;[z: number]: string;}// 如:将数组索引的返回值改成number// interface Names {// [x: string]: string;// // y: number;// [z: number]: number;// }interface Names {[x: string]: any;// y: number;[z: number]: number;}