内嵌类(InnetClass)是嵌套在一个类中的类。
外层类(OuterClass)包含内嵌类的那个类。
内嵌类与外层类存在逻辑上的所属关系。
8.3.1 成员类—-对象成员
特点:
内嵌类经过编译后产生的字节码文件名为:OuterOne$InnerOne.class
内嵌类可以使用访问控制符public、protected、private修饰
内嵌类可以访问外层类的成员。如果外层类成员与内嵌类的成员存在同名现象,则按最近优先原则处理
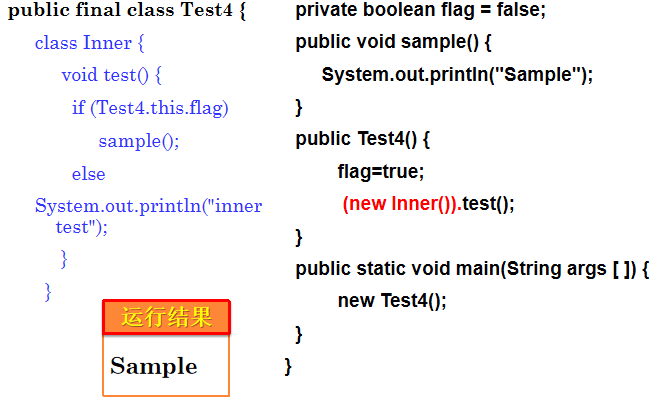
在内嵌类中,this指内嵌类的对象,要访问外层类的当前对象需加上外层类名作前缀,例如:以下内嵌类中用OuterOne.this表示访问外层类的this对象。
public class OuterOne {private int x=3;private int y=4;public void OuterMethod( ) {InnerOne ino=new InnerOne( );ino.innerMethod( );}public class InnerOne { //内嵌类private int z=5;int x=6;public void innerMethod() {内嵌类可以访问外部类的成员(包括私有成员)System.out.println("y is "+y);System.out.println("z is "+z);System.out.println("x ="+x);System.out.println("this.x="+this.x);System.out.println("OuterOne.this.x="+ OuterOne.this.x);}}} 内嵌类也是外部类的一员!在main方法中,要创建内嵌类的对象必须先创建外层类对象,然后通过外层类对象创建内嵌类对象。public static void main(String arg[]){OuterOne.InnerOne my=new OuterOne().new InnerOne();my.innerMethod();}
8.3.2 静态内嵌类—-类成员
静态内嵌类不需要通过外层类的对象来访问,静态内嵌类不能访问外层类的非静态成员。
public class Outertwo {private static int x=3;public static class Innertwo { //静态内嵌类public static void m1() {System.out.println("x is "+x); //静态方法}public void m2() { //实例方法System.out.println("x is "+x);}} //内嵌类结束public static void main(String arg[]) {Outertwo.Innertwo.m1(); //静态方法直接访问new Outertwo.Innertwo().m2(); //通过对象访问内嵌类的实例方法}}
8.3.3 方法中的内嵌类
public class OuterTwo {private int x=3;public void OuterMethod( int m ) {final int n=x+2;class InnerTwo { //方法内的内嵌类private int y=5;public void innerMethod() {System.out.println("y is "+y);System.out.println("n is "+n); //只能访问外部方法中的常量(带final修饰)System.out.println("x is "+x); //可以访问外层类的成员}} //内嵌类结束InnerTwo in2=new InnerTwo();in2.innerMethod();}public static void main(String arg[]) {OuterTwo my=new OuterTwo();my.OuterMethod(8);}}运行结果:y is 5n is 5x is 3
本程序在静态内嵌类Innertwo中定义了两个方法,方法m1( )为静态方法,在外部要调用该方法直接通过类名访问,例如:Outertwo.Innertwo.m1();
而方法m2( )为实例方法,必须通过创建内嵌类的对象来访问,但是由于这里内嵌类是静态类,所以可以通过外层类名直接访问内嵌类的构造方法,例如:new Outertwo.Inertwo().m2(); 
8.3.4 匿名内嵌类
Java允许创建对象的同时定义类的实现,但是未规定类名,Java将其定义为匿名内嵌类。
interface sample {void testMethod();}public class AnonymousInner {void OuterMethod() {new sample() {public void testMethod( ) {System.out.println("just test");}} .testMethod(); //调用内嵌类中定义的方法}public static void main(String arg[]) {AnonymousInner my=new AnonymousInner();my.OuterMethod();}}
【说明】上面程序中,第7行由接口直接创建对象似乎是不可能的,但要注意后面跟着的大招号代码中给出了接口的具体实现。实际上这里的意思是创建一个实现sample接口的匿名内嵌类对象。
【注意】编译时,匿名内嵌类同样会产生一个对应的字节码文件,其特点是以编号命名
—-字节码文件为AnonymousInner$1.class。如果有更多的匿名内嵌类将按递增序号命名