PPT讲义
博客:用PyTorch搭建卷积神经网络
原文地址
在PyTorch中神经网络的构建是通过torch.nn工具
在前馈神经网络已经介绍过autograd,而nn正是基于autograd来定义模型并求取其中的各种梯度
- nn.Module定义了网络的每一层
- forward(input)则用来计算网络的输出

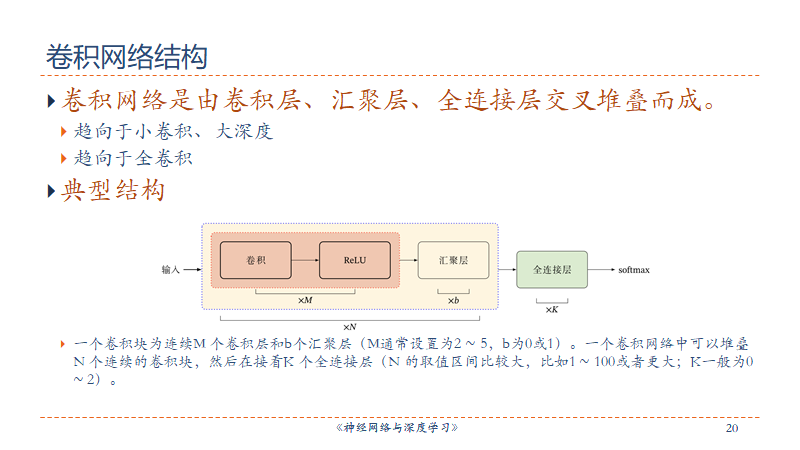
来看这样一个用来识别手写体数字的网络,一个典型的训练神经网络的步骤是:
- 1.定义一个包含一组带学习的参数的神经网络
- 2.将数据输入到神经网络中并进行前向传播
- 3.根据损失函数计算输出结果与目标值之间的差距
- 4.进行梯度反向传播到各个参数
5.更新网络参数,典型的更新方式是:weight = weight - learning_rater * gradient
Define the network
卷积核大小
什么是卷积核?
代码
import torchfrom torch.autograd import Variableimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fclass Net(nn.Module):def __init__(self):#使用super()方法调用基类的构造器,即nn.Module.__init__(self)super(Net,self).__init__()'''第1个卷积层1 input image channel, 6 output channel, 5x5 square convolution kernel1个图像通道,因为是灰度图,6个输出频道,应该指的是用6个5x5大小的卷积核(待确定)'''self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1,6,5)'''第2个卷积层6 input channel, 16 output channels, 5x5 square convolution kernel这个卷积层应该是连接上一个池化层,所以输入是6个然后使用16个5x5大小的卷积层'''self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6,16,5)#an affine operation: y = WX+bself.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5,120)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(85,10)def forward(self,x):'''x是网络的输入,然后将x前向传播,最后得到输出下面两句定义了两个2x2的池化层'''x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)),(2,2))#if the size is square you can only specify a single numberx = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)),2)x = x.view(-1,self.num_flat_features(x))x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))x = self.fc3(x)return xdef num_flat_features(self,x):size = x.size()[1:] #all dimensions except the batch dimensionnum_features = 1for s in size:num_features *= sreturn num_featuresnet = Net()print(net)
以上是定义了一个网络,并且定义了值得前向传播过程,可以进行各种Tensor可以进行的运算,而在梯度反向传播得时候,要用到上章介绍的autograd。
卷积运算
这是卷积核矩阵和输入矩阵中的感受野矩阵之间的内积,也就是两个向量之间的内积,如两个维向量
和
的内积为
那么torch.nn.Conv2d()是怎么运算的呢?先来看下它有哪些参数(把这些参数的作用搞清楚,就基本弄清了卷积层的具体工作方式):
- in_channels(int) : Number of channels in the input image.
- out_channels(int): Number of channels producted by the convolution.
- kernel_size(int or tuple): Size of the convolution. Default: 1.
- stride(int or tuple, optional): Zero-padding added to both sides of the input. Default: 0.
- dilation(int or tuple, optional): Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
- groups(int, optional): Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
- bias(bool, optional): If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True.
点击这里,PyTorch的详细文档
网络的输入用四元组来表示,输出表示为
。其中:
和
分别表示矩阵的高和宽
表示数据的batch dimension,即批处理的数据一批有多少个
表示输入数据的通道数,按上图中可以理解为输入该层的有几个矩阵
表示输出数据的通道数,可以理解为输出有多少个矩阵
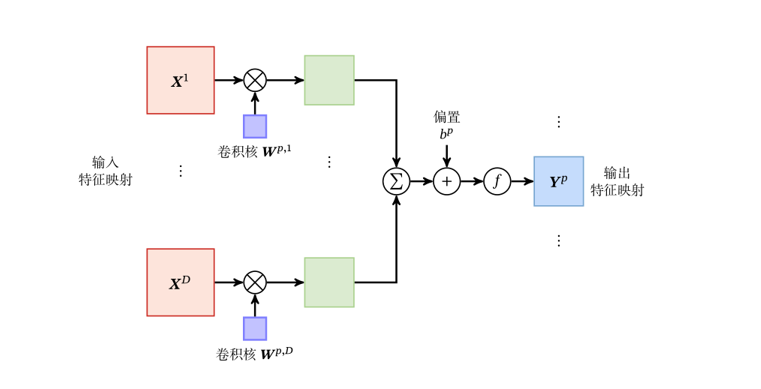
卷积层的输出满足这样的表达式:
现在只看其中一个数据,即为一个常数,代表当前数据是batch中的第几个数据,以上面定义的网络的第一个卷积层为例:
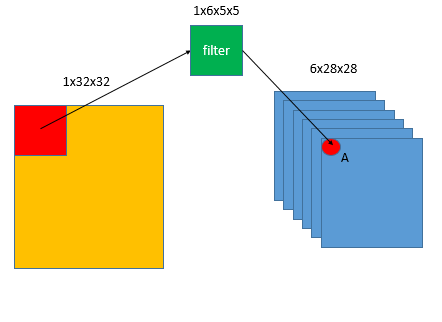
蓝色方框中的红点称为A元素,对这一层上面表达式的各个数值为:
:假设为一批数据中的第1个,即
:输出有6个通道,
,对A点
:输入通道,只有1个通道
:是计数器,对应着输入数据的每一个通道,这里只有一个
:偏置参数,维度和
一致
卷积核或者说过滤器是一个
的多维向量,
确定了其第一维,
确定了其第二维。对于输入向量
,
确定了其第一维。于是求和符号里就是两个向量的内积。当
大于1时,来看第二个卷积层:
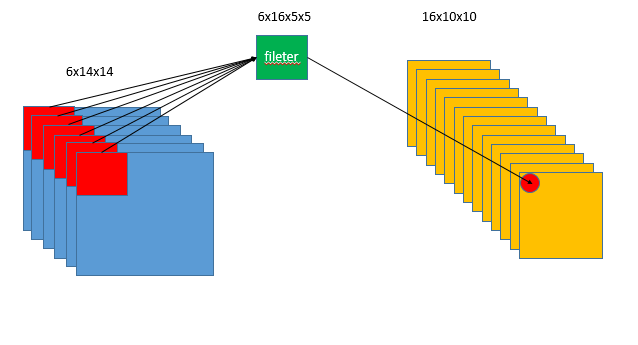
这时有6个取值,求和符号
中,
,以右侧红点元素为例:当
时是绿色
的向量和左边第一个红色
的向量做内积,然后
是绿色
的向量和第二个红色
的向量做内积,做了6次之后,把这6个内积的结果加和,再加上和第一个输出通道对应的
,就得到了右侧红点元素的值。
然后左侧红色方框即感受野再按步长移动,输出向量的尺寸是这样的(floor代表向下取整):
可以看到上面两个式子涉及到了torch.nn.Conv2d()中的4个参数,kernel_size和stride都好理解,分别是卷积核尺寸和移动步长。
零填充
在网络的早期层中,我们想要尽可能多地保留原始输入内容的信息,这样我们就能提取出那些低层的特征。比如说我们想要应用同样的卷积层,但又想让输出量维持为 32 x 32 x 3 。为做到这点,我们可以对这个层应用大小为 2 的零填充(zero padding)。零填充在输入内容的边界周围补充零。
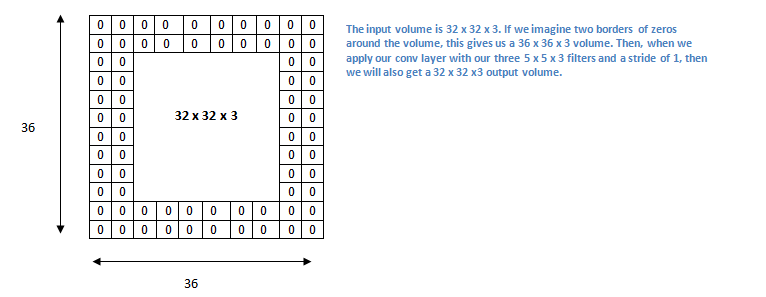
关于padding图片来自这里,这是一个很好的讲解卷积神经网络的文章,还有文字来自对这篇文章翻译的中文版。
dilation:对于这个参数,链接中的最后一个图是关于dilation的。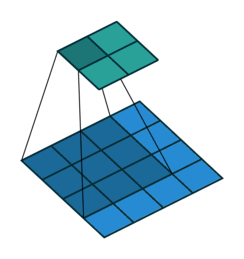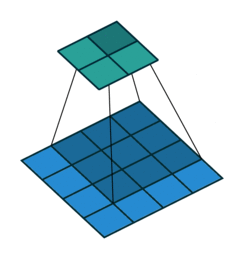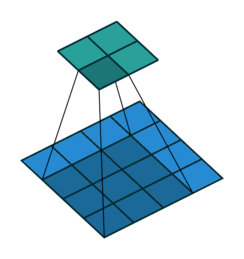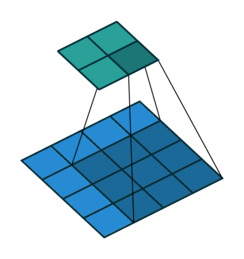
来自这个问题下贾扬清的回答,有几个说明卷积运算过程的图(其中KxK代表卷积核的size,其他符号和上文所用的一致):
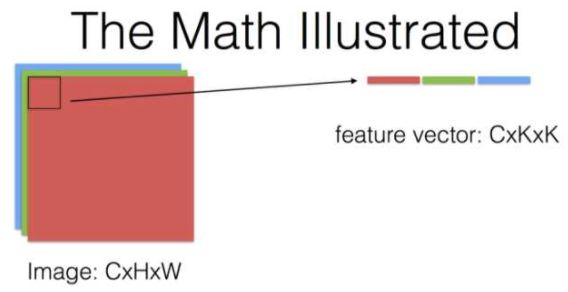
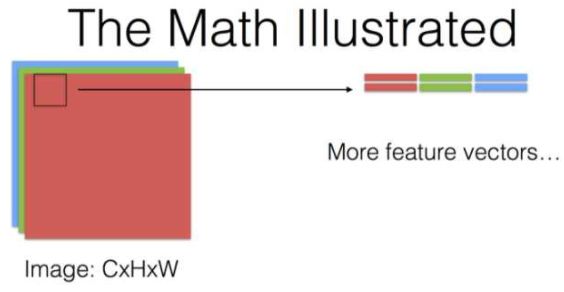
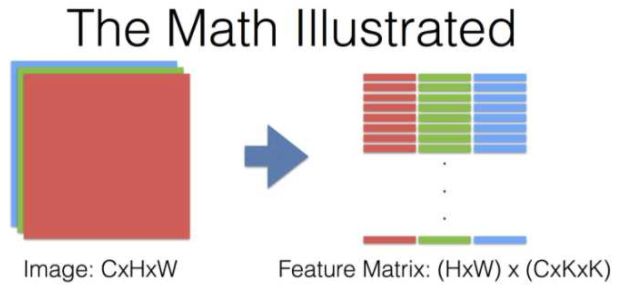
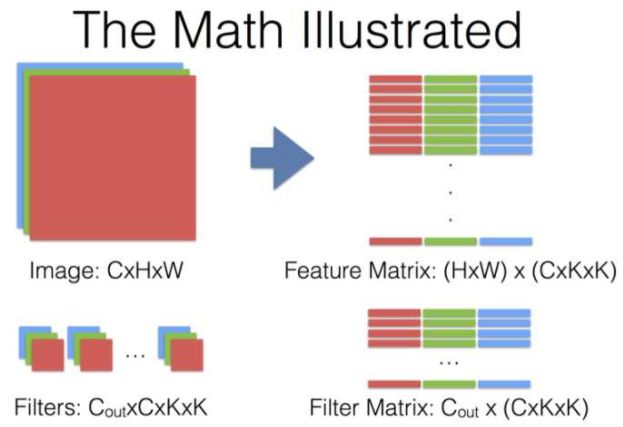
对于卷积神经网络每一层究竟做了什么,提取出什么特征,这里有个将神经网络可视化的视频
参数个数
对于卷积层来说,参数个数就是向量和
向量的元素个数和,比如对第二个卷积层来说,就是
可以通过:
net.parameters()
来获得网络的参数。
params = list(net.parameters())print(len(params))for i in range(len(params)):print(params[i].size())+++++++++10torch.Size([6,1,5,5])torch.Size([6])torch.Size([16,6,5,5])torch.Size([16])torch.Size([120,400])torch.Size([120])torch.Size([84,120])torch.Size([84])troch.Size([10,84])torch.Size([10])++++++++++
网络的输入与输出
下面来给网络一个输入:
input = Variable(torch.randn(1,1,32,32))out = net(input)print(out)+++++++Variable containing:0.0246 0.0021 -0.0395 -0.0225 -0.0905 -0.0091 -0.0931 -0.0234 -0.1005 0.0795[torch.FloatTensor of size 1x10]+++++++
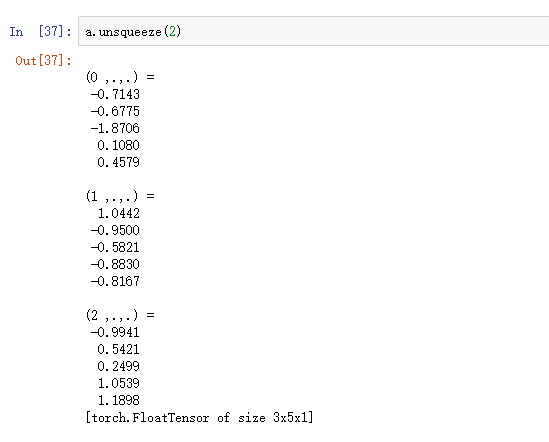
在前面写卷积运算的时候也提到过,实际上网络的输入向量,第一个维度是批处理数据的个数。在torch.nn方法中必须有这一维的数值,即输入的向量必须是
这样的四维向量。而如果数据没这第一个维度,也就是并不是一批数据,那么可以通过:
torch.Tensor.unsqueeze(0)
损失函数
如何定义损失函数也很简单的:
output = net(input)target = Variable(torch.arange(1,11))#a dumy target, for examplecriterion = nn.MSELoss() #mean-squared error between the input and targetloss = criterion(output,target)print(loss)
torch.nn中还有很多损失函数可以使用,点击这里查看
梯度的反向传播
这就要用到autograd.Variable()中的backward()功能。在学习autograd.Variable时也发现,如果Variable.grad已经存储有梯度值,那么当再次写出backward()命令进行梯度回传时,计算出的值将与各个创建变量(graph leaves)的grad已有的值累加。所以对于神经网络,要使用net.zero_grad()清楚掉原有的梯度值。
net.zero_grad() #zeroes the gradient buffers of all parametersprint('conv1.bias.grad before backward')print(net.conv1.bias.grad)loss.backward()print('conv1.bias.grad after backward')print(net.conv1.bias.grad)

如果原来已有梯度值,然后执行net.zero_grad(),梯度值就变为0,如果原来没有梯度值,那么变量x处的梯度x.grad = None
参数更新
使用torch.optim可以方便的定义参数更新算法:
import torch.optim as optim#create your optimizer,such as SGDoptimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr = 0.01)#lr is learning rate#in your training loop:optimizer.zero_grad() #zero the gradient buffersoutput = net(input)loss = criterion(output,target)loss.backward()optimizer.step() #Does the update
使用PyTorch搭建前馈神经网络对图片进行分类
一、数据集
数据集的来源,该数据集主要是10个种类的衣服,然后90%用作训练集,10%用作测试集。所有图像的大小都是(28*28)的灰度图像。数据集中的两个文件夹,每个都是.csv文件,该文件具有图像的id和相应的标签。
fashion-mnist-master.zip
在PyTorch的手册中,有关于用TensorBoard来训练数据的教程,链接。但是我是在Google Colab中写的代码,所以没有使用这种方式。
二、博客2
这篇博客讲的是使用PyTorch进行的分类。
读取展示图片
from skimage.io import imread import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline
创建验证集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
评估模型
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score from tqdm import tqdm
PyTorch的相关库
import torch from torch.autograd import Variable from torch.nn import Linear, ReLU, CrossEntropyLoss, Sequential, Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Module, Softmax, BatchNorm2d, Dropout from torch.optim import Adam, SGD
- 加载数据集现在,让我们加载数据集,包括训练,测试样本:```python#加载数据集train = pd.read_csv('train_LbELTWX/train.csv')test = pd.read_csv('test_ScVgIM0/test.csv')sample_submission = pd.read_csv('sample_submission_I5njJSF.csv')train.head()
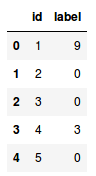
- 该训练文件包含每个图像的id及其对应的标签
- 另一方面,测试文件有id,我们必须预测它们对应的标签
- 样例提交文件将告诉我们预测的格式
我们将一个接一个地读取所有图像,并将它们堆叠成一个数组。我们还将图像的像素值除以255,使图像的像素值在[0,1]范围内。这一步有助于优化模型的性能,让我们来加载图像:
#加载训练图像train_img = []for img_name in tqdm(train['id']):#定义图像路径image_path = 'train_LbELtWX/train/' + str(img_name) + '.png'#读取图片img = imread(image_path, as_grey=True)#归一化像素值img /= 255.0#转换为浮点数img = img.astype('float32')#添加到列表train_img.append(img)#转换为numpy数组train_x = np.array(train_img)#定义目标train_y = train['label'].valuestrain_x.shape
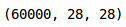
如你所见,我们在训练集中有60,000张大小(28,28)的图像。由于图象是灰度格式的,我们只有一个单一通道,因此形状为(28,28)。现在让我们研究数据和可视化一些图像:
#可视化图片i = 0plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))plt.subplot(221), plt.imshow(train_x[i], camp='gray')plt.subplot(222), plt.imshow(train_x[i+25], camp='gray')plt.subplot(223), plt.imshow(train_x[i+50], camp='gray')plt.subplot(224), plt.imshow(train_x[i+75], camp='gray')
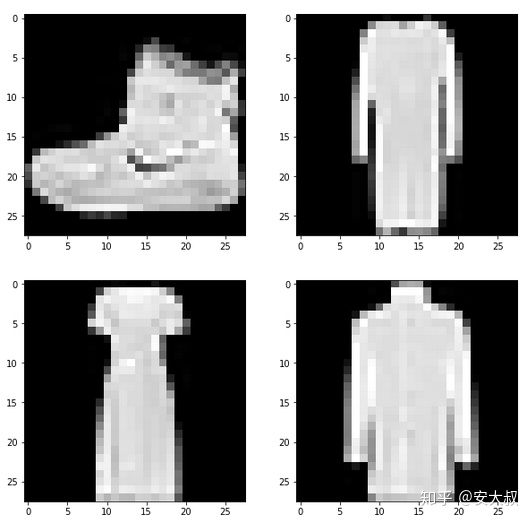

以下是来自数据集的一些示例。接下来,我们把图像分成训练集和验证集。
- 创建验证集并对图像进行预处理
#创建验证集train_x, val_x, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(train_x,train_y,test_size = 0.1)(train_x.shape, tain_y.shape), (val_x.shape, val_y.shape)
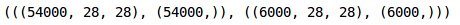
我们在验证集中保留了10%的数据,在训练集中保留了10%的数据。接下来将图片和目标转成torch格式: ```python转换为torch张量
train_x = train_x.reshape(54000, 1, 28, 28) train_x = torch.from_numpy(train_x)
转换为torch张量
train_y = train_y.astype(int); train_y = torch.from_numpy(train_y)
训练集形状
train_x.shape, train_y.shape
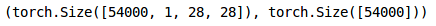<br />同样,我们将转换验证图像:```python#转换为torch张量val_x = val_x.reshape(6000, 1, 28, 28)val_x = torch.from_numpy(val_x)#转换为torch张量val_y = val_y.astype(int);val_y = torch.from_numpy(val_y)#验证集形状val_x.shape, val_y.shape
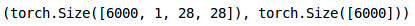
我们的数据现在已经准备好了。最后,我们要创建CNN模型。
- 使用PyTorch实现CNNS
我们将使用一个非常简单的CNN结构,只有两个卷积层来提取图像的特征。然后,我们将使用一个完全连接的Dense层将这些特征分类到各自的类别中,让我们定义一下架构:
class Net(Module):def__init__(self):super(Net,self).__init__()self.cnn_layers = Sequential(#define 2D convolution layersConv2d(1, 4, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),BatchNorm2d(4),ReLU(inplace=True),MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),#define another 2d convolution layerConv2d(4, 4, kernel_size_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),BatchNorm2d(4),ReLU(inplace=True),MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),)self.linear_layers = Sequential(Linear(4 * 7 * 7, 10))#forward propogationdef forward(self, x):x = self.cnn_layers(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.liear_layers(x)return x'''We call the model defined now, and then define the optimizer and the loss function of the module'''#define the modulemodule = Net()#define a optimizeroptimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.07)#define the loss functioncriterion = CrossEntropyLoss()#check for the availability of the GPUif torch.cuda.is_available():model = model.cuda()criterion = criterion.cuda()print(model)
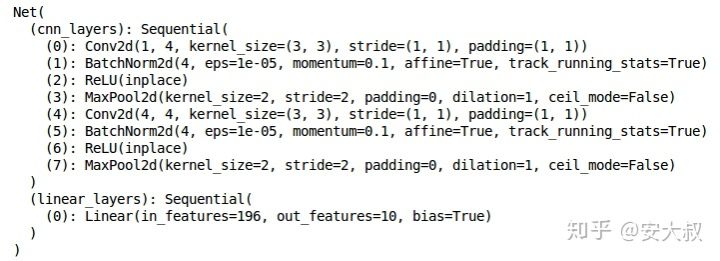
这是模型的架构,我们有两个卷积层和一个线性层。接下来,我们将定义一个函数来训练模型:
def train(epoch):model.train()tr_loss = 0#acquisition the training datasetx_train, y_trian = Variable(train_x), Variable(train_y)#acqusition the validating datasetx_val, y_val = Variabel(val_x), Variable(val_y)#transform the variable into GPU formatif torch.cuda.is_availabel():x_train = x_train.cuda()y_train = y_train.cuda()x_val = x_val.cuda()y_val = y_val.cuda()#clear the gradientoptimizer.zero_grad()#predict the training and validating datasetoutput_train = model(x_train)output_val = model(x_val)#calculate the loss of training and validating datasetloss_train = criterion(output_train, y_train)loss_val = criterion(output_val, y_val)train_losses.append(loss_train)val_losses.append(loss_val)#update the weightloss_train.backward()optimizer.step()tr_loss = lss_train.item()if epoch%2 == 0:#print the loss of validating datasetprint('Epoch:',epoch+1,'\t','loss:',loss_val)
最后,我们将对模型进行25个epoch的训练,并存储训练和验证损失:
#define the times of trainingn_epochs = 25#store the loss of training with empty listtrain_losses = []#store the loss of validating with empty listval_losses = []#train the modulefor epoch in range(n_epochs):train(epoch)
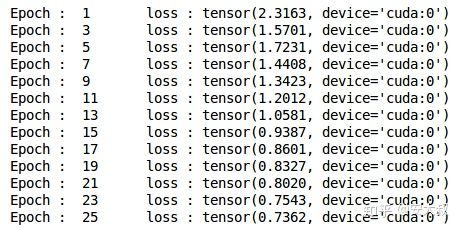
可以看出,随着epoch的增加,验证损失逐渐减小,让我们通过绘图来可视化训练和验证的损失:
#drwa the curve of the lossplt.plot(train_losses, label='Training loss')plt.plot(val_losses, label='Validation loss')plt.legend()plt.show()
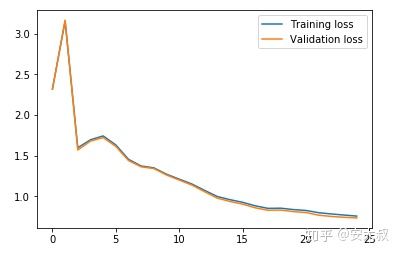
我们可以清楚地看到,训练和验证损失是同步的,这是一个好迹象,因为模型在验证集上进行了很好的泛化。让我们在训练和验证集上检查模型的准确性: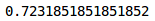
#prediction of the training datasetwith torch.no_grad():output = model(train_x.cuda())softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()prob = list(softmax.numpy())predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)#the accuracy of training datasetaccuracy_score(train_y,predictions)
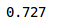
训练集的准确率约为72%,相当不错。让我们来检查验证集的准确性:
# prediction of validation datasetwith torch.no_grad():output = model(val_x.cuda())softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()prob = list(softmax.numpy())predictions = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)#the accuracy of validation datasetaccuracy_score(val_y, predictions)
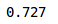
正如我们看到的损失,准确度也是同步的,我们在验证集得到了72%的准确度。
- 为验证集生成预测
最后为测试机生成预测。我们将加载测试集中的所有图像,执行与训练集相同的预处理步骤,最后生成预测。所以,让我们开始加载测试图像:
#load the training imagestest_img = []for img_name in tqdm(test['id']):#define the path of imagesimage_path = 'test_ScVgIM0/test/' + str(img_name) + '.png'#read the pictureimg = imread(image_path, as_gray=True)#normalize the pixelimg /= 255.0#transform the dtype of image into floatimg = img.astype('float32')#add the image to listtest_img.append(img)#transform the "test_img" into numpy arrsytest_x = np.array(test_img)test_x.shape
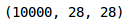
现在,我们将对这些图像进行预处理步骤,类似于我们之前对训练图像所做的:
#transform the "test_x" into torch formattest_x = test_x.reshape(10000, 1, 28, 28)test_x = torch.from_numpy(test_x)test_x.shape
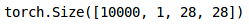
最后,我们将生成对测试集的预测:
#generate the prediction of training datasetwith torch.no_grad():output = model(test_x.cuda())softmax = torch.exp(output).cpu()prob = list(softmax.numpy())predicitons = np.argmax(prob, axis=1)
用预测替换样本提交文件中的标签,最后保存文件并提交到排行榜
#replace the label of sample submission file with predictionsample_submission['label'] = predictionssample_submission.head()
#save the filesample_submission.to_csv('submission.csv',index=False)
你将在当前目录中看到一个名为submission.csv的文件。你只需要把它上传到问题页面的解决方案检查器上,它就会生成分数,点击链接。我们的CNN模型在测试集上给出了大约71%的准确率,这与我们在上一篇文章中使用简单的神经网络得到的65%的准确率相比是一个很大的进步。
- 结尾
在这篇文章中,我们研究了CNNs是如何从图像中提取特征的。他们帮助我们将之前的神经网络模型的准确率从65%提高到71%,这是一个重大的进步。你可以尝试使用CNN模型的超参数,并尝试进一步提高准确性。要调优的超参数可以是卷积层的数量、每个卷积层的滤波器数量、epoch的数量、全连接层的数量、每个全连接层的隐藏单元的数量等。