前面介绍了Netty的线程模型及基本用法,今天我们以一个简单的例子,深入了解Netty的启动原理及主从Reactor线程模型的底层实现,以下是简单的Netty服务端程序
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 创建两个线程组bossGroup和workerGroup, 含有的子线程NioEventLoop的个数默认为cpu核数的两倍// bossGroup只是处理连接请求 ,真正的和客户端业务处理,会交给workerGroup完成EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8);try {// 创建服务器端的启动对象ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();// 使用链式编程来配置参数bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //设置两个线程组// 使用NioServerSocketChannel作为服务器的通道实现.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)// 初始化服务器连接队列大小,服务端处理客户端连接请求是顺序处理的,所以同一时间只能处理一个客户端连接。// 多个客户端同时来的时候,服务端将不能处理的客户端连接请求放在队列中等待处理.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//创建通道初始化对象,设置初始化参数,在 SocketChannel 建立起来之前执行@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//对workerGroup的SocketChannel设置处理器ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());}});System.out.println("netty server start。。");// 绑定一个端口并且同步, 生成了一个ChannelFuture异步对象,通过isDone()等方法可以判断异步事件的执行情况// 启动服务器(并绑定端口),bind是异步操作,sync方法是等待异步操作执行完毕ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(9000).sync();// 等待服务端监听端口关闭,closeFuture是异步操作// 通过sync方法同步等待通道关闭处理完毕,这里会阻塞等待通道关闭完成,内部调用的是Object的wait()方法cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}-------------------------------------------------------------public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {/*** 当客户端连接服务器完成就会触发该方法** @param ctx* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {System.out.println("客户端连接通道建立完成");}/*** 读取客户端发送的数据** @param ctx 上下文对象, 含有通道channel,管道pipeline* @param msg 就是客户端发送的数据* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {//Channel channel = ctx.channel();//ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline(); //本质是一个双向链接, 出站入站//将 msg 转成一个 ByteBuf,类似NIO 的 ByteBufferByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;System.out.println("收到客户端的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}/*** 数据读取完毕处理方法** @param ctx* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("HelloClient".getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);}/*** 处理异常, 一般是需要关闭通道** @param ctx* @param cause* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {ctx.close();}}
回顾一下Netty整体架构设计,看源码时要时刻想起这幅图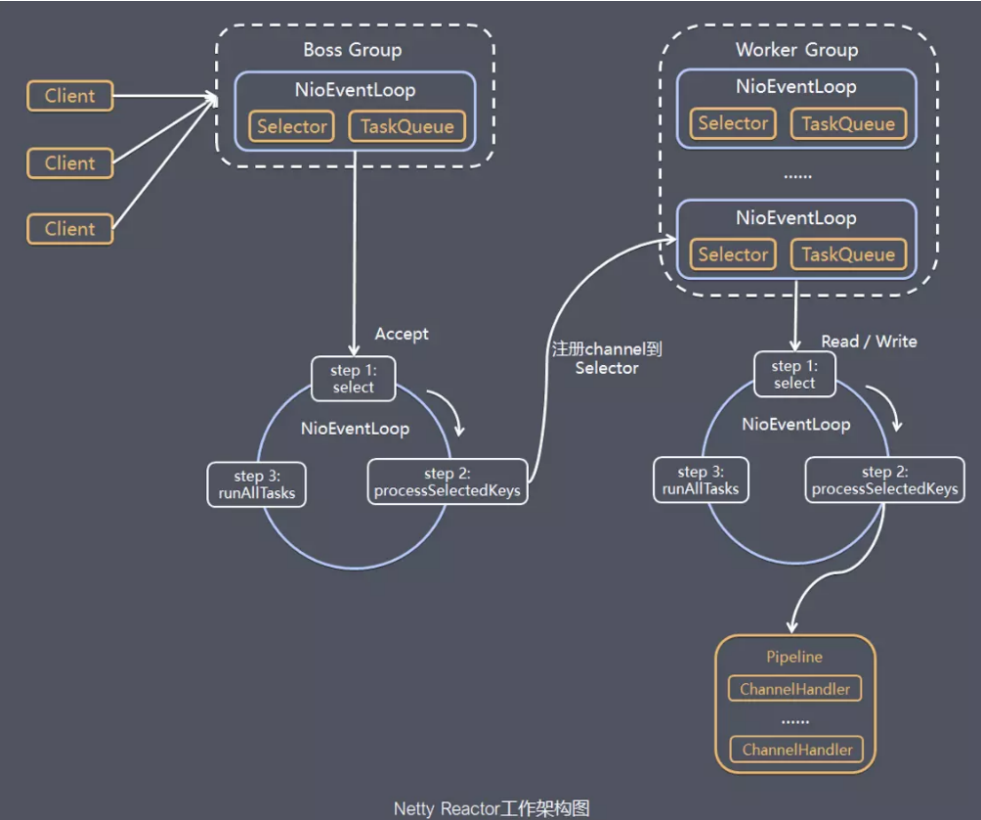
neety线程模型及基本用法可以参考《Netty线程模型》
创建NioEventLoopGroup
在启动 server 时,首先需要启动两个线程组 NioEventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);//若没有指定线程数量,默认是cpu核数的两倍EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
若没有指定 eventLoopGroup 的线程数,默认是CPU核数的两倍
//默认线程数是cpu核数两倍private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS =Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);}
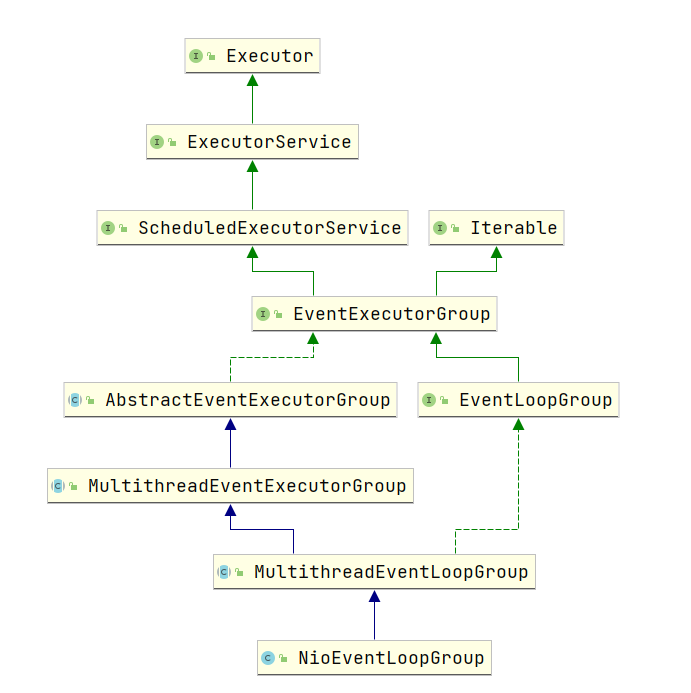
以下是 eventLoopGroup 的具体构造方法,创建了一个线程池 executor 及线程数组childern[],数组每个元素对应一个 NioEventLoop(创建的线程池executor后续用于给NioEventLoop的父类SingleThreadEventExecutor中executor属性赋值)
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args){this.terminatedChildren = new AtomicInteger();this.terminationFuture = new DefaultPromise(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);if (nThreads <= 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));} else {if (executor == null) {//传进来的executor参数默认为null,创建一个ThreadPerTaskExecutor类型的线程池executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(this.newDefaultThreadFactory());}//创建线程数组,大小为我们指定的线程数或默认线程数this.children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];int j;for(int i = 0; i < nThreads; ++i) {boolean success = false;boolean var18 = false;try {var18 = true;//创建nThreads个NioEventLoop赋值给数组//并且传入了上面创建的线程池,后续用于给父类SingleThreadEventExecutor的executor属性赋值this.children[i] = this.newChild((Executor)executor, args);success = true;var18 = false;} catch (Exception var19) {throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", var19);} finally {//分支逻辑......}if (!success) {//分支逻辑......}}this.chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(this.children);FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {if (MultithreadEventExecutorGroup.this.terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == MultithreadEventExecutorGroup.this.children.length) {MultithreadEventExecutorGroup.this.terminationFuture.setSuccess((Object)null);}}};EventExecutor[] var24 = this.children;j = var24.length;for(int var26 = 0; var26 < j; ++var26) {EventExecutor e = var24[var26];e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);}Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet(this.children.length);Collections.addAll(childrenSet, this.children);this.readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);}}
创建NioEventLoop
调用NioEventLoopGroup的newChild()方法创建NioEventLoop,其构造方法会创建TaskQueue,并调用JDK中NIO底层代码,创建了多路复用器Selector(对应了上面的架构图,是不是有点感觉了?)
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider)args[0], ((SelectStrategyFactory)args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler)args[2]);}---------------------------------------------NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider, SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {//调用父类的构造方法会创建我们的TaskQueue,是一个LinkedBlockingQueuesuper(parent, executor, false, DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_TASKS, rejectedExecutionHandler);if (selectorProvider == null) {throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider");} else if (strategy == null) {throw new NullPointerException("selectStrategy");} else {this.provider = selectorProvider;//调用NIO底层的openSelector()方法,创建多路复用器NioEventLoop.SelectorTuple selectorTuple = this.openSelector();this.selector = selectorTuple.selector;this.unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;this.selectStrategy = strategy;}}
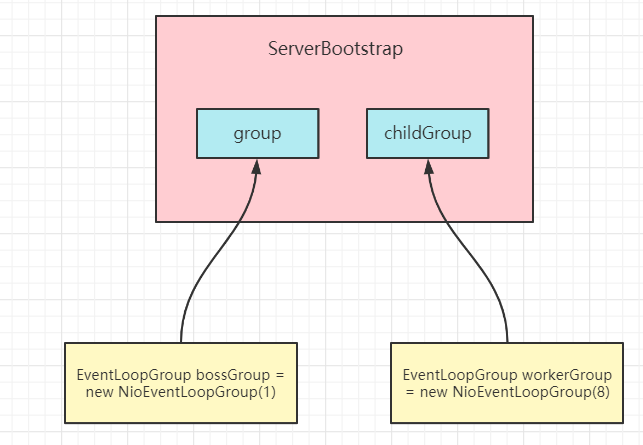
创建服务端启动对象
创建服务端启动对象ServerBootstrap,通过链式编程为ServerBootstrap的各种属性赋值
group()
调用group()方法设置将bossGroup赋值给group属性,将workerGroup赋值给childGroup属性
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {super.group(parentGroup);if (childGroup == null) {throw new NullPointerException("childGroup");} else if (this.childGroup != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");} else {//将workerGroup赋值给childGroup属性this.childGroup = childGroup;return this;}}--------------------------------------public B group(EventLoopGroup group) {if (group == null) {throw new NullPointerException("group");} else if (this.group != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("group set already");} else {//将bossGroup赋值给group属性this.group = group;return this.self();}}
channel()
调用 channel() 方法,指定使用NioServerSocketChannel(对NIO中的ServerSocketChannel进行了封装)作为服务器的通道实现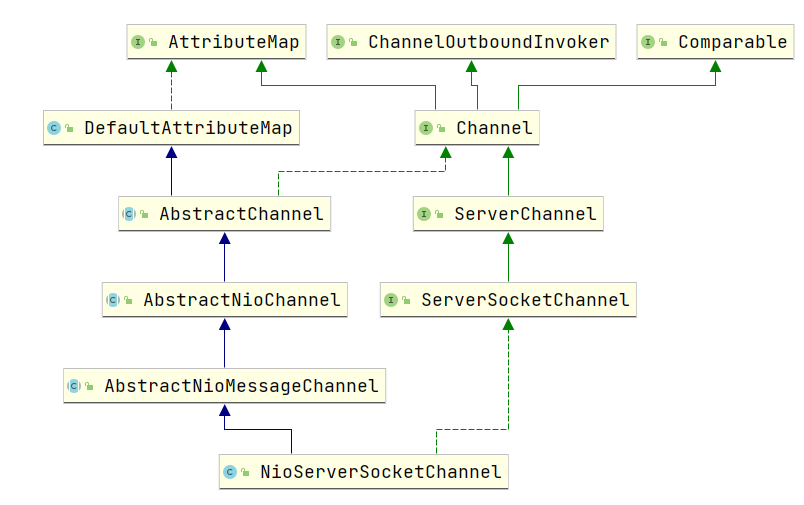
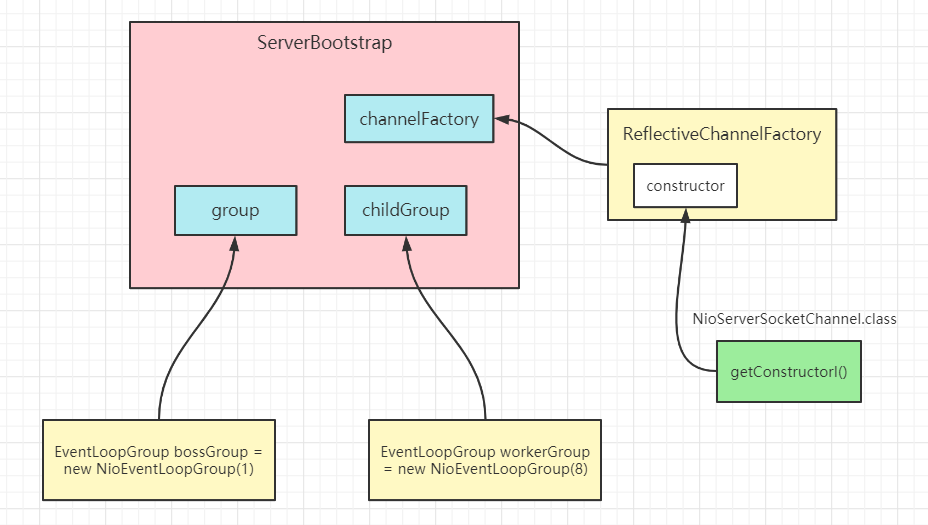
创建channelFactory,通过反射获取NioServerSocketChannel的构造方法(空构造方法),复制给constructor属性,后续通过该构造方法创建NioServerSocketChannel
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {if (channelClass == null) {throw new NullPointerException("channelClass");} else {//创建ReflectiveChannelFactory对象,赋值给当前服务器启动对象ServerBootstrapreturn this.channelFactory((io.netty.channel.ChannelFactory)(new ReflectiveChannelFactory(channelClass)));}}---------------------------------------public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class<? extends T> clazz) {ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(clazz, "clazz");try {//通过反射获取NioSocketChannel的空构造方法,赋值给ReflectiveChannelFactory的constructor属性this.constructor = clazz.getConstructor();} catch (NoSuchMethodException var3) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Class " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) + " does not have a public non-arg constructor", var3);}}
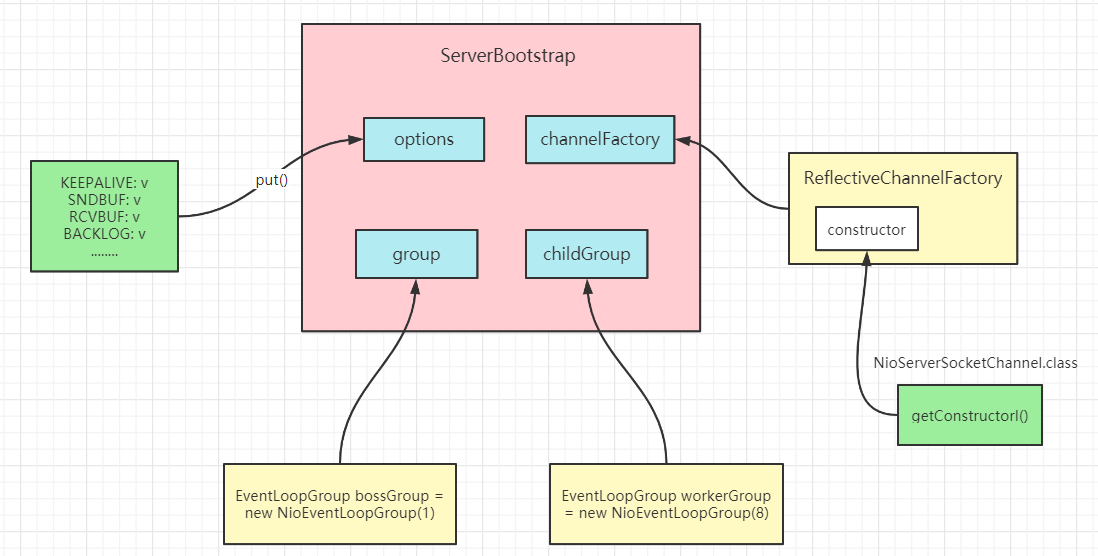
option()
设置TCP相关参数(KEEPALIVE、RCVBUF、SNDBUF、TIMEOUT…….),把配置的参数及对应的值放到一个Map中
public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value) {if (option == null) {throw new NullPointerException("option");} else {if (value == null) {synchronized(this.options) {this.options.remove(option);}} else {synchronized(this.options) {//将配置的参数放入到Map中this.options.put(option, value);}}return this.self();}}
childHandler()
创建通道初始化对象,重写initChannel()方法(客户端连接服务端成功会回调该方法,往pipeline中添加我们自定义的Handler)
//创建通道初始化对象,设置初始化参数,在 SocketChannel 建立起来之前执行childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//对workerGroup的SocketChannel设置处理器ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());}});---------------------------public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {if (childHandler == null) {throw new NullPointerException("childHandler");} else {//为childHandler赋值this.childHandler = childHandler;return this;}}
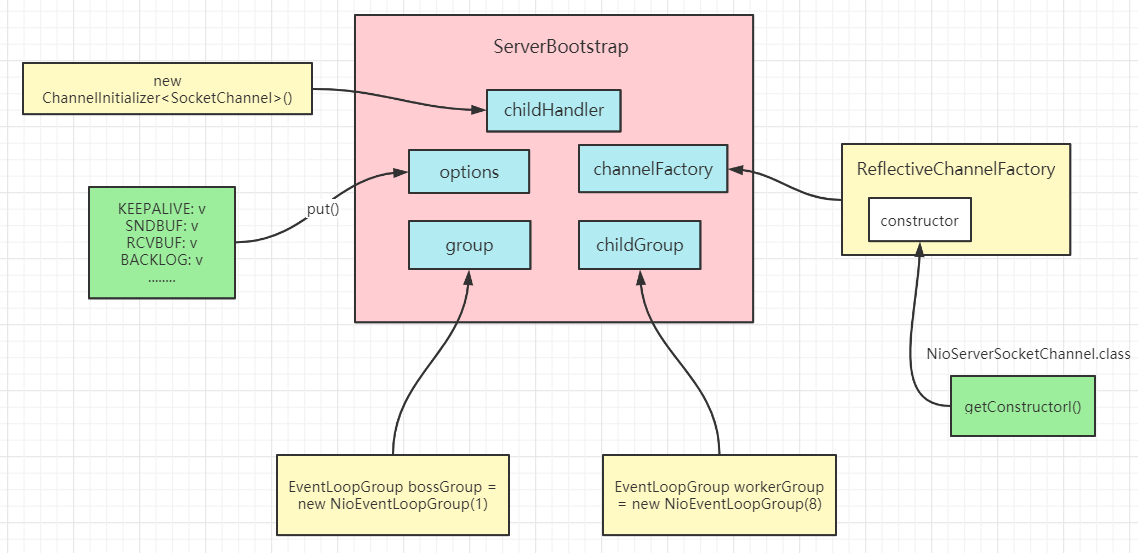
此时服务端启动对象基本构建完毕,记住这些属性,后续在调用bind()方法中都会用到

