所谓心跳,即在 TCP 长连接中,客户端和服务器之间定期发送的一种特殊的数据包,通知对方自己还在线,以确保 TCP 连接的有效性,如果服务端一段时间内没有收到客户端信息则视客户端断开。
IdleStateHandler
在 Netty 中,为我们提供了一个 IdleStateHandler,该 Handler 是实现心跳机制的关键,我们来看一看其构造函数(主要做的是为属性赋值)
public IdleStateHandler(int readerIdleTimeSeconds, int writerIdleTimeSeconds, int allIdleTimeSeconds) {this((long)readerIdleTimeSeconds, (long)writerIdleTimeSeconds, (long)allIdleTimeSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}--------------------------------------public IdleStateHandler(boolean observeOutput, long readerIdleTime, long writerIdleTime, long allIdleTime, TimeUnit unit) {this.writeListener = new ChannelFutureListener() {public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {IdleStateHandler.this.lastWriteTime = IdleStateHandler.this.ticksInNanos();IdleStateHandler.this.firstWriterIdleEvent = IdleStateHandler.this.firstAllIdleEvent = true;}};this.firstReaderIdleEvent = true;this.firstWriterIdleEvent = true;this.firstAllIdleEvent = true;if (unit == null) {throw new NullPointerException("unit");} else {this.observeOutput = observeOutput;if (readerIdleTime <= 0L) {this.readerIdleTimeNanos = 0L;} else {//为readerIdleTimeNanos属性赋值为传进来的参数readerIdleTimethis.readerIdleTimeNanos = Math.max(unit.toNanos(readerIdleTime), MIN_TIMEOUT_NANOS);}if (writerIdleTime <= 0L) {this.writerIdleTimeNanos = 0L;} else {//为writerIdleTimeNanos属性赋值为传进来的参数writerIdleTimethis.writerIdleTimeNanos = Math.max(unit.toNanos(writerIdleTime), MIN_TIMEOUT_NANOS);}if (allIdleTime <= 0L) {this.allIdleTimeNanos = 0L;} else {//为allIdleTimeNanos属性赋值为传进来的参数allIdleTimethis.allIdleTimeNanos = Math.max(unit.toNanos(allIdleTime), MIN_TIMEOUT_NANOS);}}}
- readerIdleTime:读超时时间,即当在指定的时间间隔内没有从 Channel 读取到数据时, 会触发一个 READER_IDLE 的 IdleStateEvent 事件(主要用于检查服务端在该时间内有无收到数据)
- writerIdleTime:写超时,即当在指定的时间间隔内没有数据写入到 Channel 时, 会触发一个 WRITER_IDLE 的 IdleStateEvent 事件(主要用于检查客户端在该时间内有无向服务端发送数据)
- allIdleTime:读/写超时,即当在指定的时间间隔内没有读或写操作时,会触发一个 ALL_IDLE 的 IdleStateEvent 事件
下面我们以一个简单的例子实现心跳检测机制
客户端
客户端定时向服务端发送数据
public class HeartBeatClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());pipeline.addLast(new HeartBeatClientHandler());}});System.out.println("netty client start。。");Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 9000).sync().channel();String text = "Heartbeat Packet";Random random = new Random();//定时向服务端发送数据while (channel.isActive()) {int num = random.nextInt(8);Thread.sleep(num * 1000);channel.writeAndFlush(text);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}}-------------------------------------public class HeartBeatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {@Overrideprotected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {System.out.println(" client received :" + msg);if (msg != null && msg.equals("idle close")) {System.out.println(" 服务端关闭连接,客户端也关闭");ctx.channel().closeFuture();}}}
服务端
添加两个Handler,一个是 dleStateHandler,设置对应的超时时间;一个是我们自己定义的Handler,处理超时逻辑
public class HeartBeatServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();bootstrap.group(boss, worker).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());//IdleStateHandler的readerIdleTime参数指定超过3秒还没收到客户端的连接,//会触发IdleStateEvent事件并且交给下一个handler处理,下一个handler必须//实现userEventTriggered方法处理对应事件pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));pipeline.addLast(new HeartBeatServerHandler());}});System.out.println("netty server start。。");ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(9000).sync();future.channel().closeFuture().sync();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {worker.shutdownGracefully();boss.shutdownGracefully();}}}
HeartBeatServerHandler() ,重写 userEventTriggered() 实现超时逻辑
public class HeartBeatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {int readIdleTimes = 0;@Overridepublic void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {//获取超时事件IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;String eventType = null;switch (event.state()) {//如果是读超时事件case READER_IDLE:eventType = "读空闲";readIdleTimes++; // 读空闲的计数加1break;//如果是写超时事件case WRITER_IDLE:eventType = "写空闲";// 不处理break;case ALL_IDLE:eventType = "读写空闲";// 不处理break;}System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "超时事件:" + eventType);if (readIdleTimes > 3) {System.out.println(" [server]读空闲超过3次,关闭连接,释放更多资源");ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("idle close");ctx.channel().close();}}@Overrideprotected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String s) throws Exception {System.out.println(" ====== > [server] message received : " + s);if ("Heartbeat Packet".equals(s)) {ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("ok");} else {System.out.println(" 其他信息处理 ... ");}}@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {System.err.println("=== " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " is active ===");}}
管道激活
当客户端连接服务端后,服务端会触发 Handler 中的 channelActive() 方法
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {this.initialize(ctx);super.channelActive(ctx);}
我们来看一看这个initialize() 方法干了什么
private void initialize(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {switch(this.state) {case 1:case 2:return;default:this.state = 1;this.initOutputChanged(ctx);this.lastReadTime = this.lastWriteTime = this.ticksInNanos();//创建定时任务检查管道中是否有数据读取if (this.readerIdleTimeNanos > 0L) {this.readerIdleTimeout = this.schedule(ctx, new IdleStateHandler.ReaderIdleTimeoutTask(ctx), this.readerIdleTimeNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);}//创建定时任务检查是否往管道中写入数据if (this.writerIdleTimeNanos > 0L) {this.writerIdleTimeout = this.schedule(ctx, new IdleStateHandler.WriterIdleTimeoutTask(ctx), this.writerIdleTimeNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);}if (this.allIdleTimeNanos > 0L) {this.allIdleTimeout = this.schedule(ctx, new IdleStateHandler.AllIdleTimeoutTask(ctx), this.allIdleTimeNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);}}}
可以看到,该方法就是创建一些定时任务放入到 scheduledTaskQueue 中,其作用无非就是定时检查客户端有没有定时往服务端发送心跳数据。
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(final ScheduledFutureTask<V> task) {//如果当前线程是NioEventLoop所绑定的线程if (this.inEventLoop()) {//直接将定时任务放入到scheduledTaskQueuethis.scheduledTaskQueue().add(task);//如果当前线程不是NioEventLoop所绑定的线程} else {this.execute(new Runnable() {//调用runAllTask()方法时会将该定时任务放入到scheduledTaskQueue()中public void run() {AbstractScheduledEventExecutor.this.scheduledTaskQueue().add(task);}});}return task;}
心跳检测
心跳检测主要就是靠上面创建的定时任务来实现的,我们来看一下该任务做了什么
private final class ReaderIdleTimeoutTask extends IdleStateHandler.AbstractIdleTask {protected void run(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {//将nextDelay赋值为我们设置的定时时间long nextDelay = readerIdleTimeNanos;if (!reading) {//nextDelay = nextDelay - (当前时间 - 上次从channel读取数据的时间)//即当前距离上次从channel中获取数据的时间nextDelay -= ticksInNanos() - lastReadTime;}//如果 nextDelay<0,即在指定时间类没有收到数据if (nextDelay <= 0L) {//重新设置定时任务,进行下一次检查IdleStateHandler.this.readerIdleTimeout = IdleStateHandler.this.schedule(ctx, this, IdleStateHandler.this.readerIdleTimeNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);boolean first = firstReaderIdleEvent;IdleStateHandler.this.firstReaderIdleEvent = false;try {//构造读超时事件IdleStateEvent event = IdleStateHandler.this.newIdleStateEvent(IdleState.READER_IDLE, first);//针对超时时间执行对应的逻辑IdleStateHandler.this.channelIdle(ctx, event);} catch (Throwable var6) {ctx.fireExceptionCaught(var6);}//在指定时间类收到数据} else {//重新设置一个定时任务,等待下一次检查IdleStateHandler.this.readerIdleTimeout = IdleStateHandler.this.schedule(ctx, this, nextDelay, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);}}}
- 如果在指定时间内收到了数据,重新设置一个定时任务进行下一次检查
- 如果在指定时间内没有收到数据,还是会设置同样的定时任务,同时会触发下一个 handler 的 userEventTriggered() 方法,即我们自己实现的超时逻辑
protected void channelIdle(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, IdleStateEvent evt) throws Exception {ctx.fireUserEventTriggered(evt);}
到这里应该知道 IdleStateHandler 的作用是什么了吧。不过有一点要注意的是,定时任务的实现是通过任务的嵌套调用实现的。而且在指定时间内收到消息后,下一次执行任务的时间并不是我们指定的时间,而是 指定时间 - 当前距离上次读取数据的时间,如果我们指定超时时间为 3s ,而 2s 前从channel中读取了数据,那么下次定时任务在1s 后执行
IdleStateHandler.this.readerIdleTimeout = IdleStateHandler.this.schedule(ctx, this, nextDelay, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
为什么要这么设计呢?我们看下面的图就知道了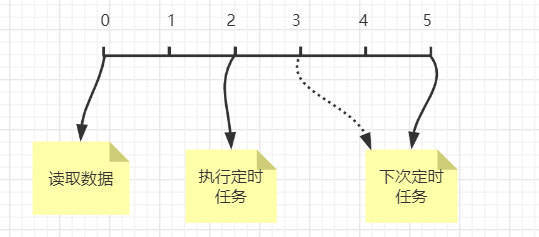
当执行定时任务时发现上次读取数据是 2s 前,如果下次定时任务继续是 3s 后执行,但是这期间再没有发送数据,那么此次检验距离上次发送数据是 5s 后,显然是超时了。所以定时任务是以读取到数据的时刻往后 3s 执行。

