描述
思路
单调栈的思路是如下图的例子
维持一个单调递增的栈,当新的元素(当前元素)大于栈顶元素的时候,就说明以栈顶元素为长的长方形,其宽度最多可以达到当前元素前一个位置。这样子看就可以理解下面的代码了。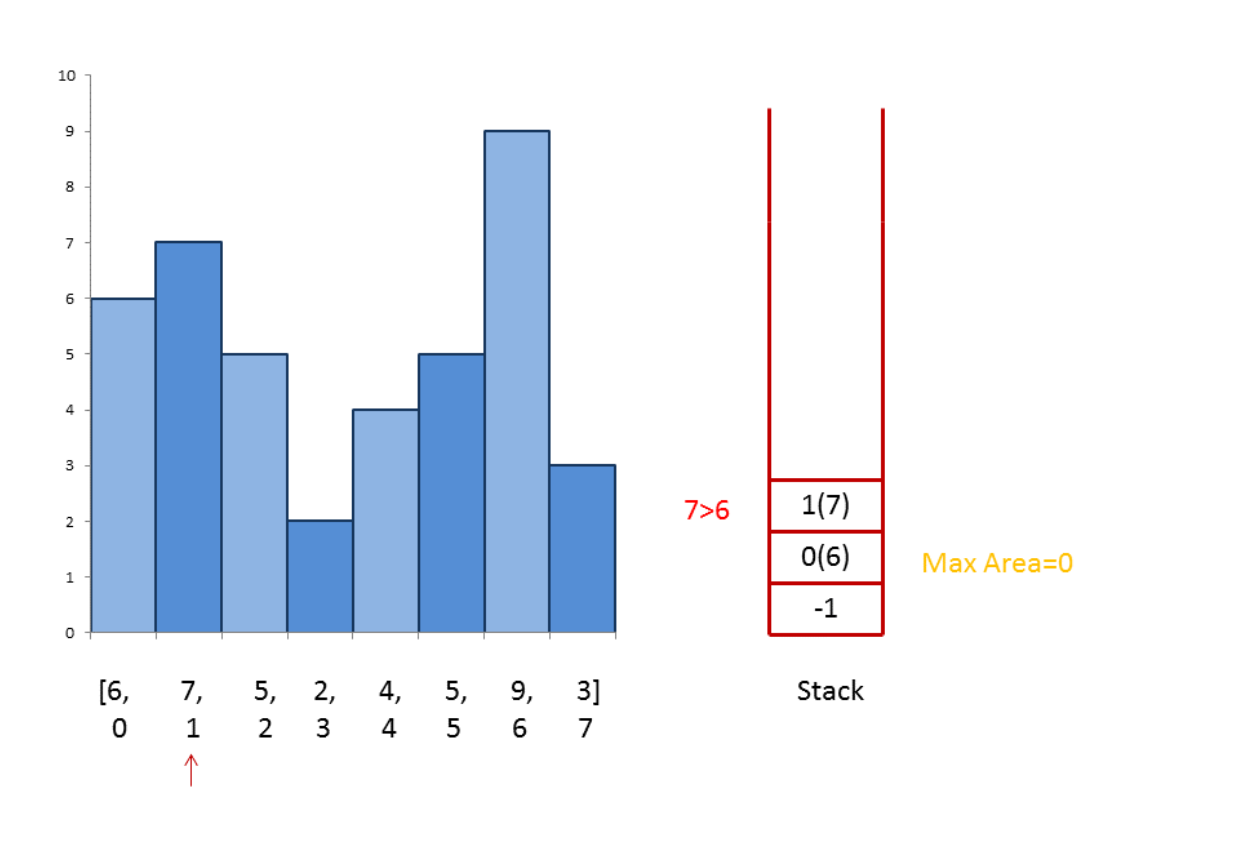
代码
class Solution{public:int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {stack<int> stk;stk.push(-1);int max_area = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {while (stk.top() != -1 and heights[stk.top()] >= heights[i]) {int current_height = heights[stk.top()];stk.pop();int current_width = i - stk.top() - 1;max_area = max(max_area, current_height * current_width);}stk.push(i);}while (stk.top() != -1) {int current_height = heights[stk.top()];stk.pop();int current_width = heights.size() - stk.top() - 1;max_area = max(max_area, current_height * current_width);}return max_area;}// int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights)// {// // use deque, store index of heights// // the elements of deque is monothly increasing, front is the smallest and back is the largest// list<pair<int, int>> m_deque;// int res = heights[0];// m_deque.push_back(make_pair(0,0));// for(int i = 1; i < heights.size(); i++)// {// res = max(res, heights[i]);// bool flag = true;// for(auto it : m_deque)// {// int index = it.first;// int pre_index = it.second;// res = max(res, min(heights[i], heights[index]) * (i - pre_index + 1));// if(heights[i] <= heights[index])// {// flag = false;// while(m_deque.back().first != index)// {// m_deque.pop_back();// }// auto back = m_deque.back();// m_deque.pop_back();// m_deque.push_back(make_pair(i, back.second));// break;// }// }// if(flag)// {// m_deque.push_back(make_pair(i, i));// }// }// return res;// }};

