零,题目描述
There are n cities connected by m flights. Each flight starts from city u and arrives at v with a price w.
Now given all the cities and flights, together with starting city src and the destination dst, your task is to find the cheapest price from src to dst with up to k stops. If there is no such route, output -1.
Example 1:
Input:
n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]]
src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph looks like this: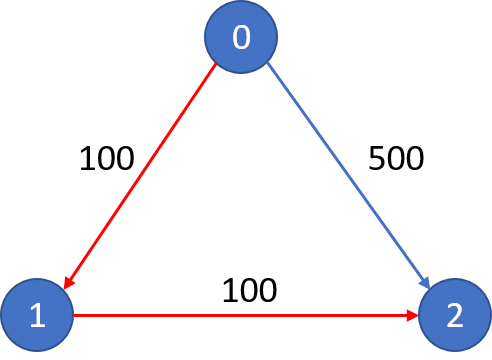
The cheapest price from city 0 to city 2 with at most 1 stop costs 200, as marked red in the picture.
Example 2:
Input:
n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]]
src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph looks like this: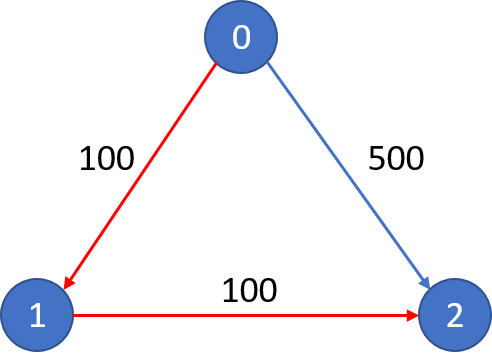
The cheapest price from city 0 to city 2 with at most 0 stop costs 500, as marked blue in the picture.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes
nwill be in range[1, 100], with nodes labeled from0ton`` - 1. - The size of
flightswill be in range[0, n * (n - 1) / 2]. - The format of each flight will be
(src, ``dst``, price). - The price of each flight will be in the range
[1, 10000]. kis in the range of[0, n - 1].- There will not be any duplicated flights or self cycles.
一,题目分析
(1)Dijkstra
单源最短路径问题,一上来的想法就是dijkstra算法,只不过这里dijkstra算法有限制条件。解决办法就是当发现当前累积长度大于K+1的时候放弃,寻找priority queue中的下一条edge。
dijkstra的常规做法是初始化一个优先队列priority queue,以目前已知的起点到终点的长度作为优先级依据。
然后不断地取出queue中的元素,relax每个点的目前已知的最近距离。
不同于常规的做法,我们把每一次relax过后更新的三元组 {当前花费cost,终点u,stops代表的(K - 步长 + 1)} 都加入队列
typedef tuple<int, int, int> ti;int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>> &flights, int src, int dst, int K){//首先建立一个图,类似于邻接矩阵,但是空间更少,不直接相接的节点没有分配空间vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> vp(n);for (const auto &f:flights)vp[f[0]].emplace_back(f[1], f[2]);priority_queue<ti, vector<ti>, greater<ti>> pq;pq.emplace(0, src, K + 1);while (!pq.empty()){//中间节点长为(K - stops + 1),目的地为u,当前的花费为costauto[cost, u, stops] = pq.top();pq.pop();//一旦找到目的地就返回,这个是dijkstra算法能够保证的,具体可以去看下CS61B中关于这点的证明if (u == dst)return cost;//只要步长大于K了,!stops表明stops不为0//stops = K - 步长 + 1; 当stops = 0即表示中间节点的数量有K + 1个了,此时忽略该路径,继续。if (!stops)continue;for (auto to:vp[u]){auto[v, w] = to;pq.emplace(cost + w, v, stops - 1);}}return -1;}
(2)DFS
其实也可以使用DFS做,在普通的单源最短路径算法中,比方说下面两幅图(来自CS61B spring 2019 lecture25)
DFS是有问题的,因为我们DFS访问过的节点就不再访问了,这会导致,如果后续的更新发现了到达节点F的更短的路径,而节点F已经访问过了,就不会再更新节点F的后续节点。
因此一个完善的做法是,标记已访问节点只在DFS路径中标记,回退(递归函数返回前)的时候要重新标记为未访问。
比如说下面的第二幅图。DFS(C)之后,从A到达节点B的距离被更新为了2,这时我们需要重新DFS(B),更新B的后续节点。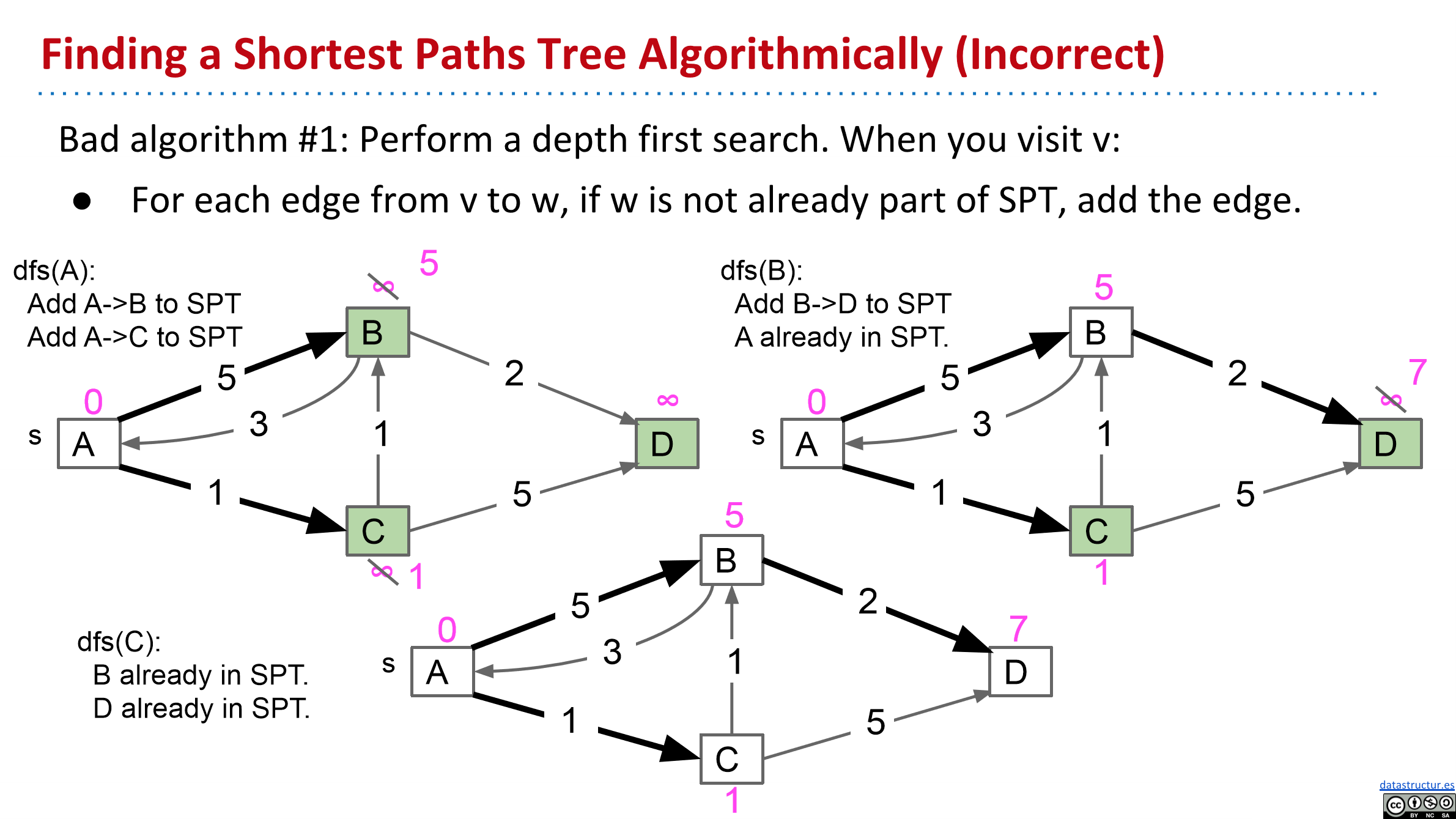
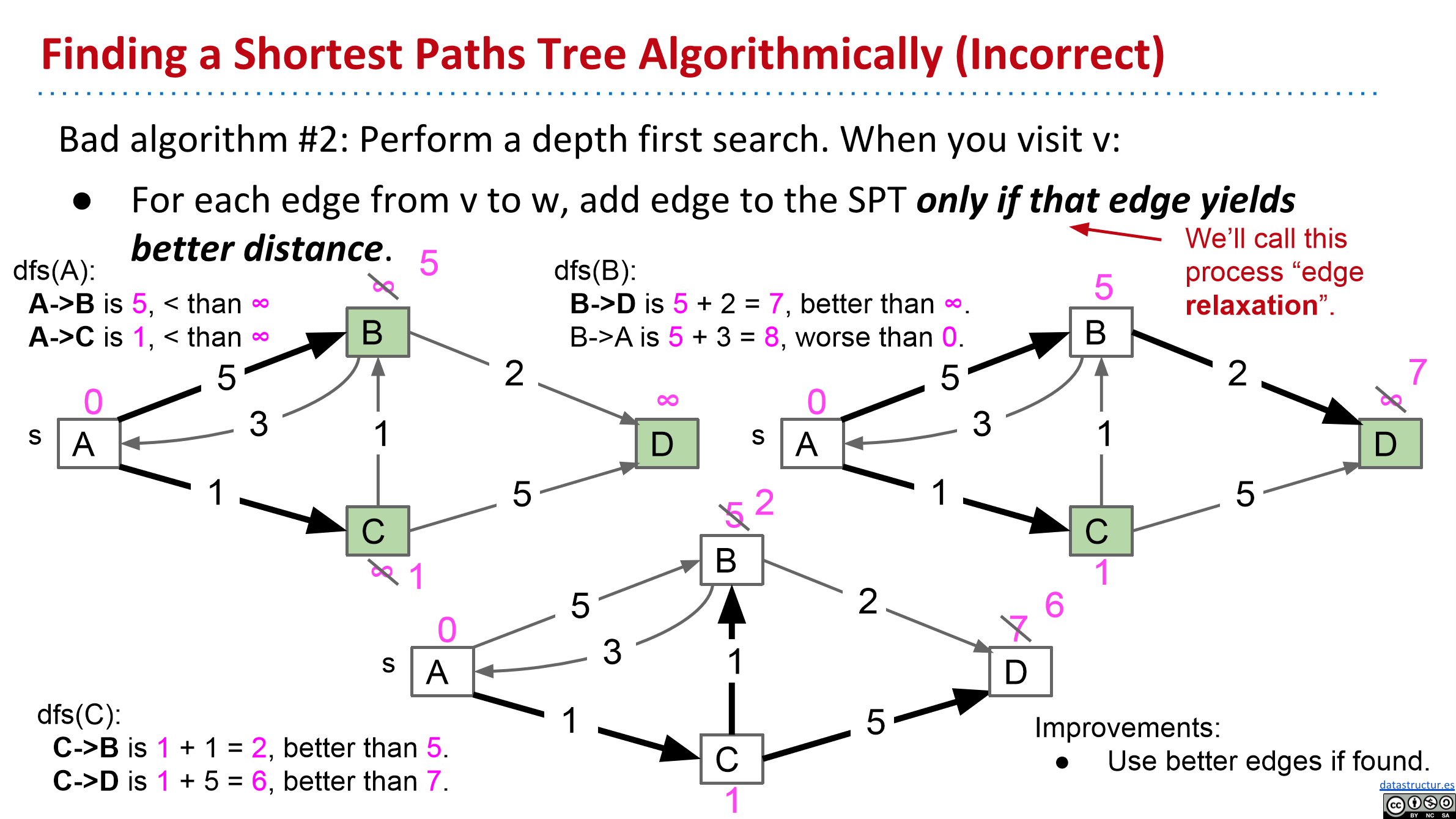
因此这道题也可以用DFS求解,DFS遍历所有的可能路径(但是要做剪枝,类比于回溯法)。
// Author: Huahua
// Running time: 36 ms
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
g_.clear();
for (const auto& e : flights)
g_[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]);
vector<int> visited(n, 0);
visited[src] = 1;
int ans = INT_MAX;
//记录一个全局最优解ans
dfs(src, dst, K + 1, 0, visited, ans);
return ans == INT_MAX ? - 1 : ans;
}
private:
//构建的图(邻接矩阵)
unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> g_;
void dfs(int src, int dst, int k, int cost, vector<int>& visited, int& ans) {
if (src == dst) {
ans = cost;
return;
}
if (k == 0)
return;
for (const auto& p : g_[src]) {
if (visited[p.first])
continue; // do not visit the same city twice.
//剪枝,防止递归爆栈
if (cost + p.second > ans)
continue; // IMPORTANT!!! prunning
visited[p.first] = 1;
dfs(p.first, dst, k - 1, cost + p.second, visited, ans);
//回退的时候标记为未访问
visited[p.first] = 0;
}
}
};
(3)BFS
BFS其实和DFS很像,也是遍历了全部的可行解,但是剪枝掉已经大于当前最优解的路径。
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> g;
for (const auto& e : flights)
g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]);
int ans = INT_MAX;
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
q.push({src, 0});
int steps = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
while (size--) {
int curr = q.front().first;
int cost = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (curr == dst)
ans = min(ans, cost);
for (const auto& p : g[curr]) {
if (cost + p.second > ans) continue; // Important: prunning
q.push({p.first, cost + p.second});
}
}
if (steps++ > K) break;
}
return ans == INT_MAX ? - 1 : ans;
}
};
(4)Bellman-Ford algorithm
一种DP方法。
核心状态转移方程是
DP[k][dst] = min(DP[k][dst], DP[k - 1][src])
DP[k][dst] 表示,最大K - 1个中间节点的情况下,从src起点到达终点dst的最少花费。
Bellman-Ford 算法描述:
- 创建源顶点 v 到图中所有顶点的距离的集合 distSet,为图中的所有顶点指定一个距离值,初始均为 Infinite,源顶点距离为 0;
- 计算最短路径,执行 V - 1 次遍历;
- 对于图中的每条边:如果起点 u 的距离 d 加上边的权值 w 小于终点 v 的距离 d,则更新终点 v 的距离值 d;
- 检测图中是否有负权边形成了环,遍历图中的所有边,计算 u 至 v 的距离,如果对于 v 存在更小的距离,则说明存在环;
关于贝尔曼-福特算法的介绍。
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
//设置一个最大值(infinity)
constexpr int kInfCost = 1e9;
vector<vector<int>> dp(K + 2, vector<int>(n, kInfCost));
dp[0][src] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= K + 1; ++i) {
//记得设置为0,因为无论最多多少个中间节点,从起点到起点都是0
dp[i][src] = 0;
for (const auto& p : flights)
dp[i][p[1]] = min(dp[i][p[1]], dp[i-1][p[0]] + p[2]);
}
return dp[K + 1][dst] >= kInfCost ? -1 : dp[K + 1][dst];
}
};

